Analysis of reactivated characteristics and influencing factors of the Lamajue landslide in Meigu County of Sichuan Province
-
摘要: 工程建设的扰动成为老滑坡复活的重要因素,老滑坡复活反过来影响了工程建设及其安全运营。四川美姑拉马阿觉滑坡属于前缘复活的巨型老滑坡,通过现场监测和数值模拟手段,对滑坡复活变形特征与影响因素进行了分析,结果表明:(1)降雨及人类工程活动是诱发老滑坡复活的主要因素,复活滑坡位于老滑坡体前缘,滑坡蠕滑变形的体积约为255.6×104 m3;(2)滑坡体呈刚性滑动,表现出单滑面及岩质滑坡的特征,且滑动面大体位于基覆界面位置;(3)经过前后两期治理,抗滑桩阻挡滑体的效果明显,滑体稳定性得到了明显提高,目前滑体变形趋于稳定,可以满足电力设施正常工作的稳定性要求。文中的研究是基于工程实例开展的,其研究成果为滑坡的稳定性评价、防治工程设计、治理后工程效果评价提供一定的理论依据。Abstract: Engineering construction disturbs old landslides and becomes an important factor for the revival of old landslides.The revival of the old landslide affects the construction and safe operation of the project.The Meigu Ramajue landslide in Sichuan is a typical giant old landslide, the leading edge of the old landslide is reactivated, through field monitoring and numerical simulation, the characteristics and influencing factors of landslide revival deformation were studied, the results show that: (1) Rainfall and human engineering activities are the main factors that induce the resurrection of the old landslide.The resurrected landslide is located at the front of the old landslide, and the creep deformation volume of the landslide is about 2.556 million cubic meters. (2)The landslide body slides rigidly, showing the characteristics of single sliding surface and rocky landslide, and the sliding surface is generally located at the base-covering interface. (3) After two stages of treatment, the anti-sliding piles have obvious effect of blocking the sliding body, and the stability of the sliding body has been significantly improved. At present, the deformation of the sliding body tends to be stable, which can meet the deformation and stability requirements of the normal operation of power facilities.The research of this paper is carried out based on engineering examples, and its research results provide a certain theoretical basis for landslide stability evaluation, prevention and control engineering design, and engineering effect evaluation after treatment.
-
Keywords:
- old landslide /
- revival /
- deformation /
- influence factor /
- anti-slide pile
-
0. 引言
受地质构造及其活动特征影响,老滑坡主要分布在山区河谷[1-2],大型老滑坡把岸坡地貌改造为相对开阔平缓的斜坡,通常处于稳定状态,常为铁路、公路、厂房、水电开发等山区建设和开发规划所利用。但工程建设、降雨、地震等易引起老滑坡复活[3-6],老滑坡的复活又影响工程建设及其安全运营,这些是工程建设需要关注的主要问题[7-8]。
针对老滑坡复活的机理、变形破坏特征、数值模型等方面的研究,前人进行了较多的研究。殷跃平等[9]以藕塘滑坡为例认为库水位的升降以及降雨因素是促使滑坡复活变形的主要因素;黄润秋[10]、王恭先等[11]、殷志强[12]对滑坡在加载与降雨的条件下其稳定性因素及成因机制进行了分析研究;魏昌利等[3]、杜飞等[13]通过数值模拟方法认为地震、降雨等对滑坡的复活起到促进作用。
滑坡监测工作是了解和掌握滑坡体的变形动态特征,对滑坡正确分析、评价、预测、预报及治理工程等提供可靠资料和科学依据的重要手段。同时,监测结果也是检验滑坡分析评价及滑坡防治工程效果的尺度[14]。基于此,文中以美姑拉马阿觉滑坡为例,通过采用现场地质调绘、现场监测并结合数值模拟等方法,详细分析了滑坡复活变形特征与影响因素分析,并对滑坡治理工程的效果进行评价,以期为同类工程防治提供借鉴。
1. 滑坡概况
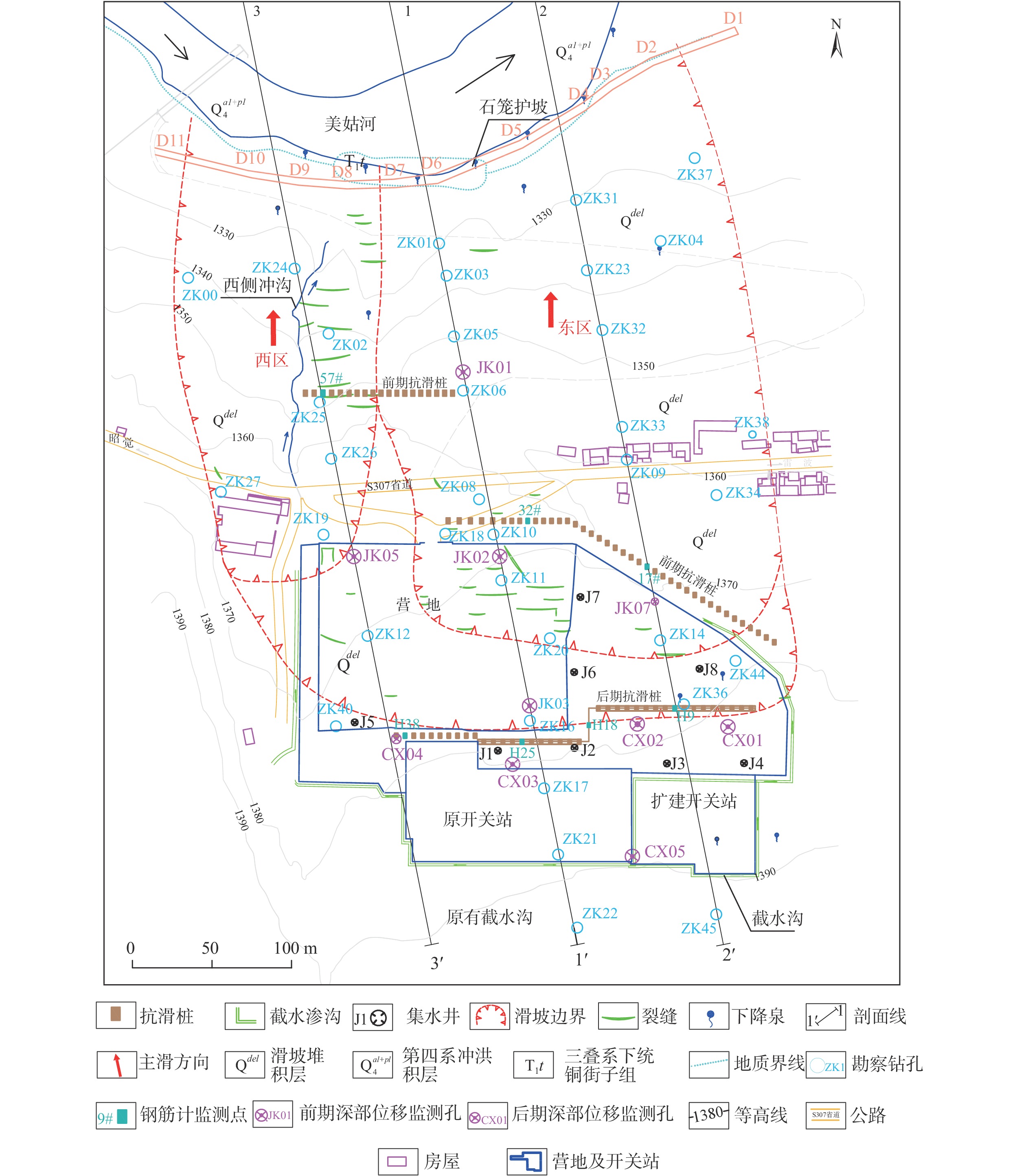
老滑坡位于四川省美姑县拉马阿觉乡瓦尼村,美姑河右岸,省道307从复活体中前部横向穿过,滑坡全景照见图1。复活体上建有四川美姑河水电开发有限公司营地与220 kV 联合开关站,居住有营地工作人员及瓦尼村村民,其余为耕地。拉马阿觉老滑坡沿河宽3.0~3.6 km,纵向长6.0~6. 5 km,前缘直达美姑河岸,后缘一直到后侧基岩陡壁[15]。据现场调查,局部复活滑坡位于老滑坡西侧前缘,长约355 m,宽约360 m,平面上呈方形,滑体厚度20~30 m,滑坡蠕滑变形的体积约为255.6×104 m3[16](图2)。
滑坡区属侵蚀构造单斜低中山地貌,地势为阶梯状斜坡,总体上是南高北低,老滑坡相对高差约680 m,整体地形平缓,坡角一般为8°~20°。老滑坡体上冲沟发育,西侧发育一常年流水冲沟,为复活体西侧边界;东侧发育一季节性冲沟,于20世纪70年代复活滑坡后缘以下冲沟被人为填埋形成耕地,为复活体东侧边界。
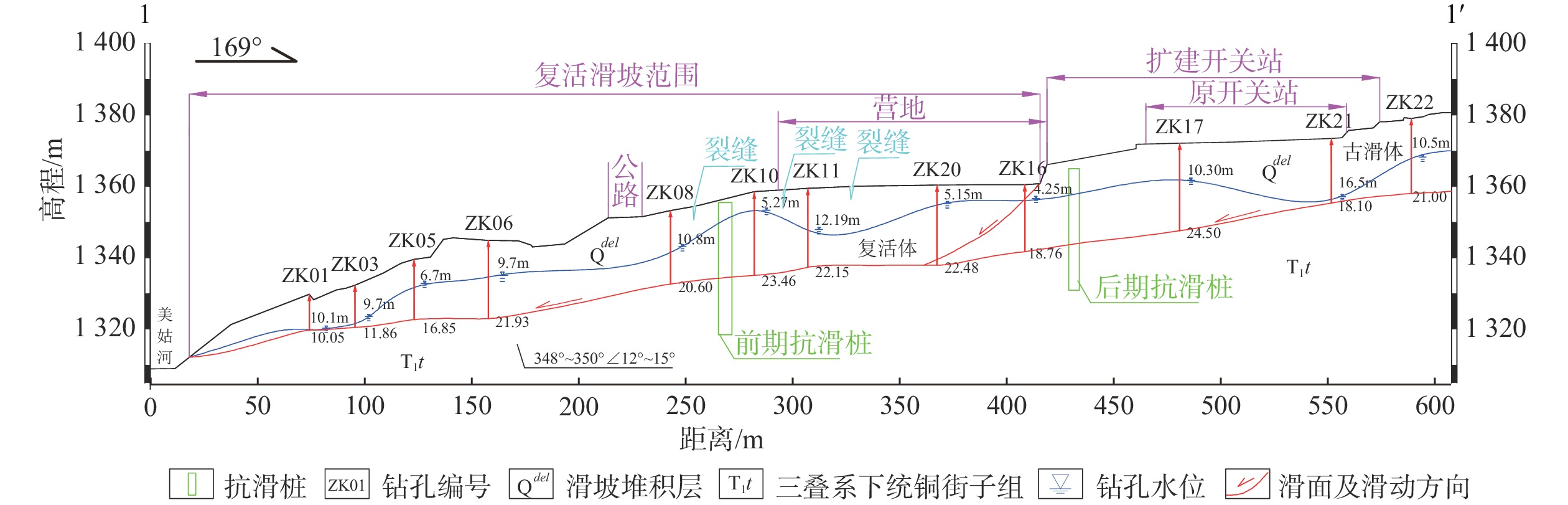
滑坡体为第四系松散层覆盖,第四系由滑坡堆积、残坡积、崩积物组成,主要为紫红色、棕红色含碎块石粉质黏土、黄灰色含角砾粉质黏土、粉质黏土、红褐色粉质黏土及碎块石组成。滑坡区出露基岩为三叠系下统铜街子组(T1t),岩性为灰绿色泥岩、紫红色粉砂质泥岩、黄灰色泥岩、灰色细砂岩、粉砂岩及灰绿色白云岩,,铁铝质或钙质填充, 裂隙较发育,其中细砂岩为基岩裂隙水含水层,其透水性中等;泥岩为隔水层,透水性差,也是滑坡的滑床,产状:348°~350°∠12°~15°。滑坡1-1'工程地质剖面见图3。
2. 现场监测
2.1 滑坡前、后期治理工程措施与监测系统
2.1.1 滑坡前期治理工程措施与监测系统
滑坡前期治理于2008年1月开始实施,至2008年6月施工完成。滑坡前期治理措施主要为在滑坡前缘实施了钢筋石笼护坡(D1—D11)、滑坡中部59根抗滑桩、集水井(J1—J8)、截水沟等措施。
前期监测系统包括5个滑体深部位移监测孔(JK01—JK03、JK05、JK07)、5个地下水位监测孔(JK01—JK03、JK05、JK07)、桩身内力(钢筋计)(17#、32#、57#)(图2),经历了施工期、营运期监测[17-19]。
2.1.2 滑坡后期治理工程措施与监测系统
根据开关站及其扩建工程的范围,治理工程于2012年7月开始实施,至2013年2月施工完成。治理措施主要在开关站下侧实施了39根抗滑桩(第二级支挡)桩顶用冠梁相连,开关站扩建工程外围修复截水沟的综合治理措施。
主要针对开关站扩建工程范围,开展了施工期监测[17,20-21],布设了5个滑坡体深部位移监测孔(CX01—CX05)、桩身内力(钢筋计)(H9、H18、H25、H38)、5个地下水位监测孔(CX01—CX05)等(图2)。
2.1.3 监测系统监测时间及施工情况
根据现场监测情况,文中选取3个代表性监测孔进行分析,其各自的监测时间及施工情况见表1。
表 1 前、后期监测系统监测时间及施工时间表Table 1. Pre-and post-monitoring system monitoring time and construction schedule编号 开始日期 结束日期 抗滑桩施工完成日期 前期监测 JK02 2008年4月7日 2009年5月5日 2008年6月1日 后期监测 CX02 2012年7月27日 2013年6月9日 2013年2月11日 CX05 2012年7月24日 2013年7月26日 2.2 监测数据分析
2.2.1 深部位移监测
滑体深部位移监测是确定滑坡滑动与否、活动状态及滑动面(带)层数、深度、厚度等最直接、最可靠的手段。因此,文中主要依据滑坡体深部位移监测数据分析滑坡变形特征、对滑坡整治工程效果的检验,以保证电力设施运行安全。
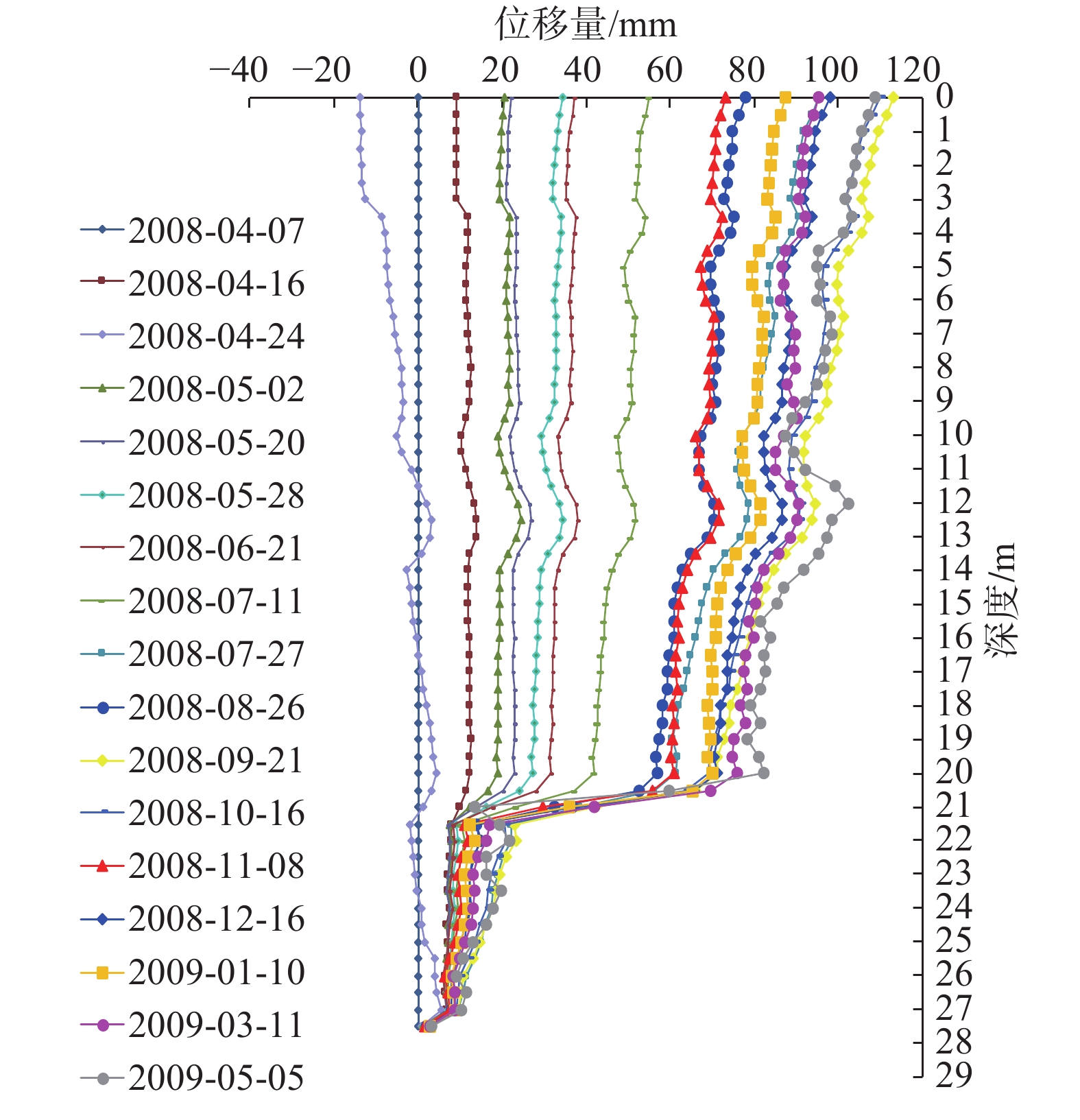
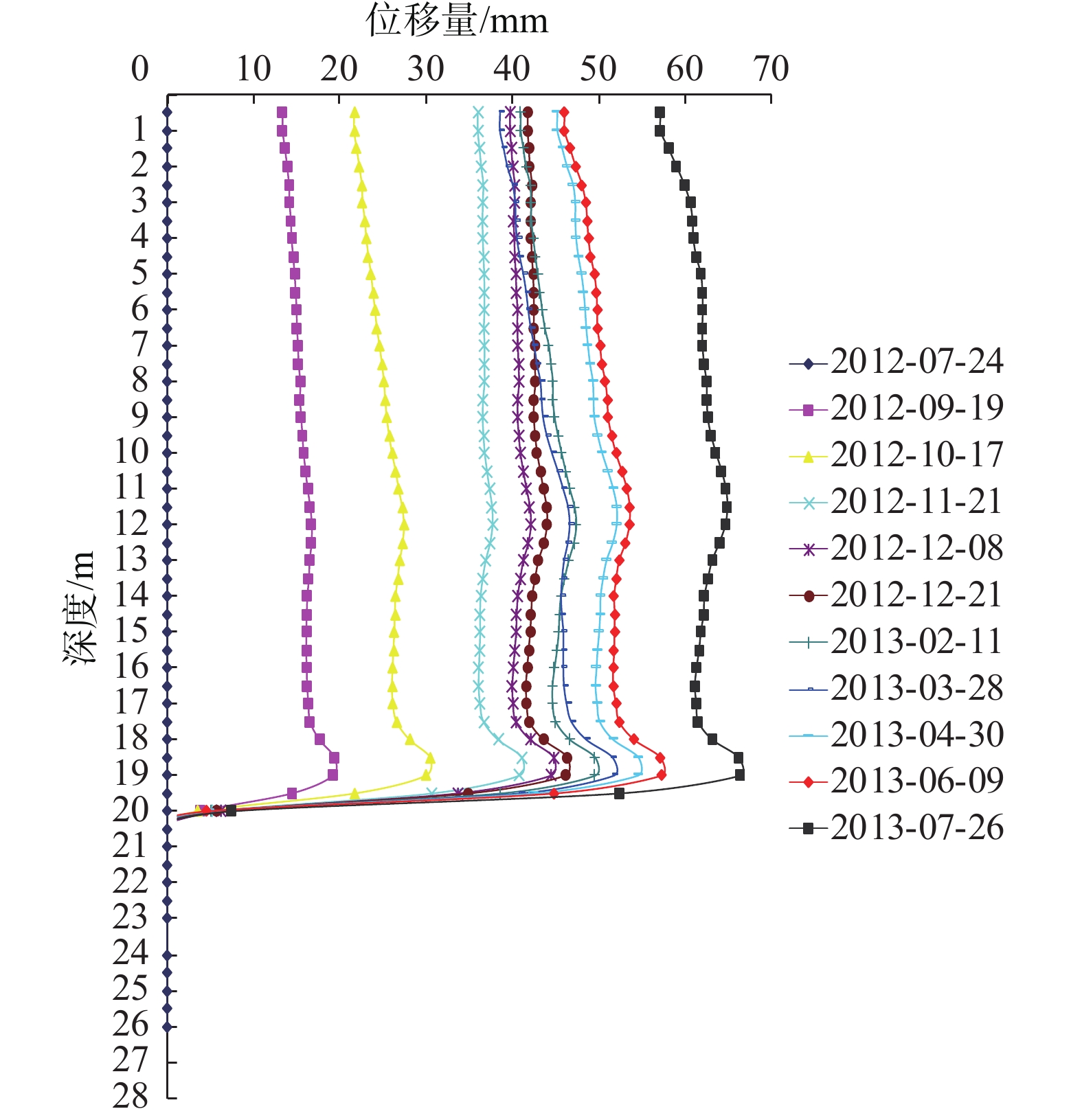
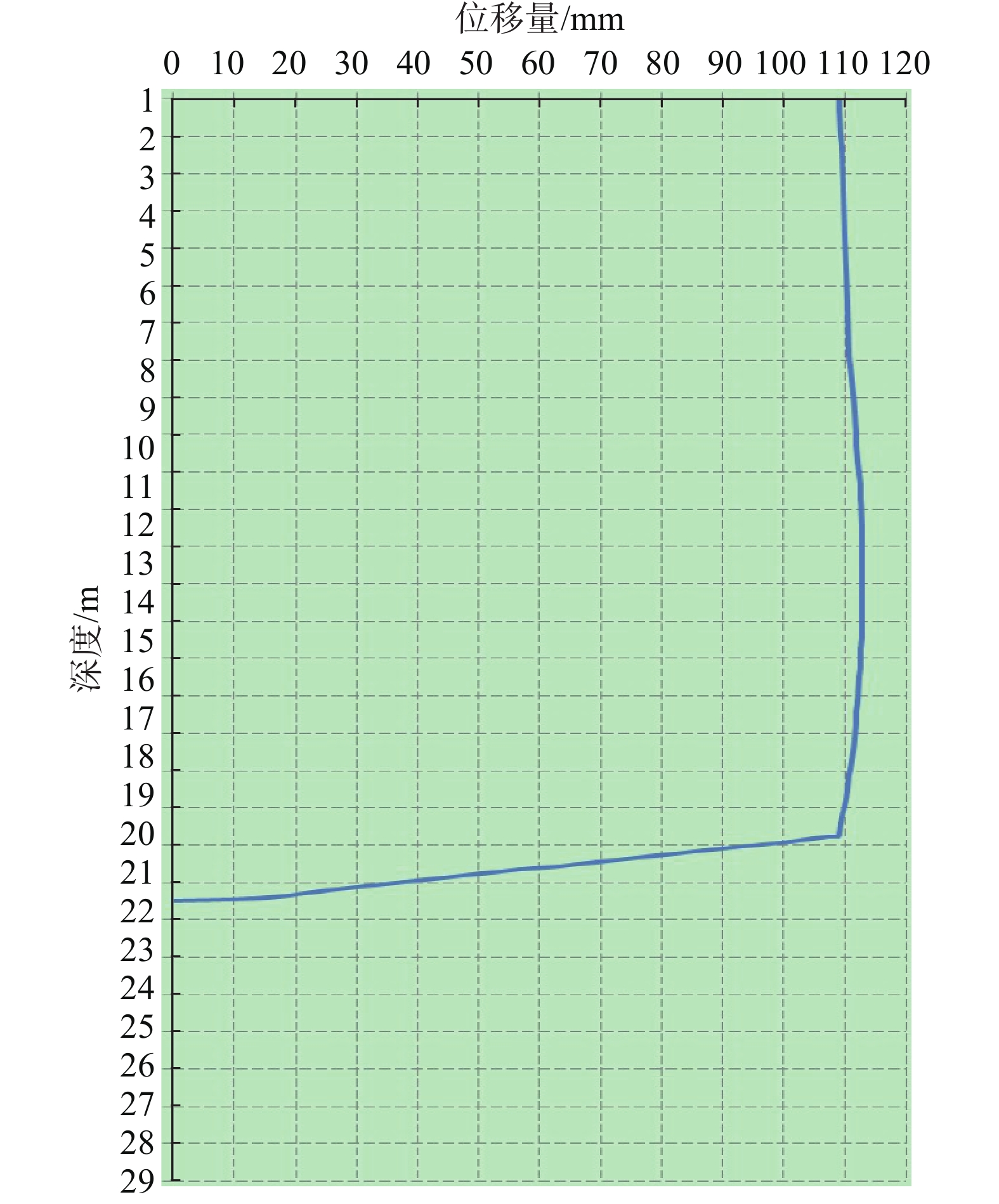
(1)图4为前期JK02监测孔滑体深部位移曲线,监测数据显示孔口滑体累计位移达110 mm,滑面达80 mm。抗滑桩等治理工程施工期间,孔口滑体位移与滑面处位移几乎相等呈竖向直线,滑体沿滑面呈现刚性滑动,表现出单滑面及岩质滑坡的特征,滑体变形随时间持续增大,变形速率虽起伏变化较大,但整体呈增大趋势,日均水平位移增量为1~3 mm;随着抗滑桩等治理工程施工完成,抗滑桩发挥作用后,滑体变形自滑面至孔口逐渐增大,深部位移曲线由竖向直线转变为上大下小斜直线,同时滑体变形速率日渐减缓,直至滑体位移趋于稳定,位移速率降低为0~0.3 mm/d。
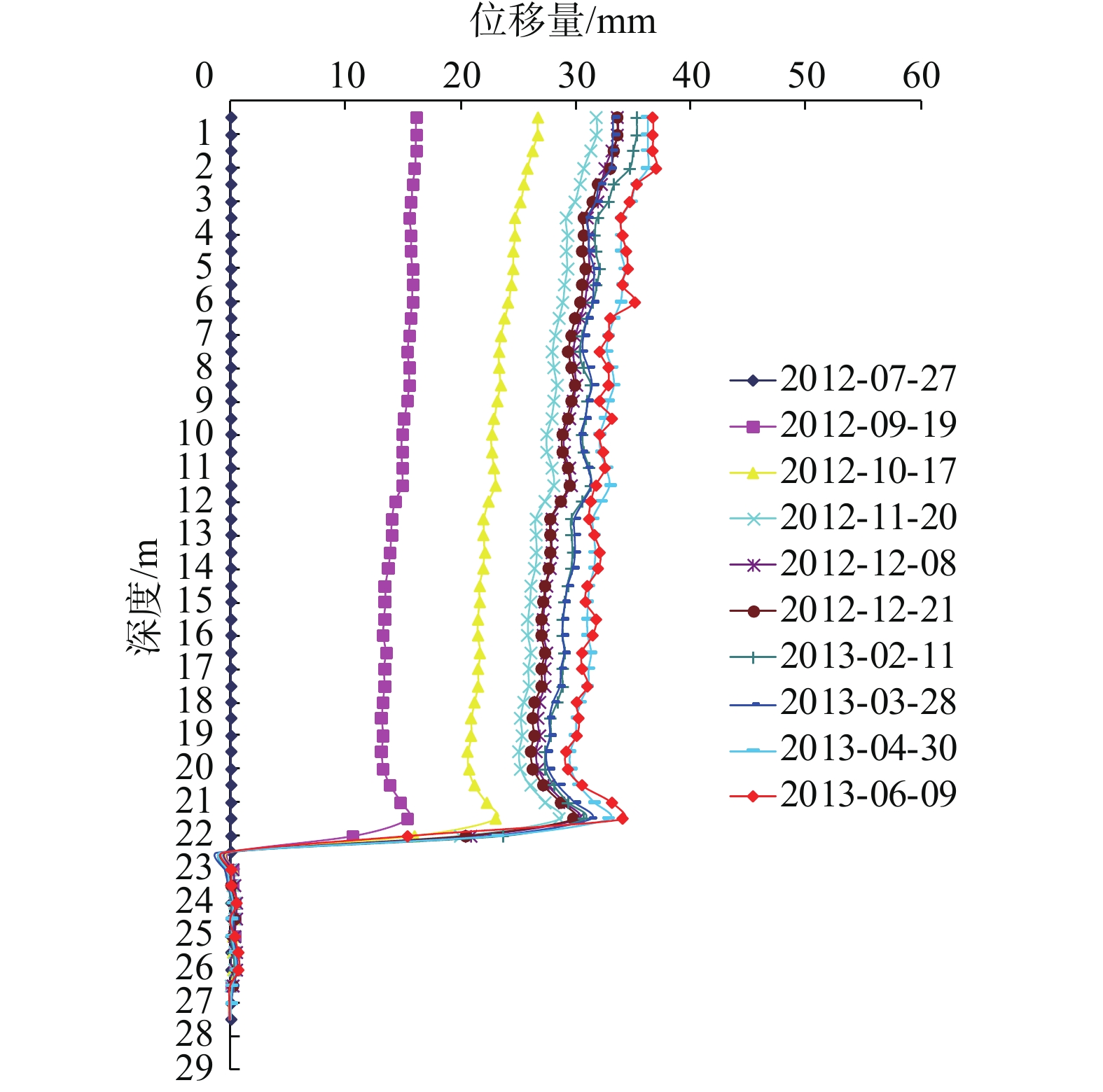
(2)图5、图6为后期CX02、CX05监测孔滑体深部位移曲线,由图分析可知,其位移主要发生在抗滑桩施工期间,孔口滑体累计35~45 mm,滑面累计位移33~57 mm,与前期相比实测的位移相对较小。抗滑桩施工期间,其滑体位移曲线形态呈竖向直线,与前期监测结果一致;但施工完成以后,其滑体位移曲线形态仍呈竖向直线,与前期监测曲线形态存在差异,位移呈现沿滑带整体滑移的特性,同时也表明了通过前期治理滑体稳定性得到了明显提高,但随着施工活动、加载、降雨入渗等外部因素的变化和影响,滑体内部仍有变形的调整,随着抗滑桩不断发挥作用,滑体变形速率减小,滑坡体趋于稳定。另外,离抗滑桩越近的CX02比离桩越远的CX05滑体位移收敛更快,且累计位移也较之更小,这说明了抗滑桩对距离桩较近的桩后滑体位移的限制作用比较远处的滑体显著。
(3)由图4、图5、图6可知,监测曲线在某一深度处位移均发生突变,突变位置即滑动面埋深,其中JK02、CX02、CX05滑动面埋深分别为20~21.5 m、21.5~22.5 m、18.5~20.5 m,与现场勘察钻孔岩芯所揭示的实际滑动面基本一致,由此可以推断该滑坡具有明显的滑动面,且滑动面大体位于基覆界面位置。
2.2.2 地下水位监测
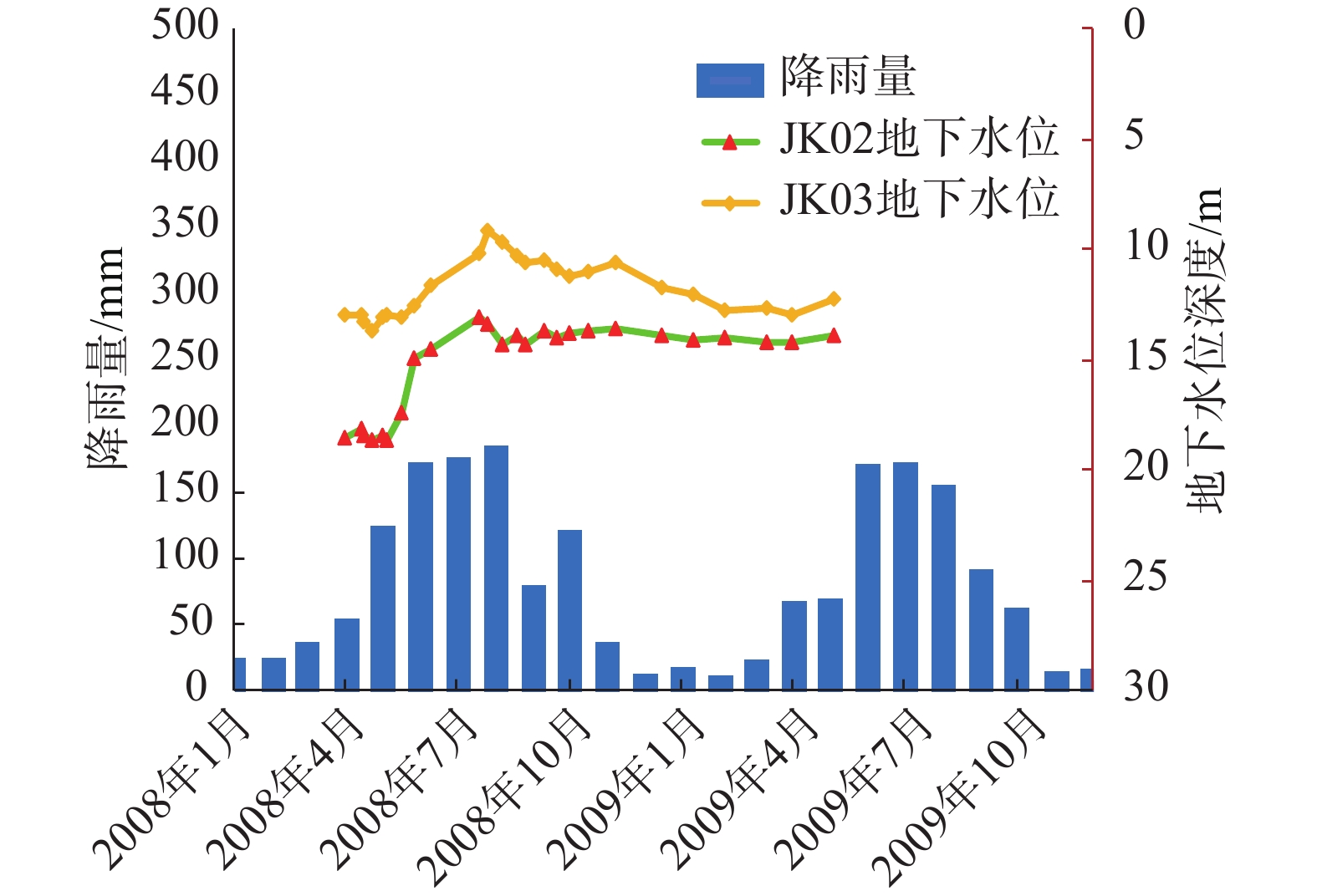
图7为2008年4月1日—2009年5月5日期间滑坡地下水位与降雨—时间关系曲线,由图7可知,地下水位经历了持续下降到逐步回升,再到相对比较稳定的过程,分别回升了5.65 m、4.58 m,分析其原因,主要是与抗滑桩施工及降雨量有关。
3. 老滑坡复活影响因素分析
3.1 降雨对老滑坡复活的影响
根据2008—2013年研究区降雨量统计显示,降雨一般集中在每年6—9月,且其降雨量占全年降雨量80%以上。由以上分析可知,降雨入渗至滑坡体内,滑坡体内地下水位升高,岩土体由非饱和状态转为饱和状态,同时降低滑带土的抗剪强度,引起滑坡的下滑力增加、抗滑力下降,再加上地下水运移使滑坡体内产生动水压力、浮托力等作用,加剧滑坡体变形,最终诱发老滑坡复活。
3.2 人类工程活动对老滑坡复活的影响
根据现场调查访问,在老滑坡复活前,斜坡体上进行了营地及开关站大规模修建,由于大量开挖,使大量的地表水沿裂缝渗入到滑坡体中,改变滑坡体的渗流场,从而影响滑坡整体的稳定性;另外,斜坡体上新建了多幢2~3层楼房及开关站相应设施,位于滑坡中部,对滑坡滑动有一定的促进作用。据介绍,四川美姑河水电开发有限公司营地自2004年7月人员驻进以来发现局部地面开裂,职工活动室及部分围墙也出现裂缝,这说明受加载影响显著。
4. 三维数值模拟
FLAC3D软件是一款连续介质力学分析软件,采用有限差分方程近似代替实际的微分方程组,然后进行等效替代,将微分方程组化为代数方程来求解。因其计算速度快,数据占用空间小,可以模拟分析斜坡的受力状态和稳定性。除此之外,FLAC3D软件在计算大变形的问题时,大变形值是通过各个时步的小变形叠加而得来的,用显式时间差分来求解,这样既节省了时间,也达到了解决多单元模型的目的。
4.1 参数选取
文中计算模型的本构力学模型将采用摩尔-库伦模型,模型的破坏包络线和Mohr-Coulomb强度准则(剪切屈服函数)以及拉破坏准则(拉屈服函数)相对应,岩土体相关计算参数取值参考本项目的室内试验、工程地质类比法、参数反演分析及《岩石力学参数手册》等进行综合取值,具体各岩土体物理力学取值见表2。
表 2 数值计算参数取值Table 2. Numerical calculation parameter value岩土体名称 重度/
(kN·m−3)弹性模量/
MPa泊松比 黏聚力/
kPa内摩擦角/
(°)滑体 23.10 180
200.28 4.0 24 滑带 23.10 0.33 11.3 12 滑床 26.80 6700 0.25 2180 34 抗滑桩 25.00 28000 0.20 − − 4.2 计算模型的建立
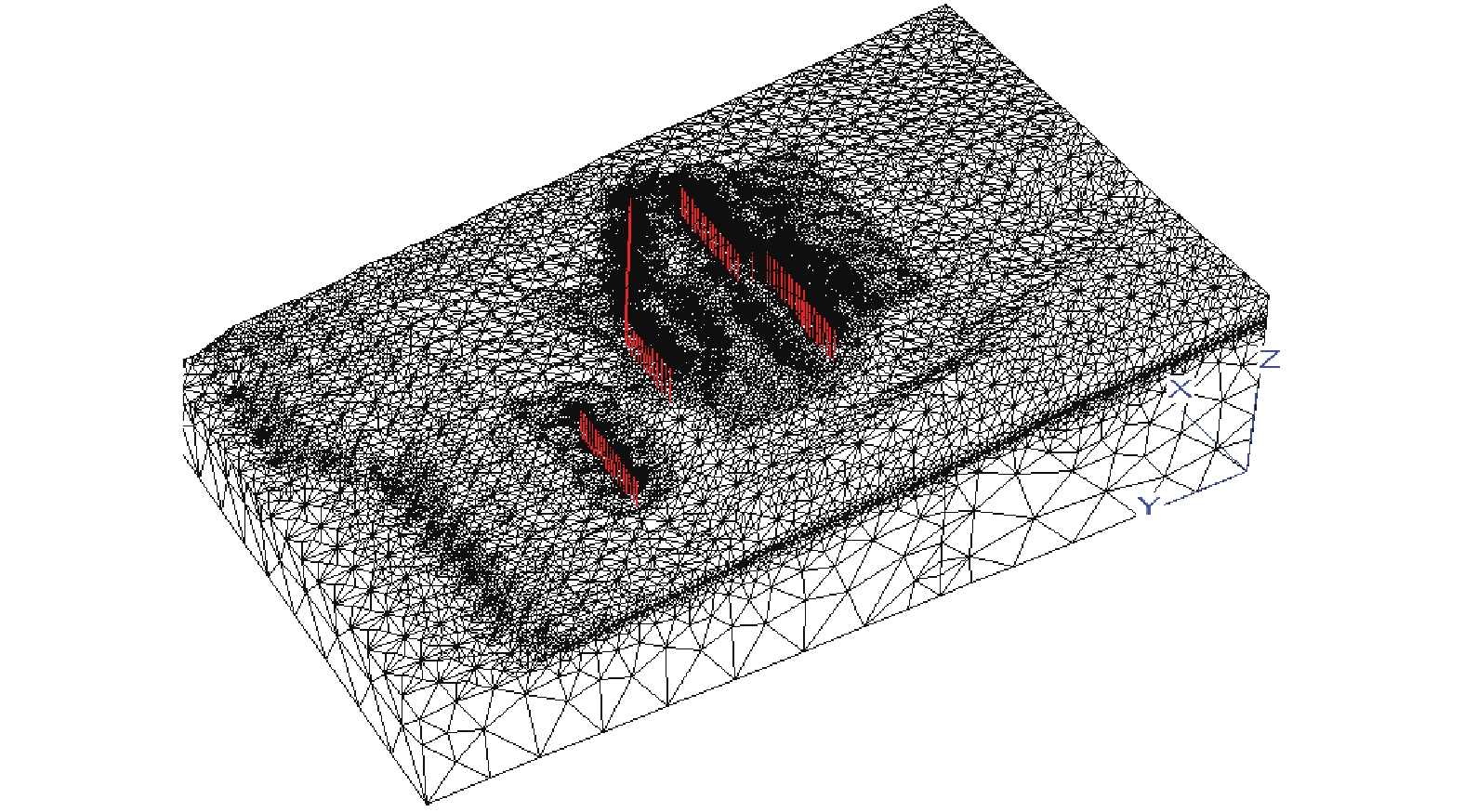
模型的边界宽度取复活滑坡体宽度的十分之一时,滑坡的安全系数趋于稳定,而且范围取得越大影响越小,而滑带以下基岩的深度对结果影响不大[22]。因此,根据滑坡明显复活边界条件及结合滑坡区域地形地貌特征确定FLAC3D的计算模型东西宽度(X方向)取480 m,两边超出滑坡侧边界60 m,模型底部取到高程1225 m,比滑带最低高程低80 m;模型南北向(Y方向)的长度取765 m,北侧边界取至美姑河对岸,南侧边界超出后缘边界40 m(图8)。
模型材料分为3种,即滑床、滑带及滑体,由于滑带在各钻孔的厚度不一,将滑带的厚度统一简化为1.5 m,地表面形态根据地形线确定,而滑面根据钻孔中滑面高程插值计算出滑面等值线。采用Ansys软件的Solid45号单元(八节点六面体)对模型网格自由划分,滑带的网格稍密,考虑到设桩处的网格大小,对设桩处的网格沿桩身进行加密处理,计算模型的单元总数为2014449个,节点总数为360149个(图9)。
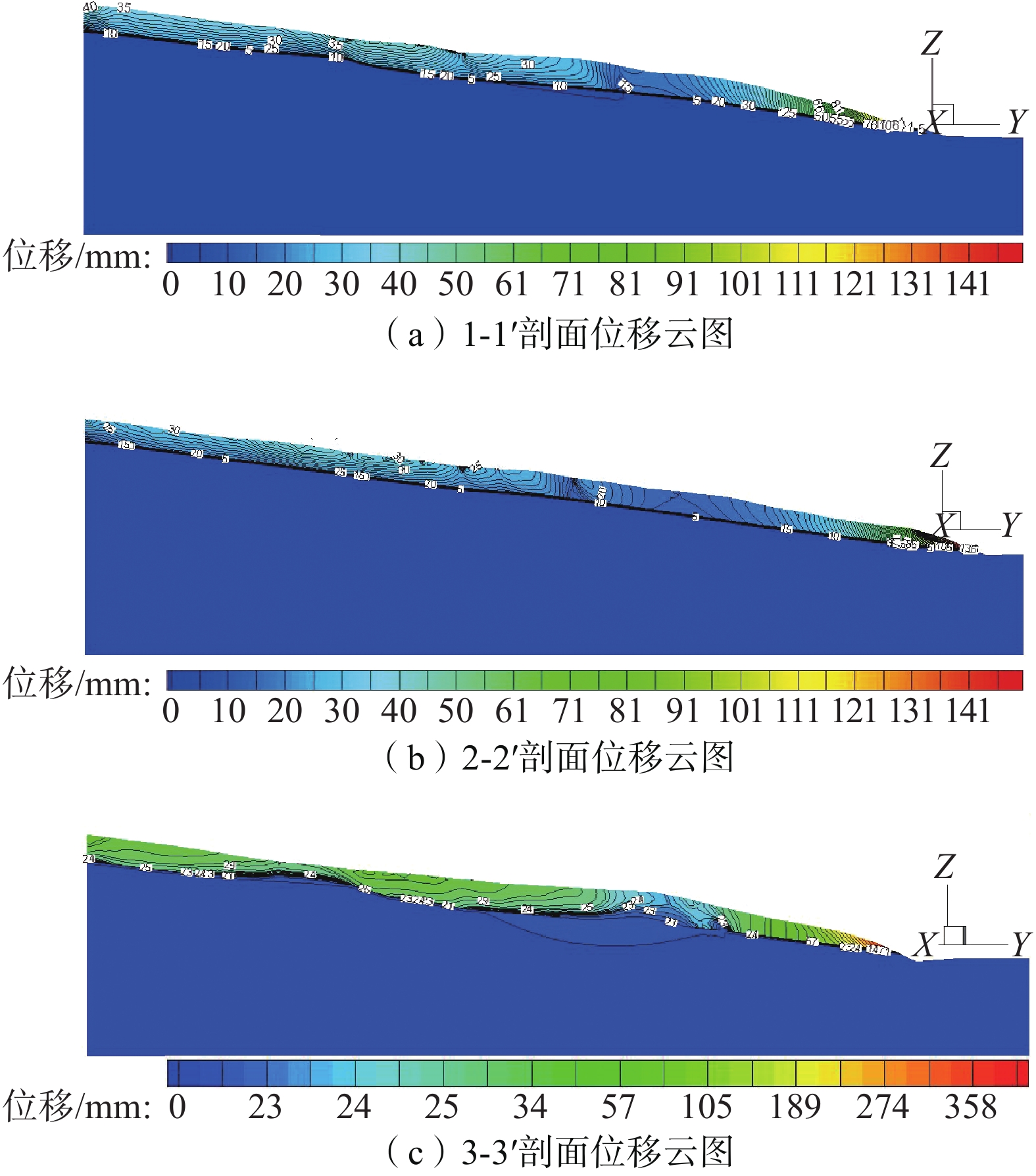
由图10可知,抗滑桩设置后,加固效果明显,对于滑床部分位移几乎为零,滑体和滑带有不同程度的变形;桩后一定范围内的位移值较剖面上其它位置的位移小,桩前滑体由于前面没有支挡而自由向临空面变形,位移较大,特别是前缘的位移更突出,表现为牵引式滑坡,与该滑坡机制相符合;桩前滑体位移等值线基本竖直,说明桩前滑体具有沿滑带整体滑移的特性,桩后滑体的位移等值线较为凌乱,体现出桩后滑体内部状态仍有变形的调整;设桩位置的等值线向上凸,突出部分顶点的位移值较大,可说明靠近桩顶位移大,往深处位移变小。
由图11可知,同样高度的滑体中,桩前滑体的正应力明显小于桩后滑体的正应力,说明桩前滑体受到桩后滑坡推力较小,桩后滑体的应力大部分传给了抗滑桩,说明抗滑桩阻挡滑体的效果明显。
4.3 对比分析
通过三维数值模拟与现场监测数据对比分析,由JK02监测孔处数值计算的滑体深部位移曲线图12可知,曲线在20.0~21.5 m发生突变,即为滑动面位置,数值计算的孔口累计位移约109 mm,与实际监测数据吻合;数值计算的滑体深部位移曲线形态整体上呈竖直的形态,与实测深部位移曲线形态不同,这是因为数值计算采用的是同一参数,是一种均质的材料,而滑体并不是一致均质的岩土体。
设置抗滑桩后,抗滑桩与桩后滑体相互作用,滑体受抗滑桩阻挡,随着抗滑桩逐步发挥作用,滑体变形趋于稳定,滑体稳定性得到明显提高,抗滑桩阻挡滑体的效果明显,且抗滑桩对离桩近的桩后滑体位移的限制作用比较远处的桩后滑体明显。
5. 结论
前后两期监测都经历了施工期、营运期监测,监测目的是为了获得滑坡变形动态特征,研究施工活动、降雨对滑坡变形的影响,对滑坡治理后的稳定性进行评价、预测,为整治工程设计提供重要依据,检验滑坡治理工程的治理效果,并评价其对电站安全运行的影响有重要意义[23-24]。得到以下结论:
(1)根据前后两期监测,监测曲线在某一深度处位移均发生突变,突变位置即滑动面埋深,与现场勘察钻孔岩芯所揭示的实际滑动面基本一致,且滑动面大体位于基覆界面位置。
(2)滑体呈刚性滑动,表现出单滑面及岩质滑坡的特征,降雨及人类工程活动是诱发老滑坡复活的主要因素。
(3)前期抗滑桩治理以后,滑体稳定性得到了明显提高,但随着施工活动、加载、降雨入渗等外部因素的变化和影响,滑体内部仍有变形的调整。
(4)经过前后两期治理,抗滑桩阻挡滑体的效果明显,且抗滑桩对离桩近的桩后滑体位移的限制作用比较远处的桩后滑体明显,随着抗滑桩逐步发挥作用,滑体变形趋于稳定,滑体稳定性得到了明显提高,目前滑体变形趋于稳定,可以满足电力设施正常工作的变形稳定要求。
-
表 1 前、后期监测系统监测时间及施工时间表
Table 1 Pre-and post-monitoring system monitoring time and construction schedule
编号 开始日期 结束日期 抗滑桩施工完成日期 前期监测 JK02 2008年4月7日 2009年5月5日 2008年6月1日 后期监测 CX02 2012年7月27日 2013年6月9日 2013年2月11日 CX05 2012年7月24日 2013年7月26日 表 2 数值计算参数取值
Table 2 Numerical calculation parameter value
岩土体名称 重度/
(kN·m−3)弹性模量/
MPa泊松比 黏聚力/
kPa内摩擦角/
(°)滑体 23.10 180
200.28 4.0 24 滑带 23.10 0.33 11.3 12 滑床 26.80 6700 0.25 2180 34 抗滑桩 25.00 28000 0.20 − − -
[1] 孙东,殷志强,李大猛,等. 美姑河流域地质构造对大型滑坡孕育的控制作用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(6):49 − 58. [SUN Dong,YIN Zhiqiang,LI Dameng,et al. Development of the large-scale landslides controlled by geological structures in Meigu River basin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(6):49 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.06.07 SUN Dong, YIN Zhiqiang, LI Dameng, et al. Development of the large-scale landslides controlled by geological structures in Meigu River Basin[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(6): 49-58. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.06.07
[2] 殷志强,孙东,张瑛,等. 美姑河流域滑坡时空展布及成生机制研究[J]. 第四纪研究,2018,38(6):1358 − 1368. [YIN Zhiqiang,SUN Dong,ZHANG Ying,et al. Study on spatial temporal distribution characteristics and forming mechanism of landslides in the Meigu River basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences,2018,38(6):1358 − 1368. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.06.04 YIN Zhiqiang, SUN Dong, ZHANG Ying, et al. Study on spatial temporal distribution characteristics and forming mechanism of landslides in the Meigu River basin[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 2018, 38(6): 1358-1368. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11928/j.issn.1001-7410.2018.06.04
[3] 魏昌利,张瑛,冯文凯,等. 泯江上游槽谷曲流段大型古滑坡成因与复活性分析—以松潘县元坝子古滑坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(6):141 − 149. [WEI Changli,ZHANG Ying,FENG Wenkai,et al. Formation mechanism and reactivation analyses of large ancient landslides in the meandering trough valley of the upper Minjiang River:A case study of the Yuanbazi ancient landslide in Songpan County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(6):141 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract) WEI Changli, ZHANG Ying, FENG Wenkai, et al. Formation mechanism and reactivation analyses of large ancient landslides in the meandering trough valley of the upper Minjiang River: A case study of the Yuanbazi ancient landslide in Songpan County[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(6): 141-149. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 吴瑞安,马海善,张俊才,等. 金沙江上游沃达滑坡发育特征与堵江危险性分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(5):120 − 128. [WU Ruian,MA Haishan,ZHANG Juncai,et al. Developmental characteristics and damming river risk of the Woda landslide in the upper reaches of the Jinshajiang river[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(5):120 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202104036 WU Ruian, MA Haishan, ZHANG Juncai, et al. Developmental characteristics and damming river risk of the Woda landslide in the upper reaches of the Jinshajiang River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2021, 48(5): 120-128. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=SWDG202105013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SWDG202105013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.202104036
[5] 黄达,匡希彬,罗世林. 三峡库区藕塘滑坡变形特点及复活机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(5):127 − 135. [HUANG Da,KUANG Xibin,LUO Shilin. A study of the deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the Outang landslide near the Three Gorges Reservoir of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(5):127 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.05.17 HUANG Da, KUANG Xibin, LUO Shilin. A study of the deformation characteristics and reactivation mechanism of the Outang landslide near the Three Gorges Reservoir of China[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(5): 127-135. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=SWDG201905018&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SWDG201905018&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.16030/j.cnki.issn.1000-3665.2019.05.17
[6] 张彦锋,铁永波,白永健,等. 云南永善县上坝老滑坡复活机制及新滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):41 − 49. [ZHANG Yanfeng,TIE Yongbo,BAI Yongjian,et al. Reactivation mechanism of the old landslide and stability analysis of the new landslide in Shangba,Yongshan County of Yunnan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):41 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Yanfeng, TIE Yongbo, BAI Yongjian, et al. Reactivation mechanism of the old landslide and stability analysis of the new landslide in Shangba, Yongshan County of Yunnan Province [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Contro, 2020, 31(3): 41-49. ( in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDH202003008&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[7] 窦晓东,张泽林. 甘肃舟曲垭豁口滑坡复活机理及成因探讨[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(2):9 − 18. [DOU Xiaodong,ZHANG Zelin. Mechanism and causal analysis on the Yahuokou landslide reactivation and causes(Zhouqu County,Gansu,China)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(2):9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.02.02 DOU Xiaodong, ZHANG Zelin. Mechanism and causal analysis on the Yahuokou landslide reactivation and causes(Zhouqu County, Gansu, China)[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(2): 9-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=ZGDH202102002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDH202102002&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.02.02
[8] 张永双,吴瑞安,郭长宝,等. 古滑坡复活问题研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展,2018,33(7):728 − 740. [ZHANG Yongshuang,WU Ruian,GUO Changbao,et al. Research progress and prospect on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Advances in Earth Science,2018,33(7):728 − 740. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.07.0728 ZHANG Yongshuang, WU Ruian, GUO Changbao, et al. Research progress and prospect on reactivation of ancient landslides[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 2018, 33(7): 728-740. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=DXJZ201807006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DXJZ201807006&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.11867/j.issn.1001-8166.2018.07.0728
[9] YIN Y P,HUANG B L,WANG W P,et al. Reservoir-induced landslides and risk control in Three Gorges project on Yangtze River,China[J]. Journal of Rock Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering,2016,8(5):577 − 595. DOI: 10.1016/j.jrmge.2016.08.001
[10] 黄润秋. 20世纪以来中国的大型滑坡及其发生机制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2007,26(3):433 − 454. [HUANG Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th Century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2007,26(3):433 − 454. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001 Huang Runqiu. Large-scale landslides and their sliding mechanisms in China since the 20th century[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2007, 26(3): 433-454. (in Chinese with English abstract)]http: //www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=yslxygcxb200703001 DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2007.03.001
[11] 王恭先, 许峻岭, 刘光代, 等. 滑坡学与滑坡防治技术[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2004 WANG Gongxian, XU Junling, LIU Guangdai, et al. Landslide science and landslide control technology[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2004. (in Chinese)
[12] 殷志强. 黄河上游因人工加载和降雨引发的虎头崖滑坡[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2014,25(4):10. [YIN Zhiqiang. Hutouya landslide caused by artificial loading and rainfall in the upper reaches of the Yellow Rive[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2014,25(4):10. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2014.04.003 YIN Zhiqiang. Hutouya landslide caused by artificial loading and rainfall in the upper reaches of the Yellow Rive [J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2014, 25(4): 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=ZGDH201404003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2014.04.003
[13] 杜飞,任光明,夏敏,等. 地震作用诱发老滑坡复活机制的数值模拟[J]. 山地学报,2015,33(2):233 − 239. [DU Fei,REN Guangming,XIA Min,et al. Numerical simulation of ecurrence mechanism of old landslide under earthquake loading[J]. Mountain Research,2015,33(2):233 − 239. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000030 DU Fei, REN Guangming, XIA Min, et al. Numerical simulation of ecurrence mechanism of old landslide under earthquake loading[J]. Mountain Research, 2015, 33(2): 233-239. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=SDYA201502013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SDYA201502013&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000030
[14] 周平根. 滑坡监测的指标体系与技术方法[J]. 地质力学学报,2004,10(1):19 − 26. [ZHOU Pinggen. Indicator system and techniques of landslide monitoring[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2004,10(1):19 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2004.01.003 ZHOU Pinggen. Indicator system and techniques of landslide monitoring[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2004, 10(1): 19-26. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=DZLX200401003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DZLX200401003&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2004.01.003
[15] 杨建. 柳洪拉马阿觉滑坡形成机制初步探讨[J]. 水电站设计,1995,11(1):41 − 44. [YANG Jian. Preliminary study on the formation mechanism of Lamajue landslide in Liuhong[J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station,1995,11(1):41 − 44. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Jian. Preliminary study on the formation mechanism of maajue landslide in Liuhong [J]. Design of Hydroelectric Power Station, 1995, 11(1): 41-44. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SDSJ501.007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
[16] 宋亚伟,王卫,赵德庆. 拉马古滑坡前部局部复活变形特征及成因分析[J]. 山西建筑,2008,34(31):14 − 15. [SONG Yawei,WANG Wei,ZHAO Deqing. Analysis on deformation characteristics and reasons of revival local front of fossil landslide in Lama[J]. Shanxi Architecture,2008,34(31):14 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2008.31.008 SONG Yawei, WANG Wei, ZHAO Deqing. Analysis on deformation characteristics and reasons of revival local front of fossil landslide in Lama[J]. Shanxi Architecture, 2008, 34(31): 14-15. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=JZSX200831007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=JZSX200831007&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2008.31.008
[17] 四川美姑河水电开发有限公司营地及220KV联合开关站地质勘察报告[R]. 西昌: 四川凉山地质勘察施工公司, 2006 Geological Investigation Report on the camp and 220 KV joint switch station of Sichuan Meigu River Hydropower Development Co. Ltd[R]. Xichang: Sichuan Liangshan Geological Survey and Construction Company, 2006. (in Chinese)
[18] 四川美姑河水电开发有限公司营地滑坡治理工程施工图设计报告[R]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2008 Design report on construction drawing of landslide treatment project in the camp of Sichuan Meigu river hydropower development Co. Ltd[R]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2008. (in Chinese)
[19] 四川美姑河水电开发有限公司营地滑坡体监测报告[R]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009 Monitoring report on landslide in the camp of Sichuan Meigu river hydropower development Co. Ltd[R]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese)
[20] 凉山220KV美姑河开关站扩建工程滑坡治理施工图设计报告[R]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2011 Design report on construction drawing of landslide control for extension project of 220 KV Meigu river switchgear station in Liangshan[R]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2011. (in Chinese)
[21] 凉山220KV美姑河开关站扩建工程滑坡体监测报告[R]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2013 Monitoring report on landslide of 220 KV Meigu river switch station extension project in Liangshan[R]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2013. (in Chinese)
[22] 陈新泽,唐辉明,杨有成,等. 基于FLAC3D强度折减法滑坡三维稳定性研究—以三峡库区白果树古滑坡群为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2008,35(2):24 − 29. [CHEN Xinze,TANG Huiming,YANG Youcheng,et al. 3D analysis of landslide stability based on strength reduction FLAC3D:Taking Baiguoshu paleo-landslide group in the Three Gorges Reservoir area as example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2008,35(2):24 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.02.005 CHEN Xinze, TANG Huiming, YANG Youcheng, et al. 3D analysis of landslide stability based on strength reduction FLAC3D: taking Baiguoshu paleo-landslide group in the Three Gorges Reservoir area as example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2008, 35(2): 24-29. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=SWDG200802009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=SWDG200802009&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3665.2008.02.005
[23] WANG W, LI T B, WANG L S. The design of anti-slide pile and the interaction between anti-slide pile and slip mass[C]//Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Engineering Geology in Developing Countries, 2002.
[24] 沈军辉,孙宝俊,靳晓光,等. 位移监测在滑坡评价预测中的应用[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版),2002,32(5):813 − 817. [SHEN Junhui,SUN Baojun,JIN Xiaoguang,et al. Application of displacement monitoring in appraising and forecasting landslide[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition),2002,32(5):813 − 817. (in Chinese with English abstract) SHEN Junhui, SUN Baojun, JIN Xiaoguang, et al. Application of displacement monitoring in appraising and forecasting landslide[J]. Journal of Southeast Univwrsity (Natural Science Edition), 2002, 32(5): 813-817. (in Chinese with English abstract)]https: //kns. cnki. net/KCMS/detail/detail. aspx?filename=DNDX200205028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQhttps: //oversea.cnki.net/KCMS/detail/detail.aspx?filename=DNDX200205028&dbname=CJFD&dbcode=CJFQ
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 涂正楠,冯君,邓应进,潘激扬. 四川甘洛县比依市村滑坡运动特征分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 92-99 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 党杰,杨亮,段方情,范宣梅. 贵州晴隆红寨大型古滑坡复活变形特征及成因分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(04): 25-35 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 徐伟,郑玄,欧文,铁永波,付小麟,宋钰朋,殷万清. 四川凉山州地质灾害灾情特征与主要致灾类型. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 78-89 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 马海善,吴瑞安,赵文博,王计博,齐畅,邓盼,李英钧. 西藏山南鲁麦古滑坡发育特征与复活变形机制研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 32-41 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 林灿阳. 某古滑坡病害成因与整治措施研究. 路基工程. 2024(06): 205-212 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 汪美华,李勇,裴叶青. 甘肃临夏盆地韩集北山滑坡群致灾特征与稳定性评价. 地质通报. 2023(Z1): 460-468 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 蒋涛,崔圣华,冉耀. 开挖和降雨耦合诱发滑坡机理分析——以四川万源前进广场滑坡为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(03): 20-30 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 赵海松,向波,邵江,魏安辉,邬凯,张磊,柳松. 青岗古滑坡体前缘开挖后局部复活特征及防治. 科技和产业. 2023(16): 263-268 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)




 下载:
下载:


 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS