Analysis of landslide mechanism induced by excavation and rainfall: A case study of the Qianjin square landslide in Wanyuan City, Sichuan Province
-
摘要: 近年来人类工程活动和降雨环境耦合诱发的地质灾害事件频发,而耦合作用机制还待深入研究。文中以开挖和降雨耦合诱发的四川万源前进广场滑坡为例,结合前进广场滑坡地表位移及深部位移监测数据和降雨数据分析滑坡变形破坏特征和形成机理。研究表明:(1)前缘基坑的开挖是导致老滑坡复活最主要的原因,降雨起到了激发和加速作用;(2)前缘基坑开挖一方面为滑坡提供了良好的临空面条件,另一方面导致后方土体失去支撑,导致滑坡由前至后产生多级台坎状拉裂下错变形;(3)基坑开挖后,研究区长时间强-中降雨,地表水通过开挖导致的张拉裂缝进入坡体内部,一方面基岩裂隙水受大气降雨补给,导致部分非饱和土变为饱和土、承压水压力增大、有效应力下降,另一方面,部分地下水可能到达滑带,驱动变形发展。最终文中提出了由于斜坡前缘基坑开挖与降雨耦合导致滑坡的“基坑开挖-斜坡多级拉裂-集中降雨-滑带弱化-加速变形”演化过程机制。Abstract: In recent years, there has been a frequent occurrence of geological disasters caused by the coupling of human engineering activities and rainfall environment. However, research on the mechanism of coupling has not been deeply explored. In this paper, the landslide of Qianjin square in Wanyuan City induced by the coupling of excavation and rainfall is taken as an example, and the characteristics and formation mechanism of landslide deformation and failure are analyzed by combining the monitoring data of surface displacement and deep displacement of the landslide of Qianjin square and the rainfall data. The study shows that: (1) excavation is the main reason for the reactivation of the old landslide, while rainfall plays a triggering and accelerating role; (2) excavation provides good airspace conditions for the landslide on the one hand , and on the other hand causes the soil behind it to lose support, leading to the misalignment of the landslide from front to back; (3) after excavation, long-term strong to moderate rainfall in the study area, combined with tension cracks caused by excavation, make it easier for surface water to enter the interior of the slope. The bedrock fracture water is replenished by atmospheric rainfall, resulting in some unsaturated soil becoming saturated soil, increasing the pressure of pressurized water and decreasing effective stress. Additionally, groundwater may reach the slip zone and drive the deformation development. Finally, the process mechanism of landslide induced by excavation and rainfall coupling is proposed as “excavation-slope multi-stage cracking-concentrated rainfall-slip zone weakening-accelerated deformation”.
-
0. 引 言
近年来随着国家经济发展战略重心逐渐向中西部偏移,西南地区基础建设快速发展。由于西南地区特殊的地理环境和气候条件,兴建的市政工程频繁涉及到边坡问题[1-2],人类工程活动和降雨耦合诱发边坡失稳频发,对人民的生命财产造成严重威胁。
边坡的变形与破坏属于渐进破坏演变过程[3],引起因素有边坡脚开挖。叠加强降水作用而滑动的实例很多[4],开挖和降雨对边坡变形破坏作用的案例被大量研究[5-8]。张志兼等[9]利用地理探测器分析了滑坡分布的驱动因子,揭示了人类活动逐渐成为诱发滑坡的关键因素。黄晓虎等[10]通过现场调查、人工位移监测数据、自动GPS监测数据等分析开挖和降雨对滑坡复活的影响和主次关系。裴向军等[11]基于FLAC3D数值模拟方法,研究开挖过程中坡体稳定性变化规律及滑坡启动机理。宋琨等[12]基于长时间的监测数据分析了强降雨诱发老滑坡的动态作用。李巍岳等[13]统计拟合降雨强度与历时的关系,并构建了降雨滑坡响应阈值。杨城[14]通过采用Geo-Studio 和 Midas/GTS 有限元数值模拟软件分别分析了开挖和降雨对黄土边坡的影响。
部分学者基于位移监测数据和数值模拟等手段,分析了降雨工况下,开挖边坡的变形破坏机理[15-17]。肖超等[3]基于边坡位移监测结果和数值模拟,研究了湖北湘西山区公路边坡在开挖和降雨条件下坡体变形位移的过程。徐兴华等[18]采用数值模拟和极限平衡法,分析了在坡脚开挖过程中,不同强降雨条件下路堑斜坡的饱和—非饱状态和暂态渗流场变化。吴江鹏等[19]讨论了不同开挖时步以及不同工况下的边坡稳定性系数,并探讨了该滑坡的变形破坏机理。蔡军等[20]利用FLAC3D软件分析了降雨工况下航道工程开挖边坡的渗流场,分析降雨期间边坡失稳的普遍规律。
以上研究都是讨论开挖和降雨同时进行的滑坡变形破坏机理,但是对于先开挖再连续性强降雨,开挖与降雨时间非同步耦合影响下滑坡的变形破坏机理研究较少。本文以位于万源市太平镇前进广场后山的前进广场斜坡为例,基于边坡地表位移和深部位移数据分析滑坡的变形破坏特征,结合降雨数据,对人工开挖与降雨诱发城市滑坡的形成机制进行研究,通过对诱发滑坡的因素进一步分析讨论,研究前进广场滑坡变形破坏的整个演化过程。
1. 滑坡概况
1.1 区域环境条件
万源市地区位于大巴山弧形构造中段的南侧,区内构造线展布方向多,构造以褶皱为主,断裂发育[21](图1)。区内褶皱轴线多呈弧形,岩层倾角变化频繁,并常有挠曲现象。岩石的节理裂隙较为发育。
万源市气候温和,雨量充沛,夏季降雨强度大,日最大降水量在100 mm以上。在全球变暖的背景下,青藏高原的积雪明显减少[22],夏季高原地区为下游地区提供的水汽增加,从而导致万源市在6−7月份的降雨量逐年增加。
1.2 前进广场滑坡
滑坡区为侵蚀构造中山岭脊-峡谷地形,为山前台地。研究区整体地势南高北低,地形陡缓相间,地形坡度变化较大,最低点位于滑坡区北面长征路,标高639 m,最高点位于滑坡区南面山坡,标高890 m,总体地形坡度5°~25°,地貌单元属山前坡地(图2)。
斜坡变形体总体呈“舌”状,斜坡变形分布于斜坡中下部,前缘高程约639 m,后缘高程约839 m,滑移方向334°,变形体平均厚度约30 m,体积约5.20×106 m3,属大型深层土质斜坡。通过钻孔ZK02、ZK06、ZK10等(图3),滑带主要位于基覆界面,埋深10~46 m,在斜坡变形上部分布较浅,中部及下部较深,滑带土主要为含碎石粉质黏土,可塑-软塑状,结构松散。斜坡基岩滑床主要为三叠系上统须家河组地层(T3xj)砂岩。岩层产状32°∠25°~260°∠61°,岩层产状变化大(图3)。
在坡体上顺坡向分布有3条小冲沟,西侧冲沟有小股水流,流量约0.7 L/s,其余2条小冲沟均已干涸,冲沟在雨季具有猛涨猛落的特点。
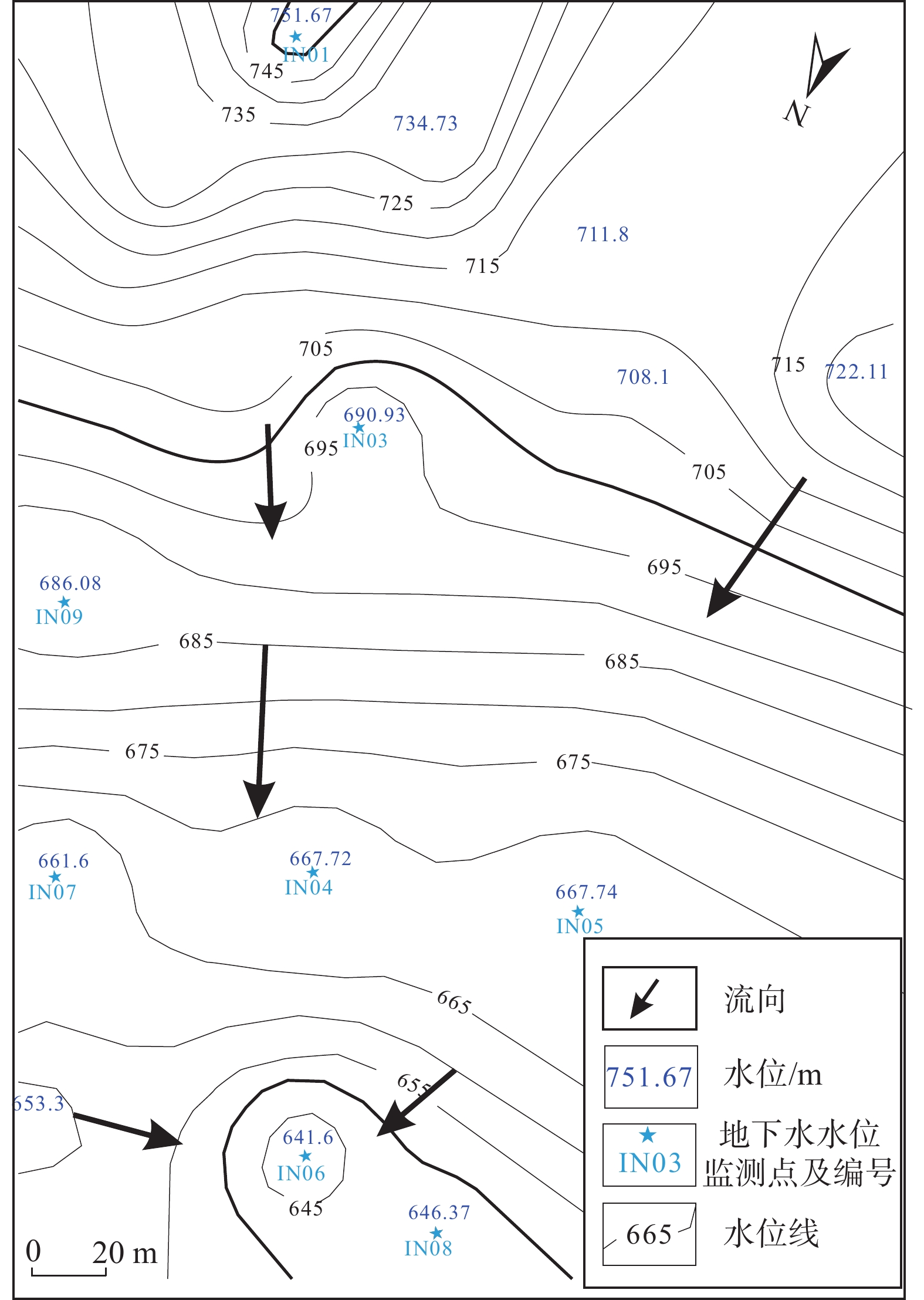
依据地下水等值线图(图4)可知,地下水从东南流向东北。坡体中部:左侧从东南流向西北流动,右侧从南流向东北流动,大致方向为从坡体右侧向坡体左侧流动;坡体前部:坡体两侧向中间流动。
2. 前进广场滑坡变形监测数据分析
2.1 变形监测
针对斜坡变形的监测主要有地表位移监测、深部位移监测和地表自动化监测3种。
本斜坡主要为土质滑坡,主要监测从变形监测和影响因素监测2方面进行。土质滑坡受外界因素影响较大,较不稳定,暴雨、地震等都能使其失稳滑移,但其滑动方向较单一,滑动范围的边界易于掌控,故对土质滑坡常采用十字形布设方法(图5)。
2.2 数据分析
2.2.1 地表位移数据分析
地表位移监测点共布设34个,编号Q1-Q11、H01-H13、Z01-Z10,前期每6 h采集一次数据,后期减缓为12 h一次,时段降雨量监测数据同上(图6)。
(1)坡体前部
坡体前部2019年7月中旬以前主要以垂直位移为主,之后以水平位移为主;以图6(a)(b)所列数据可知,8月中旬之前水平位移呈波动增长趋势,8月中旬到9月中旬,由于坡体应力调整,水平位移有的增大有的减小,9月下旬之后,由于坡体应力调整较缓,前缘基本趋于平稳。
(2)坡体中部
坡体中部在水平位移变化速率在7月中旬前坡体的垂直和水平位移都较小,之后突然变大,垂直方向上的位移整体上呈匀速下滑趋势;水平方向上的位移整体呈减缓趋势,持续增加,在8月中旬之后水平方向上的位移明显减小。
如图6(c)(d)所示,Z05水平位移变化速率整体近线形持续增加趋势;Z06水平位移变化速率整体呈减缓趋势,持续增加;Z07水平位移变化速率整体呈缓陡缓的趋势,波动持续增加。
(3)坡体后部
坡体后部地表位移监测数据见图6(e)(f)。可知,坡体后部在7月中旬之前变化较小,之后突然增大,垂直位移的整体上以匀速下降为主,水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,在8月中旬之后,水平位移变化速率明显变缓解,局部增加较大。
H02水平位移速率整体呈波动缓慢增加的趋势;H03水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,增长的速率在减缓,局部增加较大;H04水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,增长的速率在减缓;H06水平位移速率整体呈波动缓慢增加的趋势,现已趋缓;H07水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,增长的速率在减缓,局部增加较大;H08水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,增长的速率在减缓;H09水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,呈陡缓趋势;H10水平位移速率整体呈持续缓慢增加的趋势,呈陡缓趋势。
从地表位移监测数据分析可知,坡体前部基本趋于稳定,坡体中部水平位移速率为0.39~0.5 mm/d,局部为0.75~1.36 mm/d,坡体后部右侧位移速率0.63~0.87 mm/d,坡体后部左侧位移速率0.06~0.13 mm/d,观景平台以上位移速率0.21~0.36 mm/d,因此,斜坡变形体后部存在次级剪出的可能。
2.2.2 深部位移数据分析
本次应急阶段深部位移监测孔共布设了8个点,编号IN01−IN08,目的是查明斜坡变形的滑面位置及发展趋势,与钻探数据进行相互验证(图5)。
从深部位移监测数据(图7)分析可知:
(1)坡体前部
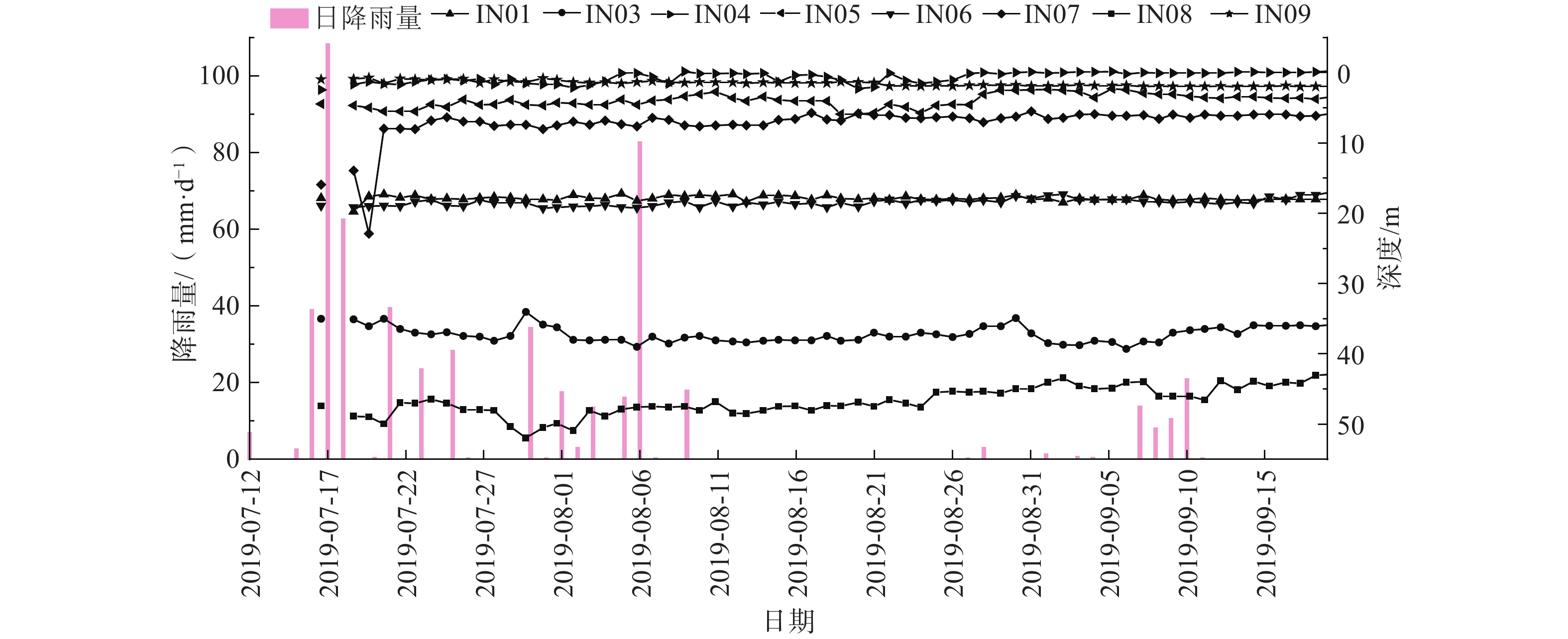
坡体前部的滑面通过监测数据分析变化较大,IN06监测推测滑面为深47 m处,速率越来越缓,至2019年9月8日累计水平位移为20.28 mm。IN08监测推测滑面为深24 m处,该滑面呈波动较缓速率增长—渐稳趋势,至2019年9月8日累计水平位移为15.42 mm。
(2)坡体中部
坡体中部通过深部位移数据分析,推测滑面在深36.5~40 m处,滑面呈较缓速率增长(局部波动)—趋稳趋势,至2019年9月8日累计水平位移为15.5 mm。
(3)坡体后部
坡体后部从IN01到IN03,监测推测滑面由浅到深,IN01推测滑面为深16 m处,水平累计位移以较缓速率增长(局部呈波动状态),增长波动较大,至2019年9月8日增长到40.63 mm(局部波动);IN03推测滑面为深39 m处,增长不明显,至2019年9月8日累计水平位移为11.05 mm。
从深部位移监测数据分析可知,在2019年7月的监测中,坡体后部的累计位移变化量最大且平均位移速率最快,相比较中部累计变化量较小,平均位移速率较慢。而在2019年8月的监测中,坡体中后6-6’剖面处的累计位移变化量最大且平均位移速率最快,相比较后部累计变化量较小,平均位移速率较慢。故蒋家院子和钟家院子平台后部较陡斜坡体,在陡缓交界处有次级剪出的可能。
2.2.3 降雨数据分析
从日降雨情况看,在2019年6月份以前主要以小雨为主,且降雨较分散,6月以后降雨明显增多,大雨和暴雨频次明显增多,且降雨较集中。据调查,前缘鼓胀裂缝、斜坡裂缝和房屋开裂变形,主要集中在2019年6月底。
连续降雨导致地下水水位变化,根据水位监测情况(图8),坡体中、上部地下水位基本无变化,坡体中下部斜坡变形西半侧水位有所浮动(幅值1.5~2.0 m),东半侧水位基本无变化,坡体下部地下水位基本无变化,由此可知,该坡体渗透性较大,排泄快的特点。由此可知,该坡体中下部地下水丰富,且具有一定的承压性。
3. 前进广场滑坡成因机制讨论
该斜坡变形稳定性影响因素受多种因素控制,主要从地形地貌、地层岩性、人类工程活动和降雨等因素进行分析。
3.1 控制因素分析
(1)地形地貌
斜坡变形整体地势南高北低,地形陡缓相间,地形坡度变化较大,整体呈“缓-陡-缓-陡-缓”的特点,地形坡度5°~25°,均坡度20°,斜坡变形后缘高与前缘高程相对高差约200 m,斜坡变形纵向长约640 m,横向宽约270 m,斜坡变形两侧发育小型冲沟,地形较复杂,为滑坡形成提供了较好的地形条件。
(2)地层岩性
该斜坡为一个老滑坡,地质结构脆弱。斜坡变形体主要由第四系块石土、碎石及角砾组成,粉质黏土充填,块石大小分布不均匀,最大可达5 m,坡体结构较松散,架空现象严重,且含碎石粉质黏土成层分布,连续性较好,下伏基岩为砂岩,透水性弱,为斜坡滑动提供了必要的物质条件。
3.2 影响因素分析
(1)人类工程活动
2019年4月,斜坡前缘棚户区改造基坑开始进行开挖,2019年4月中旬出现少量裂缝。据调查,前缘下部抗滑桩与板已脱离较长时间,说明该斜坡局部处于欠稳定状态,坡体处于不断调整应力的状态。同年3—7月,基坑监测单位对周边房屋监测的水平位移累计值已经大大超出了预警值。
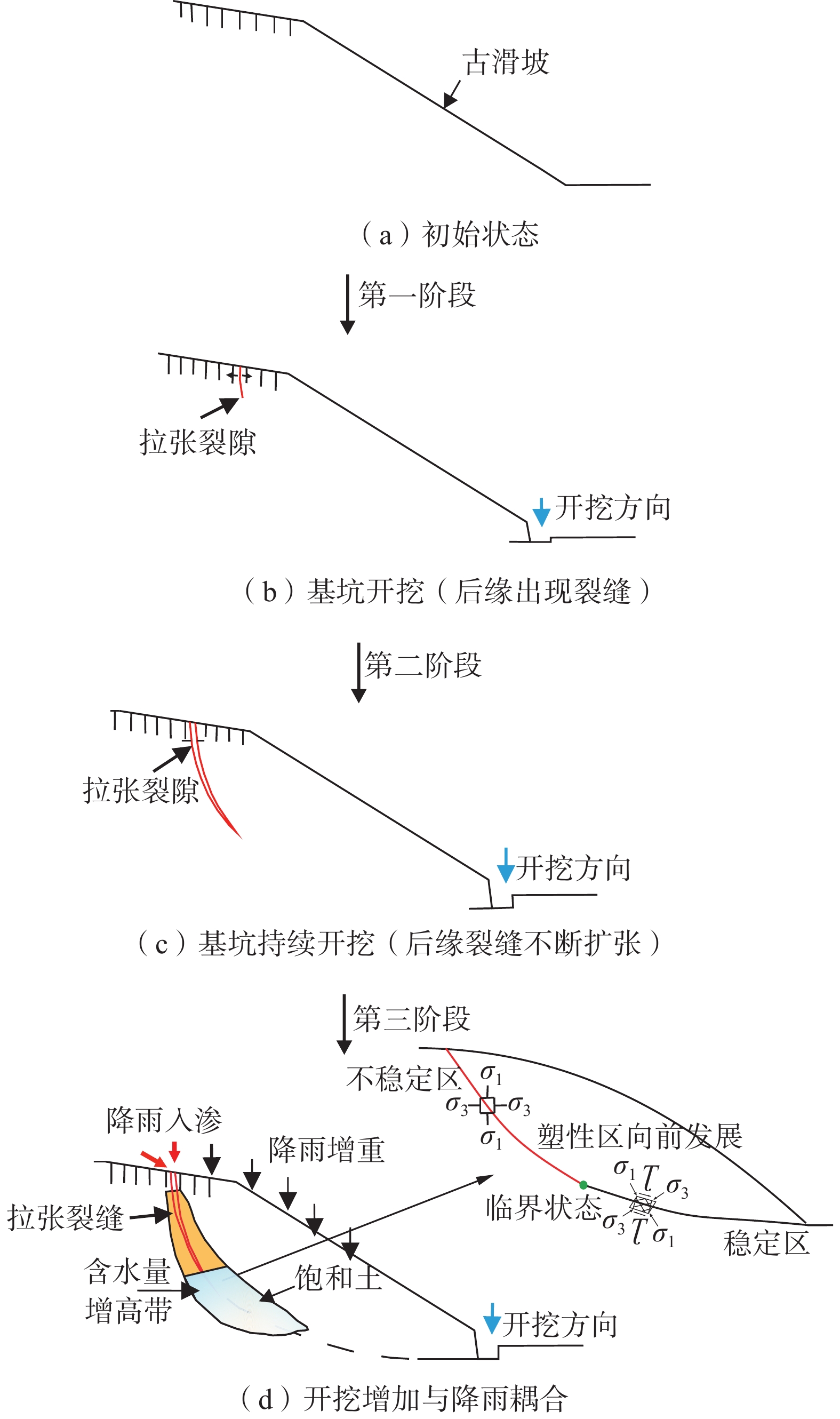
斜坡在原始地形时,推测斜坡处于欠稳定状态。由于斜坡前缘基坑开挖,相当于对斜坡进行前缘减载,基坑开挖后,该斜坡处于极限平衡状态;斜坡长期处于该状态,坡体应力重分布,前缘基坑的开挖不断持续,由于坡体变形补偿,引起斜坡后部应力不断调整,最终促使斜坡变形出现剪切带,应力调整促使斜坡变形剪切带形成也会导致抗剪强度的降低,诱发斜坡变形失稳。
(2)降雨
不少研究表明[23-24] ,降雨是滑坡失稳诱因中最常见和最活跃的诱发因素之一,长时间的强降雨不仅仅在降雨时影响坡体稳定性且在结束后较长时间会持续影响坡体稳定性[25]。
据统计,万源市夏季降雨强度大,日最大降水量在100 mm以上(图9),从坡体地表位移监测与该时段降雨量关系图(图6)可知,坡体与降雨变形具有明显的对应性,在强降雨或者持续性降雨期间,多个地表位移监测点出现位移加速的现象,且深部位移监测孔也开始出现疑似滑面。
综上所述,人工开挖和连续降雨且降雨强度较大是斜坡变形稳定性的主要影响因素。
3.3 时空变形特征析
结合地表位移监测数据、深部位移监测数据以及时段降雨数据分析,自2019年4月斜坡前缘棚户区改造基坑开始进行开挖,后方土体失去支撑,同时由于基岩裂隙水不断受到大气降雨的补给,斜坡上部的基岩裂隙水又不断补给中部和下部的第四系松散层潜水,导致部分非饱和土变为饱和土,有效应力降低,滑面参数降低,发生蠕变,同时也有少量地表水下渗至滑体内,形成张拉裂缝后,地表水更容易直接进入坡体内部,促进斜坡变形加速发展。2019年6月,随着基坑开挖深度不断加大,日段降雨量持续增加,最终导致老滑坡复活。
在雨季来临前,斜坡处于较稳定状态,进入雨季后,斜坡逐渐产生裂缝变形,由此可见降雨是诱发本次滑坡的因素之一。在基坑工程开挖前,3月份左右斜坡裂缝并未产生,4月份动工后,少量裂缝逐渐显现,斜坡发生局部变形,证明此时斜坡已处于不稳定状态。由此可见人类工程活动和降雨构成了滑坡产生变形破坏的主要因素。
3.4 人类活动和降雨耦合诱发滑坡过程机制
从地形上看,该斜坡地形“陡-缓-陡”的特征,形成多级台地;从斜坡变形特征分析,斜坡变形中部拉张裂缝较发育,且其走向基本与滑动方向垂直,多条张拉裂缝可见明显下错,裂缝发育特征符合推移式的典型特征。从裂缝形成时间来看,裂缝发育过程与基坑开挖卸荷时间基本一致。另外前进广场出现大量鼓胀裂缝。从监测数据分析可知,总体斜坡变形体呈现后部大于中部、中部大于前部、广场区大于基坑区的特点,体现出在该阶段斜坡变形不断从上向下推挤,并存在转向推挤的现象。综合分析,该斜坡变形破坏模式主要为推移式[26]。
滑坡区坡体后部地下水以基岩裂隙水为主,坡体中部和前部为第四系潜水层(图5),由于局部存在粉质黏土分布,且局部承压,一方面增大了滑带土孔隙水压力[27],有效应力降低,从而降低滑带土抗剪强度,另一方面,承压水对滑带土形成的扬压力对斜坡变形稳定性也有较大影响;由于土体含较多粉质黏土等细粒成分,透水性相对较差,地表水下渗量小,但也不容忽视,特别是在裂缝开始形成后,导致地表水下渗量不断增大,将加速斜坡变形的发展。
据此,将滑坡破坏可分为3个阶段(图9)。第一阶段:本滑坡在人工开挖坡脚的作用下,在坡体前方产生局部变形,坡体内部的主应力向临空方向集中,从而使得坡体中后缘与后缘形成多条张拉裂缝,为雨水入渗创造了有利条件。第二阶段:降雨后雨水与地表水顺着裂缝进入坡体,一方面让斜坡土体自重增大,导致坡体下滑力增强,另一方面大量水分入渗使土体软化,部分非饱和土变为饱和土,有效应力降低,从而降低滑带土抗剪强度,同时承压水对滑带土形成的扬压力降低了斜坡变形稳定性,斜坡内部裂缝持续往下扩展。第三阶段:坡体由局部破坏逐渐演变成大变形直至发生整体破坏,当在降雨量达到峰值时,整体的破坏使得后部土体抗剪强度进一步降低,从而在后部发生表层松散体的破坏。
4. 结 论
本文基于地表位移监测数据、深部位移监测数据以及降雨数据对前进广场滑坡的变形特征进行分析,得到了以下成果:
(1)该斜坡地形“陡-缓-陡”的特征,形成多级台地,根据深部位移监测数据分析,监测滑面大致位于基覆界面位置,埋深在10~46 m不等,在斜坡变形上部分布较浅,中部及下部较深,结合斜坡变形特征,推测前进广场滑坡属于推移式滑坡。
(2)依据地表位移监测数据和变形迹象可知,坡体中部水平位移速率为0.39~0.5 mm/d,局部为0.75~1.36 mm/d,坡体后部右侧位移速率0.63~0.87 mm/d,斜坡变形体后部及中部陡缓交界处有次级剪出的可能,暴雨工况下稳定性差。
(3)滑坡形成原因受多种因素影响,主要是人工开挖与降雨耦合,前缘基坑的开挖是导致老滑坡复活最主要的原因,降雨起到了激发和加速作用。
(4)滑坡的形成演化模式为:前缘棚户区改造基坑开挖卸荷,一方面为边坡提供了良好的临空面,另一方面后方土体失去支撑。同时由于基岩裂隙水不断受到大气降雨的补给,部分饱和土变成不饱和土,有效应力降低,滑面参数降低,发生蠕变,同时也有少量地表水下渗至滑体内,形成张拉裂缝后,地表水更容易直接进入坡体内部,促进斜坡变形加速发展。随着基坑开挖深度不断加大,降雨量持续增加,最终导致老滑坡复活。
-
-
[1] ZHAO Bo,YUAN Lei,GENG Xueyu,et al. Deformation characteristics of a large landslide reactivated by human activity in Wanyuan City,Sichuan Province,China[J]. Landslides,2022,19(5):1131 − 1141. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-022-01853-3
[2] 薛振勇,侯书云. 人类活动诱发的地质灾害—天水锻压机床厂滑坡[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,1991,2(4):54 − 62. [XUE Zhenyong,HOU Shuyun. The geological hazard induced by human activity:The landslide in Tianshui forging &. pressing machine tool factory[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,1991,2(4):54 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.1991.04.007 XUE Zhenyong, HOU Shuyun. The geological hazard induced by human activity—the landslide in Tianshui forging &. pressing machine tool factory[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 1991, 2(4): 54-62. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.1991.04.007
[3] 肖超,金福喜,刘海鸿,等. 开挖与降雨作用下边坡失稳机理及模拟分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(1):37 − 43. [XIAO Chao,JIN Fuxi,LIU Haihong,et al. Mechanism of slope failure and numerical simulation analysis under slope excavation and rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(1):37 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.01.006 XIAO Chao, JIN Fuxi, LIU Haihong, et al. Mechanism of slope failure and numerical simulation analysis under slope excavation and rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2012, 20(1): 37-43. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.01.006
[4] 刘震涛,尚彦军,邵鹏,等. 降雨与开挖联合作用下边坡位移矢量及速率变化分析—以韩江高陂水利枢纽右岸尾水渠边坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(1):122 − 131. [LIU Zhentao,SHANG Yanjun,SHAO Peng,et al. Analysis on variations of displacement rates under influences of rainfall and excavation:Taking right bank slope of Gaobei key water control project as case study[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(1):122 − 131. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-294 LIU Zhentao, SHANG Yanjun, SHAO Peng, et al. Analysis on variations of displacement rates under influences of rainfall and excavation—taking right bank slope of Gaobei key water control project as case study[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2020, 28(1): 122-131. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2019-294
[5] 李明, 石晋旭, 王昌贤, 等. 滑坡耦合效应及耦合参数研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 2006, 25(增刊1): 2650-2655 LI Ming, SHI Jinxu, WANG Changxian, et al. Study on coupling effect and coupling parameter of the landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2006, 25(Sup 1): 2650-2655. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] ZHOU Zhou,SHEN Junhui,LI Ying,et al. Mechanism of colluvial landslide induction by rainfall and slope construction:A case study[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2021,18(4):1013 − 1033. DOI: 10.1007/s11629-020-6048-9
[7] 王伟,王卫,戴雄辉. 四川美姑拉马阿觉滑坡复活特征与影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):9 − 17. [WANG Wei,WANG Wei,DAI Xionghui. Analysis of reactivated characteristics and influencing factors of the Lamajue landslide in Meigu County of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):9 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) WANG Wei, WANG Wei, DAI Xionghui. Analysis of reactivated characteristics and influencing factors of the Lamajue landslide in Meigu County of Sichuan Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 9-17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 李高,谭建民,王世梅,等. 滑坡对降雨响应的多指标监测及综合预警探析—以赣南罗坳滑坡为例[J]. 地学前缘,2021,28(6):283 − 294. [LI Gao,TAN Jianmin,WANG Shimei,et al. Multi-index monitoring and comprehensive early warning of landslides in response to rainfall:An example of the Luo’ao landslide in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2021,28(6):283 − 294. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.7.17 LI Gao, TAN Jianmin, WANG Shimei, et al. Multi-index monitoring and comprehensive early warning of landslides in response to rainfall: an example of the Luo’ao landslide in southern Jiangxi Province[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2021, 28(6): 283-294. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13745/j.esf.sf.2021.7.17
[9] 张志兼,黄勋,蔡雨微,等. 三峡库区武隆段滑坡灾害驱动因子演变格局与人类活动的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(3):39 − 50. [ZHANG Zhijian,HUANG Xun,CAI Yuwei,et al. The evolution pattern and influence of human activities of landslide driving factors in Wulong section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(3):39 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Zhijian, HUANG Xun, CAI Yuwei, et al. The evolution pattern and influence of human activities of landslide driving factors in Wulong section of the Three Gorges Reservoir area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(3): 39-50. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 黄晓虎,易武,龚超,等. 开挖致使古滑坡复活变形机理研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(7):1276 − 1285. [HUANG Xiaohu,YI Wu,GONG Chao,et al. Reactivation and deformation mechanism of ancient landslides by excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(7):1276 − 1285. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Xiaohu, YI Wu, GONG Chao, et al. Reactivation and deformation mechanism of ancient landslides by excavation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(7): 1276-1285. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 裴向军,袁广,张晓超,等. 坡脚开挖诱发滑坡机理—以沙井驿滑坡为例[J]. 山地学报,2017,35(2):195 − 202. [PEI Xiangjun,YUAN Guang,ZHANG Xiaochao,et al. Study on the mechanism of the loess landslide triggered by slope toe excavation:For the example of the landslide of shajingyi[J]. Mountain Research,2017,35(2):195 − 202. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000212 PEI Xiangjun, YUAN Guang, ZHANG Xiaochao, et al. Study on the mechanism of the loess landslide triggered by slope toe excavation—for the example of the landslide of shajingyi[J]. Mountain Research, 2017, 35(2): 195-202. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16089/j.cnki.1008-2786.000212
[12] 宋琨,陈伦怡,刘艺梁,等. 降雨诱发深层老滑坡复活变形的动态作用机制[J]. 地球科学,2022,47(10):3665 − 3676. [SONG Kun,CHEN Lunyi,LIU Yiliang,et al. Dynamic mechanism of rain infiltration in deep-seated landslide reactivate deformation[J]. Earth Science,2022,47(10):3665 − 3676. (in Chinese with English abstract) SONG Kun, CHEN Lunyi, LIU Yiliang, et al. Dynamic mechanism of rain infiltration in deep-seated landslide reactivate deformation[J]. Earth Science, 2022, 47(10): 3665-3676. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 李巍岳,刘春,SCAIONI M,等. 基于滑坡敏感性与降雨强度-历时的中国浅层降雨滑坡时空分析与模拟[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2017,47(4):473 − 484. [LI Weiyue,LIU Chun,SCAIONI M,et al. Spatio-temporal analysis and simulation on shallow rainfall-induced landslides in China using landslide susceptibility dynamics and rainfall I-D thresholds[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae),2017,47(4):473 − 484. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.1360/N072016-0129 LI Weiyue, LIUChun, SCAIONI M, et al. Spatio-temporal analysis and simulation on shallow rainfall-induced landslides in China using landslide susceptibility dynamics and rainfall I-D thresholds[J]. Scientia Sinica (Terrae), 2017, 47(4): 473-484. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.1360/N072016-0129
[14] 杨城. 降雨与开挖方式对黄土边坡稳定性影响分析——以榆林市清涧县某边坡为例[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2020 YANG Cheng. Analysis of the influence of rainfall and excavation methods on the stability of loess slopes: Taking a slope in Qingjian County, Yulin City as an example[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 熊珅,易武,王力,等. 三峡库区八字门滑坡变形破坏机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):9 − 18. [XIONG Shen,YI Wu,WANG Li,et al. Analysis of deformation and failure mechanism of Bazimen Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):9 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.05.02 XIONG Shen, YI Wu, WANG Li, et al. Analysis of deformation and failure mechanism of Bazimen Landslide in Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(5): 9-18. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2019.05.02
[16] 胡华,吴轩,张越. 基于模拟试验的强降雨条件下花岗岩残积土斜坡滑塌破坏机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):92 − 97. [HU Hua,WU Xuan,ZHANG Yue. Experimental study on slope collapse characteristics of granite residual soil slope under heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):92 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.05-11 HU Hua, WU Xuan, ZHANG Yue. Experimental study on slope collapse characteristics of granite residual soil slope under heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2021, 32(5): 92-97. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2021.05-11
[17] WANG Huanling,JIANG Zihua,XU Weiya,et al. Physical model test on deformation and failure mechanism of deposit landslide under gradient rainfall[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2022,81(1):66. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-021-02566-y
[18] 徐兴华,尚岳全,唐小明,等. 降雨作用及坡脚开挖激发路堑滑坡的灾变效应[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(4):6 − 15. [XU Xinghua,SHANG Yuequan,TANG Xiaoming,et al. Catastrophic effect of landslide under rainfall condition and excavation at foot[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(4):6 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2013.04.010 XU Xinghua, SHANG Yuequan, TANG Xiaoming, et al. Catastrophic effect of landslide under rainfall condition and excavation at foot[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2013, 24(4): 6-15. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2013.04.010
[19] 吴江鹏,章广成,侯赠. 开挖及降雨作用下土质边坡变形破坏机理[J]. 湖南科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,30(2):73 − 79. [WU Jiangpeng,ZHANG Guangcheng,HOU Zeng. Analysis on soil slope deformation failure mechanism under slope excavation and rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition),2015,30(2):73 − 79. (in Chinese with English abstract) WU Jiangpeng, ZHANG Guangcheng, HOU Zeng. Analysis on soil slope deformation failure mechanism under slope excavation and rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Hunan University of Science & Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 30(2): 73-79. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 蔡军,许胜才. 基于FLAC3D软件FISH语言二次开发的降雨工况下航道工程开挖边坡渗流场的分析[J]. 水电能源科学,2021,39(10):156 − 159. [CAI Jun,XU Shengcai. Seepage field analysis of channel slope excavation under rainfall condition based on secondary development of FLAC3D software with the FISH language[J]. Water Resources and Power,2021,39(10):156 − 159. (in Chinese with English abstract) CAI Jun, XU Shengcai. Seepage field analysis of channel slope excavation under rainfall condition based on secondary development of FLAC3D software with the FISH language[J]. Water Resources and Power, 2021, 39(10): 156-159. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 向贵府,许模,崔杰,等. 四川省万源市花楼乡董家梁滑坡特征及成因机制[J]. 南水北调与水利科技,2017,15(1):145 − 149. [XIANG Guifu,XU Mo,CUI Jie,et al. Study on characteristics and formation mechanism of Dongjialiang landslide in Hualou Town,Wanyuan City,Sichuan Provinc[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology,2017,15(1):145 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2017.01.024 XIANG Guifu, XU Mo, CUI Jie, et al. Study on characteristics and formation mechanism of Dongjialiang landslide in Hualou Town, Wanyuan City, Sichuan Provinc[J]. South-to-North Water Transfers and Water Science & Technology, 2017, 15(1): 145-149. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13476/j.cnki.nsbdqk.2017.01.024
[22] 杨耀先,胡泽勇,路富全,等. 青藏高原近60年来气候变化及其环境影响研究进展[J]. 高原气象,2022,41(1):1 − 10. [YANG Yaoxian,HU Zeyong,LU Fuquan,et al. Progress of recent 60 years’ climate change and its environmental impacts on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology,2022,41(1):1 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract) YANG Yaoxian, HU Zeyong, LU Fuquan, et al. Progress of recent 60 years’ climate change and its environmental impacts on the Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Plateau Meteorology, 2022, 41(1): 1-10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[23] 雷德鑫,易武. 三峡库区王家坡滑坡降雨阈值分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):95 − 101. [LEI Dexin,YI Wu. Analysis of rainfall threshold of the Wangjiapo Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):95 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.16 LEI Dexin, YI Wu. Analysis of rainfall threshold of the Wangjiapo Landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2018, 29(5): 95-101. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16031/j.cnki.issn.1003-8035.2018.05.16
[24] 张珍,李世海,马力. 重庆地区滑坡与降雨关系的概率分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(17):3185 − 3191. [ZHANG Zhen,LI Shihai,MA Li. Probability analysis of relationship between landslide and rainfall in Chongqing area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(17):3185 − 3191. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.17.029 ZHANG Zhen, LI Shihai, MA Li. Probability analysis of relationship between landslide and rainfall in Chongqing area[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2005, 24(17): 3185-3191. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.17.029
[25] 胡爱国,周伟. 地震与强降雨作用下堆积体滑坡变形破坏机理及防治方案分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(1):27 − 34. [HU Aiguo,ZHOU Wei. Deformation and failure mechanism and analysis on prevention measures of colluction landslide under earthquake and heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(1):27 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Aiguo, ZHOU Wei. Deformation and failure mechanism and analysis on prevention measures of colluction landslide under earthquake and heavy rainfall[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(1): 27-34. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] 王恭先. 滑坡学与滑坡防治技术[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2004 WANG Gongxian. Landslide science and landslide prevention technology[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2004. (in Chinese )
[27] 王刚,孙萍,吴礼舟,等. 降雨诱发浅表层黄土滑坡机理实验研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(5):1252 − 1263. [WANG Gang,SUN Ping,WU Lizhou,et al. Experimental study on mechanism of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(5):1252 − 1263. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.05.010 WANG Gang, SUN Ping, WU Lizhou, et al. Experimental study on mechanism of shallow loess landslides induced by rainfall[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2017, 25(5): 1252-1263. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13544/j.cnki.jeg.2017.05.010
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 李朝辉,张柯宏. 藏东南某滑坡成因分析及稳定性评价. 铁道勘察. 2025(01): 13-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张卫雄,杨校辉,丁保艳,朱文杰,任永忠. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡堆积层剪切特性与强度参数分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 65-72 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:





 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS