Risk assessment of mass debris flow based on numerical simulation: An example from the Malu River basin in Min County
-
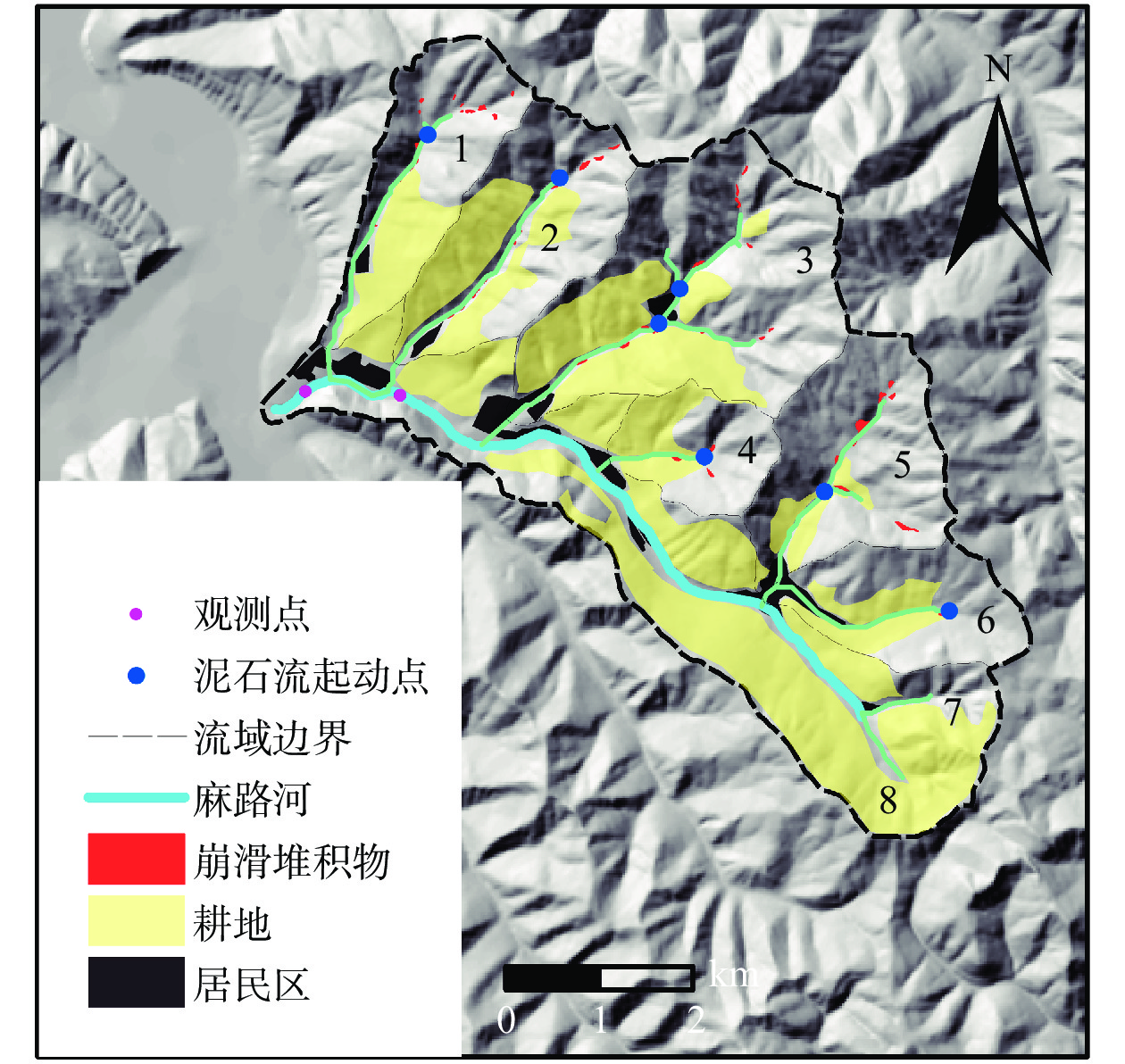
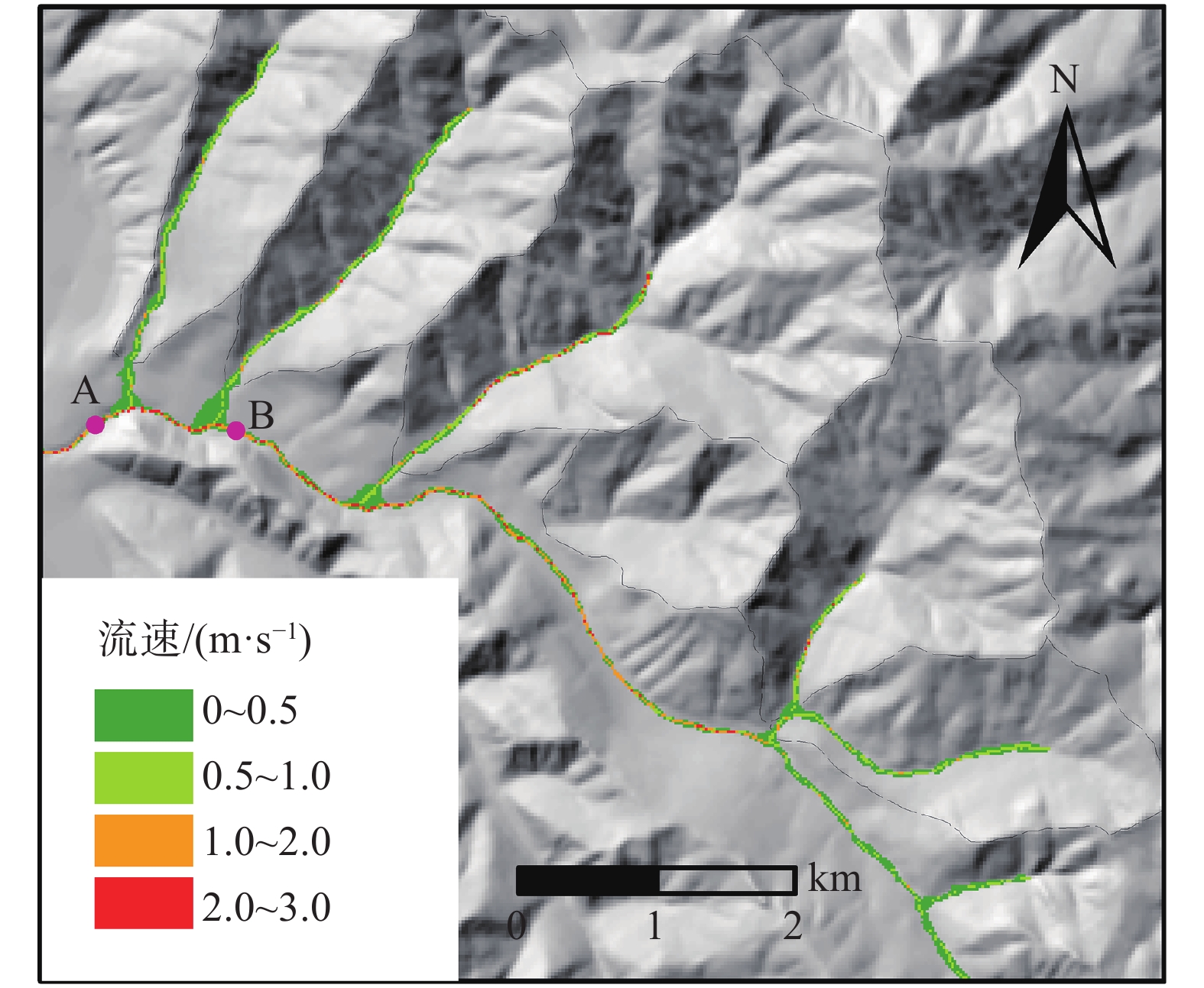
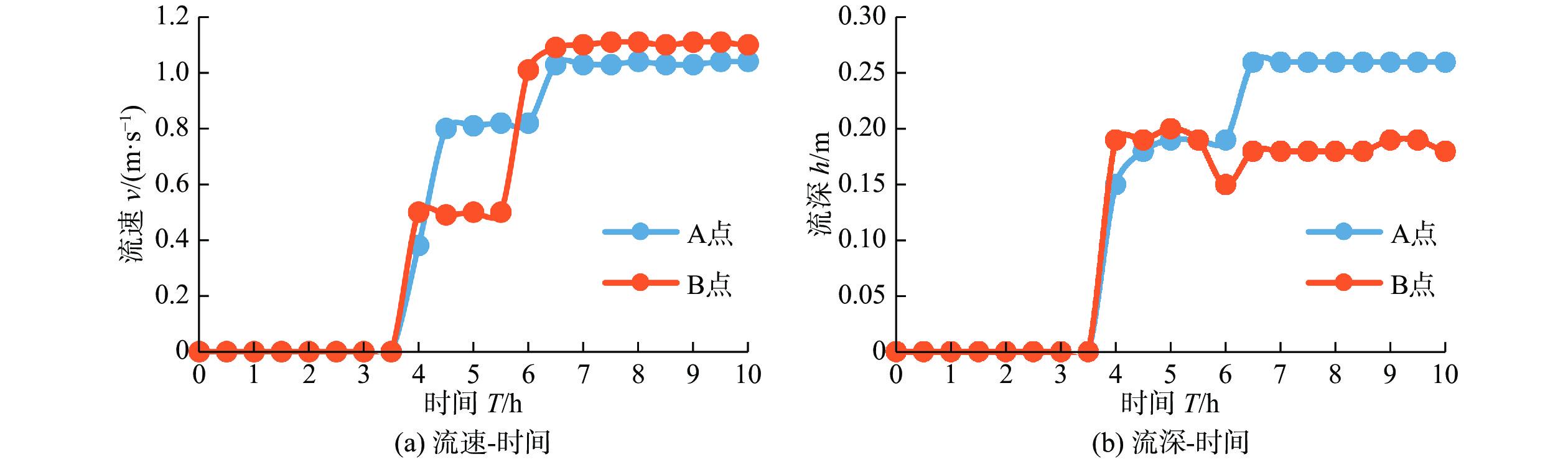
摘要: 岷县是甘肃南部泥石流频发地区。岷县泥石流多分布于洮河干支流两岸,为群发性泥石流。为了研究群发性泥石流的运动及堆积特征,选取了甘肃岷县麻路河流域为研究区域,以流域内2012年“5·10”暴发泥石流造成重大损失的6条泥石流沟作为整体研究对象,并考虑主河对泥石流堆积物的冲刷携带,运用FLO-2D模拟降雨前主河流动情况及不同降雨频率条件下主河及泥石流的流动情况。根据野外调查结果对比2%降雨频率条件下泥石流模拟结果,验证模型的可靠性。基于模拟结果用ArcGIS进行危险性评价,识别流域内高危险泥石流沟并划定高危险居民区,统计受冲击范围,为泥石流防治和预警工作提供科学依据。Abstract: Min County is an area with frequent debris flow in the south part of Gansu Province. In order to study the movement and accumulation characteristics of debris flow, the Malu River basin in Min County, Gansu Province, which was affected by serious debris flow on May 10, 2012, is selected as the research area. Six debris flow gullies in the basin are taken as the research object, which are taken as a whole. Considering the main river's scouring and carrying of debris flow deposits, FLO-2D is used to simulate the flow situation and different rainfall frequency of the main river before rainfall. According to the field investigation results, the debris flow simulation results under the condition of 2% rainfall frequency are compared to verify the accuracy of the model. Based on the simulation results, ArcGIS is used to carry out the risk assessment, identify the high-risk debris flow gully in the basin, delimit the high-risk residential area, and make statistics of the impacted area, so as to provide scientific basis for debris flow prevention and early warning.
-
Keywords:
- Malu River basin /
- mass debris flow /
- risk assessment /
- FLO-2D /
- ArcGIS
-
2010年8月8日凌晨,舟曲县城北侧三眼峪沟和罗家峪沟同时暴发特大山洪泥石流,城区三分之一被淹,共造成1435人死亡,330人失踪,直接经济损失超过10亿元[1-2],给舟曲县城居民生命财产造成了巨大损失,也给当地生产生活带来严重困难。灾害引起了党中央、国务院、中央军委及全国人民的高度关注,启动国家二级救灾应急响应,同时批复专项资金进行治理。其中,重力式拦挡坝是舟曲泥石流治理中的最主要工程之一。
周龙茂等[3]认为拦挡坝在泥石流治理中发挥着重要作用,但同时拦挡坝也是最易遭受破坏、失去防灾功能的泥石流防治构筑物,因此,在泥石流设计中,为了拦挡坝不被破坏,往往设计得很保守,王念秦等[4]提出这种设计容易造成两个极端现象:保守,造成资金浪费;冒进,防治工程失败。要做到既能保证拦挡坝安全,又能将投资最小化,就要求对泥石流拦挡坝抗冲击力验算方法提出新要求。传统的泥石流冲击力计算经验公式[5]只能通过大量试算表述结果,不能表述过程。而将三维有限元数值分析方法应用到泥石流拦挡坝稳定性验算中[6-7],能将过程和结果同时呈现,即通过分步加载的方法,逐步呈现拦挡坝的位移情况和抗冲击力过程中的破损情况。
关于拦挡坝的数值模拟研究还比较少,本文将考虑损伤的混凝土本构模型与有限元计算方法相结合,对舟曲泥石流混凝土拦挡结构进行力学分析,最终确定了拦挡坝的抗冲击力合理区间,以期为泥石流治理工程的设计提供借鉴。
1. 模型建立及相关参数的设定
杨东旭等[8]、许海亮等[9]、张睿骁等[10]认为冲击力是破坏防治工程构筑物的主要作用力之一,其大小与泥石流流量、流速、容重等有关。泥石流冲击力是泥石流防治工程设计的重要参数,分为流体整体冲击力和个别石块的冲击力两种,在设计中取两种计算结果较高者为设计依据。文章采用《泥石流灾害防治工程设计规范》(DZT 0239—2004)中的经验公式[5]作为数值计算结果的参考和验证。
流体整体冲击力计算公式:
$$f = K\frac{{{\gamma_C}}}{g}v_c^2$$ (1) 式(1)中:f−冲击力/Pa;
K−系数,取2.5;
${\gamma_C} $ −泥石流重度/(t·m−3);g−重力加速度,取9.8 m·s−2;
vc−断面处泥石流流速(m·s−1)。
个别石块的冲击力计算公式:
$${F_b} = \sqrt {\frac{{48EJ{V^2}W}}{{g{L^3}}}} \cdot \sin \alpha $$ (2) 式(2)中:Fb−泥石流大石块冲击力/(t·m−2);
E−工程构件弹性模量/(t·m−2);
J−工程构件界面中心轴的惯性矩/m4;
V−石块运动速度(m·s−1);
W−石块重量/t;
L−构件长度/m;
α−石块运动方向与构件受力面的夹角/(°)。
泥石流具体参数和计算结果见表1,编号和《甘肃省舟曲县三眼峪沟泥石流灾害设计报告》[1]中保持一致。
表 1 泥石流冲击力计算参数及结果Table 1. Debris flow impact calculation parameters and results编号 ${\gamma _c}$/(t·m−3) ${v_c}$/(m·s−1) $L$/m $W$/t $V$/(m·s−1) $\sin \alpha $ $E$/(t·m−2) $J$/m4 $f$/(t·m−2) ${F_b}$/(t·m−2) 大1号坝 2.09 6.56 5.5 162 10.55 0.946 2.8 274.63 22.49 7.14 大2号坝 2.09 6.60 2.8 81 7.53 0.946 2.8 274.63 22.76 7.34 大3号坝 2.03 6.61 8.6 259.2 13.20 0.946 2.8 216.00 22.17 19.95 大4号坝 2.03 8.67 4.3 94.5 9.33 0.946 2.8 421.88 38.15 19.62 小2号坝 2.03 6.56 3.1 83.7 7.92 0.946 2.8 421.88 21.84 4.28 小3号坝 2.13 9.86 5.8 129.6 10.84 0.946 2.8 274.63 51.77 8.98 小4号坝 2.13 5.49 2.8 75.6 7.53 0.946 2.8 421.88 16.05 14.17 小6号坝 2.13 8.12 4.7 121.5 9.76 1.000 2.8 512.00 35.11 37.01 主1号坝 2.13 6.53 11.2 361.8 15.06 0.946 2.8 421.88 22.71 44.35 主2号坝 2.13 6.16 7.5 234.9 12.32 0.946 2.8 343.00 20.21 12.44 计算区域按地质资料分高程、分区域模拟。模型向上游及下游分别延伸至坝体厚度的2倍,模型高度方向自坝基向下延伸坝体垂直部分的2倍。以大2号坝为例进行数值模拟,砼坝体和地基土数值分析具体参数见表2。
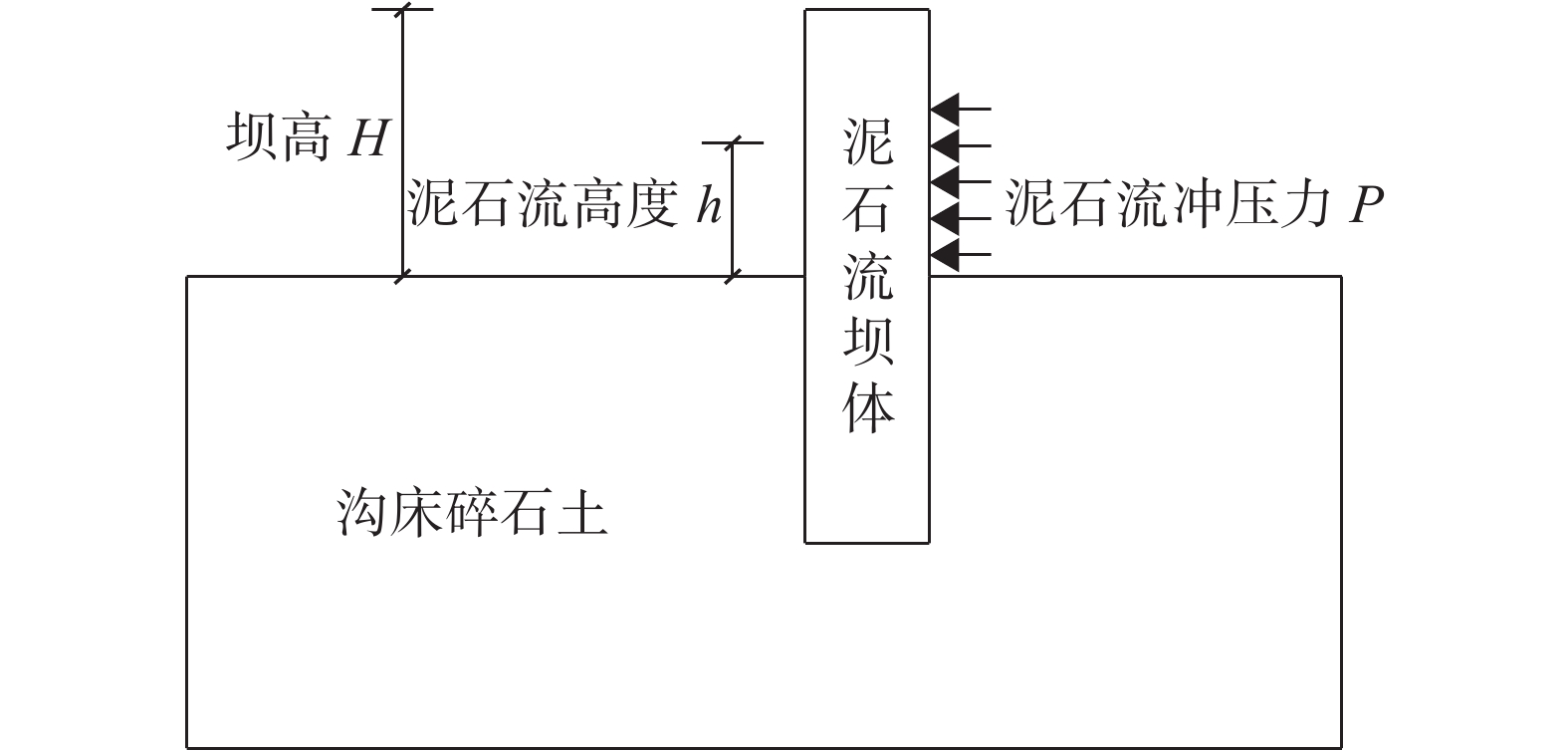
分析中将泥石流流体的冲击力P简化为静力加载到坝体侧面,计算坝体的极限抗冲击能力,简化计算力学模型如图1所示。
表 2 混凝土坝和地基碎石土参数Table 2. Concrete dam and gravel soil parameter名称 坝体 沟床碎石土 弹性模量/GPa 泊松比 损伤阈值 拉压强度比 弹性模量/MPa 泊松比 黏聚力/kPa 内摩擦角/(°) 剪胀角/(°) 取值 24.0 0.2 2×10−4 0.15 240 0.2 5.0 40 40 2. 重力式拦挡坝抗冲击力数值分析
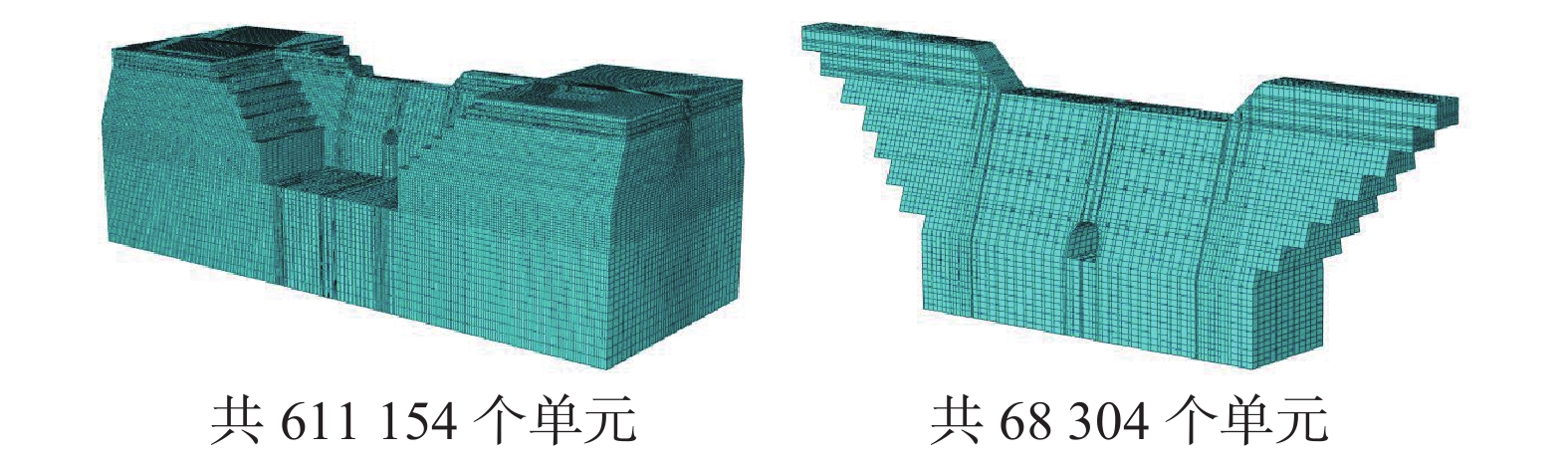
数值模拟使用有限元软件ABAQUS进行计算分析。冯帅等[11]认为数值计算出的泥石流的极限抗冲压力大于经验公式计算出的泥石流整体冲击压力。因此,本文分别按泥石流流体高度h=H/2坝高(工况1)及h=H(工况2)两种工况进行分析,将数值计算出的抗冲击力限定在一合理区间。计算中加载每一荷载增量后均计算至收敛,并记录坝体的最大位移。加载至破坏时(计算不收敛,坝体位移不断增大)的压力P与坝体最大位移曲线由倾斜直线变为水平线,坝体所能承受的最大冲击力Pu可由压力P与坝体最大位移曲线水平段的和坐标求出。应力以拉为正,以压为负,应力的单位为Pa,长度单位为m,位移单位为mm,其他单位均采用国际单位制。具体模型边界和网格划分图2所示。
2.1 工况1条件下重力式拦挡坝抗冲击力数值分析
大坝按泥石流冲击高度h=H/2坝高计算,在拦挡坝的一侧施加泥石流冲击力,荷载增量取值100 kPa,每加一次荷载,计算至收敛,并且记录一次坝体的最大位移;一直持续加载至破坏时,即计算不收敛且坝体位移不断增大时停止计算。
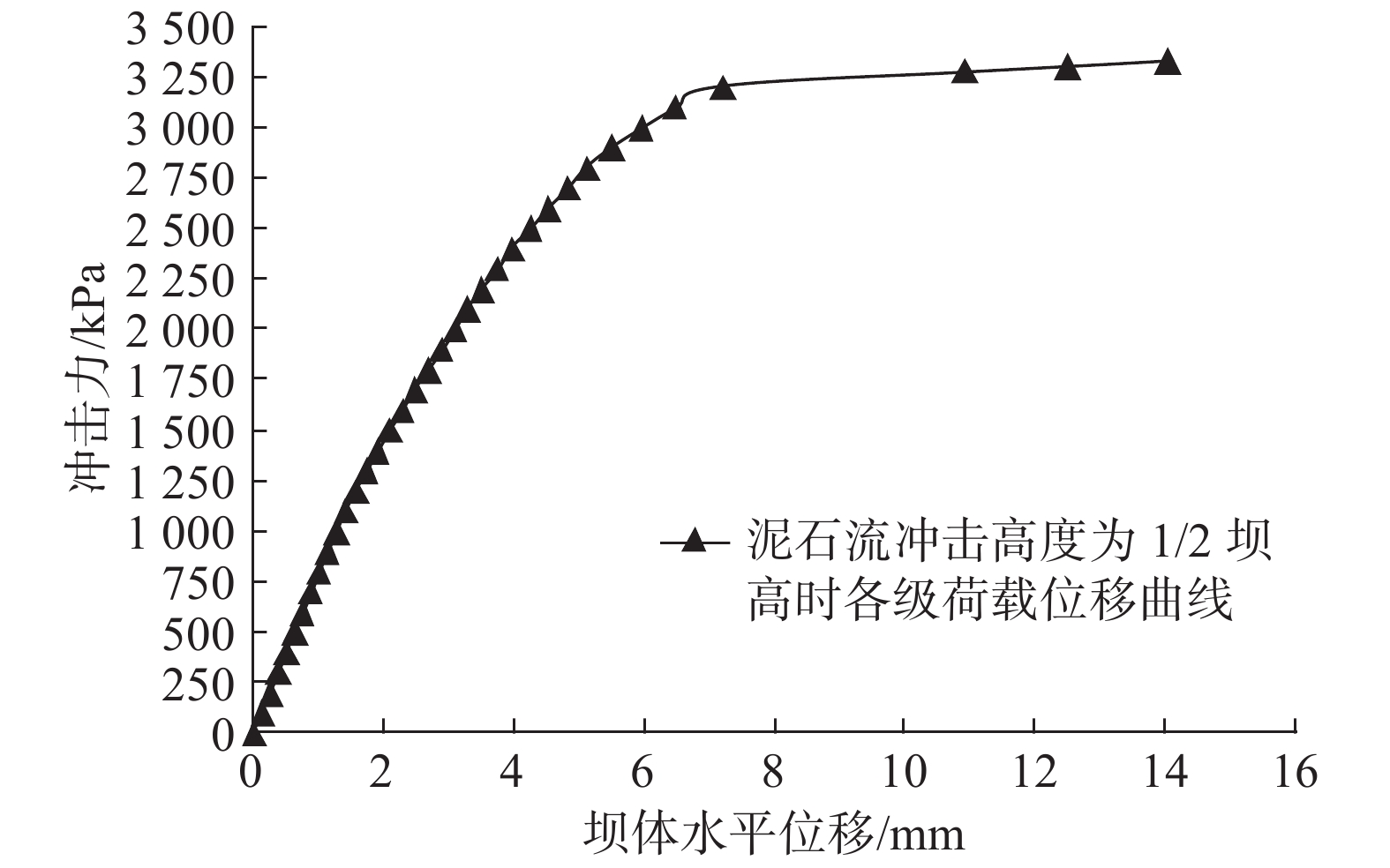
周勇等[12]采用结构动力学的方法,建立了泥石流冲击荷载与拦挡坝的动力方程,提出拦挡坝的坝顶处有最大的位移,为本次工程力学计算提供了一种思路。将泥石流冲击力与相应荷载下坝体位移进行统计,形成图3所示冲击力与坝体最大位移关系曲线,会发现坝体水平位移随着拦挡坝冲击力增大呈对数曲线递增,泥石流流体高度h=H/2工况条件下施加的最大冲击力Pu=3500 kPa(357.14 t/m2)。
坝体损毁过程如图4所示,冲击力达到800 kPa(水平位移1 mm)时坝体开始出现初始损伤;冲击力达到1100 kPa(水平位移1.4 mm)时两侧坝肩和基础局部都出现较明显损伤;冲击力达到1400 kPa时(水平位移2 mm),泄水孔和泄水涵洞边缘出现局部损伤;冲击力达到2700 kPa(水平位移4.8 mm)时,基础出现大面积损伤,沿正面泄水涵洞和泄水孔形成纵向损伤;冲击力达到3200 kPa(水平位移7.2 mm)时,坝肩、基础及坝体正中损伤贯通,损伤区呈“W”型,坝体已基本失去功能,在工程实际应用中已达到破坏极限;冲击力达到3500 kPa时,坝体大面积损伤,超过坝体总面积的2/3,水平位移高达14 mm,整体性降低或消失,这只是一种模拟现象,在工程实际应用中泥石流物质沿坝体破坏处流通,坝体已不存在整体位移现象。
2.2 工况2条件下重力式拦挡坝极限抗冲压数值分析
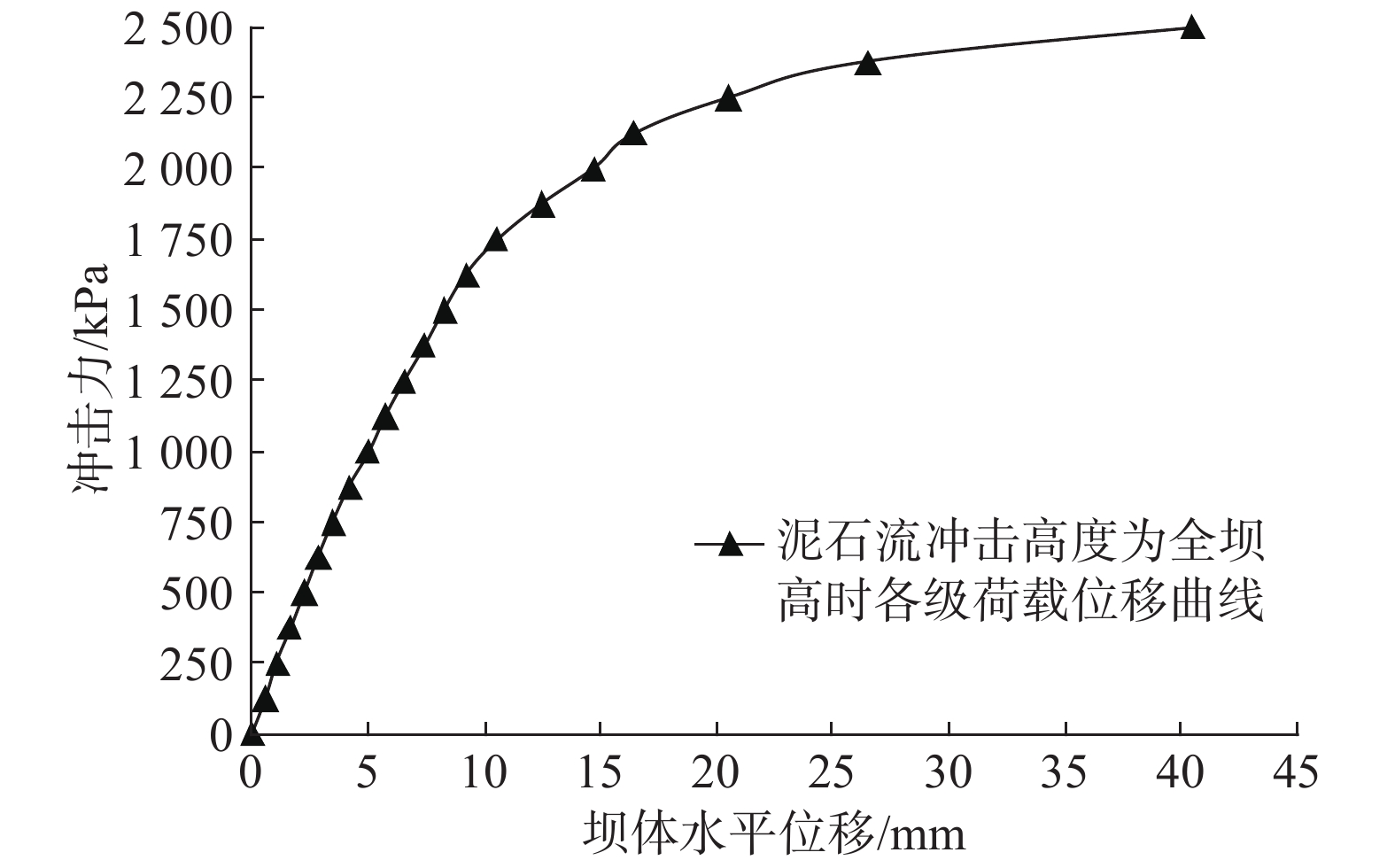
大坝按泥石流冲击高度h=H坝高计算,荷载增量取值125 kPa,每加一次荷载,计算至收敛,同时记录一次坝体的最大位移,将泥石流冲击力与相应荷载下坝体位移进行统计,形成图5所示冲击力与坝体最大位移关系曲线,会发现坝体水平位移随着拦挡坝冲击力增大也呈对数曲线递增,泥石流流体高度h=H工况条件下施加的最大冲击力Pu=2490 kPa(254.08 t/m2)。
坝体损毁过程如图6所示,冲击力达到375 kPa(水平位移1.7 mm)时坝体开始出现初始损伤;冲击力达到500 kPa(水平位移2.3 mm)时两侧坝肩和基础局部都出现较明显损伤;冲击力达到1250 kPa(水平位移6.6 mm)时,泄水孔和泄水涵洞边缘出现局部损伤;冲击力达到1500 kPa(水平位移8.4 mm)时,基础出现局部损伤,沿正面泄水涵洞和泄水孔形成纵向损伤,两侧坝肩损伤较严重;冲击力达到2000 kPa(水平位移14.8 mm)时,严重损伤区呈“W”型,坝肩、基础和坝体中心部位损伤基本贯通,坝体已基本失去功能,在工程实际应用中已达到破坏极限;冲击力达到2490 kPa时,坝体大面积损伤,超过坝体总量的2/3,水平位移高达40.4 mm,整体性降低或消失,这也只是一种模拟现象,在工程实际应用中泥石流物质沿坝体破坏处流通,坝体已不存在整体位移。
3. 坝体冲击力安全验算
同样方法计算三眼峪及各支沟泥石流重力式拦挡工程冲击力,得到表3,结合表1可以看出,泥石流经验公式计算的单宽冲击力均小于工况1数值模拟验算结果,均大于工况2数值模拟验算结果,与工况1和2的平均值接近。2012年建成至今,大部分坝体库容淤积过半,部分甚至已淤满,说明拦挡坝经受住了各种泥石流冲击破坏的考验。
表 3 重力坝冲击力数值模拟验算结果对比表(单位:t/m2)Table 3. Comparison of results of numerical simulation of impact of gravity dam (unit: t/m2)编号 经验公式
计算冲击力h=H/2
最大冲击力h=H
最大冲击力计算平均值 大1号坝 22.49 27.00 17.55 22.28 大2号坝 22.76 27.36 17.78 22.57 大3号坝 22.17 26.64 17.32 21.98 大4号坝 38.15 45.84 29.80 37.82 小2号坝 21.84 26.28 17.08 21.68 小3号坝 51.77 62.16 40.40 51.28 小4号坝 16.05 19.32 12.56 15.94 小6号坝 37.01 44.52 28.94 36.73 主1号坝 44.35 53.28 34.63 43.96 主2号坝 20.21 24.36 15.83 20.10 4. 讨论
4.1 泥石流冲击高度对坝体影响
将2种工况进行比较,工况1的冲击力达到800 kPa时坝体开始出现初始损伤,最大冲击力为3500 kPa,而工况2的冲击力达到375 kPa时桩体开始出现初始损伤,最大冲击力为2490 kPa。说明冲击高度对坝体的影响较大,随高度增加,达到初损的冲击力荷载几乎成倍数减少,而最大冲击力也减少1000 kPa。这说明在拦挡坝设计中泄水涵洞和泄水孔的预留很重要,为减少拦挡坝的冲击破坏,应尽量选择低坝,同时在不影响坝体安全和停淤功能的基础上,应多布设泄水涵洞和泄水孔,降低坝前壅水位,最大可能避免或减少高水位过流。
4.2 拦挡坝损伤过程对拦挡坝设计的指导意义
拦挡坝的损伤从两侧坝肩开始,再到拦挡坝中间部位的泄水涵洞及泄水孔边缘,然后到基础,最后坝肩、中间部位和基础形成“W”型的贯通破坏,其破损部位按先后顺序依次为“坝肩—泄水涵洞及泄水孔—基础—“W”型贯通”4个过程。设计时应重点考虑这几处薄弱环节,要相应的进行专门的加固处理。
4.3 拦挡坝冲击力设计的合理范围
从安全和经济方面考虑,在拦挡坝设计中冲击力的考虑应该取工况1和工况2之间值较合理,工况1存在风险,工况2偏保守,而工况1和2的中间值接近经验公式计算冲击力。从表3中可知,三眼峪设计中的冲击力选择也是工况1和2的平均值,从而保障了拦挡坝的安全运行。
4.4 可作为现有泥石流设计理论的有效补充
由于真实模拟泥石流重力式拦挡坝的室内大型实验难度比较大,野外测定随机性太大,故本文采用数值模拟的方式来分析三眼峪沟拦挡坝的受力情况。结果表明数值模拟对分析问题有一定的指导意义,可以和现有的泥石流设计理论结合,为以后工程设计提供安全对比,但是不能代替物理实验和理论计算。
5. 结论
(1)本文通过有限元软件ABAQUS进行拦挡坝数值模拟计算和分析,比较2种工况条件发现:随着泥石流冲击高度增加,达到初损的冲击力荷载成倍数减少,而最大冲击力也减少1000 kPa;拦挡坝的损伤从两侧坝肩开始,再到拦挡坝中间部位的泄水涵洞及泄水孔边缘,形成“W”型的贯通破坏。
(2)通过与经验公式计算冲击力比较,发现拦挡坝设计中冲击力选择工况1和2的平均值较合理,可以为工程设计提供安全对比。
-
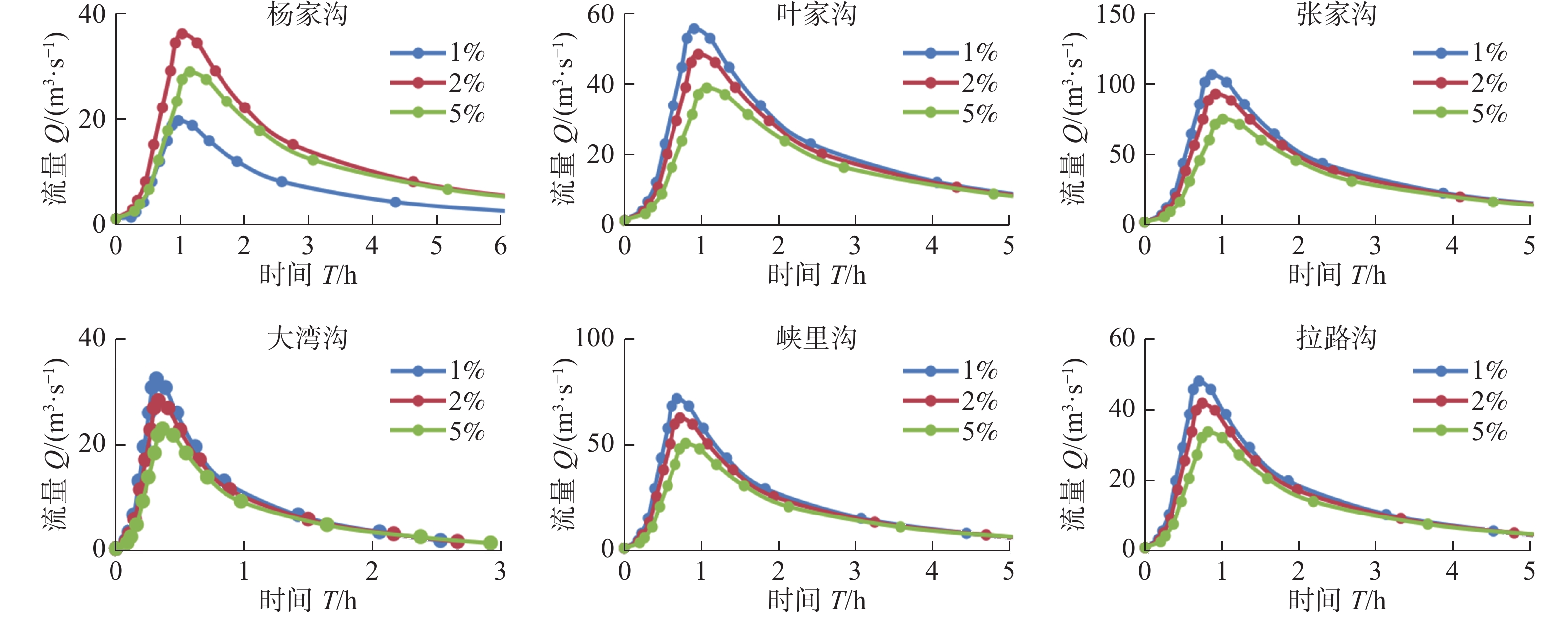
表 1 泥石流沟特征参数表
Table 1 Characteristic parameters of debris flow gullies
沟名 汇水面积/km2 纵比降/(‰) 主沟长度/km 相对高差/m 杨家沟 3.26 207 3.09 640 叶家沟 4.04 169 2.83 480 张家沟 7.19 209 3.3 690 大湾沟 1.83 366 1.01 370 峡里沟 3.98 213 2.29 490 拉路沟 2.75 174 2.01 350 表 2 麻路河流域泥石流沟松散物质量(单位:104 m3)
Table 2 Volume of loose material in debris flow gullies of Malu River basin (unit: 104 m3)
沟名 松散物质体积量 坡面耕地 崩塌滑坡 沟道淤积 人工弃渣 杨家沟 19.87 4.59 3.90 0.19 叶家沟 35.20 4.19 2.10 0 张家沟 52.12 5.76 4.80 0 大湾沟 15.97 2.35 1.29 0 峡里沟 8.21 5.53 3.45 1.72 拉路沟 15.58 1.55 1.80 0 表 3 层流阻滞系数表
Table 3 Laminar retardation coefficient
地面条件 K值范围 混凝土/沥青 24~108 裸露沙土 30~120 级配土 90~400 被侵蚀的粘性土 100~500 稀疏植被 1 000~4 000 矮草原 3 000~10 000 早熟禾属植物草地 7 000~50 000 表 4 不同频率的降雨参数(单位:mm)
Table 4 Rainfall parameters at different frequencies(unit: mm)
暴雨历时 设计频率 1% 2% 5% H1p 42.0 33.2 28.4 H6p 52.9 48.2 42.2 表 5 模拟-调查误差率表
Table 5 Simulation & survey comparison table
沟名 堆积扇范围/m2 堆积扇均厚/m 调查值 模拟值 误差比率 调查值 模拟值 误差比率 杨家沟 42 469.19 45 200 6.43% 0.30 0.239 −20.33% 叶家沟 79 884.45 81 600 2.15% 0.46 0.406 −11.74% 张家沟 50 921.10 56 800 11.55% 0.71 0.509 −28.31% 大湾沟 26 773.79 31 600 18.03% 0.25 0.210 −16.00% 峡里沟 29 760.92 40 400 35.75% 2.20 0.706 −67.91% 拉路沟 表 6 数值模拟精度表
Table 6 Numerical simulation accuracy table
沟名 堆积扇范围/m2 Ac 调查值 模拟值 重叠值 杨家沟 42 469.19 45 200 36 800 0.71 叶家沟 79 884.45 81 600 72 000 0.80 张家沟 50 921.10 56 800 46 800 0.76 大湾沟 26 773.79 31 600 25 600 0.77 峡里沟 29 760.92 40 400 27 600 0.63 拉路沟 表 7 泥石流危险性分区指标
Table 7 Risk classification of debris flow
危险性 堆积深度/m 逻辑关系 堆积深度流速乘积 高 H>1.5 or VH>1.5 中 0.5<H≤1.5 and 0.5<VH≤1.5 底 0.1<H≤0.5 and 0.1<VH≤0.5 表 8 1%、2%、5%降雨频率条件下泥石流堆积区危险性分区统计表
Table 8 Statistical table of hazard zoning of debris flow accumulation area in 1%、2%、5% rainfall frequency
降雨频率 沟名 高危险面积/m2 占总面积比例 中危险面积/m2 占总面积比例 低危险面积/m2 占总面积比例 P=1% 杨家沟 6 800 30.36% 10 800 48.21% 4 800 21.43% 叶家沟 12 400 36.47% 17 600 51.76% 4 000 11.76% 张家沟 18 800 68.12% 6 400 23.19% 2 400 8.70% 大湾沟 4 400 34.38% 6 400 50.00% 2 000 15.63% 峡里沟 20 400 69.86% 6 400 21.92% 2 400 8.22% 拉路沟 P=2% 杨家沟 5 600 25.93% 10 000 46.30% 6 000 27.78% 叶家沟 8 800 31.43% 14 800 52.86% 4 400 15.71% 张家沟 16 400 62.12% 7 200 27.27% 2 800 10.61% 大湾沟 3 600 29.03% 6 400 51.61% 2 400 19.35% 峡里沟 17 200 64.18% 7 200 26.87% 2 400 8.96% 拉路沟 P=5% 杨家沟 4 800 24.00% 9 200 46.00% 6 000 30.00% 叶家沟 7 200 26.87% 14 400 53.73% 5 200 19.40% 张家沟 11 600 45.31% 10 800 42.19% 3 200 12.50% 大湾沟 2 400 20.69% 6 400 55.17% 2 800 24.14% 峡里沟 15 600 62.90% 6 800 27.42% 2 400 9.68% 拉路沟 -
[1] 黄崇福. 自然灾害基本定义的探讨[J]. 自然灾害学报,2009,18(5):41 − 50. [HUANG Chongfu. A discussion on basic definition of natural disaster[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2009,18(5):41 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.05.007 [2] 程瑛, 黄武斌, 沙宏娥. 甘肃岷县两次强降水致山洪泥石流灾害特征对比分析[J]. 干旱区地理,2018,41(3):443 − 448. [CHENG Ying, HUANG Wubin, SHA Honger. Cause of two heavy rainfall causing massive mudslide in Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography,2018,41(3):443 − 448. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 王春磊, 徐大录. 甘肃省定西市岷县地质灾害详细调查报告[R]. 兰州: 甘肃省地矿局水文地质工程地质勘察院, 2013. WANG Chunlei, XU Dalu. Detailed investigation report on geological disasters in Min County, Dingxi City, Gansu Province[R]. Lanzhou: Institute of Hydrogeology and Engineering Geology, Bureau of Geology and Mineral Resources, Gansu Province, 2013. (in Chinese)
[4] 胡凯衡, 韦方强. 基于数值模拟的泥石流危险性分区方法[J]. 自然灾害学报,2005,14(1):10 − 14. [HU Kaiheng, WEI Fangqiang. Numerical-simulation-based debris flow risk zoning[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2005,14(1):10 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2005.01.002 [5] 段学良, 马凤山, 郭捷, 等. 基于Massflow模型的西藏仁布杰仲沟泥石流运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(6):25 − 33. [DUAN Xueliang, MA Fengshan, GUO Jie, et al. Movement characteristics of Jiezhonggou debris flow of Renbu, Tibet based on massflow model[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(6):25 − 33. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 侯圣山, 曹鹏, 陈亮, 等. 基于数值模拟的耳阳河流域泥石流灾害危险性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(2):143 − 151. [HOU Shengshan, CAO Peng, CHEN Liang, et al. Risk assessment of debris flow disaster in eryang River Basin Based on numerical simulation[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(2):143 − 151. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 杨涛, 唐川, 常鸣, 等. 基于数值模拟的小流域泥石流危险性评价研究[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2018,27(1):197 − 204. [YANG Tao, TANG Chuan, CHANG Ming, et al. Study on debris flow risk assessment of small watershed based on numerical simulation[J]. Resources and Environment of Yangtze River Basin,2018,27(1):197 − 204. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 颜恒明. 基于FLO-2D的干沟泥石流风险评价[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2016. YAN Hengming.. Risk assessment of debris flow in main gully based on FLO-2D[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 余斌, 王涛, 朱渊. 浅层滑坡诱发沟谷泥石流的地形和降雨条件[J]. 水科学进展,2016,27(4):542 − 550. [YU Bin, WANG Tao, ZHU Yuan. Research on the topographical and rainfall factors of debris flows caused by shallow landslides[J]. Progress in Water Science,2016,27(4):542 − 550. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] O'BRIEN, J. S. FLO-2D Reference manual version 2009[R]. 2009.
[11] 郭富赟, 孟兴民, 尹念文, 等. 甘肃省岷县耳阳沟“5·10”泥石流基本特征及危险度评价[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2014(5):628 − 632. [GUO Fuyun, MENG Xingmin, YIN Nianwen, et al. Formation mechanism and risk assessment of debris flow of “5·10” in Eryang Gully of Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2014(5):628 − 632. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] WOOLHISER DA. Simulation of unsteady overland flow. In: Mahmood K, Yevjevich V (eds) Unsteady flow in open channels[J]. Water Resources Publications, Fort Collins,1975: 485–508.
[13] 王裕宜, 詹钱登, 韩文亮, 等. 粘性泥石流体的应力应变特性和流速参数的确定[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2003,14(1):9 − 13. [WANG Yuyi, ZHAN Qiandeng, HAN Wenliang, et al. Stress-strain properties of viscous debris flow and determination of volocity parameter[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2003,14(1):9 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2003.01.002 [14] 翟淑花, 冒建, 南赟, 等. 基于遗传规划的泥石流多因子融合预测方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):111 − 115. [ZHAI Shuhua, MAO Jian, NAN Yun, et al. Multi-factors fusion method of debris flow prediction based on genetic programming[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):111 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 刘晶晶, 马春, 李春雨. 粘性泥石流入汇区河床堆积动力学研究的问题与展望[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(4):544 − 555. [LIU Jingjing, MA Chun, LI Chunyu. Fundamental problems and prospects in the study of deposition dynamics of viscous debris flow in the gully-river junction[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(4):544 − 555. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] JAKOB M, STEIN D, ULMI M. Vulnerability of buildings to debris flow impact[J]. Natural Hazards,2012,60(2):241 − 261. DOI: 10.1007/s11069-011-0007-2
[17] CALISTA MONIA, MENNA VALERIA, MANCINELLI VANIA, et al. Rockfall and debris flow hazard assessment in the SW escarpment of montagna del morrone ridge (Abruzzo, Central Italy)[J]. Water,2020,12(4):1206. DOI: 10.3390/w12041206
-
期刊类型引用(26)
1. 李超然,袁广祥. 甘肃省宕昌县地质灾害易发性评价. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2025(01): 21-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 兰盈盈,郭昶成,朱云福. 地质灾害易发性评价方法综述. 地质与资源. 2024(01): 65-73 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨晶晶,肖玉,安泉,刘浩,公斌. 黔东北地区地质灾害时空分布规律及孕灾地质环境研究. 中国煤炭地质. 2024(02): 64-68 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李晓玮,刘翠娜. 基于AHP法山区公路边坡稳定性评价及危害性分析. 河北地质大学学报. 2024(02): 61-65+134 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 南赟,翟淑花,李岩,曹颖,罗守敬,王云涛,郭学飞. 北京地区“23·7”特大暴雨型地质灾害特征及预警成效分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(02): 66-73 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 曾欣,黄梦妮,胡毓灵,邓新林,谢倩雯. 株洲市地质灾害特征与降雨量的关系. 气象研究与应用. 2024(01): 83-89 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 唐朝. 基于ArcGIS的当涂县地质灾害风险调查与评价. 现代矿业. 2024(04): 187-190+196 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 蔡佳明. 北京东部山区地质灾害危险性评价. 地质灾害与环境保护. 2024(02): 49-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 李晓玮. 北京北宫镇大灰厂路牵引式岩质滑坡勘查及防治对策. 城市地质. 2024(02): 139-148 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 赵丹凝,焦润成,杨春. “23·7”强降雨对北京西山曹家坊泥石流隐患易发性影响. 城市地质. 2024(03): 353-364 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 尹展,郝玉军,卜鹏,杨艳绪. 湘南中低山区滑坡孕灾因子分析及易发性评价——以江华县为例. 矿产勘查. 2024(10): 1878-1884 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 李晓玮,郑晓钰,史昕宇. 北京西部采空区初勘及场地适宜性评价. 防灾减灾学报. 2024(04): 7-12 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 支泽民,刘峰贵,周强,夏兴生,陈琼. 基于流域单元的地质灾害易发性评价——以西藏昌都市为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(01): 139-150 .  本站查看
本站查看
14. 王涛,李鹏洋,逯兴娅,苏生瑞,董永超. 陕西省韩城市地质灾害易发性评价. 甘肃科学学报. 2023(02): 55-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 张群,冯辉,贾三满,张沁瑞,贾磊. 基于CF与Logistic回归模型耦合的地质灾害易发性评价——以北京市大清河流域生态涵养区为例. 城市地质. 2023(01): 17-25 .  百度学术
百度学术
16. 罗琳,刘雄,翁建,王锦阳,楼雄标. 某乡镇地质灾害风险评价. 科技通报. 2023(04): 93-102 .  百度学术
百度学术
17. 孙佩,杨良哲,康全国,张驰,尹伟,周凌云,易洁伟,王雯雯. 一般调查区地质灾害易发性评价——以咸丰县为例. 资源信息与工程. 2023(04): 95-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
18. 叶泽宇,徐尚智,刘欢欢,于家烁,翟淑花,冒建. 基于信息量与逻辑回归耦合模型的北京西山崩塌易发性评价. 城市地质. 2023(03): 9-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
19. 阳清青,余秋兵,张廷斌,易桂花,张恺. 基于GDIV模型的大渡河中游地区滑坡危险性评价与区划. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(05): 130-140 .  本站查看
本站查看
20. 王海芝,曾庆利,许冰,胡福根,于淼. 北京“7·21”特大暴雨诱发的地质灾害类型及其特征分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(02): 125-132 .  本站查看
本站查看
21. 焦伟之,张明,谢鑫鹏,李成文,刘涛,庞海松. 基于GIS与加权信息量模型的城镇地质灾害易发性评价——以大新镇为例. 安全与环境工程. 2022(04): 119-128 .  百度学术
百度学术
22. 简鹏,李文彦,张治家,时伟,党发宁,郭红东,李松. 基于多因素加权指数和法的区域地质灾害易发性评价研究——以麦积区为例. 甘肃地质. 2022(03): 63-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
23. 白光顺,杨雪梅,朱杰勇,张世涛,祝传兵,康晓波,孙滨,周琰嵩. 基于证据权法的昆明五华区地质灾害易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(05): 128-138 .  本站查看
本站查看
24. 庄卓涵. 广州北部山区斜坡类地质灾害致灾机理及易发性分析——以广州从化良口—吕田一带为例. 地下水. 2022(06): 158-161 .  百度学术
百度学术
25. 王小东,罗园,付景保. 基于GIS的白龙江引水工程水源区地质灾害易发性评价. 南水北调与水利科技(中英文). 2022(06): 1231-1239 .  百度学术
百度学术
26. 郭富赟,宋晓玲,刘明霞. 黄河流域甘肃段地质灾害发育特征. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2021(05): 130-136 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(6)




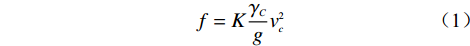
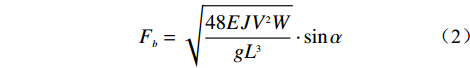
 下载:
下载:






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS