InSAR identification and monitoring of geological hazards in Ranwu region of Tibet
-
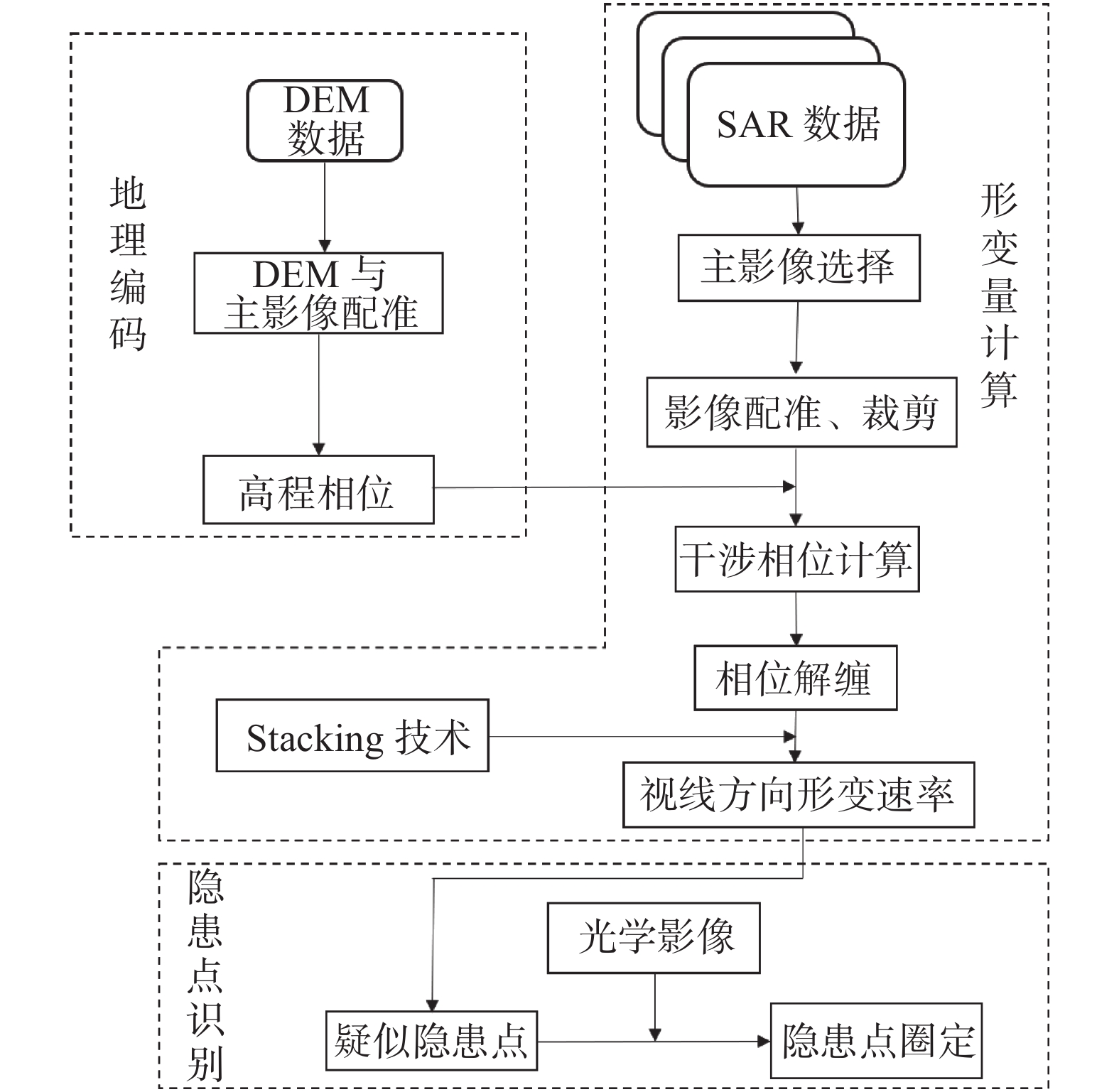
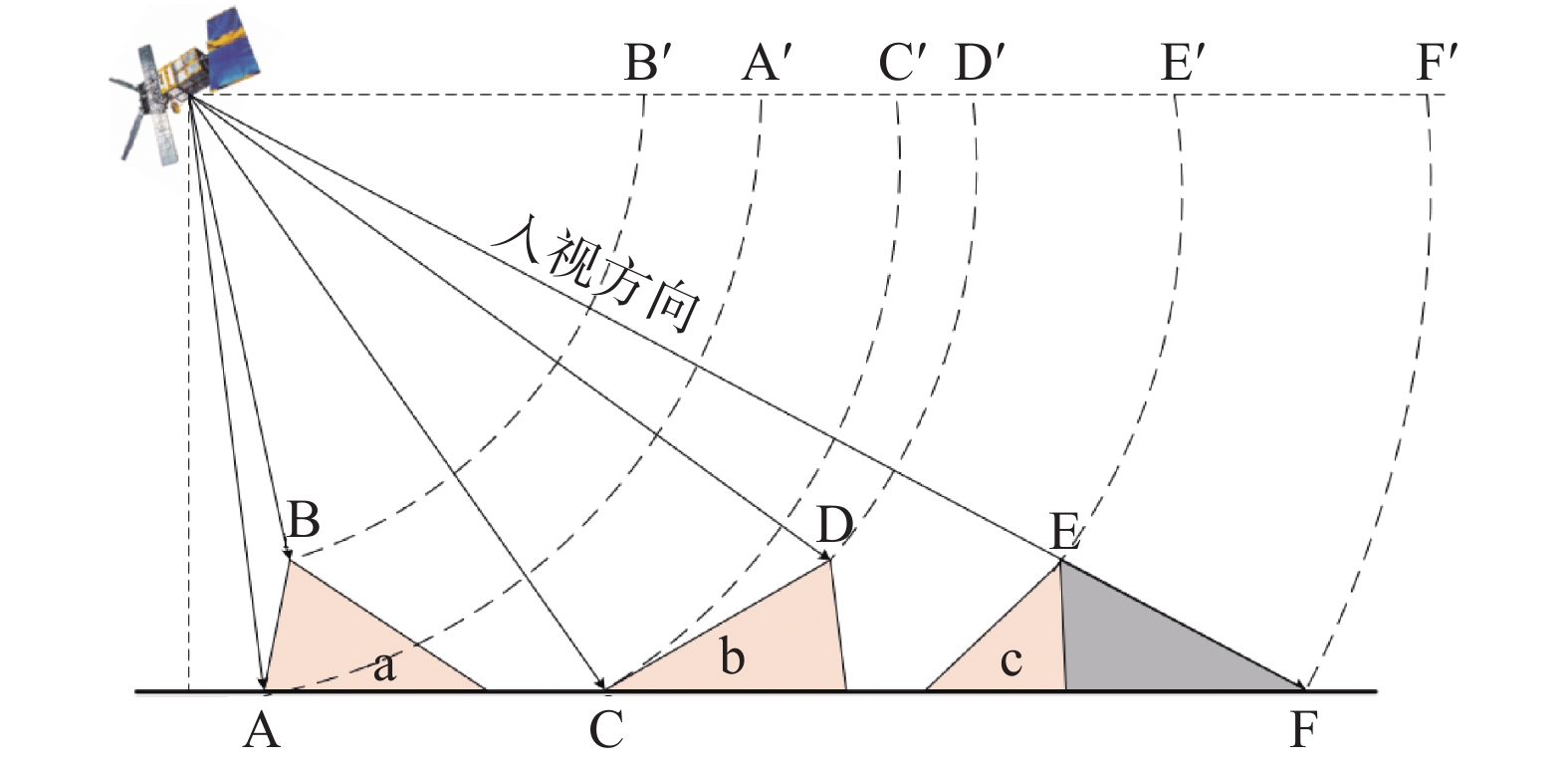
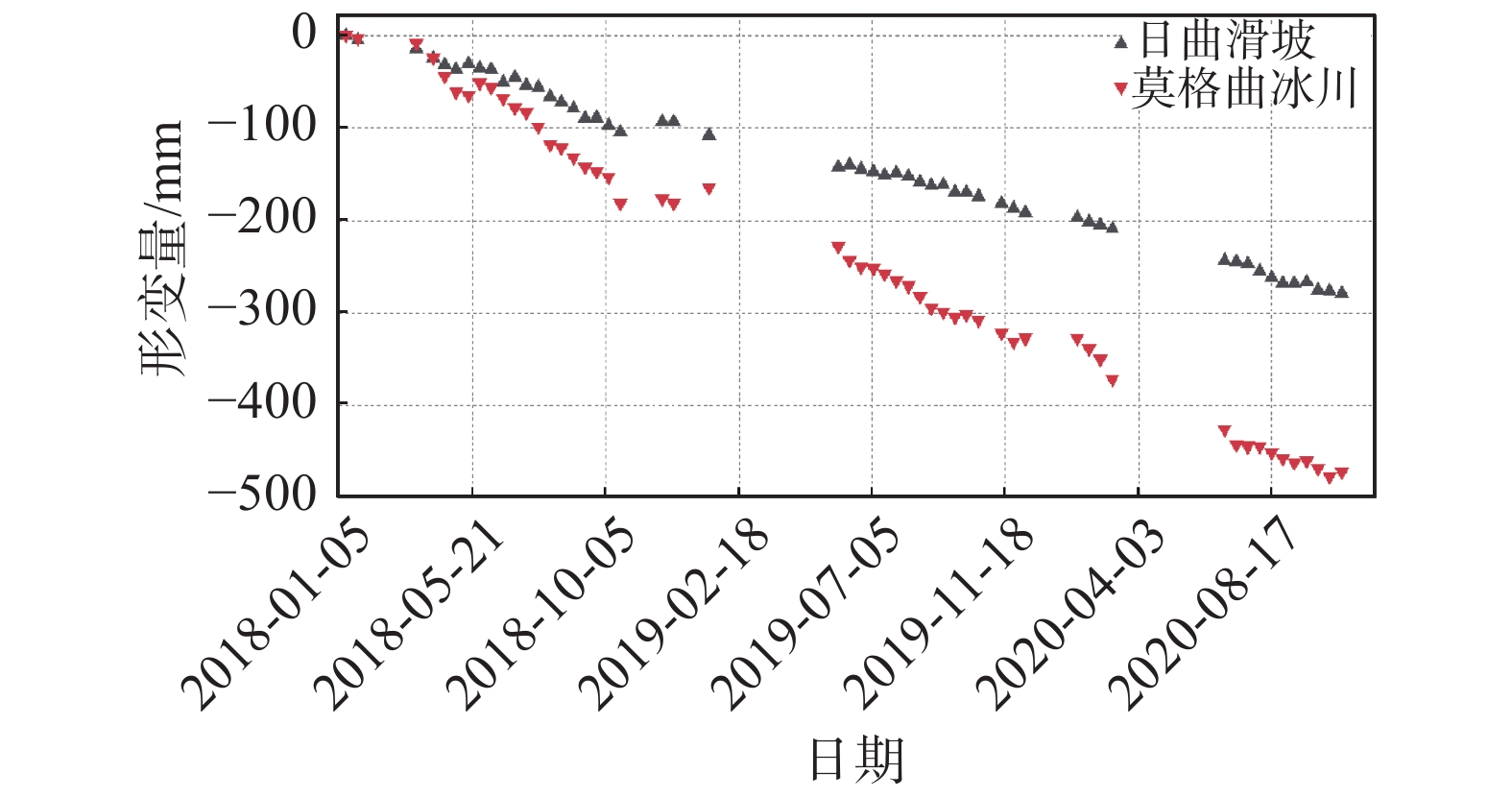
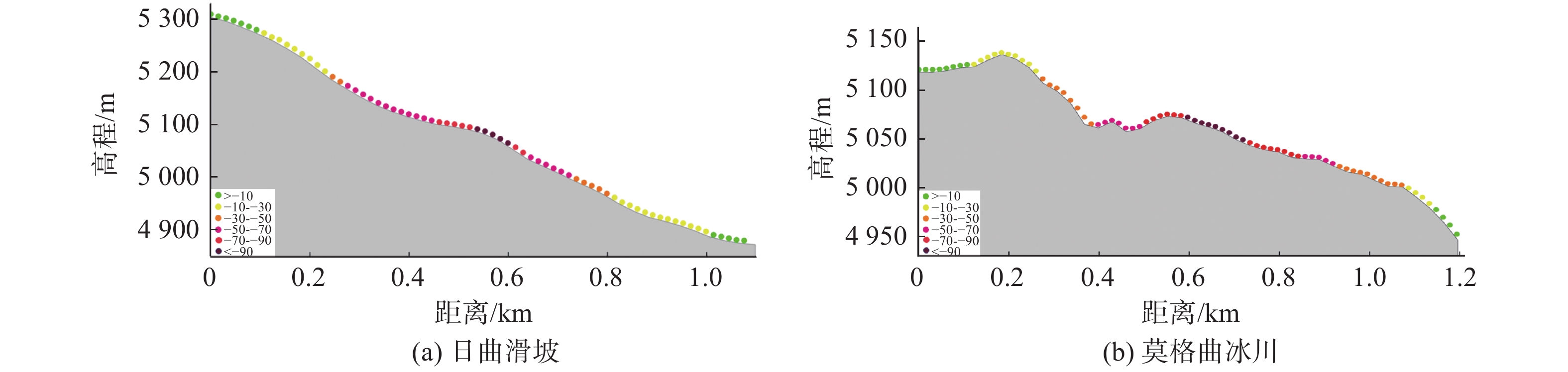
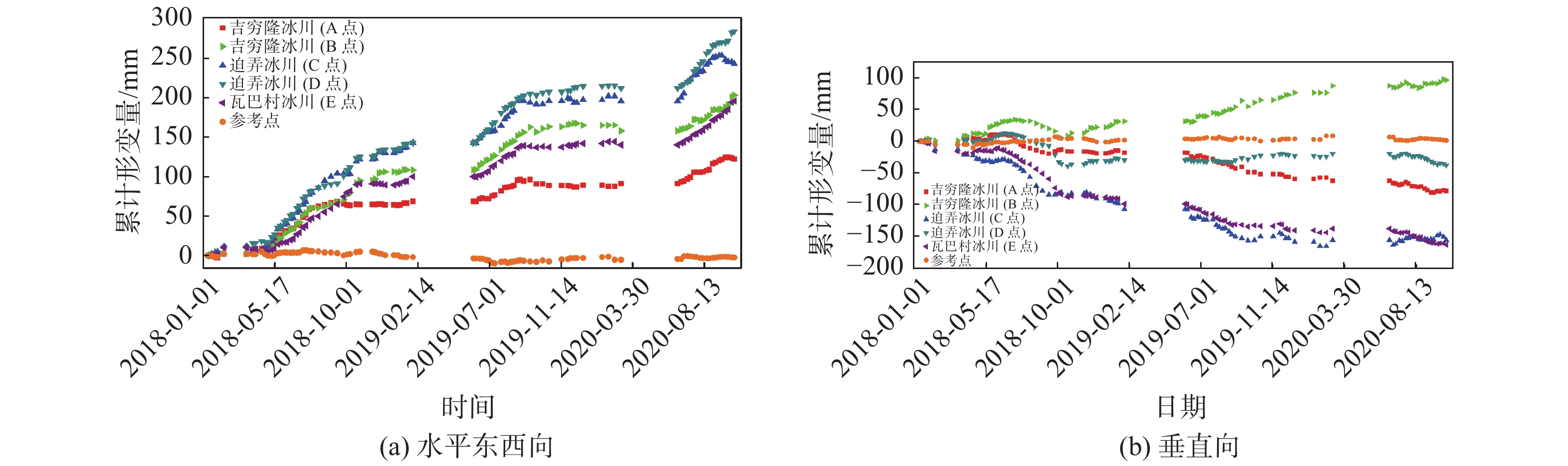
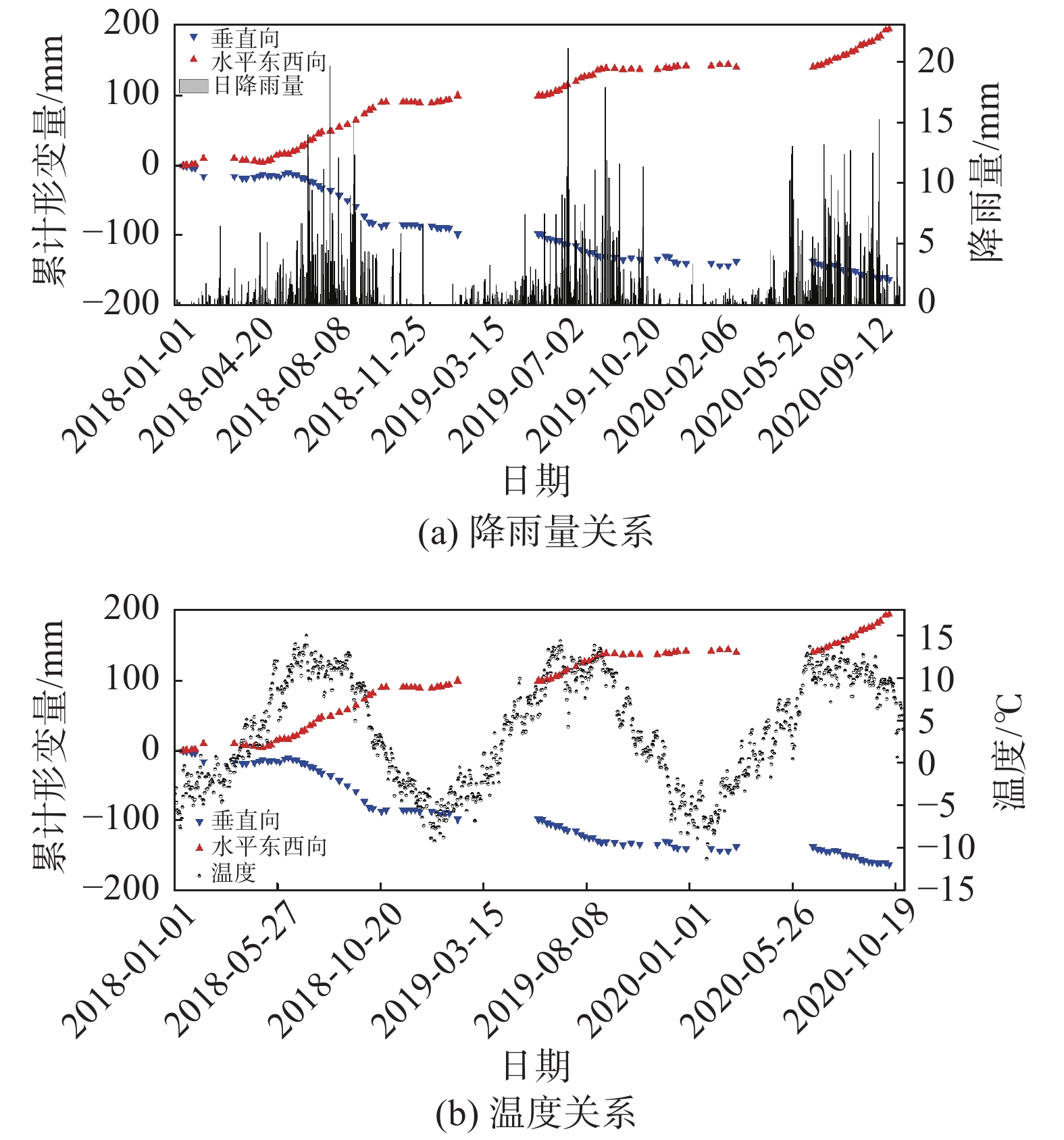
摘要: 西藏藏东南地区地处青藏高原东南部,地势陡峭。多期次板块构造运动、岩体间相互挤压运动导致地质灾害频繁发生且规模大。针对该区域的地质灾害调查与监测研究工作对防灾减灾具有重要意义。文章以藏东南然乌地区为研究区,分别利用升降轨Sentinel-1A卫星数据对该区域隐患灾害点进行识别,并分析了SAR影像几何畸变对地质灾害识别的影响。通过对InSAR监测结果进行分析,文章最终共圈定了区域内的滑坡、冰川隐患灾害点67处。同时,为了更好的分析灾害体的形变特征和规律,选取了然乌区域安目错北岸三处典型冰川灾害体,利用多维小基线子集(MSBAS)技术获取了坡体的二维(水平东西向和垂直向)形变速率和时间序列。通过对吉穷隆冰川、迫弄冰川和瓦巴村冰川三处典型冰川的形变时间序列结果进行分析,发现从2018年1月到2020年10月,三个冰川水平东西方向上的最大累计位移量分别达到了202 mm、283 mm、194 mm,垂直方向上最大累计位移量分别达到了97 mm、−155 mm、−163 mm。水平方向上三处典型冰川表现为加速变形趋势,垂直方向上表现为缓慢蠕滑变形趋势。同时分析了瓦巴村冰川二维形变时间序列与降雨量和温度相关性,结果表明降雨和温度的变化对坡体冰川形变具有一定的影响。研究成果对高山峡谷区地质灾害隐患点的识别具有较好的参考价值。Abstract: Southeast Tibet, located in the southeast part of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau, is characterized by steep terrain, frequent occurrence and large scale of geological disasters due to multiple plate tectonic movements and compression movements between rock masses. It’s of great significance to investigate and monitor geological disasters in this region. In this paper, Ranwu area in southeast Tibet is taken as the study area, and the potential disaster points in this area are identified by using sentinel-1A satellite data, and the influence of geometric distortion of SAR image on geological disaster identification is analyzed. Through the analysis of InSAR monitoring results, 67 hidden danger points of landslides and glaciers in the region were delineated. At the same time, in order to better analyze the deformation characteristics and laws of the disaster bodies, three typical glacial disaster bodies in the north bank of Anmuco in Ranwu region were selected, and the two-dimensional (horizontal EAST-west and vertical) deformation rates and time series of the slope bodies were obtained by using multidimensional small baseline subset (MSBAS) technology.Based on the analysis of the deformation time series results of Jiqilong Glacier, Polong Glacier and Waba Village Glacier, it’s found that the maximum cumulative displacement in the horizontal east-west direction from January 2018 to October 2020 is 202 mm, 283 mm and 194 mm respectively. The maximum cumulative displacement in vertical direction is 97 mm, −155 mm and −163 mm respectively. In the horizontal direction, the three typical glaciers show an accelerated deformation trend and slow creep deformation trend in vertical direction. At the same time, the correlation between the two-dimensional deformation time series of Wabacun glacier and precipitation and temperature is analyzed. The results show that the variation of precipitation and temperature has certain influence on the deformation of slope glacier. The research results of this paper have a good reference value for the identification of geological hazards in alpine and canyon areas.
-
Keywords:
- InSAR /
- stacking-InSAR technology /
- MSBAS /
- potential point identification /
- Ranwu town
-
-
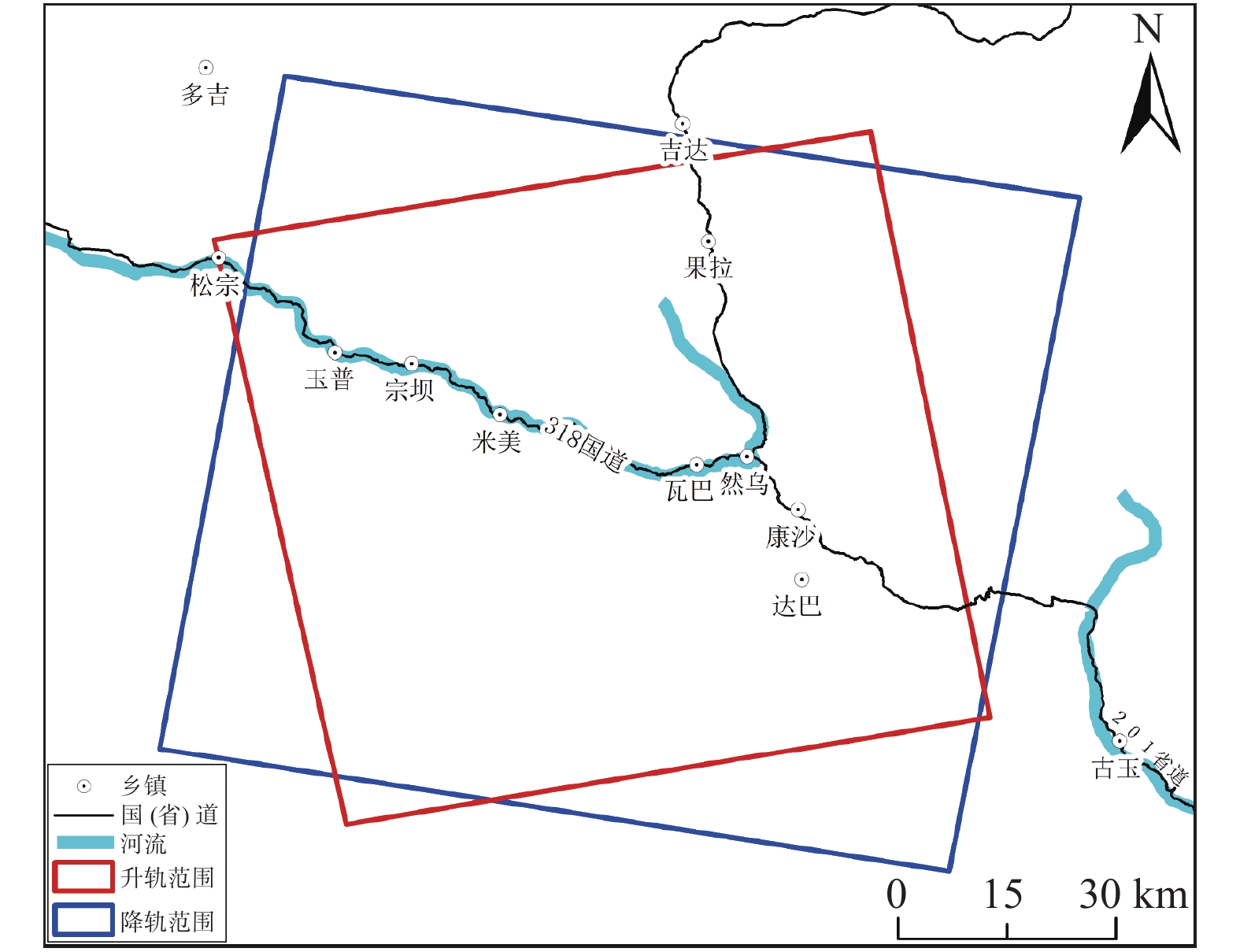
表 1 SAR数据基本参数
Table 1 Basic parameters of SAR data
卫星 Sentinel-1A Sentinel-1A 轨道方向 升轨 降轨 航向角/(°) −12.56 −167.32 入射角/(°) 33.90 33.87 波段 C C 方位向分辨率/m 2.32 2.32 距离向分辨率/m 13.98 13.98 影像数量 82 75 时间间隔 2018-1-5—
2020-11-22018-1-12—
2020-10-28注:以正北方向为基准,顺时针方向为正。 -
[1] 张倬元. 滑坡防治工程的现状与发展展望[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2000,11(2):89 − 97. [ZHANG Zhuoyuan. The present status, technical advance and development trends of landslide remedial measures[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2000,11(2):89 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 殷跃平, 王文沛. 高位远程滑坡动力侵蚀犁切计算模型研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. [YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei. A dynamic erosion plowing model of long Run-out landslides initialized at high locations[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(8):1513 − 1521. (in Chinese with English abstract) [3] 葛大庆, 戴可人, 郭兆成, 等. 重大地质灾害隐患早期识别中综合遥感应用的思考与建议[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):949 − 956. [GE Daqing, DAI Keren, GUO Zhaocheng, et al. Early identification of serious geological hazards with integrated remote sensing technologies: Thoughts and recommendations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):949 − 956. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 李鸿儒, 白玲, 詹慧丽. 嘉黎断裂带活动性研究进展[J]. 地球与行星物理论评,2021,52(2):182 − 193. [LI Hongru, BAI Ling, ZHAN Huili. Research progress of Jiali fault activity[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics,2021,52(2):182 − 193. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 黄星. InSAR和GPS技术在震间和同震形变领域的应用研究: 以嘉黎断裂西段和2015年皮山地震为例[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所, 2020 HUANG Xing. Application of InSAR and GPS techniques in interseismic and coseismic deformation—cases of the western Jiali fault and 2015 Mw6.4 Pishan earthquake[D]. Beijing: Institute of Earthquake Prediction, China Earthquake Administration, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 唐得胜, 杨永红, 常鸣. 藏东南地区冰湖溃决泥石流灾害链成因分析及防治措施[J]. 水电能源科学,2013,31(12):174 − 178. [TANG Desheng, YANG Yonghong, CHANG Ming. Cause analysis and preventive measures of debris flow disaster-chain due to glacial lake outburst in southeastern Tibet[J]. Water Resources and Power,2013,31(12):174 − 178. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 郭佳宁, 山克强, 程捷. 藏东南地区滑坡发育规律分析[J]. 资源与产业,2009,11(2):132 − 139. [GUO Jiajing, SHAN Keqiang, CHENG Jie. Study on landslide development regularity in southeast Tibet[J]. Resources & Industries,2009,11(2):132 − 139. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 赵聪, 梁京涛, 王军朝, 等. 帕隆藏布流域(波密-然乌段)冰川动态变化遥感分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(21):56 − 62. [ZHAO Cong, LIANG Jingtao, WANG Junchao, et al. Remote sensing analysis of glacier dynamic changes in Parlung Zangbo river[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(21):56 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.21.009 [9] 宋键, 唐方头, 邓志辉, 等. 青藏高原嘉黎断裂晚第四纪运动特征[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版),2013,49(6):973 − 980. [SONG Jian, TANG Fangtou, DENG Zhihui, et al. Late quaternary movement characteristic of Jiali fault in Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis,2013,49(6):973 − 980. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 赵华秋, 王欣, 赵轩茹, 等. 2008—2018年中国冰川变化分析[J]. 冰川冻土,2021,43(4):976 − 986. [ZHAO Huaqiu, WANG Xin, ZHAO Xuanru, et al. Analysis of glacier changes in China from 2008 to 2018[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2021,43(4):976 − 986. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 柳金峰, 程尊兰, 陈晓清. 帕隆藏布流域然乌-培龙段冰湖溃决危险性评估[J]. 山地学报,2012,30(3):369 − 377. [LIU Jinfeng, CHENG Zunlan, CHEN Xiaoqing. The hazard assessment of glacier-lake outburst in Palong Zangbu river from Ranwu to Peilong[J]. Journal of Mountain Science,2012,30(3):369 − 377. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 鞠建廷, 朱立平, 黄磊, 等. 基于监测的藏东南然乌湖现代过程: 湖泊对冰川融水的响应程度[J]. 科学通报,2015,60(1):16 − 30. [JU Jianting, ZHU Liping, HUANG Lei, et al. Ranwu lake, a proglacial lake with the potential to reflect glacial activity in SE Tibet[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2015,60(1):16 − 30. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.1360/N972014-00084 [13] 赵志男, 李滨, 高杨, 等. 西藏然乌湖口高位地质灾害变形特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):25 − 32. [ZHAO Zhinan, LI Bin, GAO Yang, et al. Analysis on deformation characteristics of geological hazards in Ranwu lake estuary[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):25 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 杨成生, 董继红, 朱赛楠, 等. 金沙江结合带巴塘段滑坡群InSAR探测识别与形变特征[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2021,43(2):398 − 408. [YANG Chengsheng, DONG Jihong, ZHU Sainan, et al. Detection, identification and deformation characteristics of landslide groups by InSAR in Batang section of Jinsha river convergence zone, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2021,43(2):398 − 408. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 翟会楠. 基于D-InSAR参数优化的泥石流沟谷地表形变特征研究: 以武都地区为例[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2016 ZHAI Huinan. Surface deformation characteristics of debris flow gully based on parameter optimization of D-InSAR technology—A case study of Wudu[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 田小平. 川藏公路然乌—波密段泥石流发育特征及危险性评价[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2016 TIAN Xiaoping. Development characteristics and hazard assessment of debris flows along the Ranwu-Bomi section of Sichuan-Tibet highway[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 吴文豪, 周志伟, 李陶, 等. 精密轨道支持下的哨兵卫星TOPS模式干涉处理[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(9):1156 − 1164. [WU Wenhao, ZHOU Zhiwei, LI Tao, et al. A study of sentinel-1 TOPS mode co-registration[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2017,46(9):1156 − 1164. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] SANDWELL D T, SICHOIX L. Topographic phase recovery from stacked ERS interferometry and a low-resolution digital elevation model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research:Solid Earth,2000,105(B12):28211 − 28222. DOI: 10.1029/2000JB900340
[19] 云烨, 吕孝雷, 付希凯, 等. 星载InSAR技术在地质灾害监测领域的应用[J]. 雷达学报,2020,9(1):73 − 85. [YUN Ye, LYU Xiaolei, FU Xikai, et al. Application of spaceborne interferometric synthetic aperture radar to geohazard monitoring[J]. Journal of Radars,2020,9(1):73 − 85. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12000/JR20007 [20] 葛令贵. 高效高精度InSAR自适应滤波方法与工程化应用研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2018 GE Linggui. Study on high-efficiency and high-precision adaptive InSAR filtering methods and engineering application[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 朱建军, 李志伟, 胡俊. InSAR变形监测方法与研究进展[J]. 测绘学报,2017,46(10):1717 − 1733. [ZHU Jianjun, LI Zhiwei, HU Jun. Research progress and methods of InSAR for deformation monitoring[J]. Acta Geodaetica et Cartographica Sinica,2017,46(10):1717 − 1733. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] SAMSONOV S V, FENG W P, PELTIER A, et al. Multidimensional Small Baseline Subset (MSBAS) for volcano monitoring in two dimensions: opportunities and challenges. Case study Piton de la Fournaise volcano[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research,2017,344:121 − 138. DOI: 10.1016/j.jvolgeores.2017.04.017
[23] 熊国华, 杨成生, 朱赛楠, 等. 基于MSBAS技术的金沙江上游色拉滑坡形变分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(5):1 − 9. [XIONG Guohua, YANG Chengsheng, ZHU Sainan, et al. Deformation analysis of Sela landslide in the upper reaches of Jinsha river based on MSBAS technology[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(5):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 刘国祥, 陈强, 罗小军. InSAR原理与应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2019 LIU Guoxiang, CHEN Qiang, LUO Xiaojun. Principle and Application of InSAR [M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[25] 康亚. InSAR技术在西南山区滑坡探测与监测的应用[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2016 KANG Ya. Application of InSAR technology to landslide detection and monitoring in southwest mountainous area [D]. Xi'an: Chang'an University, 2016. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 张雪,魏云杰,杨成生,刘勇,杨佳艺. 云南昭通地区滑坡隐患InSAR广域识别与监测. 地球科学与环境学报. 2025(01): 128-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王林峰,蒋辉,唐宁,黄晓明,谭国金. 无人机贴近摄影技术在高陡边坡的三维重建与结构面识别中的应用. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2025(01): 92-100 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 孙成永. InSAR技术在河南信阳新县地质灾害风险调查中的应用. 城市地质. 2024(03): 383-389 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙琪皓,刘桂卫,王飞,张璇钰,王衍汇. 铁路地质灾害早期识别与监测预警技术及应用研究. 铁道标准设计. 2024(09): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 臧烨祺,郭永刚,苏立彬,王国闻,吴升杰,秦得顺. 西藏东南地区滑坡易发性多模型评价方法研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(06): 58-69 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 鲁魏,杨斌,杨坤. 基于时序InSAR的西南科技大学地表形变监测与分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(02): 61-72 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 李凡,李素敏,杨渊,李杰,袁利伟,成睿,毛嘉骐. 基于时序InSAR的沙湾大沟滑坡型泥石流发育特征研究. 地球物理学进展. 2023(02): 532-541 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 顿佳伟,冯文凯,易小宇,张国强,吴明堂. 白鹤滩库区蓄水前活动性滑坡InSAR早期识别研究——以葫芦口镇至象鼻岭段为例. 工程地质学报. 2023(02): 479-492 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 于冰,胡云亮,刘国祥,罗小军,胡金龙. 时序InSAR反演唐山市二维地表形变时间序列. 测绘科学. 2023(06): 82-94+230 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 陈行,刘汉湖,葛宗旭. 时序SBAS-InSAR下的香格里拉市地表形变监测. 宜宾学院学报. 2022(06): 54-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 盖侨侨. PS-InSAR技术在北江下游沿线形变监测中的应用. 水利技术监督. 2022(10): 57-59+72 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)



 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS