Characteristics and stability analysis of Xiari landslide at Lenggu hydropower station in the middle reach of the Yalong river
-
摘要: 位于雅砻江中游的楞古水电站工程地质条件十分复杂,大型-巨型滑坡发育。以雅砻江楞古水电站夏日滑坡为例,在现场详细调查的基础上,采用试验测试和数值模拟等方法,研究了蓄水后滑坡的稳定性发展趋势。根据地貌形态、物质组成、钻孔资料以及现场调查,将夏日滑坡划分为三个区,其中Ⅱ区目前已经出现一定的变形破坏,稳定性最差。数值模拟表明,蓄水前,夏日滑坡整体稳定性较好,只在前缘局部出现变形;蓄水后,滑坡变形明显扩大,前缘沿先存的次级滑带滑动。提出在夏日滑坡前缘进行格构锚和抗滑桩支护,并利用InSAR技术对滑坡灾害隐患进行早期识别和监测预警。该研究为楞古水电站库岸滑坡防治提供了重要依据,并对同类型滑坡研究具有一定的参考意义。Abstract: The engineering geological conditions of Lenggu hydropower station located in the middle reaches of Yalong River are very complex, and large-scale landslides are very developed. Taking Xiari landslide of Lenggu hydropower station on Yalong River as an example, the stability development trend of landslide after impoundment is studied by means of test and numerical simulation on the basis of detailed field investigation on the spot. According to the geomorphic morphology, material composition, drilling data and field investigation, the Xiari landslide is divided into three zones, among which the zone II has been deformed and damaged to some extent, and the stability is the worst. The numerical simulation shows that the overall stability of the landslide is fairly good before the impoundment, and the deformation only occurs at the front edge. After the impoundment, the deformation of the landslide is obviously enlarged and the front edge slides along the existing secondary slip zone. It is suggested that lattice anchor and anti-slide pile should be used at the front edge of the Xiari landslide, and the InSAR technology should also be used for early identification, monitoring and early warning of landslide hazards. This study provides an important basis for the prevention and control of reservoir bank landslide in Lenggu Hydropower Station, and has a certain reference significance for the study of the same type of landslide. This study provides an important basis for the prevention and control of reservoir bank landslide in Lenggu Hydropower Station, and has a certain reference significance for the study of the same type of landslide.
-
0. 引言
我国中西部地区地形地质条件复杂,特别是环青藏高原的周边地带。伴随青藏高原的快速隆升,四川盆地周边河谷的快速下切,形成了高山峡谷地貌,同时还蕴藏了丰富的水能资源。受地形地貌特征影响,在这一地区开展了大规模的水电工程建设,加之库内水位大幅度提升,为滑坡等地质灾害的发生创造了条件[1]。如2003年7月三峡库区发生的千将坪滑坡典型案例[2]。
雅砻江主要位于青藏高原东部深切河谷区,全长1571 km。雅砻江干流共规划了22级水电站,其中楞古水电站是雅砻江中游河段梯级开发的第三级。调查发现,楞古水电站工程地质条件复杂,坝内分布有唐古栋滑坡、夏日滑坡和马河滑坡等多个特大型-巨型滑[3-5]。文中以雅砻江楞古水电站夏日滑坡为例,在现场详细调查的基础上,采用试验测试和数值模拟等方法,对夏日滑坡蓄水后滑坡体的稳定性进行了分析。该研究为楞古水电站库岸滑坡防治提供了重要依据,并对同类型滑坡研究具有一定的参考意义。
1. 研究区工程地质概况
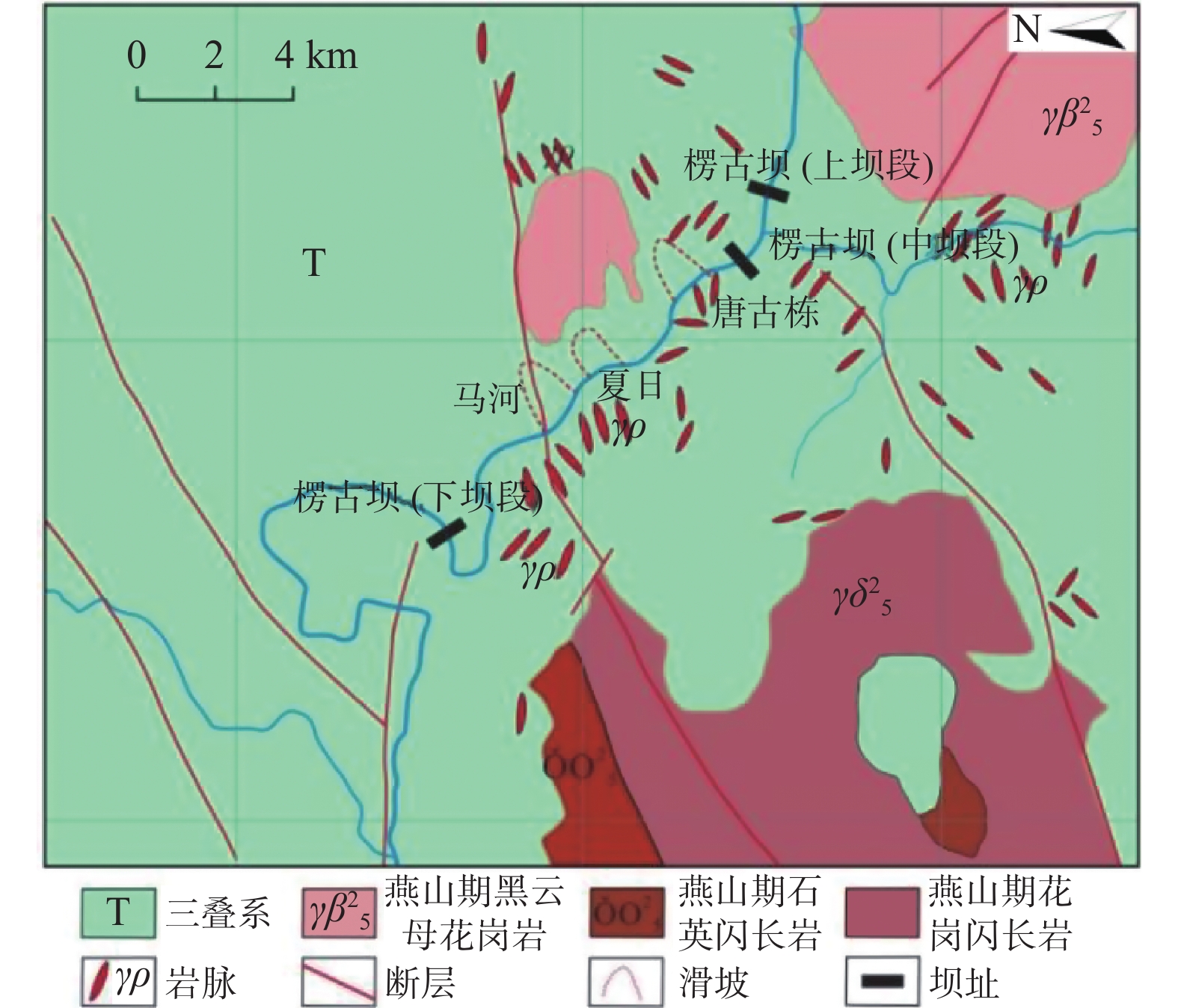
楞古水电站位于四川省甘孜州康定、雅江两县境内,控制流域面积77543 km2,占雅砻江全流域面积的57%。坝壅水高82 m,正常蓄水位以下库容2.19×108 m3,调节库容0.12×108 m3,初拟正常蓄水位2479 m。雅砻江在研究区河流走向大体为北东-南西,地势呈东西高、中部相对较低。山顶与河谷的高差达500~1000 m,谷深切呈“V”型谷,谷坡狭窄陡峻,整体坡度35°左右,为典型的高山峡谷地貌景观。研究区内河谷两岸斜坡地貌较发育,夏日滑坡位于雅砻江右岸,雅江县波斯河乡夏日村附近(图1)。
夏日滑坡区位于宋玉断层、孜河-楞古背斜以及雅砻江近南北向河谷所围限的区域之内。宋玉断层两侧花岗岩劈理化严重,并带有断层泥和断层角砾岩,活动断裂的发育导致区内河谷岸坡非常破碎(图2)。区内第四系覆盖较薄,坡体主要为基岩,以三叠系变质砂岩为主,代表性岩层产状为355°∠53°,在强烈的构造应力挤压作用下,岩石易弯曲变形形成褶皱和破裂,甚至形成密集层间劈理构造带[6-7]。夏日滑坡上部主要为印支期花岗岩,下部为三叠系块状变质粉细砂岩和第四系胶结砾石层、砂砾石层和胶结砾石、块石、砂、亚砂土、亚粘土等,岩层倾向坡内。
2. 滑坡破坏边界及发育特征
2.1 滑坡变形破坏边界
夏日滑坡在地形地貌、边坡结构以及变形破坏现状等方面有很大差别,文章根据坡体的地貌形态、物质组成、边坡岩体结构特征以及变形破坏现状,将夏日坡体划分为三个区(图3),并对各区的稳定性做出定性的工程地质评价。分区主要考虑一下几个方面的因素[8-9]:①地形地貌因素;②地层岩性与边坡结构;③变形破坏现状,特别是岩体变形迹象以及卸荷裂隙发育状况;④对工程的重要性。
Ⅰ区:为夏日边坡老滑坡区,位于夏日村坡下临江一侧[8]。老滑坡体后缘较为宽大,前缘缩口。主断壁高220 m,滑坡残体后缘高程2560 m左右,前缘河床部位高程约2350 m,横向宽350 m,厚度20~50 m,前缘剪出口位于2360~2380 m高程,高出河水面约5~30 m,沿线可见泉水呈带状渗出。Ⅰ区上下游边界清晰,两侧均为基岩陡壁。上游侧基岩因卸荷风化强烈,岩体较为破碎,在坡脚附近,可见完整的变质砂岩出露。下游侧岩体被花岗岩脉穿插,可见清晰的结构特征。
Ⅱ区:位于Ⅰ区下游侧的基岩山梁为界的下游部位,为夏日滑坡现状崩滑区,被上下游基岩山梁所围限。滑坡体物质组成为:上部为斜坡崩塌物以及基岩风化产物组成的土石混合体,下部为砂岩,岩层倾向坡内。第四系覆盖较薄,坡体主要为基岩。
Ⅲ区:为夏日滑坡后缘区,表层主要为青灰色砂岩与灰黄色花岗岩块石,地形坡度与夏日滑坡原始地表坡度相近,表现为前缘较为宽缓,后缘较陡。相对而言此区属于稳定区,故不作为重点调查区进行研究。
2.2 发育特征分析
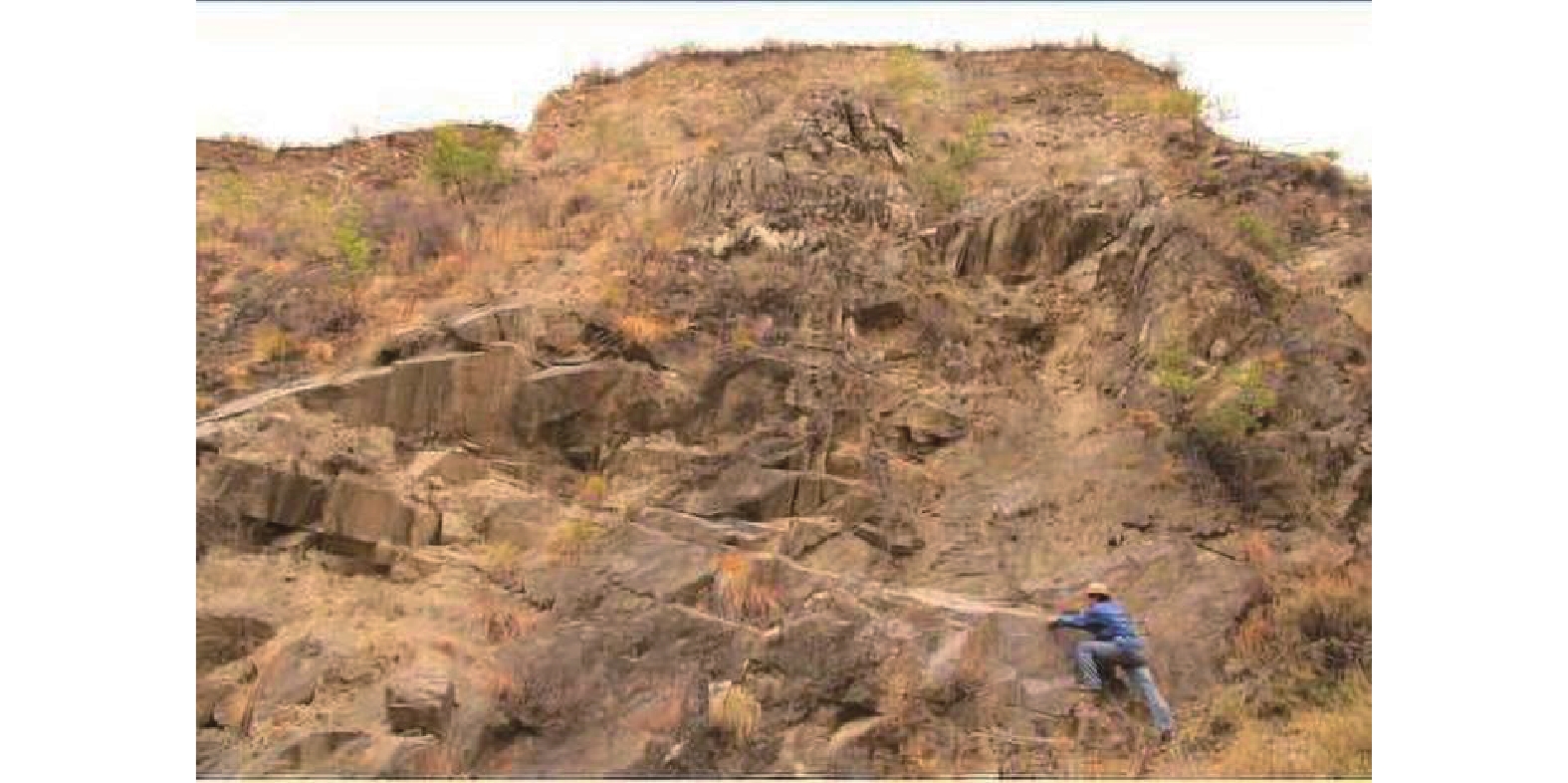
Ⅰ区:属于老崩滑堆积体,坡体后缘较为宽大,前缘缩口,滑坡后壁圈椅不呈理想弧形,推断滑坡在一定程度上受母岩的结构特性控制(图4)。现状后壁不是滑后的初始断壁,滑坡发生后在断壁顶部发育有一系列错落台坎和崩落,断壁前缘崩塌造成主断壁一定程度的后移,崩落的岩土体形成了倒石堆。滑坡残体两侧为基岩山梁,岩体卸荷风化强烈。滑坡体目前无整体复活迹象,但局部稳定性差。考虑到夏日滑坡为一高速滑坡[8],滑动后滑体滑动势能已经大幅消减,现滑坡主滑段滑面平缓,滑坡残体可获得较高的整体稳定性,不会发生大规模整体剧烈滑动,水库蓄水后滑坡体至多将以蠕滑—渐稳方式运动[10-11]。
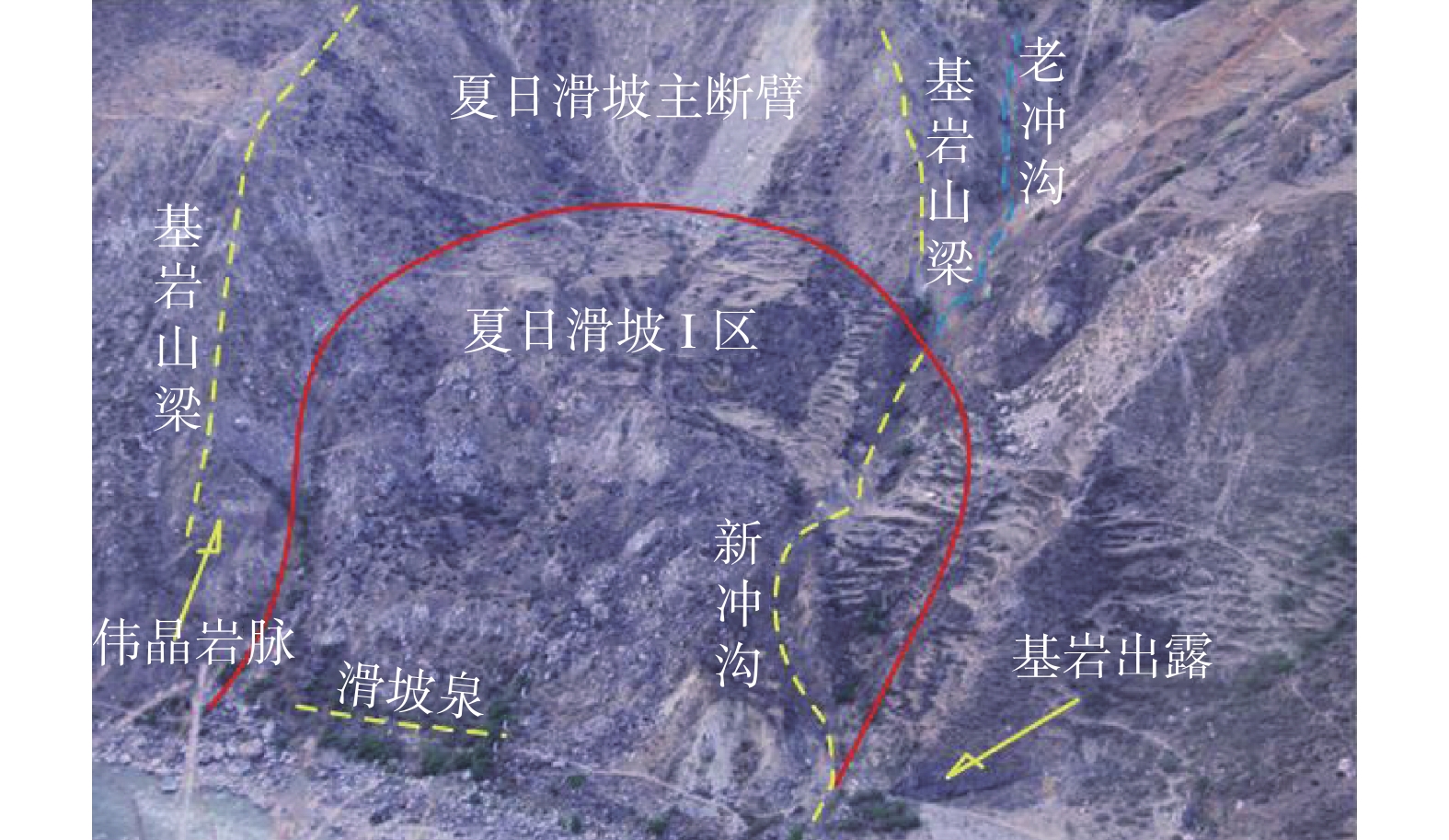
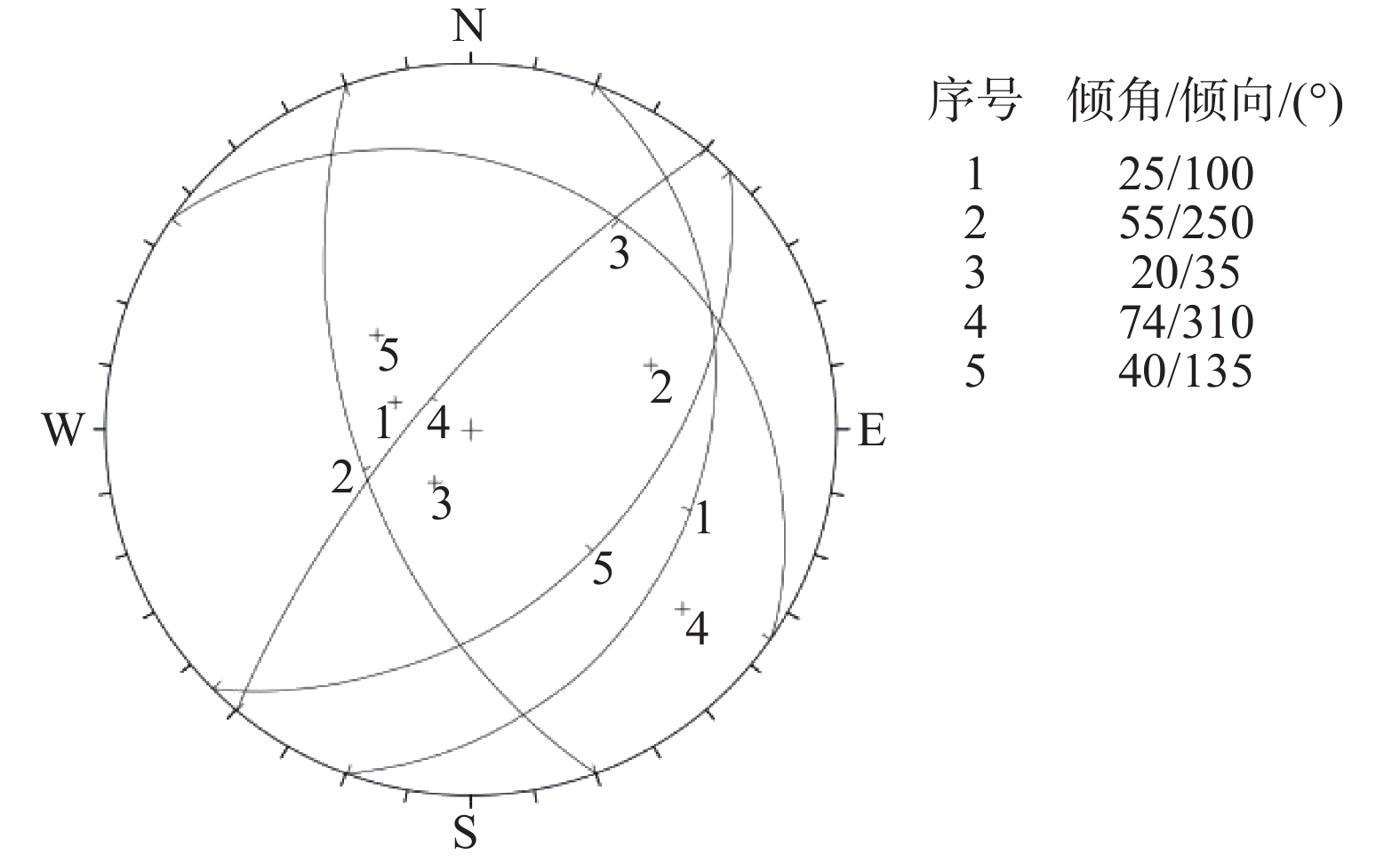
Ⅱ区:自上游到下游,可以分为基岩山梁段、泥石流冲沟段,龟背段(此段坡面较为完整,形似龟背,但呈凹形)和“勺形崩滑”段(图5、图6)。根据工程地质现场调查,周边基岩中未发现较大断层。从坡体物质组成方面看,Ⅱ区斜坡体上部主要为碎石土,并夹有少量较大块的孤石,而含量最多的还是块径比较小的岩块,这主要是由原来上部基岩风化、崩塌、滚落、堆积而形成的。Ⅱ区内表层堆积有厚度不等的崩塌物质,下部分布有全强风化层序清晰的缓倾角砂岩,并未发现大规模的滑坡体形成时局部地层翻转、崩塌和杂乱岩体相间分布的现象。下层基岩顶部风化比较强烈。从岩体结构特征方面看,本区段岩土体存在倾向坡外的不利结构特征,岩体被切割为块状结构,较为破碎,并可见错动擦痕,主要结构面产状为:110°∠25°、240°~267°∠53°~60°和35°∠20°,岩体被切割为块状结构(图7),结构面赤投影见图8(面⑤为坡面产状),其前缘稳定性储备不高。
Ⅱ区已经滑塌的部位并不属于典型的整体滑动,而是一种典型的“勺形崩滑[12],此种类型的崩滑体大多处于位置较高的陡倾斜坡上,母岩破碎,或为原有老滑坡或崩塌体,崩塌体高位剪出或崩落后形成长程高速碎屑流或崩塌。再考虑到整个坡体的岩体特征与“勺形崩滑”体的成生原因与1967年大洪水有关,表明其稳定性储备不高。水库建成后,本区段水位将上升129 m(图6),斜坡岩土体含水量增加和库水作用强烈,抗剪参数在饱和状态下大幅弱化,坡体前缘可能产生滑移式塌岸甚至引发大规模整体滑动[13-14]。
经上述宏观地质定性分析,自然状态下该边坡处于稳定状态,而坝内蓄水工况时对边坡的稳定性影响最大,Ⅱ区可能出现失稳破坏。故重点对Ⅱ区在蓄水前、后的稳定性做进一步进行定量分析和评价。
3. 夏日滑坡Ⅱ区稳定性分析
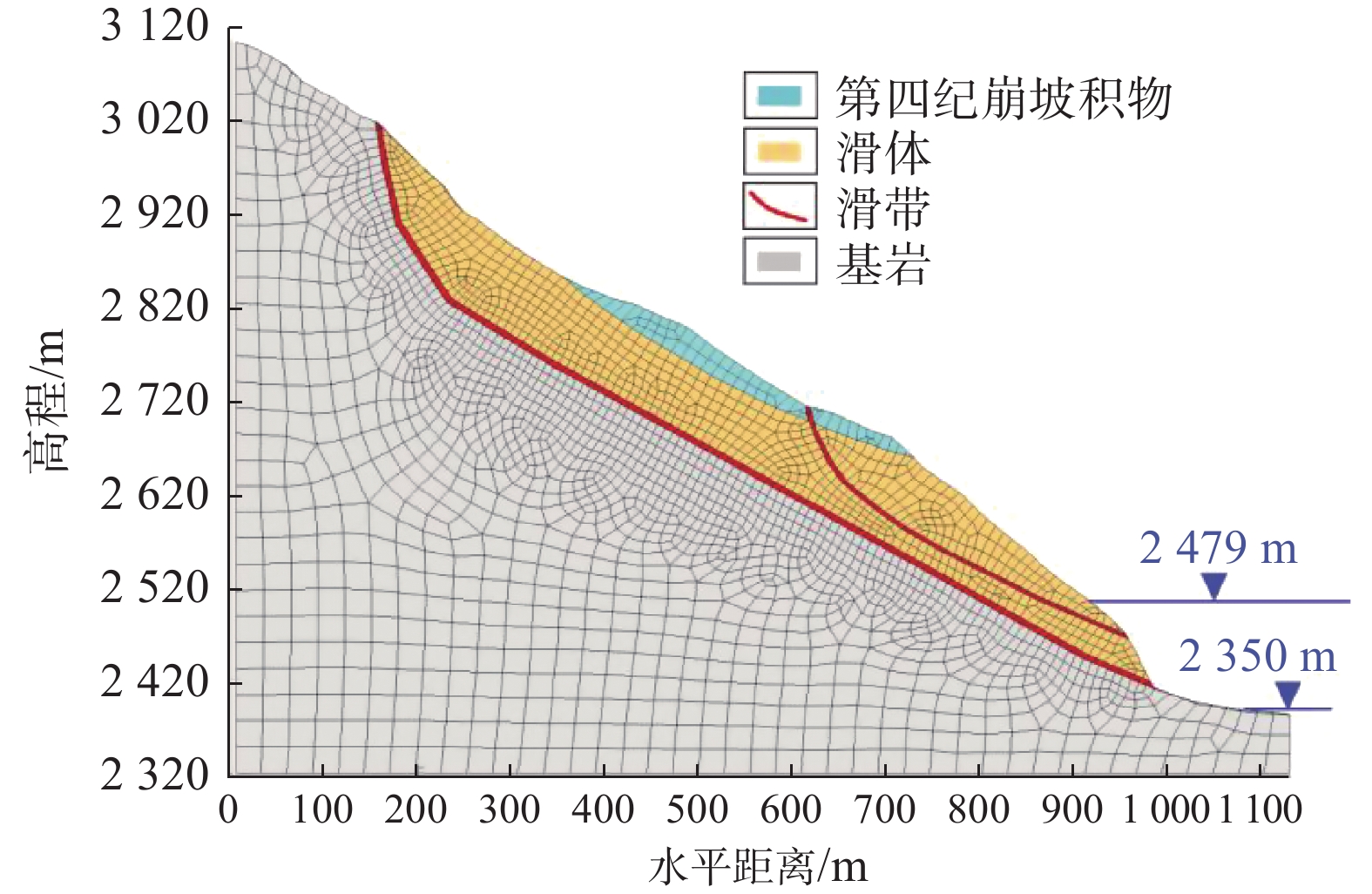
基于野外详细调查,结合勘察测试数据,采用有限差分软件FLAC3D重点对夏日滑坡Ⅱ区的稳定性进行了分析,岩土体参数见表1所示,计算过程采用莫尔-库仑准则[15-18]。考虑滑坡边界效应,长宽高均预留100 m,并参照夏日滑坡的实际空间几何形态,建立高800 m、长1120 m、宽10 m的计算模型(图9),模型中基岩、滑体、滑带的网格边长为分别为30 m、15 m、8 m,共划分4596个节点和2200个网格。利用CAD建立二维图形,采用ANSYS拉伸、划分网格,最后导入FLAC3D进行计算分析。
表 1 岩土体物理力学参数取值表Table 1. Values of mechanical parameters of rock and soil岩性 密度
/(g·cm−3)体积模量
/MPa剪切模量/MPa 黏聚力
/(c·kPa−1)内摩擦角
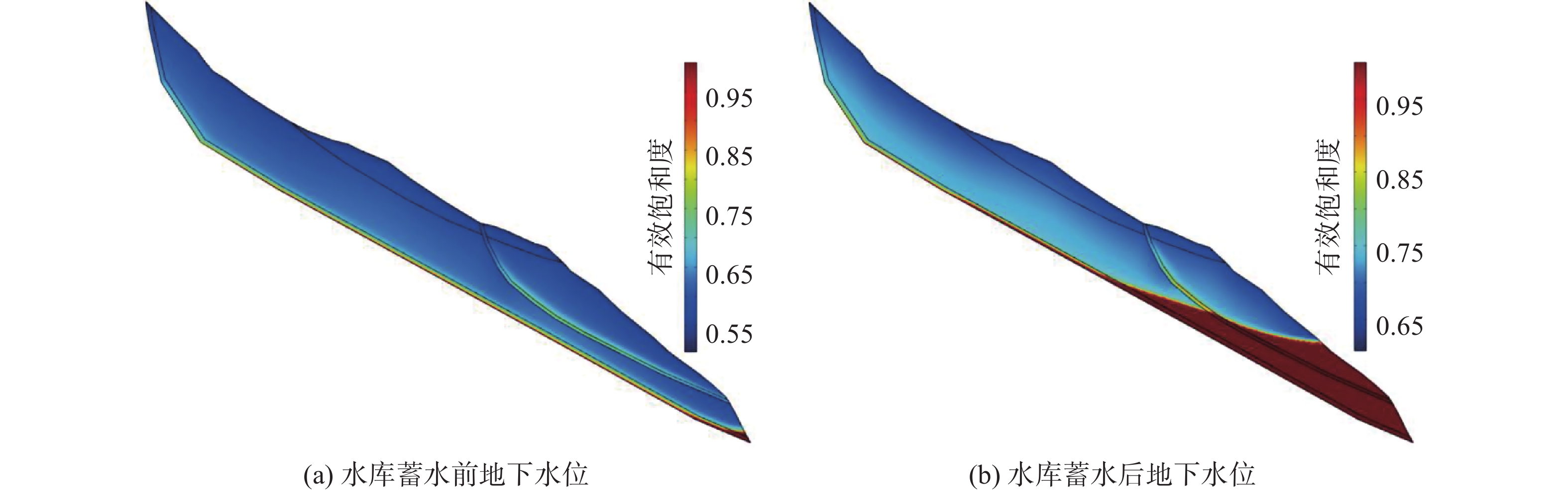
$\varphi $/(°)基岩 2.25 6200 3500 250 48 滑体(天然) 2.03 600 350 80 38 滑体(饱水) 2.09 320 180 50 31 第四纪崩坡积物 1.89 260 150 45 29 滑带(天然) 1.93 80 40 40 28 滑带(饱水) 1.98 45 20 15 22 资料表明,目前夏日滑坡坡脚水位为2350 m,楞古水电站建成蓄水后水位为2479 m。通过模拟蓄水前后不同水位对应的滑坡地下水位表明:在蓄水前,滑坡体整体处于非饱和状态,饱和部分仅分布在坡脚局部部位;蓄水后,滑坡体前部大部分已饱和(图10),此时水对滑带土的软化作用不容忽视。考虑蓄水影响,将饱和部分滑坡体和滑带土做一定程度的折减,模拟蓄水前和蓄水后工况下的夏日滑坡变形破坏特征[19-20]。
3.1 蓄水前滑坡稳定性
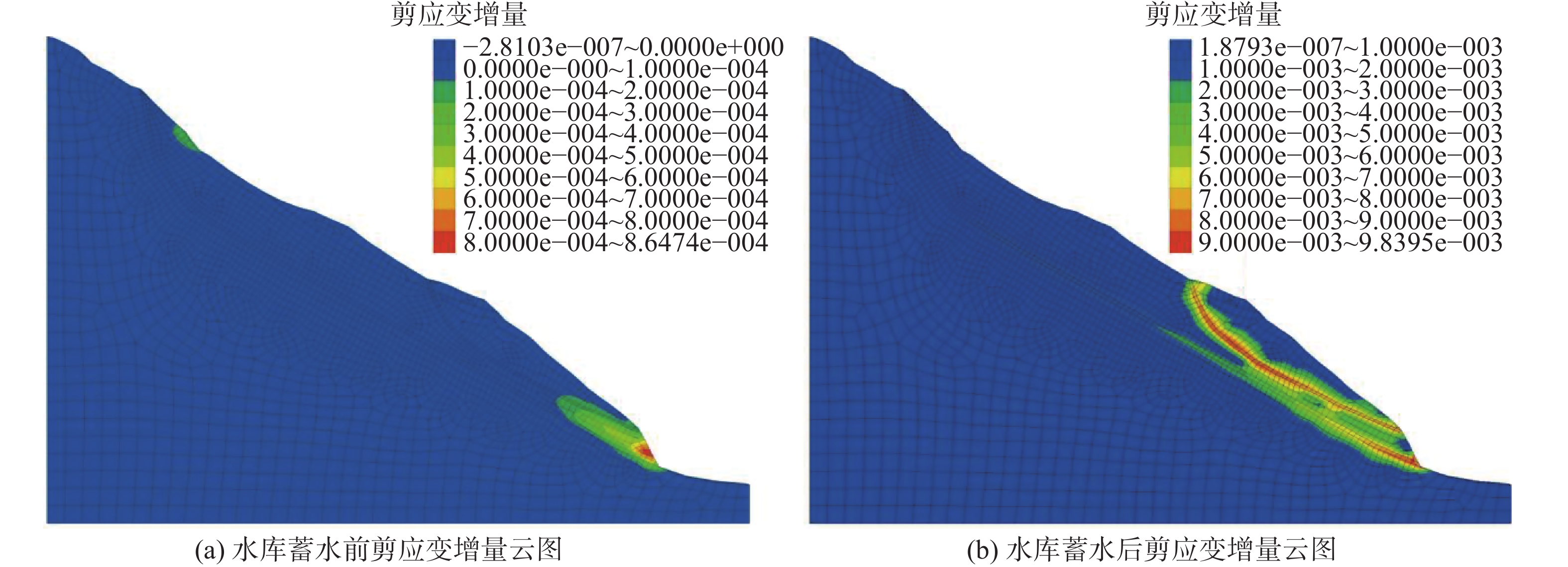
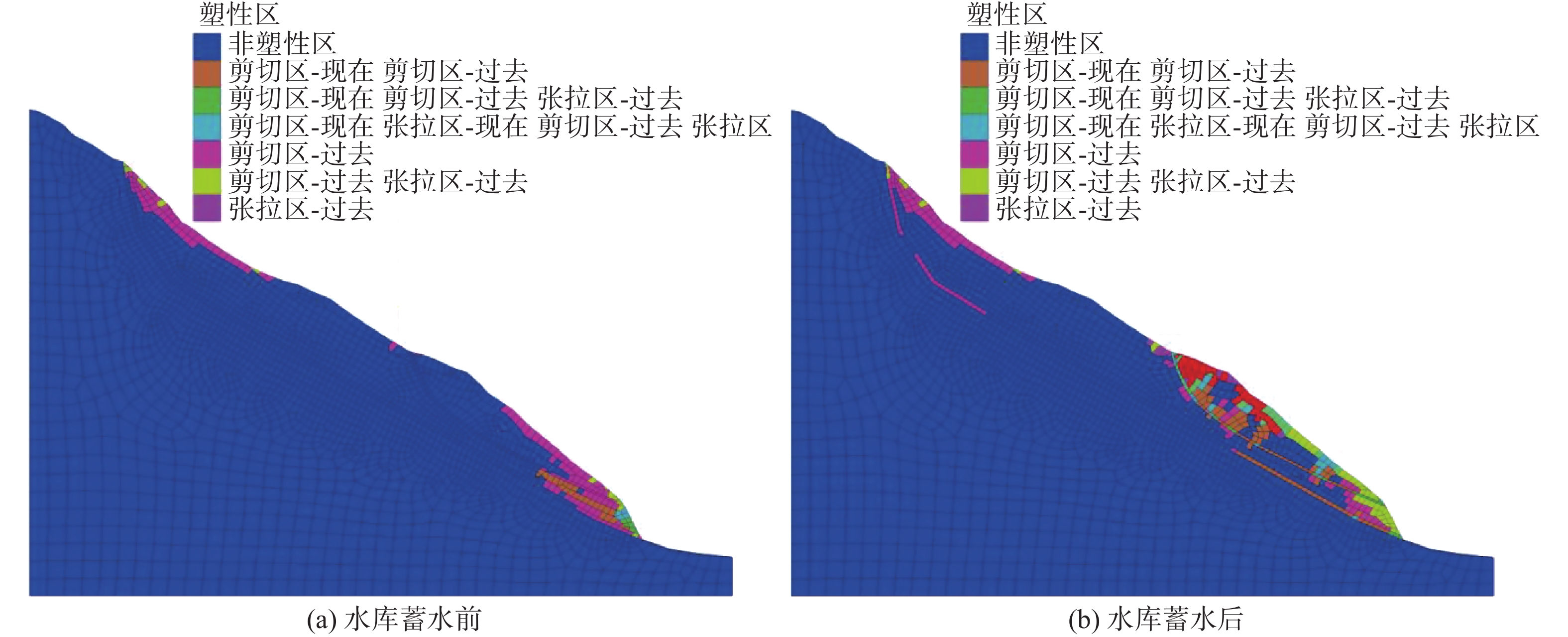
运用有限差分法对天然工况下夏日滑坡稳定性进行模拟。图11(a)为滑坡位移云图,滑坡体主要变形区位于滑坡坡脚范围,但整体位移量较小,最大位移仅为0.016 m,此外滑坡后缘局部出现浅表层变形,最大位移为0.006 m;剪应变增量云图表明,应力也主要集中在坡脚位置,见图12(a),但剪应变增量有向滑坡深部扩展的趋势;目前处于剪切破坏塑性区的单元也主要存在于前缘坡脚部位,见图13(a)。基于内置的强度折减法计算,滑坡安全系数Fs=1.23。表明在天然工况下夏日滑坡的变形主要集中于坡脚部位,但整体位移量很小,稳定性较好,这也与目前的现场调查结果一致。
3.2 蓄水后滑坡稳定性
水库蓄水对库岸滑坡稳定性具有重要的影响[21-23]。图11(b)为蓄水之后夏日滑坡的位移变化特征,显示出明显的两级滑动,前缘上部变形在0.15~0.2 m,下部变形在0.075~0.15 m,表明夏日滑坡具有沿基岩滑床向下分级牵引变形滑动的特点,坡脚部位的最大位移达到了0.2 m,为蓄水前的12.5倍,变形主要沿前缘次级滑坡滑带滑动,且越靠近前缘变形越大。前缘坡脚及剪出口处剪应变增量值最大,正处于剪切屈服状态的单元已逐渐形成条形区域,见图13(b),总体上已沿次级滑面形成一条集中贯通的剪切带,见图12(b)。此外,深层滑带也出现局部的贯通。根据前期试验测试和相关工程类比[18,24-25],采用强度折减法计算,滑坡前缘安全系数Fs=1.02。说明在库水位作用下,先期剪切带强度弱化,诱发滑坡局部滑动,破坏方式为前缘牵引式滑动。在滑坡前缘失稳破坏后,滑坡体的剪切破坏可能会继续向上逐渐发展,牵引整个滑坡发生大规模滑动。
4. 结论与建议
(1)根据坡体的地貌形态、物质组成、滑坡成因和滑动机理分析,将夏日滑坡划分为三个区。经宏观地质定性分析,Ⅰ区滑坡体无整体滑动迹象,但水库蓄水后,局部可能将以蠕滑-渐稳方式运动,但不会发生大规模整体滑动;Ⅱ区目前已经出现一定的变形破坏,稳定性最差,尤其水库建成后,坡体前缘可能产生滑移式塌岸甚至引发大规模整体滑动;Ⅲ区整体上较为稳定,不做为重点研究区。
(2)数值模拟表明,蓄水前,夏日滑坡Ⅱ区整体稳定性较好,只在前缘局部出现变形;蓄水后,Ⅱ区滑坡体变形明显扩大,前缘沿先存的次级滑带滑动。建议在夏日滑坡Ⅱ区前缘进行格构锚固和抗滑桩支护,以免水库蓄水后滑坡前缘滑动对水电设施造成破坏。
(3)建议利用现有的成熟监测技术,对滑坡灾害隐患进行早期识别和监测预警。西部高山峡谷区域,由于地域广,传统的人工监测技术较难实施,可利用InSAR技术对高山峡谷区域的滑坡灾害隐患广域进行早期识别[26-28],达到有效减灾和防灾的目的,并为水电工程建设提供安全保障。
-
表 1 岩土体物理力学参数取值表
Table 1 Values of mechanical parameters of rock and soil
岩性 密度
/(g·cm−3)体积模量
/MPa剪切模量/MPa 黏聚力
/(c·kPa−1)内摩擦角
$\varphi $/(°)基岩 2.25 6200 3500 250 48 滑体(天然) 2.03 600 350 80 38 滑体(饱水) 2.09 320 180 50 31 第四纪崩坡积物 1.89 260 150 45 29 滑带(天然) 1.93 80 40 40 28 滑带(饱水) 1.98 45 20 15 22 -
[1] 黄润秋. 岩石高边坡发育的动力过程及其稳定性控制[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(8):1525 − 1544. [HUANG Runqiu. Geodynamical process and stability control of high rock slope development[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(8):1525 − 1544. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.08.002 [2] WANG F W, ZHANG Y M, HUO Z T, et al. The July 14, 2003 qianjiangping landslide, Three Gorges reservoir, China[J]. Landslides,2004,1(2):157 − 162.
[3] 邓成进, 王孔伟, 王乐华, 等. 楞古水电站中坝线下游右岸雨日堆积体滑坡形成机理研究[J]. 水电能源科学,2010,28(3):45 − 47. [DENG Chengjin, WANG Kongwei, WANG Lehua, et al. Cause mechanism study on Yuri landslide of accumulation rock of right bank in downstream of Lenggu hydropower station[J]. Water Resources and Power,2010,28(3):45 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7709.2010.03.015 [4] 王孔伟, 邓成进, 张帆. 中国西南雅砻江流域唐古栋滑坡及雨日堆积体形成机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(6):955 − 970. [WANG Kongwei, DENG Chengjin, ZHANG Fan. Formation process of tanggudong landslide and Yuri accumulation body in Yalong river valley in southwest China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(6):955 − 970. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.06.007 [5] 肖华波, 杨静熙, 王刚, 等. 楞古水电站岸坡稳定性及对坝段选择的影响[J]. 人民黄河,2017,39(2):107 − 111. [XIAO Huabo, YANG Jingxi, WANG Gang, et al. Interactions of dam-site selection and stability of bank slope in the Lenggu hydropower project[J]. Yellow River,2017,39(2):107 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2017.02.027 [6] 中国地质烈度区划图编委会. 中国地质烈度区划图(1990)及其说明[J]. 中国地震, 1992, 8(4): 1 − 11 The compiling committee of sefsmic zoning map in China. Seismic intensity zoning map of China (1990) and its explanations [J]. Earthquake Research in China, 1992, 8(4): 1 − 11. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 曹水合, 王运生, 贺建先. 四川康定Ms6.3级地震次生地质灾害特征及成灾模式[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(4):87 − 93. [CAO Shuihe, WANG Yunsheng, HE Jianxian. Characteristics and disaster model of co-seismic landslides triggered by the Kangding Ms6.3 earthquake on the 22th of Nov, Sichuan Province, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(4):87 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 范博远, 孙少锐, 李振江, 等. 楞古水电站夏日边坡边界条件确定及稳定性评价[J]. 甘肃科学学报,2018,30(2):73 − 78. [FAN Boyuan, SUN Shaorui, LI Zhenjiang, et al. Determine Xiari slope and boundary condition and evaluate stability for Lenggu hydropower station[J]. Journal of Gansu Sciences,2018,30(2):73 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 殷跃平, 王文沛, 张楠, 等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究: 以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(5):827 − 841. [YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei, ZHANG Nan, et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area: A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province[J]. Geology in China,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12029/gc20170501 [10] 王立朝, 温铭生, 冯振, 等. 中国西藏金沙江白格滑坡灾害研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):1 − 9. [WANG Lichao, WEN Mingsheng, FENG Zhen, et al. Researches on the Baige landslide at Jinshajiang river, Tibet, China[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 卢书强, 易庆林, 易武, 等. 三峡库区卧沙溪滑坡变形失稳机制分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2013,24(2):21 − 25. [LU Shuqiang, YI Qinglin, YI Wu, et al. Analysis on deformation and failure mechanism of Woshaxi landslide in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2013,24(2):21 − 25. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震滑坡特征分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(1):29 − 38. [YIN Yueping. Features of landslides triggered by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(1):29 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.01.004 [13] 殷跃平. 三峡库区边坡结构及失稳模式研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2005,13(2):145 − 154. [YIN Yueping. Human-cutting slope structure and failure pattern at the Three Gorges reservoir[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2005,13(2):145 − 154. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2005.02.001 [14] 张御阳, 黄润秋, 裴向军, 等. 楞古水电站碎裂岩质边坡变形破坏模式研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(2):556 − 564. [ZHANG Yuyang, HUANG Runqiu, PEI Xiangjun, et al. Deformation failure mode of fractured rock mass slope in Lenggu hydropower station[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(2):556 − 564. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 王梓龙, 裴向军, 张御阳, 等. 松动岩体工程特性研究: 以雅砻江楞古水电站松动岩体为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2019,49(5):1376 − 1388. [WANG Zilong, PEI Xiangjun, ZHANG Yuyang, et al. Engineering characteristics of loose rock mass: Taking loose rock mass of Lenggu hydropower station in Yalong river as an example[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2019,49(5):1376 − 1388. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 曾阳益, 邓辉, 张咪, 等. 澜沧江上游典型倾倒—滑动组合型滑坡特征及形成机理的数值模拟[J]. 水电能源科学,2016,34(11):133 − 136. [ZENG Yangyi, DENG Hui, ZHANG Mi, et al. Landslide characteristics of typical dump-sliding combination in upstream of Lancangjiang River and its forming mechanism of numerical simulation[J]. Water Resources and Power,2016,34(11):133 − 136. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 罗忠行, 雷宏权. 基于FLAC3D的米贝复式滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):52 − 62. [LUO Zhongxing, LEI Hongquan. Study on Mibei Landslide analysis based on FLAC3D[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):52 − 62. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 卫童瑶, 殷跃平, 高杨, 等. 三峡库区巫山县塔坪H1滑坡变形机制[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):73 − 81. [WEI Tongyao, YIN Yueping, GAO Yang, et al. Deformation mechanism of the Taping H1 landslide in Wushan County in the Three Gorges Reservoir Area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):73 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 王乐, 秦世伟. 不同降雨类型与库水位波动耦合作用下的土质滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(6):103 − 111. [WANG Le, QIN Shiwei. Landslide instability induced by sudden lower in water level combined with different rainfall types[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(6):103 − 111. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 谢林冲, 王明清, 周超. 基于降雨-库水联合作用下三门洞滑坡演化过程与机制[J]. 水电能源科学,2020,38(6):128 − 132. [XIE Linchong, WANG Mingqing, ZHOU Chao. Evolution process and mechanism of sanmendong landslide based on combined effect of rainfall and reservoir water[J]. Water Resources and Power,2020,38(6):128 − 132. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 尹晓萌, 晏鄂川, 杜毅, 等. 库水位下降条件下堆积层滑坡稳定性分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(3):8 − 15. [YIN Xiaomeng, YAN Echuan, DU Yi, et al. Stability of colluvial landslide with drawdown of reservoir water level[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(3):8 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) [22] 夏庄凡者, 宋琨, 易庆林, 等. 大型岩质水库滑坡复活变形过程的影响因素分析[J]. 水电能源科学,2020,38(8):114 − 117. [XIA Zhuangfanzhe, SONG Kun, YI Qinglin, et al. Influencing factor analysis of large rock reservoir landslide during reactivation deformation process[J]. Water Resources and Power,2020,38(8):114 − 117. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 张巷生, 卢书强, 刘欣, 等. 三峡水库蓄水条件下树坪滑坡稳定性影响分析[J]. 水利规划与设计,2020(5):106 − 111. [ZHANG Xiangsheng, LU Shuqiang, LIU Xin, et al. Analysis of affecting factors of stability of shuping landslide underimpoundment of Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Water Resources Planning and Design,2020(5):106 − 111. (in Chinese) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2469.2020.05.025 [24] 肖松春. 滑坡稳定性计算和滑坡稳定性量化评分方法的适用性对比研究: 以湖南衡东某风电场公路切坡为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(3):159 − 164. [XIAO Songchun. Comparison of the landslide stability calculation and landslide stability evaluation method: A case of the cutting slope of a wind farm in Hengdong, Hunan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(3):159 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract) [25] 高杨, 贺凯, 李壮, 等. 西南岩溶山区特大滑坡成灾类型及动力学分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):14 − 23. [GAO Yang, HE Kai, LI Zhuang, et al. An analysis of disaster types and dynamics of landslides in the southwest Karst Mountain areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):14 − 23. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 刘传正, 陈春利. 中国地质灾害防治成效与问题对策[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(2):375 − 383. [LIU Chuanzheng, CHEN Chunli. Achievements and countermeasures in risk reduction of geological disasters in China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(2):375 − 383. (in Chinese with English abstract) [27] 戴可人, 铁永波, 许强, 等. 高山峡谷区滑坡灾害隐患InSAR早期识别: 以雅砻江中段为例[J]. 雷达学报,2020,9(3):554 − 568. [DAI Keren, TIE Yongbo, XU Qiang, et al. Early identification of potential landslide geohazards in alpine-canyon terrain based on SAR interferometry—A case study of the middle section of Yalong river[J]. Journal of Radars,2020,9(3):554 − 568. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12000/JR20012 [28] 侯燕军, 周小龙, 石鹏卿, 等. “空-天-地”一体化技术在滑坡隐患早期识别中的应用: 以兰州普兰太公司滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):12 − 20. [HOU Yanjun, ZHOU Xiaolong, SHI Pengqing, et al. Application of “Air-Space-Ground” integrated technology in early identification of landslide hidden danger: Taking Lanzhou Pulantai Company Landslide as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):12 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 王勇,邢振涛,李锁,闫勇,司甜. 基于SBAS-InSAR和光学遥感的天津市北部山区潜在滑坡识别研究. 灾害学. 2025(01): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 毛正君,李欢,石硕杰,孙婕文,仲佳鑫,于海泳. 面向对象的无人机遥感影像区域滑坡承灾体信息提取研究. 工程地质学报. 2025(01): 171-185 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 冯谕,曾怀恩,涂鹏飞. 遗传算法下的滑坡蠕滑位移预测模型研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 82-91 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨豹,赵瑞志,王海波,李晓光,吕钊,赵阳,王梦云. 遥感技术对地质灾害早期识别和动态监测——以昌波乡至羊拉乡段为例. 科学技术与工程. 2024(05): 1823-1836 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李恒丽,陈克全. 云南维西县新塘房滑坡形成条件及防治措施探讨. 云南地质. 2024(01): 115-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 毛正君,于海泳,梁伟,马旭,仲佳鑫,高广胜,石硕杰,田彦山. 基于无人机倾斜摄影测量三维建模的区域黄土滑坡识别及特征分析. 中国地质. 2024(02): 561-576 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 薛玉芹,滕秀华,孟大鹏. 遥感测量在采矿塌陷地监测及矿山地质灾害治理方面的应用. 世界有色金属. 2024(03): 157-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 党杰,杨亮,段方情,范宣梅. 贵州晴隆红寨大型古滑坡复活变形特征及成因分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(04): 25-35 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 孙成永. InSAR技术在河南信阳新县地质灾害风险调查中的应用. 城市地质. 2024(03): 383-389 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 孙琪皓,刘桂卫,王飞,张璇钰,王衍汇. 铁路地质灾害早期识别与监测预警技术及应用研究. 铁道标准设计. 2024(09): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 钱雨扬,孔令利,余洲,杨国兴,朋仁锋. 基于InSAR-光学影像的白鹤滩库区地质灾害隐患识别. 人民长江. 2024(S2): 107-112+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 韩民赛,刘岁海,罗明,蒋韬,孙大振. 滑坡预测预报研究与进展. 地质装备. 2023(01): 22-26+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 朱伟伟. 遥感技术在地质灾害监测与管理中的应用. 安徽地质. 2023(01): 75-77+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 黎浩良,杨莹辉,许强,宋家苇,李鹏飞,陈强,姚智博. 高寒山区地质灾害季节分区InSAR早期识别研究——以东构造结地区为例. 工程地质学报. 2023(03): 780-795 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李芳军. 黄土滑坡地质灾害监测预警方法与技术探讨. 冶金管理. 2023(15): 82-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(16)




 下载:
下载:






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS