Analysis on the effect of freeze-thaw on landslide prevention projects in seasonal frozen soil area
-
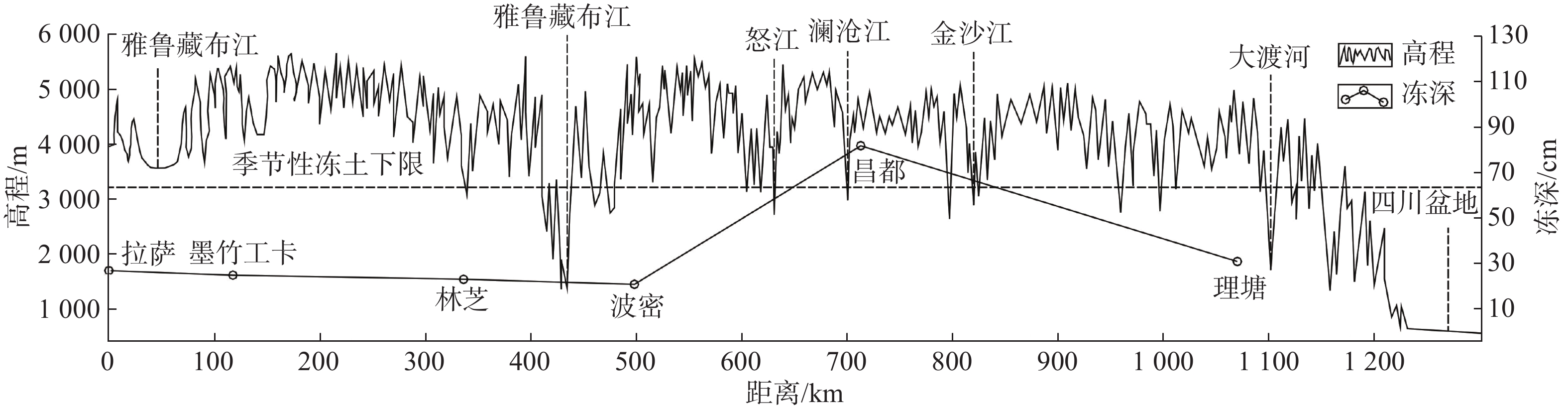
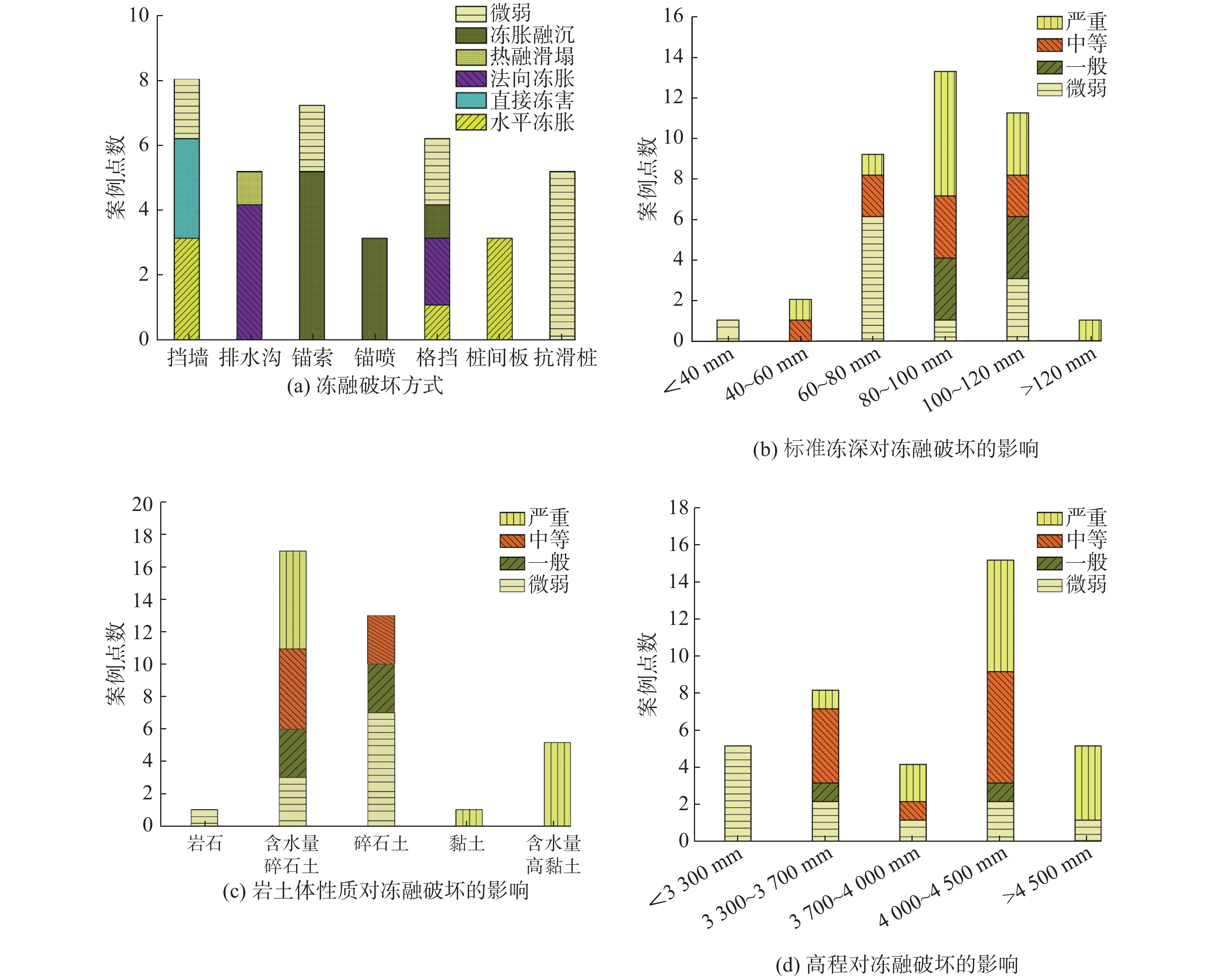
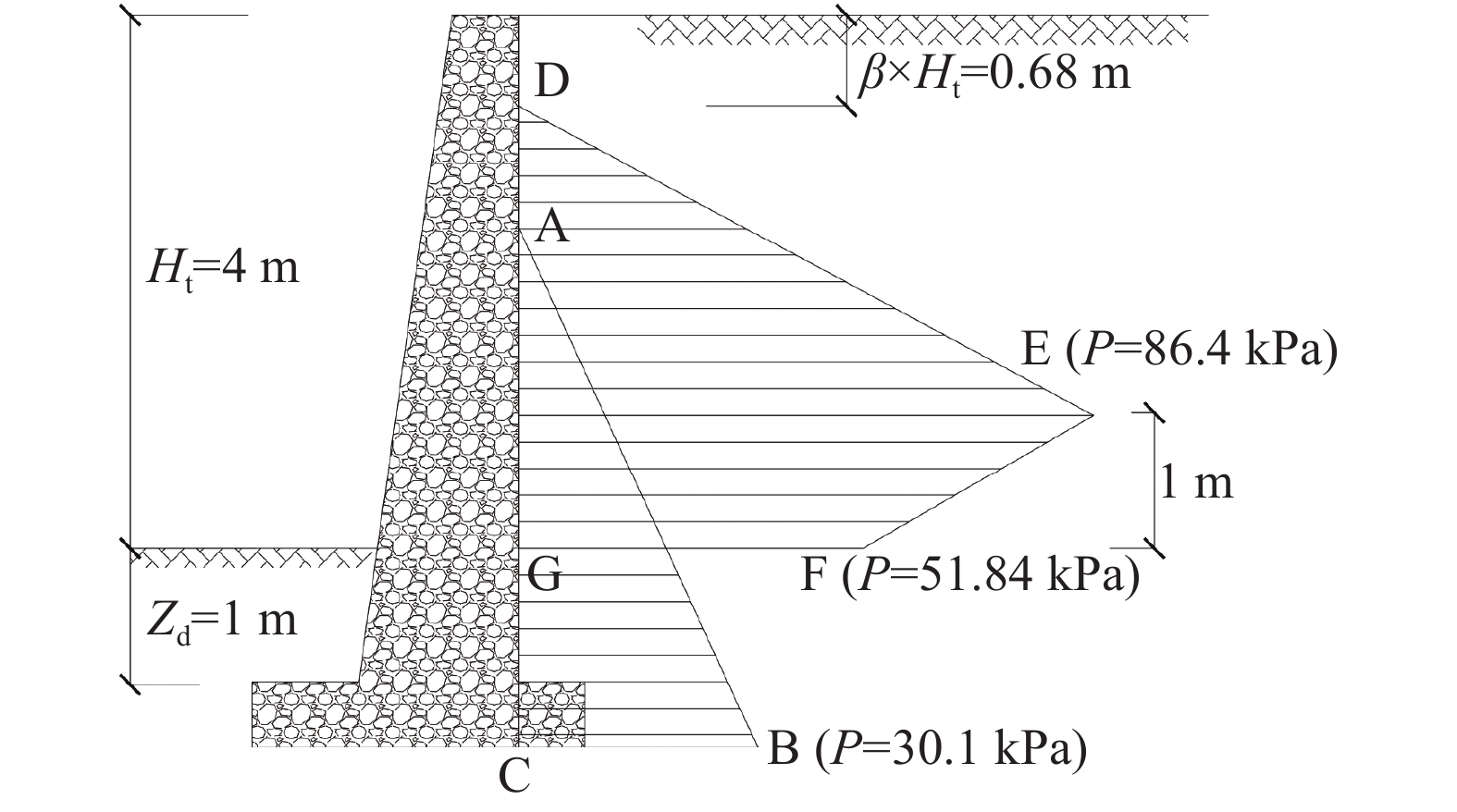
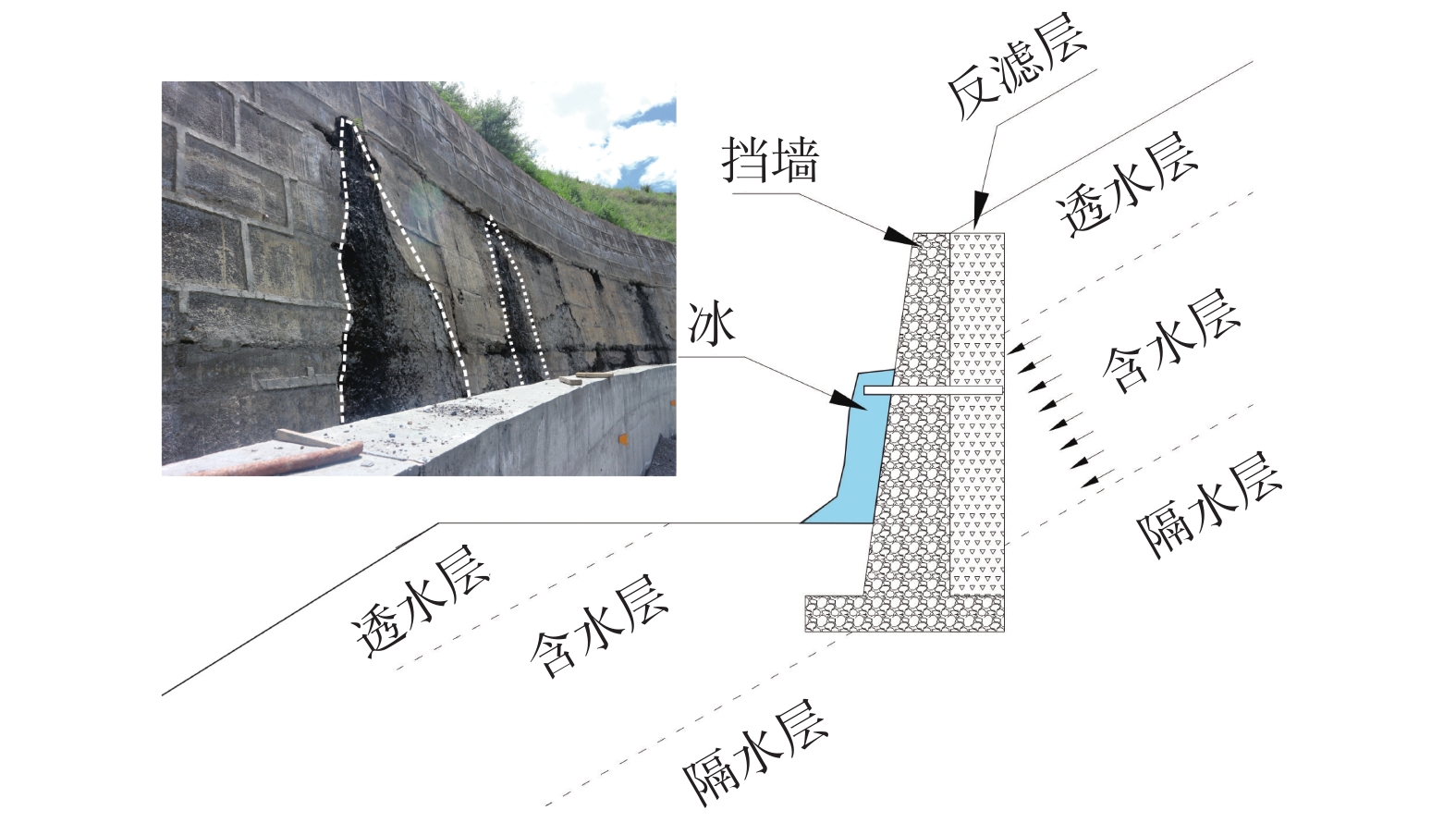
摘要: 川藏铁路规划线路穿越青藏高原东缘高寒带岛状山地冻土区,冻融环境相对复杂。文章通过对川西地区及藏东昌都地区G317、G318沿线滑坡防治工程25处典型案例进行调查,总结冻融条件下滑坡防治工程的破坏形式及受力机理,探讨了水平冻胀力、法向冻胀力的计算方法及其对挡墙、桩间板、排水沟等的影响,计算结果表明水平冻胀力远大于主动土压力,认为开放式冻胀较封闭式冻胀对防治工程的影响更大;阐明了冻胀融沉对锚索工程的影响,提出使用基于蓄能消能系统的锚索结构;探讨了季节性冻土区滑坡防治材料抗冻等级选择方法及减缓冻融效应的措施及建议,为川藏铁路沿线滑坡治理工程及拟建施工便道的边坡支护提供参考。Abstract: The planned route of the Sichuan-Tibet railway passes through the frozen soil on the eastern edge of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. The freezing-thawing environment is relatively complicated. More than 25 typical cases of landslide control projects along G317 and G318 in western Sichuan and Qamdo areas were investigated. The failure modes and force mechanisms of the projects under freeze-thaw conditions were summarized. The calculation method of horizontal frost heave force was discussed. The effects of horizontal frost heave retaining walls and drainage ditches were explored. The calculation results show that the horizontal frost heave force is much larger than the active earth pressure. The effects of frost heave and thawing on anchor cable engineering are clarified. It is considered that the effect of open frost heave on control engineering is greater than that of closed frost heave. Methods of material antifreeze grade and measures to reduce freeze-thaw effect were proposed. It can be used as a reference for landslide management projects along the Sichuan-Tibet railway.
-
Keywords:
- freeze-thaw /
- Sichuan-Tibet railway /
- seasonal frozen region /
- landslide /
- anchor
-
0. 引言
我国是地质灾害高发国家之一,各类地质灾害给人们的生命和财产造成了巨大的损失[1]。面对严峻的地质灾害问题,自上个世纪90年代起,我国开展了多轮地质灾害详细调查及排查工作,有力保障了人民群众的生命和财产安全且有助于展开之后的地质灾害调查工作[2],但部分地区地质灾害问题依旧突出。
我国西南地区地形地貌复杂,植被覆盖度较高,区内的地质灾害具有较高的隐蔽性,传统的地质灾害调查方法难以快速、准确的应对,必须借助现代高精度对地观测技术,如高精度光学遥感技术、合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术(Interferometric Synthetic Aperture Radar,In-SAR)等[3]。
卫星光学遥感技术因其时效性好、宏观性强、信息丰富的特点,已成为重大自然灾害调查分析和灾情评估的一种重要手段[4]。20世纪90年代以后,IKONOS(分辨率1 m)、QuickBird(分辨率0.6 m)、WordView2(分辨率0.5 m)等高分辨率的卫星影像被广泛应用于地质灾害探测与监测[5]。王瑞国等[6]依据WordView2卫星数据将解译结果与野外验证相结合、人机交互解译与计算机自动信息提取相结合的方法,圈定了乌东煤矿区域地质灾害点集中发育区。
合成孔径雷达干涉测量技术是近20年发展起来的一门广泛应用于监测自然灾害和人类活动导致的地表环境变化的技术,具有全天候、大范围、高精度、强时效、具有穿透性等特点[7]。刘星洪等[8]基于InSAR对雷波县区域活动性滑坡进行了早期识别;戴可人等[9]基于InSAR对雅砻江中段区域进行了高山峡谷区滑坡灾害隐患的早期识别;杨成生等[10]基于InSAR技术对金沙江结合带巴塘段滑坡群进行了滑坡探测识别。
因此,本文采用WordView2、Sentinel-1、ALOS-2遥感数据,以滇西北地区为研究区,对研究区潜在滑坡或老滑坡进行综合遥感识别,并进行野外验证,分析灾害体的光学影像、InSAR地表变形图的影像及图像特征,灾害体的发育特征,分布规律,并建立光学遥感解译标志、InSAR图像识别标志,总结识别方法,提高滇西北地区滑坡的识别率,为今后滇西北地区滑坡隐患识别、地质灾害调查与评价提供借鉴。
1. 研究区区域地质概况
研究区位于云南省西北部,包含保山、大理、丽江、临沧、怒江、德宏、普洱、迪庆、楚雄、玉溪等10个市(州)46个县(区),总面积约15×104 km2。
1.1 自然地理
滇西北属于喜马拉雅山系东部的横断山脉纵向岭谷区,北接青藏高原,东南与云贵高原相连,西部与缅甸相接。境内地质情况复杂,有高黎贡山、云岭、白马雪山等巨大山系纵贯南北,怒江、澜沧江、金沙江并流其间。
1.2 地形地貌
滇西北地势西北高、东南低,自北向南呈阶梯状逐级下降,从北到南的每千米水平直线距离,海拔平均下降6 m,属山地高原地形。
1.3 气象水文
滇西北属高原山地气候,具有终年低温干燥、夏季凉爽、冬季寒冷的特点。主要表现为:气候的区域差异和垂直变化十分明显,年温差小,日温差大,立体气候特征显著。干湿季节分明,湿季(雨季)为5—10月,集中了85%的降雨量;干季(旱季)为11月至次年4月,降水量只占全年的15%。
1.4 地层岩性
滇西北地区区内地层齐全,元古界、古生界、中生界、新生界均有出露,大部分地层均有不同程度的变质。
1.5 地质构造与地震
区内构造变形复杂,断裂活动强烈,主要的区域性断裂有20多条,将其归为16个大型构造,有:高黎贡山大型逆冲-走滑断裂构造,怒江大型逆冲-走滑断裂构造,勐统—沧源逆冲叠瓦构造等。
2. 遥感数据源与数据处理
2.1 光学数据源
光学数据源主要采用全色0.5 m精度的2018—2020年的WordView2卫星数据。
2.2 InSAR数据源
InSAR数据源主要采用2017—2020年的哨兵-1A(Sentinel-1A)雷达卫星(C波段)SAR数据和ALOS-2雷达卫星(L波段)SAR数据。
2.2.1 哨兵-1A雷达卫星数据
哨兵-1A(Sentinel-1A)是一个全天时、全天候雷达成像系统,由欧洲委员会(EC)和欧洲航天局(ESA)针对哥白尼全球对地观测项目研制的首颗卫星,于2014年10月开始逐步走向应用[11](表1)。
表 1 Sentinel-A雷达数据基本参数Table 1. Basic parameters of the Sentinel-A radar data星载SAR系统 Sentinel-1A 所属国家/机构 欧空局 轨道高度/km 693 波长/cm C(5.6) 观测时间间隔/d 12 运行时间 2014—2021 测量变形精度 毫米级 极化方式 HH+HV, VV+VH 地面分辨率/m 集束模式5×5、条带模式5×20
扫描模式20×20、加宽扫描20×40影像幅宽/km 集束模式20、条带模式80
扫描模式250、加宽扫描4002.2.2 ALOS-2雷达卫星数据
ALOS-2雷达卫星数据是日本先进的陆地观测卫星ALOS的后继星,也是目前世界上唯一一颗在轨运行的L波段合成孔径雷达卫星,具有较强的穿透性,植被覆盖茂盛,地表起伏较大、气候潮湿的地区具有更大的优势,更容易形成干涉像对[12](表2)。
表 2 ALOS-2雷达数据基本参数Table 2. Basic parameters of ALOS-2 radar dataSAR系统参数 参数内容 发射时间 2014年5月 频率/GHz 1.2 重访周期/d 14 拟用拍摄模式 Ultra-Fine 入射角/(°) 29.1~38.2 分辨率/m 3×3 幅宽/km 50 极化模式 HH+HV/VV+VH/HH/VV/HV/VH 2.3 InSAR数据处理-Stacking技术
Stacking技术通过组合多个干涉图解决常规InSAR面临的干涉失相干和大气延迟的问题,以实现区域高精度测量[13]。Stacking技术通过生成的多景差分干涉纠缠图估算线性相位速率,实际是基于最小二乘法对N组观测值线性回归的过程,估算公式为:
$$ P{h}_-rate=\sum _{i=1}^{N}\Delta {t}_{i}{\varphi }_{i}∕\sum _{i=1}^{N}\Delta {t}_{i}^{2} $$ 式中:
$ P{h}_{-}rat\mathrm{e} $ ——线性相位速率;$ \Delta {t}_{i} $ ——干涉图的时间基线;${\varphi }_{i}$ ——纠缠的差分干涉相位。Stacking技术具体流程如图1。
(1)选取主影像,对于多时相InSAR数据,选取某一景SAR影像作为主影像,其他影像配准到主影像雷达坐标系下。
(2)在SLC影像中添加精密轨道数据辅助配准。
(3)选取干涉像对,以一定时间间隔作为阈值,生成时间、空间基线分布图,时间间隔小于阈值的影像按时间先后进行两两差分干涉处理。
(4)将DEM与主影像配准,通过计算生成DEM坐标系与影像坐标系的查找表,利用多项式拟合算法,将DEM转换至主影像坐标系下。
(5)计算干涉相位和相干系数,对已配准的影像进行前置滤波,逐像元共轭相乘计算生成干涉图,依据相干系数公式,选择窗体大小,逐像元计算生成相干系数图。
(6)差分干涉计算,依据空间基线参数和地球椭球体参数,计算平地相位,利用配准后DEM计算地形相位,从干涉相位中去除平地相位和地形相位,逐像元计算差分干涉图,并对差分干涉图进行滤波降噪,逐像元计算生成相干系数图,对滤波后的的差分干涉图进行相位解缠。
(7)识别去除差分干涉图中的趋势性条纹。
(8)大气延迟相位校正,选择通用型卫星雷达改正数据(GACOS)校正对流层延迟。
(9)相位叠加处理(Stacking),选取较为理想的相位解缠图,解缠结果组合基于加权叠加估算线性形变速率处理。
(10)地理编码,利用DEM坐标系与影像坐标系的转换查找表,将形变速率图转换到地理坐标系下。
(11)剔除无效区域,综合DEM、SAR相干图和强度图、光学影像等数据剔除水域、阴影、叠掩等无效观测信息。
(12)生成地表形变结果,将地表形变结果分别生成shapefile格式的矢量点文件和geotiff格式的栅格文件,并根据地表形变量值分级设色显示。
根据上述Stacking技术原理、估算公式以及数据处理流程,得到研究区部分InSAR处理成果(图2、图3)。
3. 滑坡隐患识别
3.1 光学遥感解译标志
地质灾害隐患解译标志是指能帮助识别地质灾害类型、范围、性质、变形特征等各类要素的影像特征。研究区滑坡主要分为两大类,分别为潜在滑坡隐患点和古(老)滑坡复活隐患点。
3.1.1 潜在滑坡遥感解译标志
研究区潜在滑坡体地形破碎,起伏不平,斜坡表面有不均匀陷落的斜坡平台;滑坡后缘及两侧可见裂缝;滑坡地表湿地泉水发育,呈斑点或点状深色调;滑坡体上无植被分布或植被与周围有显著区别;滑坡各部分要素在影像上清晰可见(图4)。
3.1.2 古(老)滑坡遥感解译标志
研究区古(老)滑坡体一般具有较高的滑坡后壁,滑坡体上植被较发育;滑坡体一般规模较大;滑坡体两侧冲沟较发育,多出现双沟同源;滑坡平台上通常为耕地和居民点(图5)。
影像上白色、灰白色,崩塌壁呈不规则状,堆积物结构粗糙。崩塌常发生在上部为中厚层状岩体下部为较软岩体内,坡体坡角大于45°且高差较大,或坡体成孤立山嘴,或凹形陡坡地段,尤其是深切割的峡谷区,各江河的陡峻边岸。
3.2 光学遥感识别
研究区范围较大,北面金沙江、澜沧江、怒江三江并流,山高坡陡,河谷深切,植被覆盖率中等,为高山峡谷区域,属于地质灾害高易发区,灾害体一般规模较大,要素特征清晰;南面地形高差相对较小,植被覆盖率极高,为中、低山区域,属于地质灾害中、低易发区,灾害体一般规模较小,要素特征不明显。可根据南北区不同的滑坡发育特征进行潜在滑坡或老滑坡隐患识别。
3.2.1 北面高山峡谷区识别
高山峡谷区岸坡高陡,大规模的古(老)滑坡堆积体坡度相对较缓,地形上与两侧正常斜坡差异明显;高山峡谷区岩质滑坡较多,其中顺向中缓倾斜坡容易发生顺层岩质滑坡在光学影像上有平整的滑面;岩质滑坡规模较大,多为大型以上,后壁通常高陡,两侧边界和后壁基岩出露;古(老)滑坡平台上通常为耕地和居民点;滑坡体上通常有冲沟发育;滑坡两侧的自然沟切割较深,多出现双沟同源;滑坡平台宽大且夷平。
3.2.2 南面中、低山区识别
中、低山区河谷相对宽阔,地区植被覆盖率极高,滑坡隐患点一般以中小型为主,大型以上滑坡相对较少;低山区土质滑坡相对较多,平面形态以半圆形、舌形为主;滑坡后缘有明显的下错台坎或拉裂缝;南面植被覆盖极好,因此潜在滑坡在色调上与周围差异明显;南面以土质滑坡为主,斜坡表部通常为第四系松散堆积层沿基覆界面发生滑动,斜坡中下部的人工切坡为主要诱发因素之一,可通过人工开挖边坡等要素进行识别[15]。
3.3 InSAR识别标志
依据Sentinel-1A和ALOS-2两种数据的InSAR处理成果,对研究区潜在滑坡或老滑坡的解译识别主要采用目视解译和人工交互式解译相结合的方式从InSAR干涉形变图的图斑颜色、分布密度等方面对多期次InSAR监测成果综合识别解译。
3.3.1 典型潜在滑坡识别标志
研究区潜在滑坡的InSAR形变干涉图主要存在以下两种典型标志。当潜在滑坡形变量较大时,InSAR形变干涉图多呈现煎蛋状环形形变区,环形InSAR形变区由外向内形变量逐渐增大,InSAR形变区图斑颜色逐渐由环形外圈向中心过渡(图6);当潜在滑坡形变量较小时,InSAR形变干涉图上形变数据异常导致图斑颜色变化较为单一,与周围区域差异明显(图7)。潜在滑坡InSAR形变区范围一般即为潜在滑坡边界,因此潜在滑坡InSAR识别区平面形态多呈矩形、舌型、半圆形等。
3.3.2 典型古(老)滑坡识别标志
古滑坡体的局部复活一般形变量相对较小,InSAR形变干涉图上形变数据异常导致图斑颜色变化较为单一,与周边区域颜色差异明显。局部复活形变区的面积范围一般有限,图斑颜色异常的区域并未覆盖整个古滑坡堆积体(图8);当古滑坡体整体复活时,由于滑坡规模较大,一般而言斜坡表部形变量也相对较大,InSAR形变干涉图上形变数据异常导致图斑颜色变化较为丰富。通常整体复活形变面积范围较大,图斑颜色异常的区域能够覆盖大部分(乃至整个)的古滑坡堆积体,环形中心图斑颜色差异最为显著的区域则多为古滑坡体变形最为强烈的区域(图9)。
3.3.3 “无效变形区”InSAR特征
(1)地表沉降导致“无效变形区”
研究区内部分区域属于河谷地貌,地形平缓,坡度处于10°以内,根据潜在滑坡或老滑坡的形成条件,该区域不具备形成潜在滑坡或老滑坡的临空条件,InSAR 形变多由地表沉降、人类工程活动等原因导致,且形变量相对偏小,切关系,结合光学影像分析,该区域属于“无效形变区”(图10)。
(2)跨越斜坡单元导致“无效变形区”
研究区内部分区域属于高山峡谷地貌,地势陡峭,然而InSAR形变区由多个斜坡单元构成,连续跨越多条冲沟、山脊连片分布,斜坡坡向各异,该区域不具备构成单一潜在滑坡或老滑坡的条件,整体大面积InSAR形变也多由植被生长差异、大气延迟干扰等原因导致,结合光学影像分析,该区域属于“无效形变区”(图11)。
(3)数据误差导致“无效变形区”
研究区内部分区域分布的环形疑似形变区以及条带状疑似形变区均未见明显形变特征,不属于潜在滑坡或老滑坡范畴,InSAR形变干涉图异常多由数据处理误差等原因导致,结合光学影像分析,该区域属于“无效形变区”(图12)。
3.4 光学遥感影像与InSAR处理结果的综合分析
为了分析与验证InSAR处理结果的可靠性,选取2处已验证的滑坡点的InSAR处理结果与光学影像进行对比分析。
3.4.1 古(老)滑坡对比分析
从光学影像上看,LCGM-005滑坡区近似舌形地貌,滑坡体边界明显,滑坡区地貌类型属于构造剥蚀中起伏低中山地貌;滑坡距断裂约 765m;滑坡左侧以冲沟为界,右侧以地形转折处为界,前缘以地冲沟为界;滑坡平面形态呈不规则形,前缘剪出口位于一冲沟处,滑坡整体长1486 m,宽348 m,面积52×104 m2,冠趾相对高差510 m,坡向60 °。滑坡位于斜坡上部,剖面呈凹形,平均坡度23 °,见图13(a)。通过光学影像,依据平面和剖面的地形地貌,可以初步判定该处存在滑坡的可能。
LCGM-005滑坡点的InSAR处理结果显示:该区域图斑颜色异常的区域能够覆盖大部分滑坡堆积体,且环形中心图斑颜色差异最为显著,符合古老滑坡体局部乃至整体复活的InSAR干涉图形变特征,见图13(b)。因此,可对该滑坡点的存在情况做出进一步确认。
3.4.2 潜在滑坡对比分析
从光学影像上看,LCFQ-010滑坡平面形态近似矩形,左侧及前缘冲沟发育,右侧以地形转折处为界,后缘以地势陡缓交界处为界;滑坡整体长590 m,宽420 m,面积24×104 m2,冠趾相对高差420 m,坡向280 °,平均坡度40 °,剖面呈凹形,见图14(a)。综上所述,通过光学影像,依据平面和剖面的地形地貌,可以初步判定该处存在滑坡的可能。
LCFQ-010滑坡点的InSAR处理结果显示:该区域图斑颜色异常的区域形态规则且颜色单一,但与周围区域差异明显并分布于滑坡区右部,符合形变量较小的潜在滑坡的InSAR干涉图形变特征,见图14(b)。因此,也可对该潜在滑坡点的存在情况做出进一步确认。
3.5 潜在滑坡与老滑坡隐患综合识别
不同的遥感技术各有其优缺点,采用多种遥感技术方法开展潜在滑坡或老滑坡识别可以充分发挥不同方法的优点,互为补充。根据上文建立的不同解译标志,总结出如下适用于研究区的滑坡综合识别方法。
(1)根据不同地形地貌条件,对研究区不同区域分别进行光学遥感识别,并将有光学变形特征的隐患点和无光学变形特征的隐患点区分开来。
(2)将InSAR处理的结果与光学遥感识别结果进行综合分析,区别潜在滑坡、老滑坡和无效变形区的影像特征。
(3)对于既有光学变形特征,同时又具有InSAR地表形变特征的隐患点可直接确定,野外查证只需要进一步复核灾害的边界和不同部位的变形特征。
(4)对于具有InSAR地表形变但无光学变形特征的点,进一步划分为两种情况:
一是光学数据判识为古(老)滑坡,但在光学影像上无法识别出变形,而InSAR地表形变明显,这一类隐患点极有可能是处于变形的初期,变形量小,通过光学遥感无法识别,但可以通过InSAR对微变形的观测进行识别。在室内遥感综合识别的基础上,通过野外验证进一步确定是否存在变形。
二是光学数据判识为正常斜坡,但InSAR地表形变明显,这种情况需要结合孕灾地质背景条件进行综合判识。如InSAR地表形变区无形成地质灾害的孕灾环境条件,且变形区位于平坦的阶地、堆积扇、近水平的厚度岩质斜坡、完整平缓的岩浆岩斜坡,此时可以排除该地表形变是由斜坡地质灾害引起的。如InSAR地表形变区具有形成地质灾害的孕灾条件,且变形区位于高陡的第四系堆积体的前缘、高陡且破碎的基岩斜坡、后部或两侧边缘有断层通过,这一类隐患点则需要进一步通过野外验证确认。
4. 地质灾害隐患野外调查
根据监测对象的不同,野外调查可分为两类。第一,不考虑地质灾害要素条件,针对斜坡变形特征与InSAR监测结果吻合程度进行复核,包括形变的有无,形变的程度等;第二,考虑地质灾害要素条件,除上述内容外,还包括斜坡临空条件、物质组成及威胁对象等孕灾地质环境条件,后者是形成地质灾害的必要条件,直接影响滑坡与潜在滑坡识别的有效性。考虑到滑坡与潜在滑坡InSAR监测识别的准确率和有效性,野外调查内容应包括“变形特征”和“孕灾地质环境条件”两个方面。其中“变形特征”是野外调查内容的核心,一般来说,斜坡如果未见明显变形特征,可不进行孕灾地质环境条件调查工作。同时,只具有“变形特征”却不具备“孕灾地质环境条件”的斜坡,对于潜在滑坡早期识别来说,没有实际意义。变形特征主要表现在以下几个方面,斜坡表部裂缝的类型、数量、规模性质等;斜坡表部固定建筑物如房屋墙面、院坝及地基开裂破坏情况;斜坡表部线性工程如道路、水渠拉裂变形情况;斜坡下坐程度、表部溜滑或局部滑动变形情况等;斜坡表部植被破坏情况;斜坡已有工程如挡土墙、抗滑桩、防护网等的运行及破坏情况[14]。孕灾地质环境条件主要是指形成滑坡的凌空条件、物质组成及激发因素。临空条件包括斜坡高度、坡度、走向、平面形态等;物质组成是滑坡形成的载体,包括斜坡出露的地层岩性、产状、斜坡结构等;激发因素主要指周边人类工程、经济活动,包括修建房屋、公路、土地整理等[15]。
本次研究,共计调查验证潜在滑坡或老滑坡隐患点352处,其中,成功验证284,失败68处,总体识别成功率为80.6%。
5. 结论
(1)基于本文方法的滑坡识别更适用于中型及以上滑坡的识别。文中列举的滑坡识别成功实例均为中型及以上滑坡,无论是在光学影像上还是InSAR结果中都有良好的体现,这是由于部分小型滑坡规模过小,在图上只有像素点般大小,难以直观体现。
(2)高山峡谷地区地势复杂,斜坡单元密布,最易导致在InSAR图像上呈现无效变形区,该区域的滑坡识别需要以光学解译为主。
(3)单独基于光学遥感或者InSAR技术的滑坡识别方法较为片面,部分地区植被覆盖差异高,导致失相干,人类活动区域的部分变形也不是滑坡导致的,潜在滑坡依靠光学影像更是难以判别,为了避免误判,需两者结合,互为补充。
(4)基于本文方法的滑坡识别充分利用了遥感技术进行地质灾害调查,弥补了地面调查的不足,但考虑到误判因素,需要进行部分野外调查验证准确率。
-
表 1 锚索监测数据[19]
Table 1 Monitoring data of anchor cables[19]
编号 锁定锚固力
/kN最大锚固力
/kN最大增长率
/%稳定值
/kN339# 482 605 25.52 600 345# 638 902 41.38 620 357# 630 920 46.03 600 358# 805 1110 37.89 950 -
[1] 薛翊国, 孔凡猛, 杨为民, 等. 川藏铁路沿线主要不良地质条件与工程地质问题[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(3):445 − 468. [XUE Yiguo, KONG Fanmeng, YANG Weimin, et al. Main unfavorable geological conditions and engineering geological problems along Sichuan-Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(3):445 − 468. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 梁波, 王家东, 严松宏, 等. 多年冻土地区L型挡土墙土压力(冻胀力)的分析与试验[J]. 冰川冻土,2002,24(5):628 − 633. [LIANG Bo, WANG Jiadong, YAN Songhong, et al. Experiment and analysis of the earth pressure (frost heaving forces) on L-type retaining wall in permafrost regions[J]. Journal of Glaciolgy and Geocryology,2002,24(5):628 − 633. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2002.05.027 [3] 梁波, 王家东, 葛建军, 等. 青藏铁路L型挡土墙的土压力实测与分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2004,26(5):627 − 631. [LIANG Bo, WANG Jiadong, GE Jianjun, et al. Testing and analysis of earth pressure about L type retaining wall in Qinghai-Tibet railway[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2004,26(5):627 − 631. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2004.05.011 [4] 汪恩良, 钟华, 孙景路, 等. 加筋土挡墙冻融试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2010,32(2):265 − 270. [WANG Enliang, ZHONG Hua, SUN Jinglu, et al. Experimental study on reinforced retaining walls suffering freeze-thaw cycling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2010,32(2):265 − 270. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 赵坚, 那文杰, 曹顺星. 季节冻土区挡土墙抗冻结构设计方法[J]. 黑龙江交通科技,2001,24(5):14 − 16. [ZHAO Jian, NA Wenjie, CAO Shunxing. Design of antifreezing structure for retaining walls in seasonal frost regions[J]. Communicatios Science and Technology Heilongjiang,2001,24(5):14 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3383.2001.05.008 [6] ZHANG Y, DONG J H, DONG X G, et al. Analysis of freezing and thawing of slope improved by soil nailing structure in seasonal frozen soil region[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2017,38(2):574 − 582.
[7] 赵延凯, 彭然, 周加伟, 等. 季节性冻土深基坑支护技术研究[J]. 建筑结构,2011,41(7):119 − 122. [ZHAO Yankai, PENG Ran, ZHOU Jiawei, et al. Investigation on technology of retaining and protection for seasonal frozen soil deep foundation pit[J]. Building Structure,2011,41(7):119 − 122. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 郭红仙, 宋二祥, 陈肇元. 季节冻土对土钉支护的影响[J]. 工程勘察,2006,34(2):1 − 6. [GUO Hongxian, SONG Erxiang, CHEN Zhaoyuan. Soil nailing under the influence of the seasonal frozen soil[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Investigation & Surveying,2006,34(2):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] STOCKER M F, RIEDINGER G. The bearing behavior of nailed retaining structures[C]// Design and Performance of Earth Retaining Structures: Proceedings of a Conference Sponsored by the Geotechnical Engineering Division of the American Society of Civil Engineers. New York, June 18-21, 1990, edited by Philip C. Lambe and Lawrence A. Hansen: 612-628.
[10] KINGSBURY D W, SANDFORD T C, HUMPHREY D N. Soil nail forces caused by frost[J]. Transportation Research Record:Journal of the Transportation Research Board,2002,1808(1):38 − 46. DOI: 10.3141/1808-05
[11] LONG N T, T LIVET M, BOUTONNCT, et al. Repair of a reinforced earth wall[C]//Proc. Interactional Conference on Case Histories in Geotechnical Engineering, University of Missouri-Rolla, 1984: 335-346.
[12] 李宗龙. 川西高原川藏交通廊道季节性冻土分布规律及处置措施[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013. LI Zonglong. Distribution regularity and disposal measures of seasonal frozen soil of Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor in west Sichuan plateau[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 中华人民共和国交通运输部. 季节性冻土地区公路设计与施工技术规范: JTG/T D31-06—2017[S]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2017. Ministry of Transport of the People's Republic of China. Technical Specifications for Design and Construction of Highway in seasonal Frozen Soil Region: JTG_T D31-06-2017[S]. Beijing: People's Communications Publishing Co. Ltd., 2017. (in Chinese)
[14] 张誉,蒋利学,等. 混凝土结构耐久性概论[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2003:105-117. ZHANG Yu,JIANG Lixue, et al. Durability of concrete structure [M]. Shanghai:Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2003:105−117. (in Chinese)
[15] 董旭光, 董建华, 何天虎, 等. 多年冻土边坡的水热力耦合分析及软件开发[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):77 − 84. [DONG Xuguang,DONG Jianhua,HE Tianhu,et al. Coupling analysis and software development of moisture-heat-stressfields of permafrost slope[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):77 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 张遂, 匡航, 靳占英, 等. 高含水量冻粉黏土应力-应变曲线特性的试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):116 − 124. [ZHANG Sui, KUANG Hang, JIN Zhanying, et al. An experimental study of the stress-strain characteristics of frozen silty clay with high moisture content[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):116 − 124. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 齐子萱, 周金龙, 季彦桢, 等. 西北内陆盆地降水入渗补给季节性变化—以新疆昌吉地下水均衡试验场为例[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(5):12 − 20. [QI Zixuan, ZHOU Jinlong, JI Yanzhen,et al. Seasonal variationin recharge of infiltration from precipitation for the inland basins of northwestern China: taking the Changji groundwater balance test station in Xinjiang as an example[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(5):12 − 20. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 水工建筑物抗冰冻设计规范: GB/T 50662—2011[S]. 北京: 中国计划出版社, 2012. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of hydraulic structures against ice and freezing action: GB/T 50662—2011[S]. Beijing: China Planning Press, 2012. (in Chinese)
[19] 何伟. 西藏自治区国道318线田妥镇滑坡机理及防治技术研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆交通大学, 2012. HE Wei. Research of the Tibet autonomous region national Highway 318 Line of the landslide mechanism and the field prevention and control technology[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Jiaotong University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(15)
1. 王勇,邢振涛,李锁,闫勇,司甜. 基于SBAS-InSAR和光学遥感的天津市北部山区潜在滑坡识别研究. 灾害学. 2025(01): 30-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 毛正君,李欢,石硕杰,孙婕文,仲佳鑫,于海泳. 面向对象的无人机遥感影像区域滑坡承灾体信息提取研究. 工程地质学报. 2025(01): 171-185 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 冯谕,曾怀恩,涂鹏飞. 遗传算法下的滑坡蠕滑位移预测模型研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 82-91 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 杨豹,赵瑞志,王海波,李晓光,吕钊,赵阳,王梦云. 遥感技术对地质灾害早期识别和动态监测——以昌波乡至羊拉乡段为例. 科学技术与工程. 2024(05): 1823-1836 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李恒丽,陈克全. 云南维西县新塘房滑坡形成条件及防治措施探讨. 云南地质. 2024(01): 115-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 毛正君,于海泳,梁伟,马旭,仲佳鑫,高广胜,石硕杰,田彦山. 基于无人机倾斜摄影测量三维建模的区域黄土滑坡识别及特征分析. 中国地质. 2024(02): 561-576 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 薛玉芹,滕秀华,孟大鹏. 遥感测量在采矿塌陷地监测及矿山地质灾害治理方面的应用. 世界有色金属. 2024(03): 157-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 党杰,杨亮,段方情,范宣梅. 贵州晴隆红寨大型古滑坡复活变形特征及成因分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(04): 25-35 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 孙成永. InSAR技术在河南信阳新县地质灾害风险调查中的应用. 城市地质. 2024(03): 383-389 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 孙琪皓,刘桂卫,王飞,张璇钰,王衍汇. 铁路地质灾害早期识别与监测预警技术及应用研究. 铁道标准设计. 2024(09): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 钱雨扬,孔令利,余洲,杨国兴,朋仁锋. 基于InSAR-光学影像的白鹤滩库区地质灾害隐患识别. 人民长江. 2024(S2): 107-112+120 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 韩民赛,刘岁海,罗明,蒋韬,孙大振. 滑坡预测预报研究与进展. 地质装备. 2023(01): 22-26+39 .  百度学术
百度学术
13. 朱伟伟. 遥感技术在地质灾害监测与管理中的应用. 安徽地质. 2023(01): 75-77+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
14. 黎浩良,杨莹辉,许强,宋家苇,李鹏飞,陈强,姚智博. 高寒山区地质灾害季节分区InSAR早期识别研究——以东构造结地区为例. 工程地质学报. 2023(03): 780-795 .  百度学术
百度学术
15. 李芳军. 黄土滑坡地质灾害监测预警方法与技术探讨. 冶金管理. 2023(15): 82-84 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(16)




 下载:
下载:




















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS