Disaster mechanism of post-fire debris flow in Huayanzi gully, Mianning County, Sichuan Province
-
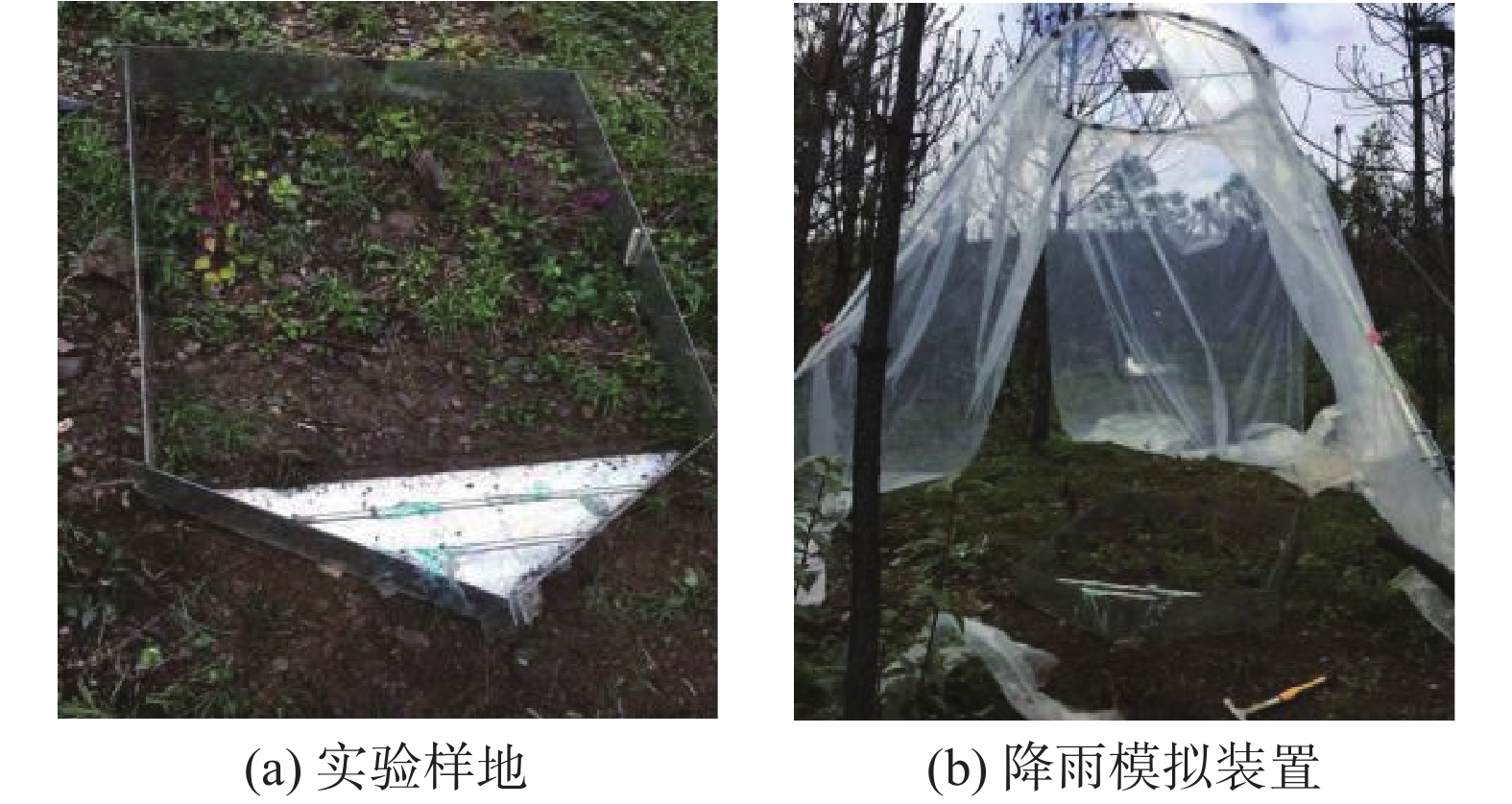
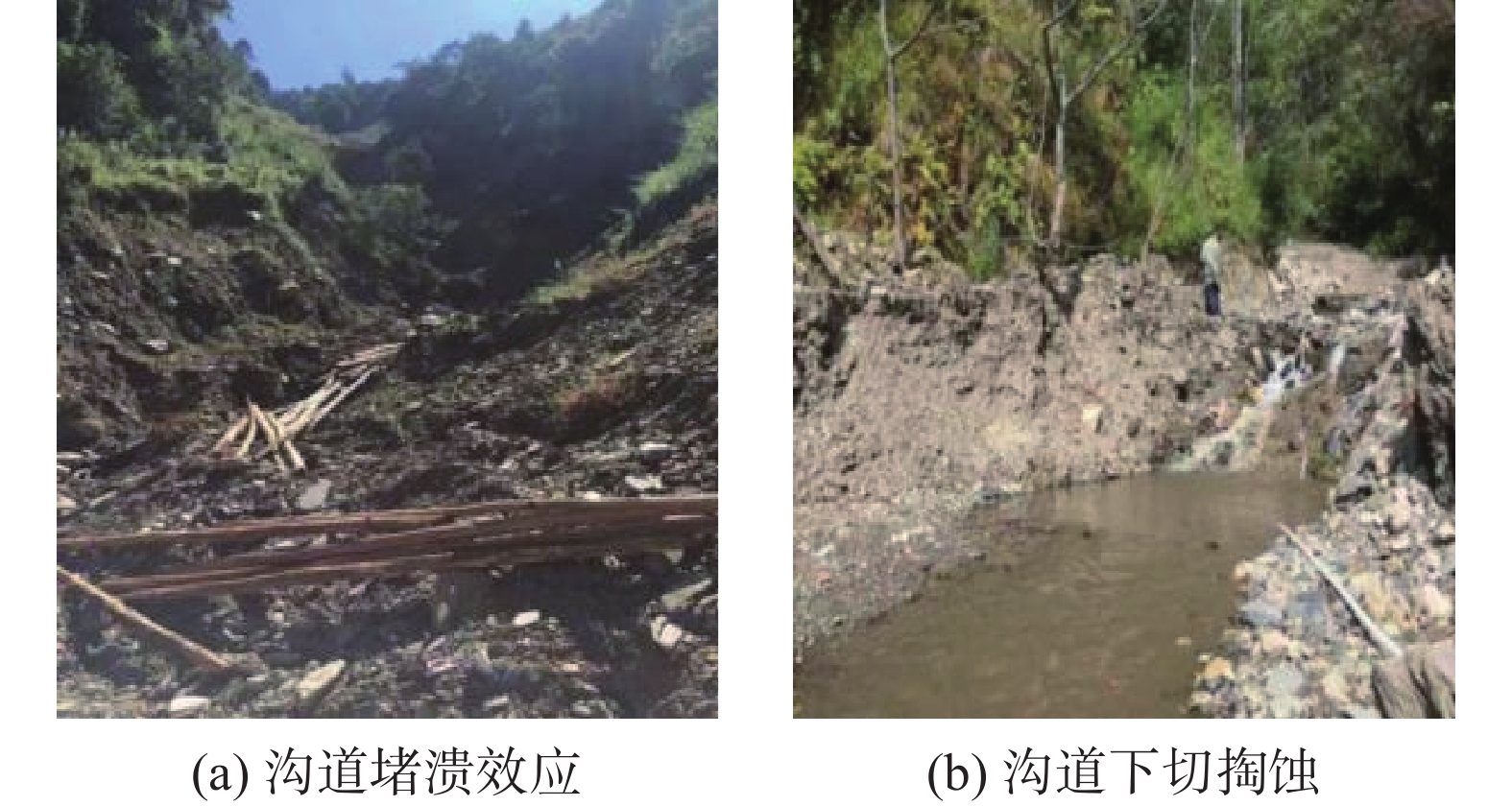
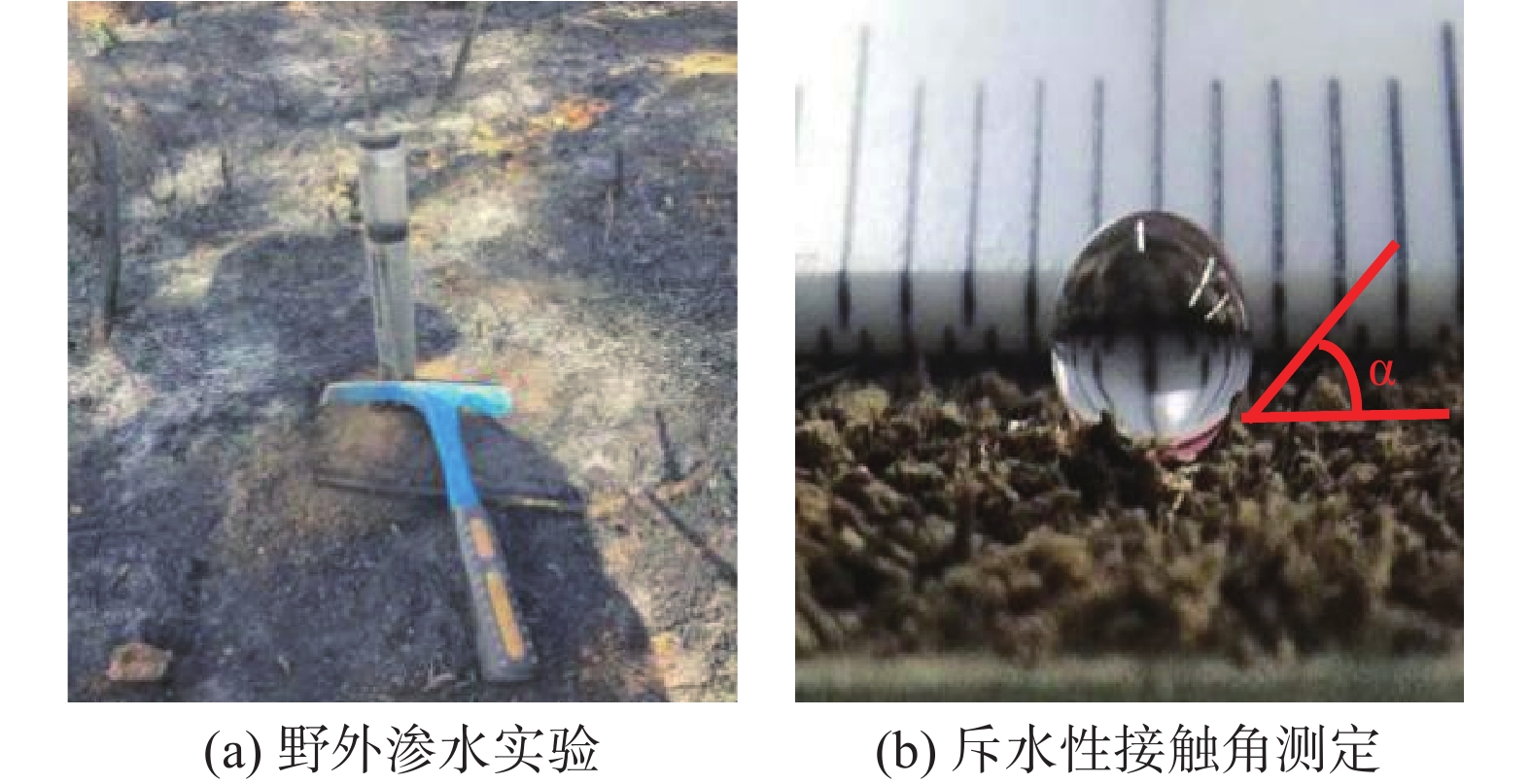
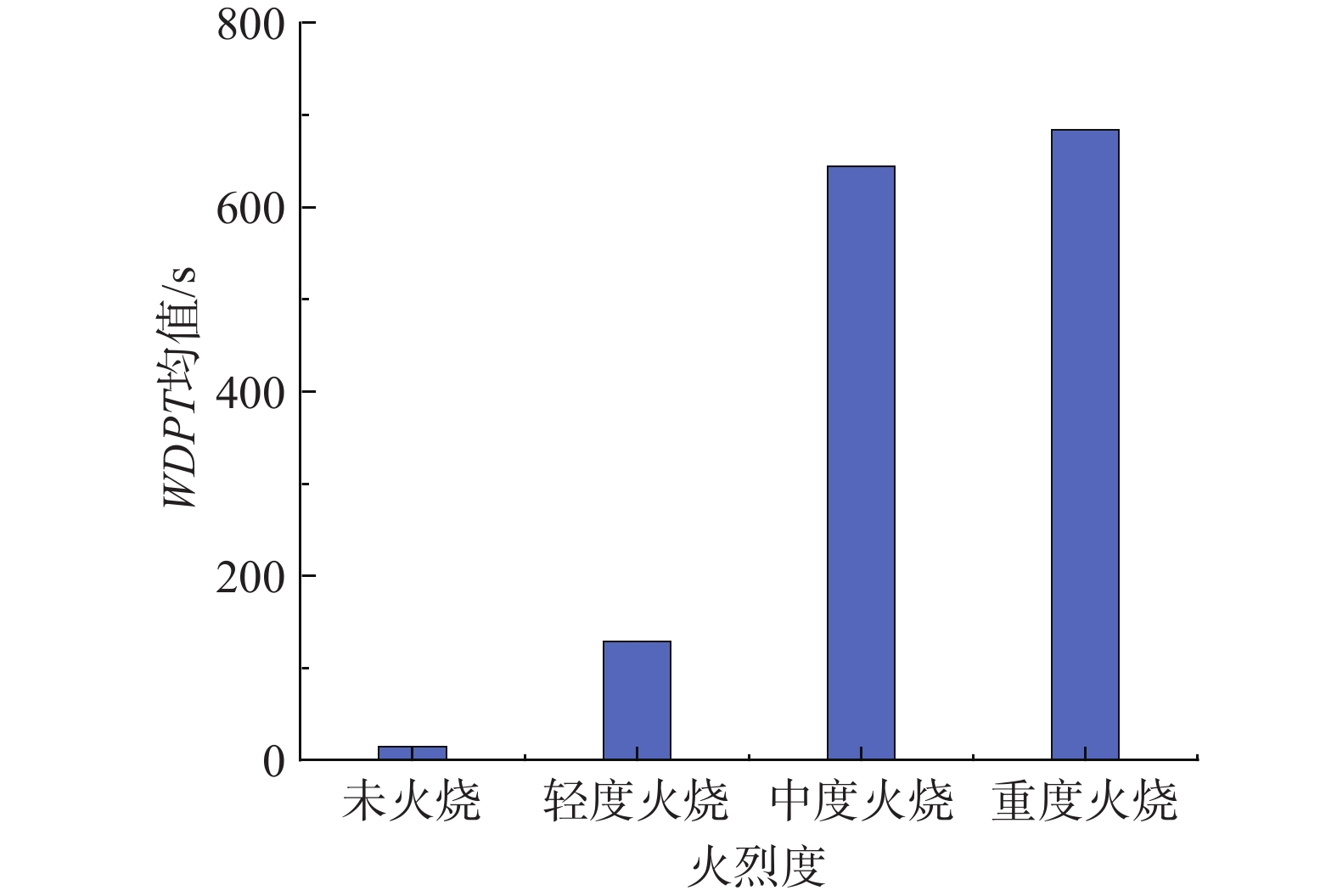
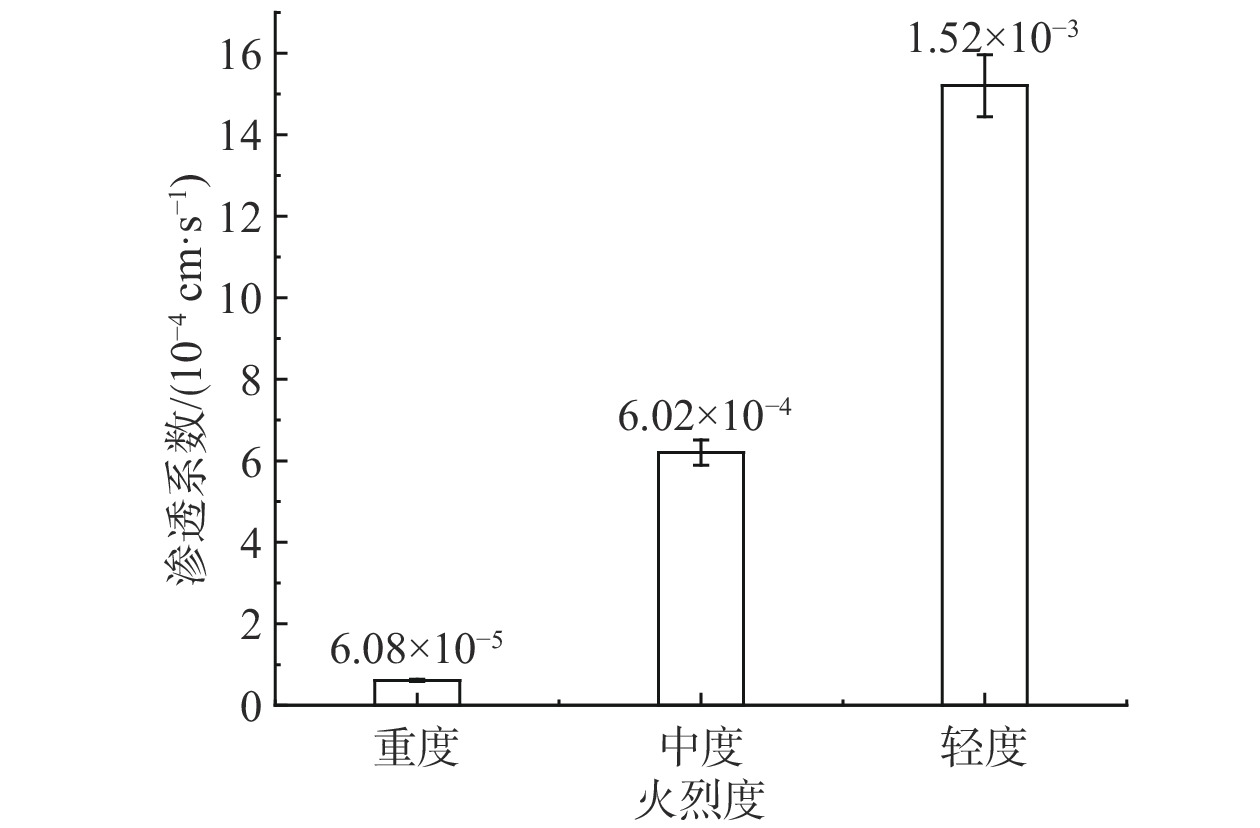
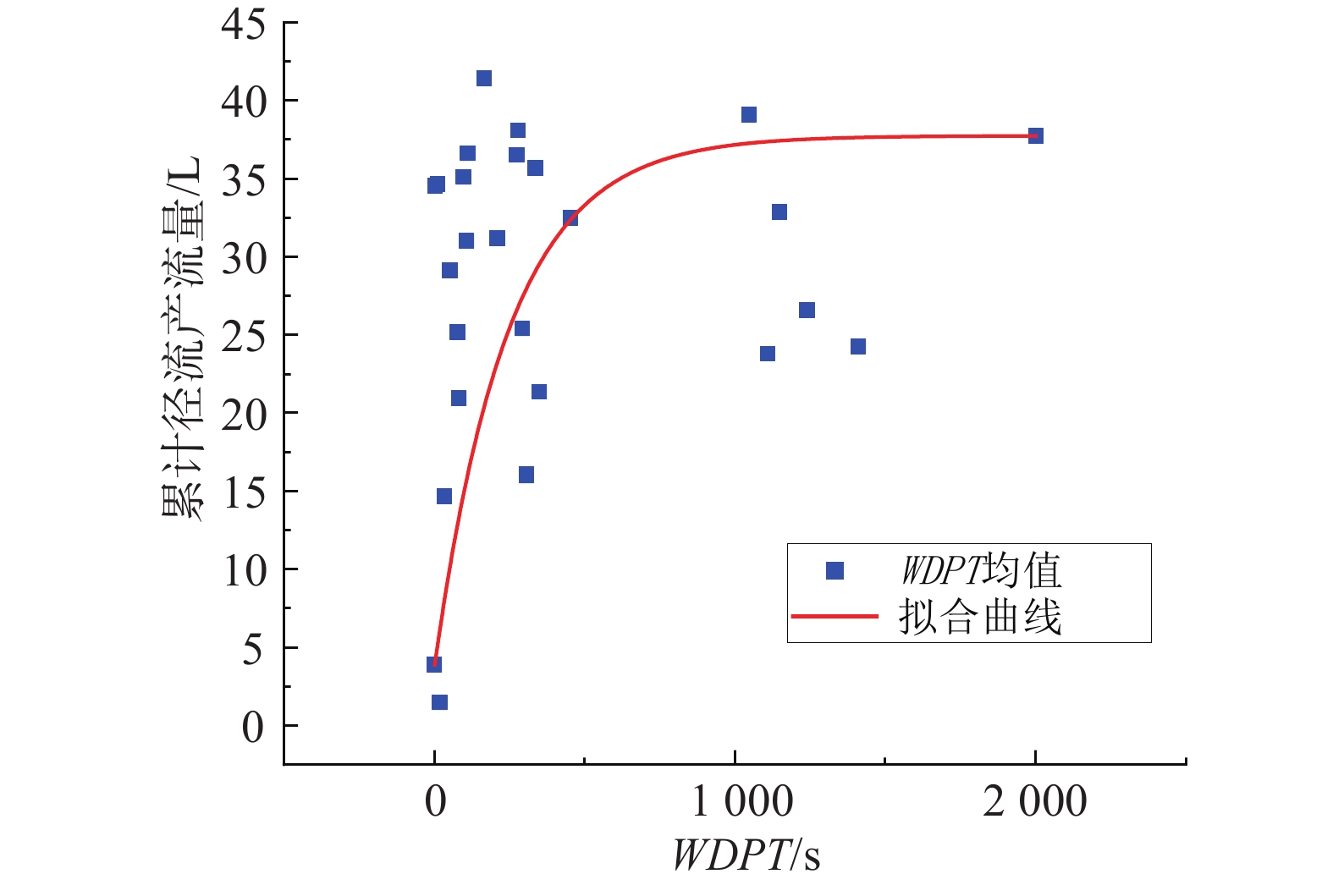
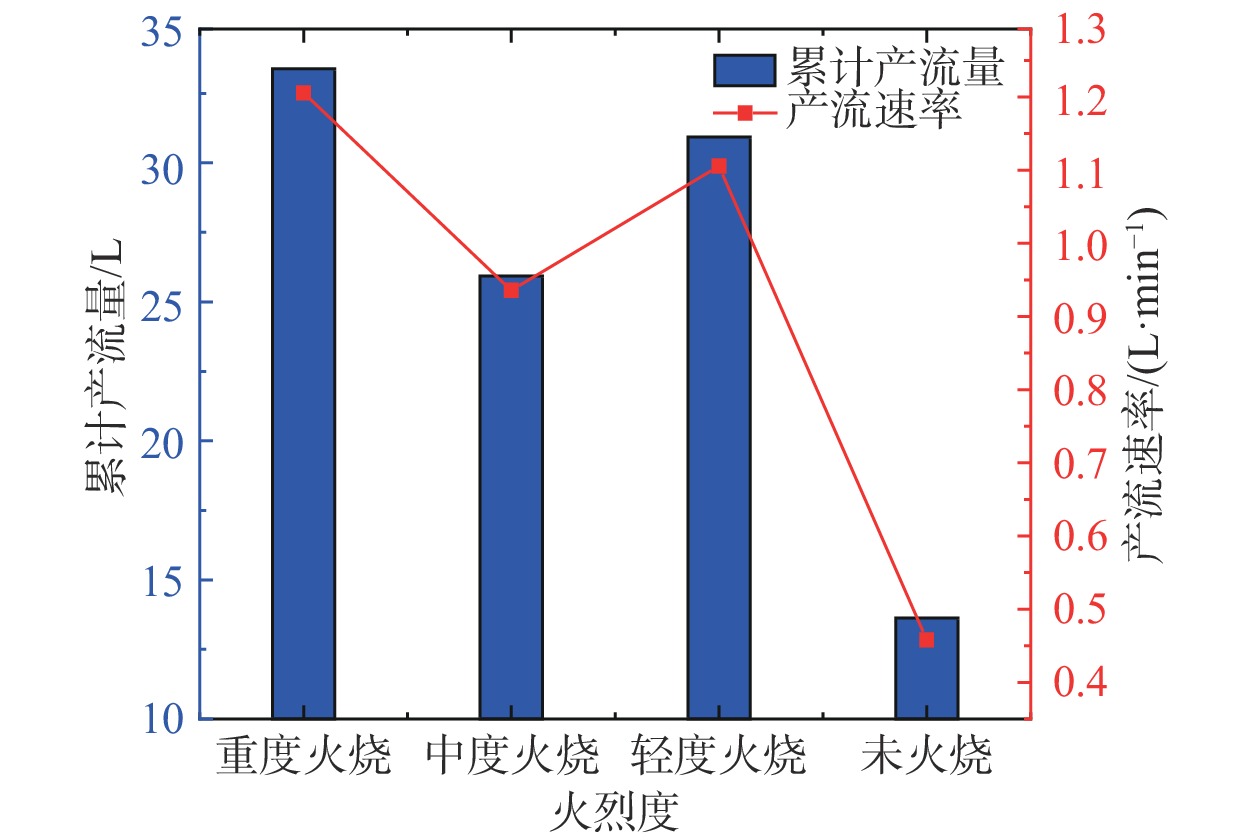
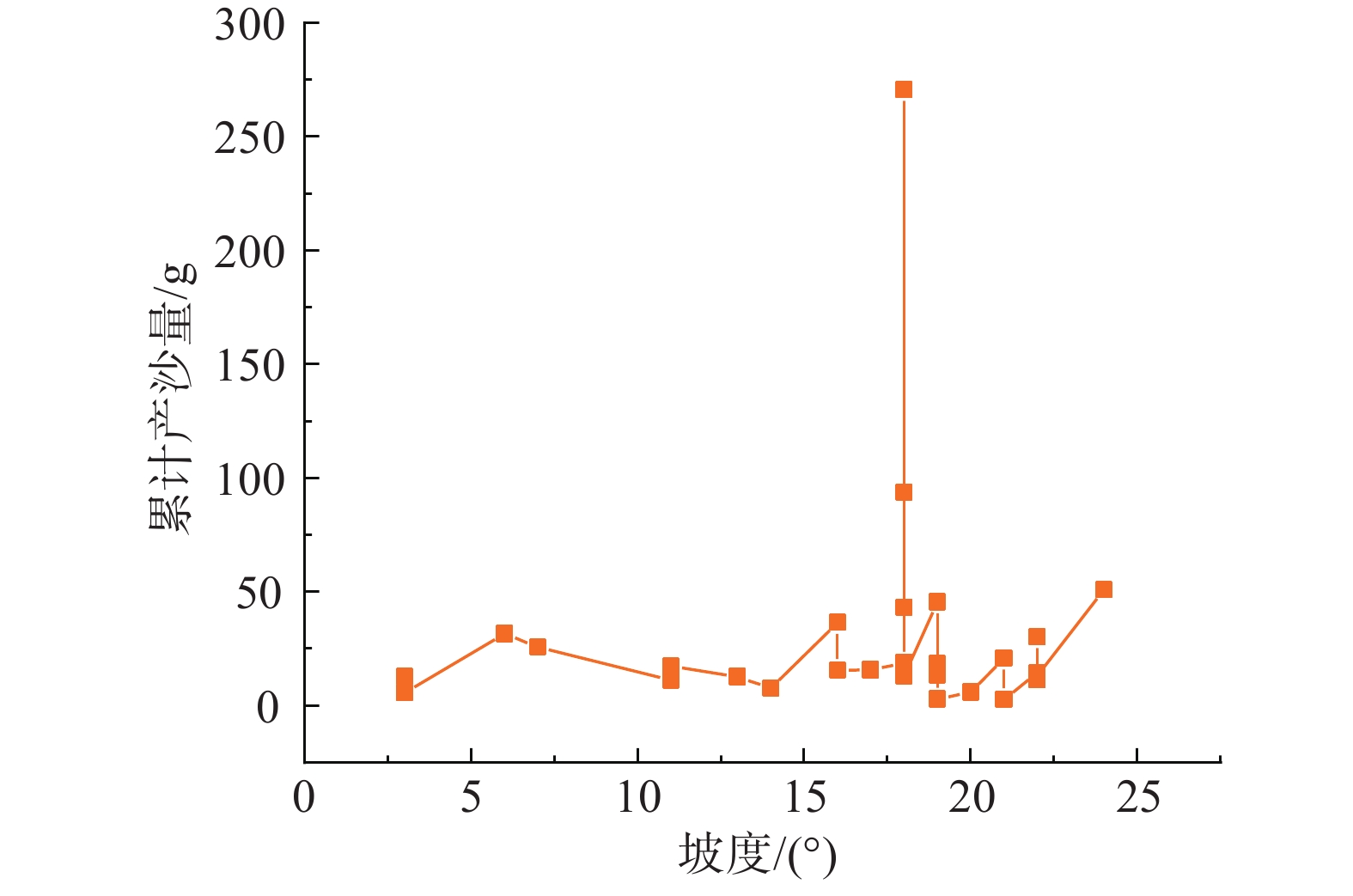
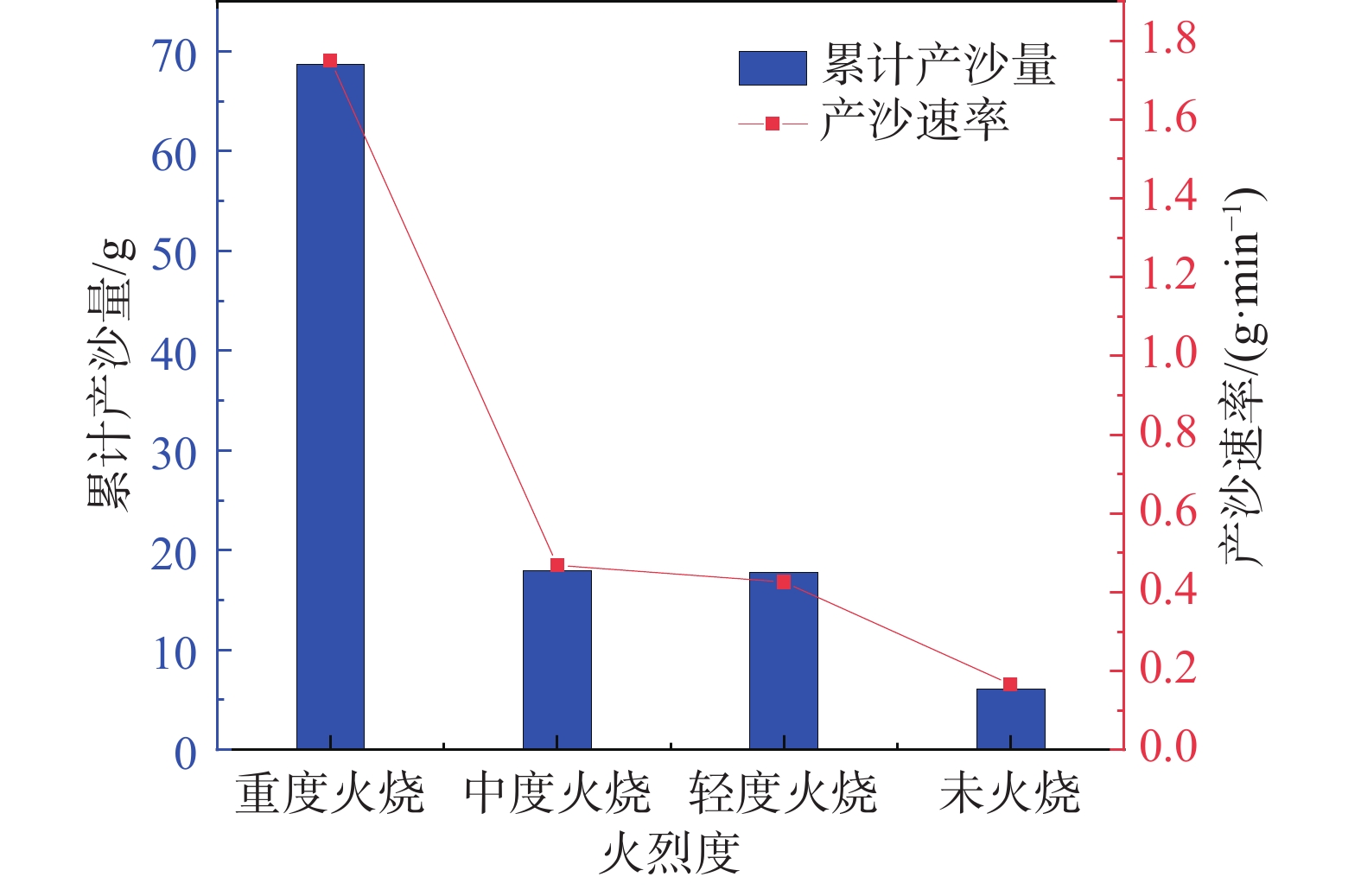
摘要: 以四川省冕宁县腊窝乡华岩子沟2019年7月发生的火后泥石流为典型案例,通过对火烧迹地现场地质勘察、降雨模拟试验研究了与火后泥石流形成相关的地形地貌、火行为分布、松散物源规模、产流产沙特征以及相应的灰烬层、斥水性、渗透性等相关试验。结果表明:(1)火烧迹地的斥水性强度越强,径流产流量越大;(2)严重火烧区的产沙量明显高于中度和轻度火烧区;(3)火烧迹地的斥水性与火烈度大致呈正相关,而渗透性恰好与之相反。研究揭示了火后泥石流的演变过程,为火后泥石流的防治和预警提供了理论依据。Abstract: This paper studied the characteristics of geomorphology, fire behavior, unconsolidated source material volume, runoff and sediment production related to post-fire debris flow formations, field investigation in the burned area and rainfall simulation experiment were adopted to study the post-fire debris flow in Huayanzi gully, Mianning County, Sichuan Province occurred on 4 July 2019. The associated ash layer, water repellency and permeability experiments were also conducted. The results suggest that (1) the runoff charge shows a positive correlation with water repellency in burned area. (2) the sediment yields in severely burned area are conspicuously larger than that in moderate and slight burned areas. (3) the water repellency in burned area is approximately positively correlated with fire severity, while the permeability presents the negative correlation. This study revealed the evolution process of post-fire debris flow, and provided theoretical basis for the prevention and early warning of post-fire debris flows.
-
0. 引言
滑坡是世界上分布广、发生频率高、造成危害大的一种地质灾害。如何对边坡的稳定性进行合理的评价以更好地预警,显得尤为重要。云模型是由李德毅等[1]提出来的一种模型,该模型在结合概率论和模糊数学理论的基础上,以样本的随机度来描述概念中的随机性和模糊性。
近年来,云模型在水文[2]、气象[3]、医疗[4]、地质灾害[5]以及隧道管理[6]等各个方面得到了较好的应用。部分学者们也对云模型在岩质边坡稳定性评价中的应用开展了较为深入的研究。张军等[7]选取影响边坡稳定性的11项指标,结合正向正态云模型和指标权重,计算边坡的综合隶属度。LIU等[8]提出了一种基于云模型的山区水电站复杂岩质边坡综合稳定性评价方法。该方法应用隶属度云模型分析每个排序因子以生成云隶属度,并将获得的云隶属度与专家给出的因子权重进行综合,以对岩石边坡进行综合稳定性评估。于伟等[9]建立了包含指标层、因子层和状态层的风险评价指标体系,并通过专家调查法和正向正态云发生器建立了风险评价模型,以最大综合确定度对应的风险等级作为边坡风险评价的结果。袁爱平[10]综合考虑坡高、坡度等多个影响因子,选出10项影响边坡稳定性的指标,并结合正向正态云模型和指标权重,计算岩质边坡的综合隶属度。方成杰等[11]根据勘察规范选取了14个评价指标,利用正向正态云发生器模拟实测样本值隶属于各等级的隶属度,并按照最大隶属度原则选择泥石流易发性等级。徐镇凯等[12]通过构建多因素协同驱动的高边坡稳定性评价指标方法及其等级划分标准,引入模糊熵和云模型,建立了适应于高边坡稳定性多维评价梯级云模型。杨文东等[13]选取坡高等7项因素作为评估风险集,通过正、逆向云发生器计算权系数矩阵和综合评判矩阵,利用Matlab软件生成评价云和“云滴”图来对比分析评价边坡风险等级。崔涛等[14]选取坡度、黏聚力、岩体基本质量指标、日最大降雨量等8个评价因子,利用层次分析法和熵权法综合得出评价因子的权重,并根据隶属度最大原则判定边坡稳定性级别。WANG等[15]提出了一种新颖的多维连接云模型,以解决指标的多重不确定性和分布特征,并描述了边坡稳定性分析中属于分类标准的实测指标值的随机性和模糊性。陈忠源等[16]对传统云模型的特征参数进行了改进,提出左右半云不对称的正态云模型,同时用区间值Fuzzy集来表达该云模型的隶属度。陈忠源等[17]同时引入云模型的评价方法对不同降雨工况下的建筑边坡稳定性进行评价,确定出滑坡时各参数的降雨阈值方程。
虽然学者们从各个角度对边坡的稳定性评价进行了深入的研究,取得了大量的成果,但仍然存在一些不足。目前大部分的模糊评价方法采用主观赋权法、客观赋权法以及主客观赋权法来确定各评价指标的权重。但无论是常权重还是变权重方法,最终得到的权重均为某一精确值。而实际上评价指标对边坡稳定性的影响是不确定的、模糊的,如果仅用某一精确值来表示其权重不太符合实际情况。因此本文拟使用信心指数的群决策层次分析法来构造指标变权重云模型以表示各指标的权重,并利用该方法对福建省的岩质边坡稳定性评价进行初步探讨。
1. 评价指标隶属于各稳定性级别的综合云模型的建立
评价指标的选取首先考虑一般的工程地质勘察的勘察要素,以确保各指标数据的易获取性,其次考虑行业规范要求,以保证各指标的政策针对性。为此,本文在总结前人研究的基础上,综合考虑《水电水利边坡工程地质勘察技术规程》(DLT5337—006)[18](以下简称为《边坡规程》)中的CSMR(边坡岩体质量分类标准)方法和《地质灾害调查技术要求》(DD 2019—08)[19]中的单体地质灾害(隐患)风险评估(半定性半定量打分表)等相关规范,选取坡高、坡角等10个因素作为评价指标,并将稳定性等级分为很稳定(Ⅰ)、稳定(Ⅱ)、基本稳定(Ⅲ)、不稳定(Ⅳ)、很不稳定(Ⅴ)五个等级。
《边坡规程》将h <10 m、10 m≤h<30 m、30≤h<100 m、h≥100 m划分为低、中、高以及超高边坡。因本方法将边坡的稳定性分为五个等级,故采用等间距法将10 m≤h<30 m和30≤h<100 m两个区间进行等分。最终坡高指标的各稳定性区间可划分为[0,10)、[10,20)、[20,30)、[30,65)、[65,100)。
对于坡角的各稳定性区间划分,《边坡规程》分别将α≤10°、10°<α≤30°、30°<α≤45°、45°<α≤65°、65°<α≤90°以及α>90°划分为缓坡、斜坡、陡坡、峻坡、悬坡和倒坡。故将坡角指标的各稳定性区间划分为[0,10)、[10,30)、[30,45)、[45,65)、[65,90)。
对于岩石强度、岩石质量指标RQD、结构面间距、结构面条件以及地下水条件评分值指标,《边坡规程》有相应评分标准(表1)。对于结构面方向修正评分值,其为结构面条件系数(λ)与结构面方位系数(F1、F2、F3)的乘积。当结构面条件为断层夹泥层、层面贯穿裂隙、节理时,λ分别取1.0,0.8~0.9,0.7。结构面方位系数(F1、F2、F3)的取值如表2所示。对于开挖方法系数修正值,当该边坡为自然边坡、预裂爆破、光面爆破、常规爆破、无控制爆破时,其值分别取5,10,8,0,−8。对于上述指标,本文采用等间距法进行区间划分,即以指标最高评分值为区间最大值,将各稳定性区间划分五个长度相等的区间,具体结果如表3所示。
表 1 评价指标评分标准表Table 1. Scoring standard table of evaluation indexes参数 评分标准 岩石强度 /MPa 点荷载 >10 4~10 2~4 1~2 <1不宜采用 单轴抗压强度 250~100 100~60 60~30 30~15 15~5 评分 15~10 8 5 3 2~0 岩石质量指标RQD /% 250~100 100~60 60~30 30~15 15~5 评分 20 17 13 8 3 结构面间距 /cm 200~100 100~50 50~30 30~5 <5 评分 20~15 13 10 8 5 结构面条件 粗糙度 很粗糙 粗糙 较粗糙 光滑 擦痕、镜面 评分 6 4 2 1 0 充填物 /mm 无 <5(硬) >5(硬) <5(软) >5(软) 评分 6 4 2 2 0 张开度 /mm 未张开 <0.1 0.1 ~1 1 ~5 >5 评分 6 5 4 1 0 结构面长度 /m <1 1~3 3~10 10~20 >20 评分 6 4 2 1 0 岩石风化程度 未风化 微风化 弱风化 强风化 全风化 评分 6 5 3 1 0 地下水条件 状态 干燥 湿润 潮湿 滴水 流水 透水率(Lu) <0.1 0.1~1 1~10 10~100 >100 评分 15 10 7 4 0 表 2 结构面方位系数取值Table 2. Orientation coefficient of structural plane破坏机制 情况 非常有利 有利 一般 不利 非常不利 滑动 γ1=ǀαj-αsǀ >30° 30°~20° 20°~10° 10°~5° <5° 倾倒 γ1=ǀαj−αs−180°ǀ 滑动,倾倒 F1 0.15 0.4 0.7 0.85 1 滑动 γ2=ǀβjǀ <20° 20°~30° 30°~35° 35°~45° >45° 滑动 F2 0.15 0.4 0.7 0.85 1 倾倒 F2 1 1 1 1 1 滑动 γ3=βj−βs >10° 10°~0° 0° 0°~−10° <−10° 倾倒 γ3=βj+βs <110° 110°~120° >120° —— —— 滑动,倾倒 F3 0 5 25 50 60 注:αs为边坡倾向;αj为结构面倾向;βs为边坡倾角;βj为结构面倾角。 表 3 岩质边坡稳定性评价指标及其各分级区间Table 3. Stability evaluation index of rock slope and its grade intervals评价指标 稳定性等级 很稳定 稳定 基本稳定 不稳定 很不稳定 坡高 /m(I1) [0,10) [10,20) [20,30) [30,65) [65,100) 坡角 /(°)(I2) [0,10) [10,30) [30,45) [45,65) [65,90) 岩石强度评分值(I3) [12,15) [9,12) [6,9) [3,6) [0,3) 岩石质量指标评分值(I4) [16,20) [12,16) [8,12) [4,8) [0,4) 结构面间距评分值(I5) [16,20) [12,16) [8,12) [4,8) [0,4) 结构面条件评分值(I6) [24,30) [18,24) [12,18) [6,12) [0,6) 地下水条件评分值(I7) [12,15) [9,12) [6,9) [3,6) [0,3) 结构面方向修正值(I8) [0,12) [12,24) [24,36) [36,48) [48,60) 边坡开挖方法修正值(I9) [6,10) [3,6) [0,3) [−4,0) [−8,−4) 年平均降雨量(I10) [1070,1580.6) [1580.6,1650.4) [1650.4,1720.2) [1720.2,1790) [1790,1859.8) 对于年平均降雨量指标,《地质灾害调查技术要求》将降雨对边坡的影响分为正常降雨、十年一遇、二十年一遇、五十年一遇以及百年一遇五种情况。谢晓平等[20]对福建省18个站点1957—2011年逐日气象资料进行了分析后得出, 1957—2011年期间福建省多年平均降雨量为1580.6 mm,最大降雨量为1790 mm,最低降雨量为1070 mm[20]。因此本文可近似认为五十年一遇的年降雨量为1790 mm;同时将多年平均降雨量1580.6 mm视为正常降雨的区间最大值。再根据等间距法在1580.6 mm和1790 mm之间进行等值插分出十年一遇、二十年一遇以及百年一遇的年降雨量,计算可得分别为:1650.4 mm、1720.2 mm以及1859.8 mm。则可将降雨指标的各稳定性区间进行划分,具体如表3所示。
对于评价指标的云模型特征,本文采用改进后的云模型为左右半云不对称的正态云模型。该云模型较符合人类对边坡稳定性评价的正常思维及常理[16]。其云模型特征参数可由式(1)得到。
$$ \left\{ \begin{aligned} & {E{x_{ij}} = \dfrac{{x_{ij}^1 + x_{ij}^2}}{2}} \\ & {E{n_{Lij}} = \left| {\dfrac{{E{x_{ij}} - E{x_{ij - 1}}}}{3}} \right|} \\ & {E{n_{Rij}} = \left| {\dfrac{{E{x_{ij + 1}} - E{x_{ij}}}}{3}} \right|} \\ & {He = k \cdot En} \end{aligned} \right. $$ (1) 式中:Exij——某一评价指标zi(i=1,2,···,n)对应的评价等级sj(j=1,2,···,n)的期望;
EnLij——某一评价指标zi(i=1,2,···,n)对应的评价 等级sj(j=1,2,···,n)左半云的熵;
EnRij——某一评价指标zi(i=1,2,···,n)对应的评价 等级sj(j=1,2,···,n)右半云的熵;
k——调整云模型的雾化程度指标。
将表1中各分级区间代入式(1),可得各评价指标的云模型三个特征参数。同时笔者在Matlab程序语言平台上开发了综合隶属度云模型程序。该程序可根据上述10个评价指标所得到的云模型特征参数分别生成相对应的综合云模型。选取坡高指标隶属于各稳定性级别的综合云模型如图1所示。
2. 评价指标的复合云模型的建立
邀请n位专家按1~9标度法对各评价指标的权重进行打分赋值,并对自己的判断给定一个“信心指数”θ,θ的取值范围为[0,1],θ越高代表信心越强。笔者通过问卷调查的方法获取各位专家对评价指标的判断数据。调查问卷通过电子邮件的方式发送至专家期刊投稿时的通信邮箱。使用层次分析法分析求出专家们对各指标的初始权重,其结果如表4所示。
表 4 各专家对评价指标的初始权重Table 4. Initial weight of each expert on the evaluation index/10−3 指标 专家
1专家
2专家
3专家
4专家
5专家
6专家
7专家
8专家
9专家
10专家
11专家
12I1 19 21 20 15 22 18 17 19 25 24 21 22 I2 76 72 60 66 76 83 79 72 78 75 78 71 I3 32 37 38 40 39 34 37 38 33 40 40 48 I4 106 103 99 93 89 87 84 105 99 97 101 93 I5 24 26 31 33 43 29 37 31 38 39 43 48 I6 158 159 158 156 158 164 164 160 166 169 182 188 I7 18 22 29 25 23 29 27 24 39 32 30 26 I8 277 283 288 280 276 275 261 271 279 261 246 220 I9 14 18 22 20 20 23 20 17 30 28 23 20 I10 276 259 255 272 253 258 273 263 213 236 237 264 根据整理各调查问卷,可得到各专家对本次调查问卷的总体信心指数分别为0.90,0.83,0.88,0.84,0.91,0.85,0.86,0.90,0.85,0.87,0.85,0.86。将该信心指数乘于表4中的相应的初始权重,同时进行归一化处理后,可得基于信心指数的权重。同时根据式(2),可得该基于信心指数的权重云模型的特征值,其结果如表5所示。
表 5 各指标的基于信心指数云模型特征值Table 5. Characteristic values of various indicators based on confidence index cloud model/10−3 指标 Ex En He I1 40 5.1 1.0 I2 66 5.4 1.9 I3 55 4.9 1.2 I4 86 7.6 1.7 I5 53 9.8 2.2 I6 148 7.3 2.3 I7 45 6.4 1.5 I8 240 20.9 8.5 I9 41 6.4 1.1 I10 227 21.2 8.6 $$ \left\{ \begin{aligned} &{Ex = \frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{u_A}_i} } \\ & {En = \sqrt {\frac{\pi }{2}} \times \frac{1}{n}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\left| {{u_A}_i - Ex} \right|} } \\ &{He = \sqrt {\frac{1}{{n - 1}}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {{{\left( {{u_A}_i - Ex} \right)}^2} - E{n^2}} } } \end{aligned} \right. $$ (2) 式中:Ex——云模型特征参数之期望;
n——各指标基于信心指数的权重个数;
En——云模型特征参数之熵;
uAi——各指标基于信心指数的权重取值;
He——云模型特征参数之超熵。
另根据高斯云的“3En规则”,指标权重的主要取值范围为[Ex−3En, Ex+3En]。设某指标的取值区间为[aA,bA],其实测值为xA,则该指标的权重ωA的表达式为:
$$ {\omega _A} = E{x_A} - 3{\alpha _\omega }E{n_A} + \frac{{{x_A} - {a_A}}}{{{b_A} - {a_A}}} \times 6{\alpha _\omega }E{n_A} $$ (3) 式中:αω——权重范围系数。
$ {\alpha }_{\omega }\in \left[0,1\right] $ ,可根据该指标的权重变化幅度进行选取。当αω取0时,式(3)变为$ {\omega _A} = E{x_A} $ ,即该指标的权重为某一常数。当αω取1时,式(3)变为${\omega _A} = E{x_A} - $ $ 3E{n_A} + \dfrac{{{x_A} - {a_A}}}{{{b_A} - {a_A}}} \times 6E{n_A}$ ,也即该指标的权重在[Ex−3En, Ex+3En]均匀分布。以指标坡高为例,其取值范围为[0,100],Ex=0.04,En=0.0051,He=0.001,利用Matlab程序编写算法,则其权重云模型图如图2所示。
从图2可以看出,指标坡高的权重在[0.035,0.045]区间的隶属度较大,在[0.03,0.035]和[0.035,0.05]区间的隶属度较小,在其他区间的隶属度更小,甚至为0。假设指标坡高的实测值为30 m,若αω取1,则代入式(4)可计算出此时指标坡高的权重ωA=0.034。再从图2可以看出,该权重的隶属度约在[0.25,0.60]范围之内。若αω取0.5,则此时ωA=0.0037,其隶属度约在[0.45,0.8]范围之内。因此可以看出,使用权重云模型的方法,不仅可以达到变权重的目的,而且还可以直观地表达权重的模糊性。因此αω的取值越小,权重的取值越靠近权重云模型的均值,其隶属度越大,隶属度范围也相对集中。反之权重值越偏离权重云模型的均值,其隶属度越小,隶属度范围也越分散。αω具体如何取值,可根据边坡的实际情况适当选用,建议在[0.2,0.5]之间选取,在进行“变权”的同时也能使最终的权重范围相对集中。
将各指标综合云模型及其相应的权重云模型进行复合,可得到该指标的复合云模型。选取坡高指标的复合云模型图如图3和图4所示。
以图3为例,同时参照图4的示意图,可以看出,Ⅱ、Ⅲ、Ⅳ三个稳定性等级的复合云模型呈类圆锥状,且各云滴较为均匀地分布在图4中的①号曲面与②号曲面围成的空间里。当评价指标的权重取其Ex值,且其实测值亦为某一稳定性等级区间的Ex值时,①号曲面与②号曲面共同相交于图4中的O点。稳定性等级为Ⅰ级的复合云模型左半侧和Ⅴ复合云模型右半侧也同样呈类圆锥状,该类圆锥状的曲线形状也是正态分布曲线。当坡高大于82.5 m时,其在单一指标的云模型中属于Ⅴ级的隶属度为1,则其复合云模型退化为单一指标的结构面间距权重云模型,如图3中的稳定性等级为Ⅴ级的复合云模型左半侧所示。因此,利用该复合云模型可以较为直观地看到评价指标在各稳定性等级中的隶属度及其相应的权重。
3. 云模型评价方法计算结果的判定
因本方法的权重函数和隶属度函数均为云模型,笔者引入区间模糊函数,用区间值Fuzzy集来表达该云模型的隶属度[16]。也即设C(x)=[C(x), C(—)(x)]。C(—)(x)和C(x)分别称为C(x)的上、下隶属函数,其表达式如式(4)所示。
$$ \left\{ \begin{aligned} &{\overline C (x) = {\rm{exp}}\left[ - \dfrac{{{{(x - Ex)}^2}}}{{2{{(En + 3He)}^2}}}\right]} \\ & {\underline C (x) = {\rm{exp}}\left[ - \dfrac{{{{(x - Ex)}^2}}}{{2{{(En - 3He)}^2}}}\right]} \end{aligned} \right. $$ (4) 根据区间值Fuzzy集的相关定义,设A和B是X上的两个指标隶属度的区间值Fuzzy集,则该两个指标的隶属度之并集可采用式(5)进行计算。
$$ \begin{aligned} (A \cup B)(x) \hfill = [\max(\underline A (x),\underline B (x)),\max(\overline A (x),\overline B (x))] \hfill \\ \end{aligned} $$ (5) 利用上述式(5)将所有指标的隶属度区间进行并集计算,可得到该边坡在各稳定性等级的综合隶属度区间。最后根据最大隶属度原理,综合隶属度区间上下限平均值最大值所在的稳定性等级即为该边坡的稳定性等级。
4. 工程实例分析
4.1 工程概况
福建省连江县黄岐镇对台客运站边坡(以下简称黄岐镇边坡)位于客运站东侧。该区域气候温暖较湿、雨量适中、台风频繁,多年平均降雨量1528.2 mm。该边坡原始地貌为低丘,场地最高海拔位于东南侧斜坡山脊,高程约50 m,最低海拔位于坡脚水泥道路路面,高程约6 m,相对高差约44 m。斜坡高程36 m以上坡段为自然斜坡,坡度约25°,植被发育,为原始生态林;斜坡高程36 m以下坡段因人工开挖改造形成阶梯状边坡,边坡高度4~20 m,未支护,边坡坡度约62°。边坡主要由碎块状强风化-中风化花岗岩组成、节理裂隙发育,其产状分别为:200°∠40°。裂隙主要为张裂隙,长度0.5~4 m不等,裂隙张开宽度2~40 mm,间距0.3~1.2 m,无充填,边坡岩体被主要结构面分割成块状或楔形体。RQD为32%~53%,岩石单轴抗压强度平均为38.2 MPa。结构面强度经验指标c=30 kPa,φ=35°。地下水的含水层主要赋存于④砂土状强风化花岗岩、⑤碎块状强风化花岗岩、⑥中风化花岗岩中的裂隙潜水,并且由于风化作用,水量分布不均匀,渗透性能一般,为弱透水层,以潜水为主。根据野外钻探取芯肉眼鉴别,结合场地原位测试和室内土工试验成果综合分析,在钻探控制深度范围内各岩土层主要特性参数如表6所示。
4.2 稳定性分析
根据上述勘察报告,可知该边坡的坡高为24.15 m,坡角为62°,该地区多年平均降雨量为1528.3 mm。因该边坡的岩石单轴抗压强度平均为38.2 MPa,查表1可得该项评分值为5。因该边坡的RQD为32%~53%,大部分处于25%~50%的区间,故查表1可得该项评分值为8。因结构面间距为0.3~1.2 m,大部分处于0.5~1.0 m的区间,故查表1可得该项评分值为13。同理可根据勘察报告计算得到结构面条件评分值为15。因该边坡为弱透水层,相当于含水率为1~10 Lu,故该项评分值为7。根据勘察报告,可求得λ、F1、F2、F3分别为0.7,0.15,0.85,60,故结构面方向修正值为5.36。因该边坡为自然边坡,未经爆破过,故边坡开挖方法修正值为5。将表5中的数值代入式(4)和式(5),可计算出该边坡各评价值在评价等级中的隶属度(表7)。
表 6 黄岐镇边坡场地内岩土层特性参数Table 6. Property parameters of strata in slope of Huangqi town序号 地层名称 天然
重度
γ/(kN·m−3)饱和
重度
γsat/(kN·m−3)天然快剪 饱和快剪 厚度/m ck/kPa φk/(°) ck/kPa φk/(°) ① 素填土 17.5 18.0 10.0 15.0 8.5 11.5 0.50~1.40 ② 坡积粉质黏土 18.64 18.78 22.0 20.0 19.19 17.45 0.5~1.3 ③ 残积砂质黏土 18.5 19.0 23.0 22.0 20.0 18.0 1.5~2.8 ④ 全风化花岗岩 19.0 19.5 25.0 27.0 22.0 23.0 0~3.0 ⑤-1 砂土状强风化花岗岩 21.0 21.5 30.0 32.0 26.0 28.0 2.3~7.3 ⑤-2 碎块状强风化花岗岩 22.0 22.5 35.0 35.0 28.0 30.0 1.1~2.4 ⑥ 中风化花岗岩 24.0 - 40.0 50.0 - - 7.4~15.4 表 7 指标评价在各评价等级中的隶属度范围Table 7. The range of the membership degree of the index evaluation in each evaluation grade评价指标 稳定性等级 很稳定 稳定 基本稳定 不稳定 很不稳定 I1 [0,0] [0,0] [0.74,0.82] [0.04,0.11] [0,0] I2 [0,0] [0.15,0.28] [0.39,0.53] [0,0] [0,0] I3 [0,0] [0.01,0.05] [0.96,0.97] [0,0] [0,0] I4 [0,0] [0,0] [0.25,0.39] [0.25,0.39] [0,0] I5 [0,0] [0,0.02] [1,1] [0,0] [0,0] I6 [0,0.02] [0,1] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] I7 [0,0] [0.95,0.97] [0.01,0.04] [0,0] [0,0] I8 [1,1] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] I9 [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] [0,0] [1,1] I10 [0,0] [0.98,0.99] [0.01,0.04] [0,0] [0,0] 从表7看出,大部分评价指标的隶属度在其中的两个稳定性等级中均有取值,而在另外三个稳定性等级取值为0。这是由于本文的云模型考虑该指标实测值的隶属度较大的两个等级,而另外三个次要等级的隶属度较小,故忽略不计。
本次评价的各评价指标的变权重复合云模型均取αω=0.3。将表代入式(3)和式(4),可求得各指标权重及其隶属度范围(表8)。
从表8可以看出,当权重的取值越靠近其均值,其平均隶属度也越大,反之越小。如表中的I7指标,其取值接近取值范围的均值,故其权重取值也接近云模型权重均值,同时其平均隶属度较大;而I5指标则相反。同时表中的I8和I10两个指标的隶属度范围变化幅度较大,其范围几乎为从0至0.99。此为各专家在问卷调查时对该两个指标的权重判断差异较大的原因,使得He的值较大。根据李德毅等[1]对云模型的特征值He取值研究发现,当He>0.3 En时,其云模型较为发散,故其隶属度范围较大。
将上述的数值输入笔者开发的应用程序可得该边坡的稳定性评价结果(图5)。
表 8 评价指标的指标权重及其隶属度范围Table 8. Weight of evaluation index and its range of membership degree评价指标 Ex 权重取值 隶属度 I1 0.040 0.037 [0.763,0.944] I2 0.066 0.067 [0.641,0.985] I3 0.055 0.054 [0.549,0.991] I4 0.086 0.085 [0.975,0.989] I5 0.053 0.050 [0.214,0.682] I6 0.148 0.147 [0.904,0.998] I7 0.045 0.045 [0.992,0.999] I8 0.240 0.223 [0.009,0.870] I9 0.041 0.043 [0.799,0.960] I10 0.227 0.230 [0,0.997] 虽然模糊数学中的隶属度与事件发生概率是从不同角度刻画不确定性的两种方法,不能等同而论,但可以将隶属度理解为发生的可能性。从图可以看出,该坡段现状是处于基本稳定状态的最小可能性为0.525,最大可能性为0.638。一般情况下,人们对某一事件判断无法给出一个精确的数值,而比较习惯给定某一范围。本方法的隶属度评价结果为某一区间,也即具有一定的模糊性,相对符合人类的判断习惯。可算出上述基本稳定状态的综合隶属度区间上下限平均值,可得0.582,同理其很稳定、稳定、不稳定以及很不稳定的上下限平均值分别为0,0.101,0.128以及0。可以看出,该坡段的稳定性为基本稳定的可能性最大,不稳定的可能性次之。也即该边坡总体处于基本稳定状态,但仍存在转化为不稳定的可能性。根据勘察报告,2016年6月17日该坡段因强降雨发生了崩塌,崩塌情况如图6所示。此结果初步验证了本方法的分析结果。
5. 结 论
文章尝试用云模型方法构建指标变权重模型,提出基于指标变权重复合云模型的岩质边坡稳定性评价方法,并在福建省连江县黄岐镇边坡进行了应用分析。使用该方法得到的稳定性等级隶属度结果为某一区间,相对更符合人类的判断习惯。通过对黄岐镇边坡的分析表明,该边坡的处于基本稳定的状态可能性最大,但仍存在不稳定的可能性。根据现场的勘察情况,也初验证了该分析结果。该方法考虑了权重的模糊性和随机性特点,对岩质边坡稳定分析的模糊分析方法进行了尝试,具有一定的可行性。但是影响岩质边坡稳定性的影响因素较多,且部分指标具有一定的地域性,如多年平均降雨量,如何根据不同的地域特点确定合理的评价指标及其分级区间,值得进一步深究。另外本文对在评价指标的隶属函数选取上均假定其服从较为广泛使用的正态函数分布,尚未进行论证其合理性。此亦是本文的下一步研究方向。
致谢:研究过程中,收到了林斌、陈仕淇、兰俊杰、程武、俞伟宏、陈林靖、徐祥、林智勇、谢裕鑫、王旭、陈德瑨、姜珂12位学者的有效问卷,在此表示衷心的感谢!
-
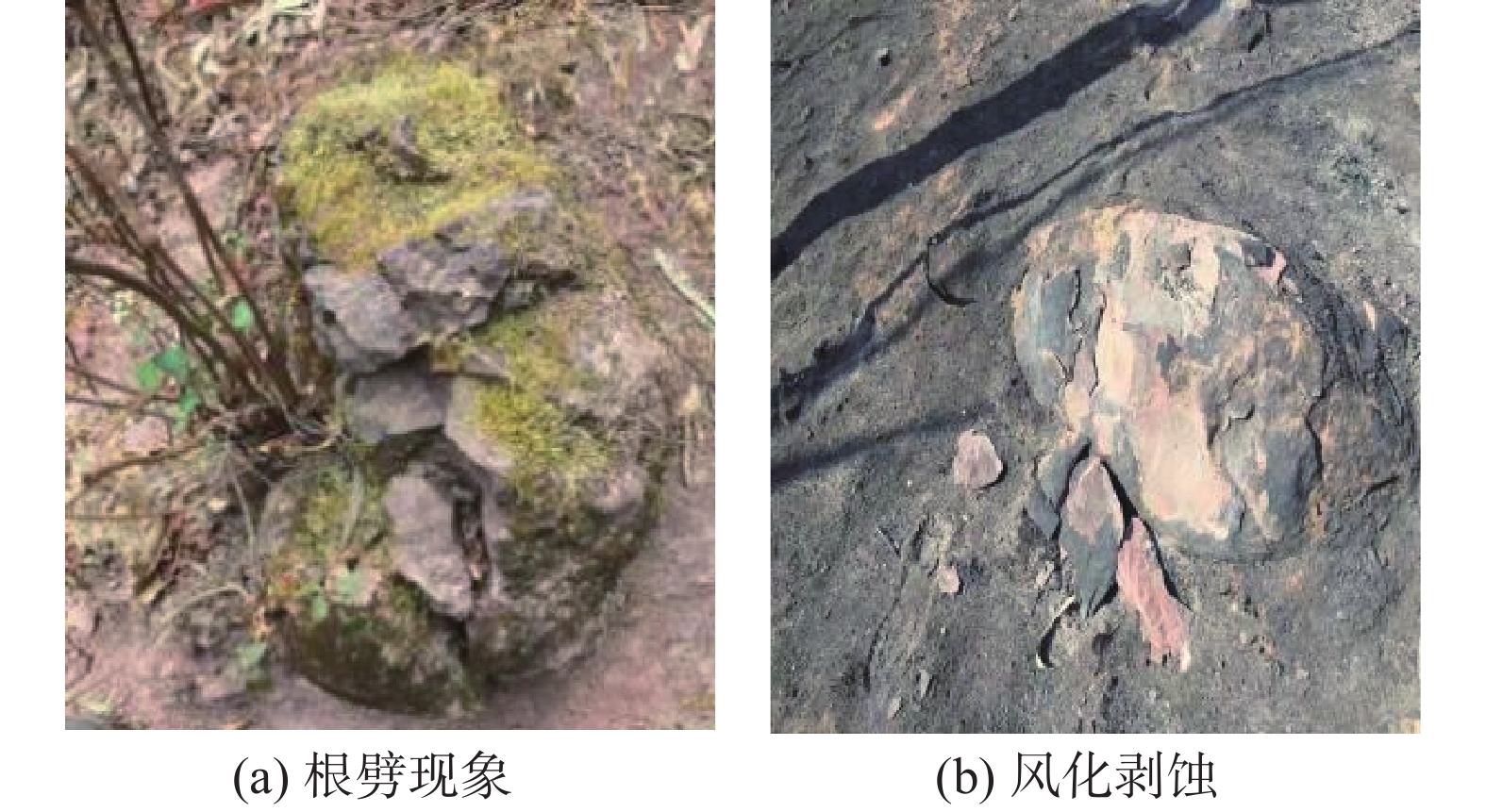
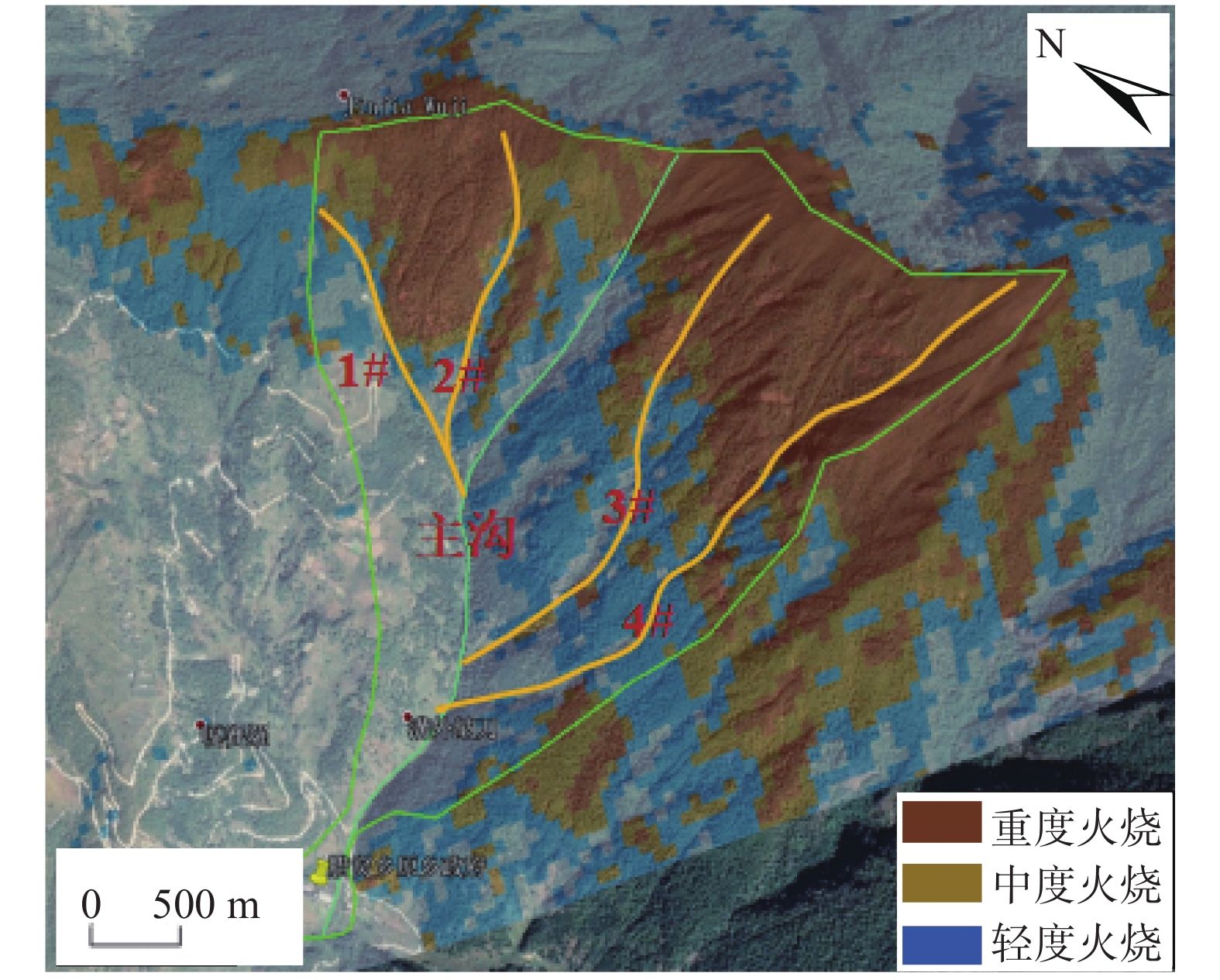
表 1 火烈度划分标准
Table 1 Fire severity classification standard
依据火烈度 地面覆盖物过火情况 树干(枝)烧黑高度 树叶烧毁情况 未火烧 未过火 未烧黑 绿色 轻度 地面草,落叶过火;
草桩,腐殖质层保留树枝未烧到,
树干烧黑小于3 m树叶基本绿色 中度 地面草,落叶,
半腐殖质层基本烧毁树干烧黑高度
5~10 m,树梢保留树叶多为黄色,
少数黑色重度 地面草,落叶,
半腐殖质层全部烧毁树干烧黑高度
大于10 m,或
全黑或树桩烧断树叶烧毁或保
留全黑树梢 -
[1] 胡卸文, 王严, 杨瀛. 火后泥石流成灾特点及研究现状[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(6):1562 − 1573. [HU Xiewen, WANG Yan, YANG Ying. Research actuality and evolution mechanism of post-fire debris flow[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(6):1562 − 1573. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] WELLS W G II. The effects of fire on the generation of debris flows in southern California[M]//Debris Flows/Avalanches: Process, Recognition, and Mitigation. Geological Society of America, 1987: 105-114.
[3] CANNON S H. Debris-flow generation from recently burned watersheds[J]. Environmental and Engineering Geoscience,2001,7(4):321 − 341. DOI: 10.2113/gseegeosci.7.4.321
[4] 任云, 胡卸文, 王严, 等. 四川省九龙县色脚沟火后泥石流成灾机理[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(6):150 − 156. [REN Yun, HU Xiewen, WANG Yan, et al. Disaster mechanism of the Sejiao post-fire debris flow in Jiulong County of Sichuan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(6):150 − 156. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] KEY C H, BENSON N C.LANDSCAPE assessment (LA) sampling and analysis methods [C]//FIREMON: Fire Effects Monitoring and Inventory System, Lutes D C edit, Rocky Mountain Research StationRMRS-GTR-164-CD, 2006.
[6] 刘发林, 杨继敏. 火干扰对径流及土壤侵蚀的模拟研究[J]. 土壤通报,2015,46(4):858 − 865. [LIU Falin, YANG Jimin. Simulation study of fire disturbance on runoff and soil erosion[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2015,46(4):858 − 865. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] DEBANO L F. Water repellent soils: a state-of-the-art[R]. U.S. Department of Agriculture, Forest Service, Pacific Southwest Forest and Range Experiment Station, 1981.
[8] 陈俊英, 吴普特, 张智韬, 等. 土壤斥水性对含水率的响应模型研究[J]. 农业机械学报,2012,43(1):63 − 67. [CHEN Junying, WU Pute, ZHANG Zhitao, et al. Response models for soil water repellency and soil moisture[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2012,43(1):63 − 67. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2012.01.013 [9] 王严, 胡卸文, 杨瀛, 等. 火烧迹地土壤斥水性和渗透性变化特性[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(6):40 − 45. [WANG Yan, HU Xiewen, YANG Ying, et al. Research on the change in soil water repellency and permeability in burned areas[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(6):40 − 45. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] BADÍ A-VILLAS D, GONZÁ LEZ-PÉ REZ J A, AZNAR J M, et al. Changes in water repellency, aggregation and organic matter of a mollic horizon burned in laboratory: Soil depth affected by fire[J]. Geoderma,2014,213:400 − 407. DOI: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2013.08.038
[11] DOERR S H, DOUGLAS P, EVANS R C, et al. Effects of heating and post-heating equilibration times on soil water repellency[J]. Soil Research,2005,43(3):261. DOI: 10.1071/SR04092
[12] DEBANO L F, SAVAGE S M, HAMILTON D A. The transfer of heat and hydrophobic substances during burning[J]. Soil Science Society of America Journal,1976,40(5):779 − 782. DOI: 10.2136/sssaj1976.03615995004000050043x
[13] SIMANTON J R, WINGATE G D, WELTZ M A. Runoff and sediment from a burned sagebrush community [M]. Proceedings of the Symposium, 1990: 14 - 17.
[14] 郝红兵, 赵松江, 李胜伟, 等. 汶川地震区特大泥石流物源集中启动模式和特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(6):159 − 165. [HAO Hongbing, ZHAO Songjiang, LI Shengwei, et al. The star-up mode on large debris flow material source in Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(6):159 − 165. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 贺小黑, 彭鑫, 谭建民, 等. 地下水渗流对崩坡积滑坡稳定性和变形的影响: 以湖南安化春风滑坡群为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(6):96 − 103. [HE Xiaohei, PENG Xin, TAN Jianmin, et al. Influence of groundwater seepage on stability and deformation of colluvial deposit landslide: Taking Chunfeng landslide group in Anhua County of Hunan Province as an example[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(6):96 − 103. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] CANNON S H, GARTNER J E. Wildfire-related debris flow from a hazards perspective Debris-Flow Hazards and Related Phenomena[J].[s.n.], 2005: 363-385.
[17] 刘云, 康卉君. 江西崩塌滑坡泥石流灾害空间时间分布特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(4):112. [LIU Yun, KANG Huijun. Analysis of spatial and temporal distribution characteristics of landslide and debris flow disasters in Jiangxi[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(4):112. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 李明威, 唐川, 陈明, 等. 汶川震区北川县泥石流流域崩滑体时空演变特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):182 − 190. [LI Mingwei, TANG Chuan, CHEN Ming, etal. The temporal and spatial evolution characteristics of landslides in the debris flow basin of Beichuan County, Wenchuan earthquake area[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):182 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 殷万清, 金涛, 胡卸文, 等. 喜德县中坝村火后泥石流发育特征及预警避险[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2021,32(3):61 − 69. [YIN Wanqing, JIN Tao, HU Xiewen, et al. Study on the development characteristics of post-fire debris flow and its early warning risk aversion in Zhongba Village, Xide County[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2021,32(3):61 − 69. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 赖波,江金进,江山,江宁,赵风顺. 珠海市南水镇金龙边坡变形破坏特征及稳定性评价. 城市地质. 2024(01): 20-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 姜波,周娟. 基于AHP-FCE法的公路路堑高边坡施工安全风险评估. 中国水运(下半月). 2024(06): 113-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨再高,郭沙,唐应志. 基于CRITIC-蛛网灰靶的边坡等级评价模型. 采矿技术. 2024(05): 231-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 姜波,周娟. 基于AHP-FCE法的公路路堑高边坡施工安全风险评估. 中国水运. 2024(12): 113-115 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 许胜军,余华中,李德海,余永强. 基于博弈论—云模型的露天矿边坡稳定性分析. 能源与环保. 2023(07): 21-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 陈忠源,戴自航,简文彬. 基于因子权重反分析的新近失稳土质边坡稳定性评价云模型. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(04): 125-133 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 张威,胡舫瑞,綦巍,彭琳,王咏林,陈枫. 基于XGBoost和云模型的地质灾害易发性评价. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(06): 136-145 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 潘瑜. 基于灰色关联分析法的边坡稳定性评价云模型研究. 华北科技学院学报. 2022(06): 101-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)




 下载:
下载:




















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS