Analysis on characteristics and reactivation mechanism of secondary landslides in the front part of the Xijitan giant landslide, Guide Basin
-
摘要:
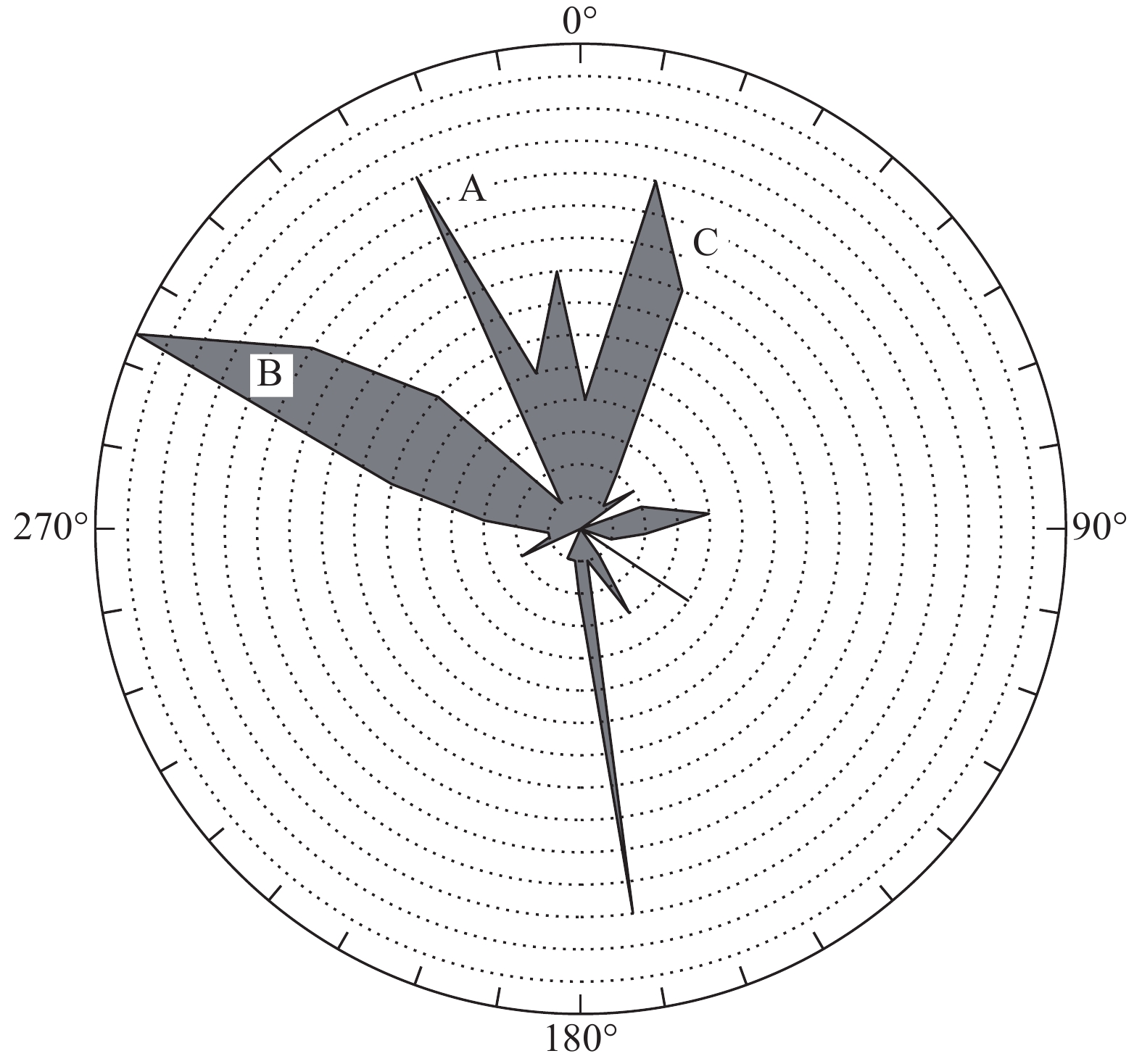
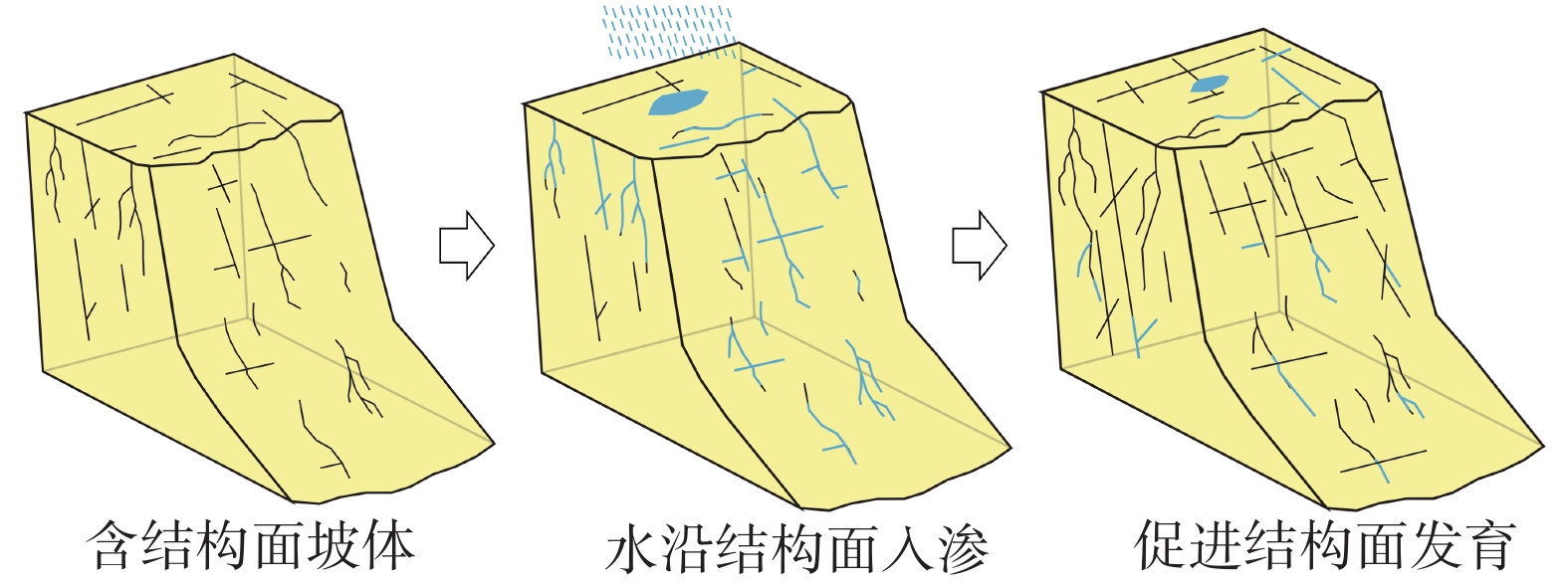
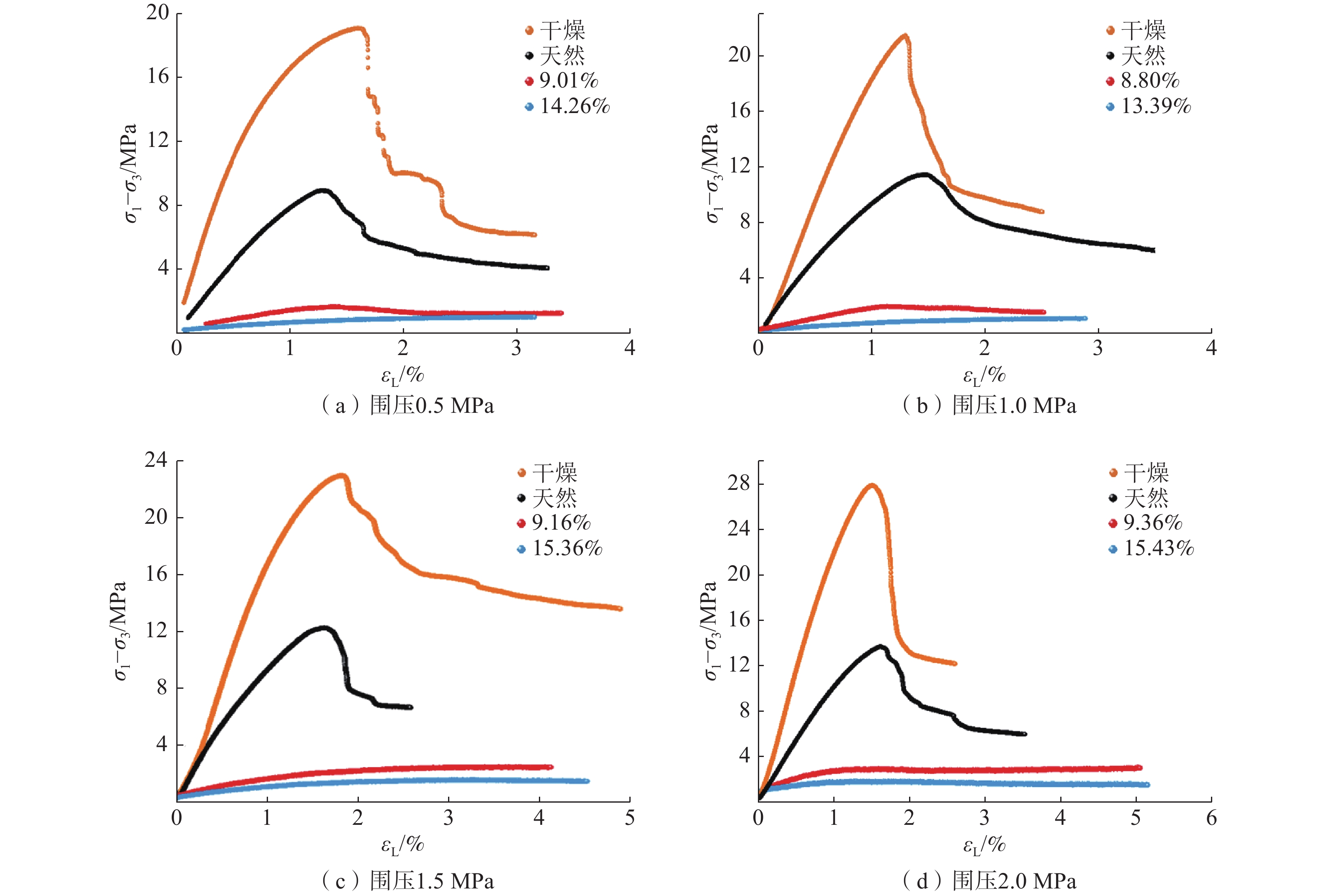
黄河上游地区位于构造活动剧烈的青藏高原东北缘,其复杂的地质条件孕育了大量的滑坡、崩塌等地质灾害。文章以青海省贵德县尕让乡江拉新村北席芨滩巨型滑坡前缘次级滑坡为研究对象,采用无人机航测、InSAR地表位移监测、现场调查和室内力学试验等手段,详细分析了滑坡的地质背景、发育特征和复活机制。现场调查发现:滑坡区岩体结构破碎疏松,主要出露地层岩性为新近系泥岩和全新统坡积物;次级滑坡后缘发育多条大型裂缝和张拉带,地表变形明显,处于蠕滑变形阶段;密集发育的结构面对次级滑坡的复活起到控制作用,集中降雨导致的泥岩软化是诱发滑坡复活的关键因素,二者的互馈作用会持续降低滑坡区岩体的完整度和强度,导致次级滑坡的变形复活。研究结果可为黄河上游地区防灾减灾工作提供理论基础。
Abstract:The upper reaches of the Yellow River, located on the northeastern edge of the tectonically active Qinghai Tibet Plateau, are characterized by complex geological conditions that have led to a high incidence of geological disasters such as landslides and collapses. This study focuses on the secondary landslide at the front part of the Xijitan landslide on the north side in Jiangla Village, Garang Township, Guide County, Qinghai Province. Using methods including unmanned aerial vehicle surveying, InSAR surface displacement monitoring, and on-site investigation methods, a detailed analysis of the geological environmental conditions, development characteristics, and reactivation mechanism of the landslide are conducted. On-site investigation results indicate that the rock mass structure in the landslide area is fragmented, with concentrated rainfall. The main exposed strata are Neogene mudstone and Holocene slope deposits. Multiple large cracks and tension bands are developed at the rear edge of the landslide, and the surface deformation is obvious, in the stage of creep deformation. Analysis of the mechanism of landslide reactivation reveals that densely developed structures play a controlling role in the reactivation of secondary landslides, and the softening of mudstone caused by concentrated rainfall is a key factor in inducing landslide reactivation. The interaction between two factors continuously reduce the integrity and strength of the rock mass, leading to the deformation and reactivation of secondary landslides. The research results aim to provide a theoretical basis for disaster prevention and reduction work in the upper reaches of the Yellow River.
-
0. 引言
凉山州地处横断山系东北缘、川滇构造带南段,受活动构造、地形地貌、河流切割等作用,地质灾害发育且频发,时常造成群死群伤和巨大经济损失,如2003年普格县“6•20”泥石流[1]、2004年德昌县“8•24”群发型泥石流[2]、2015年雷波县碉楼沟泥石流[3]、2017年普格县荞窝镇8·8泥石流[4]、2019年甘洛县群发性山洪泥石流[5]、2019年甘洛县“8•14”埃岱村滑坡[6]等。
近年来,许多学者对凉山州突发重大地质灾害的发育特征、成灾机理、破坏模式、防治措施等方面进行了研究:在滑坡灾害研究方面,以会理县老营盘村[7]、美姑县火洛村滑坡[8]、美姑县洛渣滑坡[9]、普格县姚家山滑坡[10]、宁南县水塘村滑坡[11]、西昌市太和矿北采场滑坡[12]为研究对象,开展了滑坡的形成机理和稳定性研究;在古滑坡复活研究方面,以木里县卡基娃滑坡[13]、雷波县马湖古滑坡群[14]、美姑县拉马阿觉滑坡[15]、金阳县城区古滑坡[16]、盐源县玻璃村滑坡[17]为研究对象,开展了古滑坡复活特征、成因机制、影响因素研究;在火后泥石流研究方面,以木里县黄泥巴沟泥石流[18]和项脚沟泥石流[19]、西昌市响水沟泥石流[20]和电池厂沟泥石流[21]、喜德县中坝村泥石流[22]为研究对象,开展了火后泥石流发育特征、成灾机理研究;在暴雨诱发泥石流研究方面,以2004年德昌县群发泥石流[23]、2009年金阳县地洛电站泥石流[24]等为研究对象,开展了泥石流成灾过程、特征成因、形成机理研究;在链式灾害研究方面,以白沙村滑坡-碎屑流[25]、埃岱村滑坡-碎屑流[6]、阿坡洛滑坡-堰塞湖[26]和采书组滑坡-堰塞湖[27]为研究对象,开展了滑坡发育特征、成灾机理和运动过程研究。但是,对于凉山州地质灾害的整体发育特征、灾情特征、主要致灾类型等方面缺乏系统性总结与研究。
本文基于凉山州地质灾害数据和资料,分析了凉山州地质灾害整体发育特征和灾情特征,总结提炼了7种主要致灾类型,通过实例逐一分析了灾害发育特征,以期对凉山州地质灾害的防灾减灾工作提供数据支撑和科学参考。
1. 地质环境背景
凉山彝族自治州,位于四川省西南部,地势西北高,东南低,北部高,南部低。地处杨子古陆块西缘,川滇构造带南段,境内构造发育,主要构造体系有:安宁河构造带、小江构造带、青藏川“歹”字形构造带、玉树—甘孜构造带、龙门山构造带、雷波—马边构造带。地处中国南北地震带中段,是构造地震活动强烈地区之一。位于扬子和巴颜喀拉秦岭两大地层区,金矿—木里深大断裂,以东属扬子地层区,以西的木里县和冕宁县西缘属巴颜喀拉秦岭地层区,地层复杂,变化较大。
位于川西南横断山系东北缘,界于四川盆地和云南高原之间,地形地貌复杂,地势西北高、东南低,主要山系有大凉山山系、小相岭—鲁南山山系、大雪山山系。地貌按成因分为河谷堆积地貌、中山地貌和构造剥蚀高山地貌;中山地貌占全州面积的78%,山势相对陡峭,河谷宽阔,多呈“U”型,岸坡平缓;构造剥蚀高山地貌主要分布在凉山州西北部的木里县,占全域面积的20%,切割剧烈,山高谷深,呈狭窄“V”型。
属亚热带季风气候,四季不明显,但干湿分明。全州年平均气温4.6 °C,年均降水量为995.5 mm,7月份的月均降水量最高,达274.1 mm,5—9月份降雨量约占全年总量的79.24%。金沙江干热河谷年降水量600 mm左右,气候炎热少雨,植被稀少,水土流失严重,生态十分脆弱,物理风化作用强烈,干旱易发生森林火灾,自然灾害特别突出,如木里县(2019年、2020年)、西昌市(2020年)、冕宁县(2021年)都曾发生规模较大的森林火灾,火灾造成植被和土壤不同程度的破坏,为火后泥石流等地质灾害的发生提供了丰富的物源。境内河流众多,由金沙江、雅砻江和大渡河三大水系组成。大于
1000 km2的河流11条,还有邛海、马湖、泸沽湖等23个内陆淡水湖泊。水力资源极为丰富,有溪洛渡(1.26 ×106 kW)、白鹤滩(1.305 ×106 kW)等14座在建和规划的大型水电站。人类工程活动对原有地质环境的改造,是诱发凉山州地质灾害的重要因素之一。道路建设、切坡建房等人类活动(图1—2),对边坡不合理的开挖,破坏斜坡体稳定性,在降雨、地震等诱发因素下更容易发生滑坡灾害。凉山州矿产资源丰富,矿区内废石、弃渣的不合理堆放(图3),会造成弃渣斜坡的失稳滑动,也为矿渣型泥石流的形成提供丰富物源。
2. 凉山州地质灾害发育特征
2.1 地质灾害类型
四川省是西南地区地质灾害点数量最多的省份[28],数量达30239处;凉山州所处的川西地区共发育地质灾害
16411 处[29]。依据《四川省凉山州(1∶100 000)地质灾害风险调查评价成果报告》中数据显示,凉山州地质灾害总数4016 处(截至2021年底)(图4、表1),约占全省灾害总数量的13.4%,其中滑坡2674 处、泥石流1087 处、崩塌249处、地面塌陷6处,分别占全州总数的66.6%、27.1%、6.2%、0.15%。从灾害类型和规模等级看,滑坡以中小型为主,数量达2565 处,占滑坡总数的95.9%;崩塌以中小型为主,数量达245处,占崩塌总数的98.4%;泥石流以中小型为主,数量达1061 处,占泥石流总数的97.6%。如表2所示,滑坡按物质组成统计,以土质滑坡为主,数量达2950 处,占比98.4%;崩塌按物质组成统计,以岩质崩塌为主,数量达305处,占比95.91%;泥石流按流域形态统计,以沟道型泥石流为主,数量达1177 处,占比96.55%。表 1 凉山州地质灾害发育类型及数量Table 1. Development types and quantities of geological hazards in Liangshan Prefecture规模 崩塌 滑坡 泥石流 地面塌陷 合计 占比/% 特大型 2 3 4 0 9 0.22 大型 2 106 22 0 130 3.24 中型 76 830 258 0 1164 28.98 小型 169 1735 803 6 2713 67.55 合计 249 2674 1087 6 4016 100 占比/% 6.20 66.58 27.07 0.15 100 表 2 凉山州不同类型地质灾害发育特征统计Table 2. Statistical analysis of development characteristics of different types of geological hazards in Liangshan Prefecture灾害类型 发育特征 数量/处 占比/% 滑坡 土质 2950 98.40 岩质 48 1.60 崩塌 土质 13 4.09 岩质 305 95.91 泥石流 沟道型 1177 96.55 坡面型 42 3.45 2.2 地质灾害人员伤亡及经济损失
收集和梳理凉山州各县有记录以来的历史重大地质灾害资料得到(表3),凉山州共计发生24起死亡10人以上的地质灾害,灾害类型以泥石流为主;造成伤亡最严重的灾害为1850年发生在西昌的7.5级地震,据记载地震及诱发的地质灾害造成约2.79万户人受灾,2.7万人死亡,2.6万余间房屋倒塌。
表 3 凉山州历史重大地质灾害灾情简表(死亡10人以上)Table 3. Summary of major historical significant geological disasters in Liangshan Prefecture (with 10 or more fatalities)序号 位置 发生日期 灾害类型 规模
/104 m3受灾对象 受灾人口/人 死亡/人 直接经济
损失/万元具体成因 1 西昌城区及周边乡镇 1850-09-12 7.5级地震 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 2.79万户 约27 000 不详 7.5级地震 2 会东县小田坝村下坝老街 1881-02-06 滑坡 不详 人、畜和房屋 不详 约30 不详 不详 3 喜德县东河 1891-07-05 泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 约1000 不详 暴雨 4 西昌市东河、西河 1942-06-16 山洪、泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 约120 不详 暴雨 5 西昌沿安宁河19个乡 1951-08-24 山洪、泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 15 不详 暴雨 6 西昌市东河 1955-07-14 山洪、泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 68 不详 暴雨 7 喜德县中沟 1957-06-29 泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 84 不详 暴雨 8 冕宁县泸沽镇洛瓦村4组 1970-05-26 泥石流 530 原铁道部第二工程处食堂、
仓库和工棚500 104 不详 矿山开采 9 喜德县红莫镇司金沟3社 1972-08-01 泥石流 不详 村落、房屋 不详 200 3000 暴雨 10 甘洛县乌史大桥乡利子依达沟 1981-07-09 泥石流 30万 成昆铁路利子依达大桥、
旅客列车不详 240 2000 余万暴雨 11 会东县溜姑乡三家村 1988-06-01 泥石流 不详 公路大桥桥墩、工棚 26 13 不详 暴雨及冰雹 12 冕宁县漫水湾镇二村沟1组 1989-09-04 泥石流 不详 居民点、农田 3000 51 不详 暴雨 13 冕宁县漫水湾镇胜利村 1989-09-04 泥石流 不详 居民点、农田 500 12 不详 暴雨 14 德昌县永郎镇蒲坝村 1995-07-11 泥石流 2.5 聚集区 63 10 800 暴雨 15 普格县五道箐镇采阿咀沟 2003-06-20 泥石流 70 公路、房屋、通信光缆 58 10 100 暴雨 16 盐源县平川镇骡马铺村2组 2006-07-14 泥石流 100 聚集区 168 16 500 暴雨 17 冕宁县彝海乡勒帕村 2011-06-16 泥石流 不详 聚集区 不详 17 不详 暴雨 18 宁南县白鹤滩镇和平村
1组矮子沟2012-06-27 泥石流 8 分散农户、白鹤滩水
电站施工区不详 38 530 暴雨 19 雷波县岩脚乡金沙村 2013-07-27 滑坡-涌浪 不详 金沙江航道船只、对岸码头 不详 约20 不详 暴雨 20 普格县荞窝镇耿底村
4、5组桐子林沟2017-08-08 泥石流 1.03 通村公路、房屋 577 26 16000 暴雨 21 冕宁县棉沙镇许家坪村
1、2组下草坪子滑坡2012-07-12 滑坡 不详 公路、房屋 95 13 400 持续降雨 22 德昌县茨达镇新华村 2004-08-23 滑坡、泥石流 不详 聚集区 4960 17 不详 暴雨 23 德昌县乐跃镇乐跃沟村 2004-09-24 泥石流 不详 聚集区 不详 11 不详 暴雨 24 盐源县洼里乡手爬村二组北沟段 2012-08-30 泥石流、滑坡 不详 聚集区 241 13 520 暴雨 根据2006—2020年地质灾害灾情资料,凉山州共发生46起因灾伤亡的地质灾害(表4),包括泥石流30起、滑坡9起、崩塌7起,共计死亡156人,失踪66人,受伤77人,直接经济损失
29200 万元。按照灾情等级划分,特大型2起、大型4起、中型17起、小型23起。其中2起特大型灾情分别是:2017年8月8日凌晨4点至4点30分,普格县荞窝镇耿底村4组和5组桐子林沟发生泥石流灾害,导致25人死亡,71间房屋损毁,1.6亿元经济损失;2012年6月28日,宁南县白鹤滩镇矮子沟暴发特大山洪泥石流灾害,造成白鹤滩镇1540 户6151 人受灾,白鹤滩电站水电四局施工人员20人失踪、20人遇难、13人受伤的严重后果。表 4 凉山州各县市灾情统计表(2006—2020年)Table 4. Statistical table of disaster situation for each county and city in Liangshan Prefecture (2006—2020)县/市 灾情数量/起 死亡失踪/人 经济损失/万元 县/市 灾情数量/起 死亡失踪/人 经济损失/万元 德昌县 2 3 410 冕宁县 2 20 520 甘洛县 3 4 111 木里县 3 16 220 会东县 1 2 15 宁南县 8 52 6850 会理市 2 1 75 普格县 4 31 17470 金阳县 4 13 170 喜德县 1 6 100 雷波县 7 25 745 盐源县 3 30 1470 美姑县 2 8 546 越西县 2 1 118 昭觉县 2 10 380 合计 46 222 29200 3. 主要致灾类型
梳理分析凉山州发生的重大突发地质灾害数据,总结提炼了凉山州7种地质灾害主要致灾类型,分别是红层滑坡、复活型古滑坡、库岸型滑坡、含煤层型滑坡、矿渣型泥石流、火后型泥石流、链式灾害。
3.1 红层滑坡
凉山州发育红层滑坡729处,占滑坡总数的27.3%(图5),红层地层主要发育在凉山州南部的中低山区;统计红层滑坡发育的地层年代(表5),发育在侏罗系地层的红层滑坡数量最多,占红层滑坡总数的70.6%,发育在白垩系、三叠系地层的红层滑坡数量占比分别为26.1%、3.3%。红层边坡自稳能力差,不及时治理会发生变形破坏,进而诱发滑坡、崩塌、落石等地质灾害[30]。
表 5 凉山州红层红层滑坡统计Table 5. Statistical analysis of red-bed landslide in Liangshan Prefecture红层地层 面积/km2 数量/处 灾害密度
/(处·km−2)占比/% 侏罗系 5778 515 0.089 70.6 白垩系 3177 190 0.06 26.1 三叠系 837 24 0.029 3.3 会理市新发镇铜厂村1组老包滑坡(图6),出露岩性为第四系全新统残坡积层($ \mathrm{Q}\mathrm{h}^{el+dl} $)碎石土,下覆基岩为下震旦统澄江组(Z1c)粗粒长石石英砂岩夹紫红色含砾砂泥岩,岩层产状185°∠35°,岩体易风化破碎,遇水极易软化解体。滑坡附近有一条近南北走向逆断层通过,大致沿红沙沟延伸。老包滑坡所在红沙沟位置,均为断层破碎带,岩体异常破碎,地质条件脆弱,断层是滑坡形成的主要原因之一。同时,滑坡区地层遇水易软化解体,降雨入渗使岩土体饱水,造成自重加大和软弱结构面润滑,加之良好的临空面,最终在陡坡段形成滑坡。
3.2 复活型古滑坡
古滑坡在凉山州多有分布,如普格县螺髻山镇—扯扯街一线仍保留10处大型地震古滑坡,雷波县金沙江两岸古滑坡发育,由于人类工程活动、河流冲刷等因素,易引发古滑坡变形和复活。
金阳县天地坝镇老营盘村城北滑坡,顺层牵引式深层特大型滑坡(图7)。出露地层为含碎石粉质黏土、碎石土。主滑方向106°,平均宽度570 m,纵向长约630 m,滑体平均厚度35 m,总体积约
1.253 ×106 m3,滑坡平面形态呈舌型,滑体物质组成主要为碎石土、角砾土,局部夹块石、黏土,由于滑坡年代久远,滑体物质胶结良好。下覆基岩主要为下奥陶统湄潭组(O1m)页岩、灰岩及上寒武统二道水组($\in_3 e $)白云岩。由于金阳河的不断切割,致使前缘临空面不断加大,最终导致古滑坡的发生,近年来古滑坡未出现整体变形迹象。但由于人类工程活动的加剧,新建房屋大量填方、生活污水排放、降雨入渗等原因,古滑坡体局部区域出现了变形和次级滑动,滑坡左侧中部区域变形破坏较为强烈,地表可见发育有多条明显拉裂缝,房屋变形破坏较严重,形成体积约1.368×106 m3复活体。3.3 库岸型滑坡
库岸型滑坡主要发育在凉山州的白鹤滩、溪洛渡、乌东德、官地、锦屏二级、锦屏一级等水电站库区内。受库水位消落带影响,斜坡坡脚常发生滑塌现象,进而影响坡体稳定性,如木里县锦屏库区尾库段的后所乡、列瓦镇一带,发育有23处库岸型滑坡;布拖县金沙江沿岸合井—牛角湾一带,地处溪洛渡库区库尾,受库水位影响发育有大滩滑坡,麻地湾滑坡,贾沙田滑坡等库岸型滑坡;宁南县白鹤滩电站2021年水位抬升后,发育有17处塌岸隐患,多数为土质边坡(图8)。
木里县瓦厂镇纳子店村店扎组滑坡位于木里县瓦厂镇纳子店村店扎组(图9),木里河左岸。平面形态呈舌形,坡面形态呈折线形,相对高差约120 m,宽160 m,长330 m,主滑方向270°,平均厚10.0 m,体积约为52.8×104 m3,属中型土质滑坡。滑体物质主要为全新统的滑坡堆积($ Q\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{ }}}\mathrm{\mathrm{ }}}}}^{\ del} $)的碎石土,下覆基岩为下奥陶统组瓦厂组(O1w)青灰色砂岩。受木里河立州水电站蓄水影响,在水位升降及斜坡土体饱水等作用下滑坡出现变形,2019、2020两年变形较剧烈,后部G227国道路面出现拉裂、下错,房屋墙体出现裂缝。
3.4 含煤层型滑坡
煤系地层主要发育在凉山州南部的中低山区,上三叠统白果湾组、须家河组、宝顶组等地层为主要产煤地层。布拖县勒吉村4组约坡吉乃滑坡,位于布拖县北部(图10),为一处沿基覆界面滑动的中型土质滑坡。20世纪80年代,滑坡前缘底部发现褐煤层,每到冬季当地村民集中开挖褐煤取暖,到2004年形成一高5~8 m近垂直人工边坡,2004年受强降雨影响,该人工边坡开始出现滑塌现象,边坡后缘出现贯通拉裂缝,2010年7月滑坡前缘整体垮塌,同年9月发生整体滑动。滑坡可分为强变形区、已滑区Ⅰ区、已滑区Ⅱ区。强变形区微地貌主要为陡坡、陡坎,横宽95~130 m,纵长约270 m,主滑方向89°,面积约2.45×104 m2,平均厚约12 m,总体积约29.4×104 m3,坡体基本解体,剖面形态呈三级平台,滑坡后壁坡度近垂直,相对高差约12 m,2015—2017年向右前侧滑动7~9 m;已滑区Ⅰ区位于1号滑坡体中右侧,横宽约60 m,纵向长约55 m,主滑方向99°后缘滑壁陡峭,中前部形成相对较缓的坡体,形成“上陡下缓”形态,体积约1.2×104 m3;已滑区Ⅱ区位于1号滑坡体右后侧,横向宽40~50 m,纵向长60~70 m,主滑方向59°,滑坡后壁高差约1.5 m,体积约2.57×104 m3。坡体含碎石黏土,下覆基岩为昔格达组砂质泥岩。
3.5 矿渣型泥石流
凉山州矿产资源丰富,矿山开采的矿渣、剥离废石、尾砂等废物,不合理的堆放,为泥石流灾害提供了丰富物源。雷波县西苏角河流域日格尔泥石流,位于山棱岗乡田坝村3、6组,沟口位于西苏角河(图11)。在1972年、2013年和2014年规模性暴发过,属于暴雨激发的中—高频中型稀性泥石流。单次冲淤堆积体积约0.72×104 m3,现沟内可参与泥石流活动的固体物源动储量达37.13×104 m3,2016年对该泥石流进行了排导槽治理。沟域高程差约为
1800 m,流域面积16.39 km2,主沟沟道长6.92 km,主沟呈“U”字型。由四条支沟交汇形成,汇水条件好,支沟多呈狭窄“V”字型,暴雨形成的地表径流是引发泥石流的主要水源。在流域的中上部为铅锌矿私挖开采地,采矿分选后大量的矸石沿沟道、公路堆积,成为了该沟的重要物源,现该私挖矿场已经关闭,其他物源来自于沟床侵蚀物源(沟床内松散堆积体)及坡面侵蚀物源。3.6 火后型泥石流
森林火灾是凉山州林区常见自然灾害,林火后根-土复合体的抗剪强度降低,土壤的黏聚力出现明显下降[31],火烧迹地在降雨条件下,极易发生火后泥石流,具有发生概率大幅提高、暴发所需降雨阈值明显降低等特点。冕宁县从2016年以来,每年均有火灾发生,仅2021年就发生了3次火灾,在安宁河流域集中发育有15处火后泥石流隐患点;西昌市经久乡一带2020年3月发生特大森林火灾,同年8月遭遇多次暴雨,诱发多条火后泥石流,经过火后次生灾害排查,确定了63条潜在泥石流沟。
木里县项脚乡项脚沟流域火后泥石流就是此类泥石流的典型(图12)。2020年3月28日,木里县项脚乡及其毗邻乡镇发生森林火灾,其中项脚乡项脚沟流域的中、上部火灾导致植被遭受严重破坏,过火面积约37.97 km2,中度及重度火烈度区面积占比65.81%。自6月9日山顶附近局地短时强降雨激发甲尔沟暴发火后泥石流灾害以来,项脚沟主沟及宋家沟、香樟湾沟、母猪洛沟、花岩沟、黄泥巴沟等多条支沟于6月、7月先后7次发生不等规模火后泥石流,冲出固体物质10余万方,导致沟口22户居民建筑物被淤埋,直接经济损失超
2600 万元。2021年7月5日,短时强降雨导致项脚沟流域7条支沟再次相继发生泥石流灾害,携带大量粗大树木,冲出沟口物源达1.62×106 m3,沟道内分布有大量漂石,岩性以灰岩为主,其中最大颗粒直径为3.2 m×3.1 m×1.9 m。灾害造成186间房屋和乡道2 km受损,撤离避险251户1042 人,无人员伤亡。项脚沟流域面积77.12 km2,主沟长14.95 km,平均纵比降为110‰,流域最高海拔
4130 m,沟口最低海拔1820 m,最大高差2310 m,主沟沟道以宽“U“型谷为主。中上游呈“树枝状”水系,下游呈“掌状”水系,各级支流共计30余条,其中一级支沟13条。支沟多以”V”型谷为主,山体平均坡度多在40°以上,基岩出露较多。地层以三叠系西康群及上二叠统地层为主,岩性主要为变质砂岩、砂板岩、板岩、大理岩及结晶灰岩夹层、变质玄武岩,及少量千枚岩。流域内不良地质现象发育,松散固体物质2216.4 ×104 m3,动储量为2.928×106 m3,主要为早期崩滑堆积物源、坡面侵蚀物源、历史泥石流沟道堆积物源及火灾形成的灰烬及土壤结构扰动层等物源,火烧区物源主要分布于沟域顶部。3.7 链式灾害
按照诱发因素划分,地质灾害链包括内动力地质灾害链、外动力地质灾害链、人为活动地质灾害链和复合型地质灾害链[32],在高山峡谷、高地应力场、频繁的地震活动、暴雨及人类活动等复杂的内外动力耦合作用下,河谷地段往往造成大型的崩滑堵江断流形成堰塞湖的事件,从而使得灾害范围及灾害种类进一步扩大,形成灾害链[33]。
冕宁县照壁山滑坡位于冷渍沟上游(图13),滑坡呈“圈椅状”,主滑方向为313°,滑坡区地层主要为早震旦世苏雄组一段(Z1S1)变流纹、变英安岩,三叠系白果湾群(T3bg)砂岩、页岩,以及第四系残坡积物。大规模发生于2000年7月18日,滑坡发生时体积约337×104 m3,形成的碎屑流冲出冷渍沟口约30×104 m3,堵塞安宁河河道;剩余滑坡体堆积于冷渍沟中,此后雨季冷渍沟均发生规模不等的泥石流。2003年7月19日,冕宁县遭遇50年一遇暴雨(日降雨量达218.6 mm),冷渍沟暴发大规模泥石流,约30×104 m3固体物质冲出沟口,造成堆积扇上1人死亡,3辆汽车被掩埋,同时冲入安宁河造成河道堵塞,河水淤高翻越右岸防护堤,冲毁右岸部分房屋、耕地。2007年8月7日,冷渍沟再次暴发泥石流堵塞安宁河河道。2007年8月7日,冷渍沟再次暴发泥石流堵塞安宁河河道。
4. 结 论
(1)查明了凉山州地质灾害整体发育特征和灾情特征。凉山州地质灾害以滑坡、泥石流为主,分别占全州总数的66.6%、27.1%;滑坡以中小型土质滑坡为主,泥石流以中小型沟谷泥石流为主。统计分析凉山州有记录以来的灾情发现,凉山州共计发生24起死亡10人以上的地质灾害。2006—2020年,凉山州共发生46起因灾伤亡的地质灾害,以泥石流为主,数量达30起,灾情规模以中小型为主,分别达17起、23起。
(2)通过系统梳理凉山州地质灾害的发育特征,结合实例总结提炼7种主要致灾类型:①红层滑坡,是凉山州滑坡主要类型之一,遇水易软化解体,降雨入渗使岩土体饱水,自稳能力差;②复活型古滑坡,在凉山州多有分布,由于人类工程活动、河流冲刷等因素,易引发古滑坡变形和复活;③库岸型滑坡,主要发育在木里县、布拖县、宁南县的水电站库区内,受库水位消落带影响,斜坡坡脚滑塌,坡体稳定性降低形成滑坡;④含煤层型滑坡,多发育在主要发育在凉山州南部的煤系地层区域,对斜坡前缘不合理的采煤开挖,易诱发前缘滑塌并造成整体滑动;⑤矿渣型泥石流,是凉山州泥石流主要类型之一,矿山开采的矿渣、废石、尾砂等不合理堆放,为泥石流灾害提供了丰富物源,叠加良好汇水条件和暴雨等因素,易引发泥石流;⑥火后型泥石流,凉山州常发生森林火灾,火灾形成的灰烬及土壤结构扰动层等为泥石流提供了物源条件,火烧迹地遭遇暴雨后,易诱发火后泥石流;⑦链式灾害,由于凉山州构造活动强烈,山势陡峭,沟谷发育,在沟谷上游发生崩滑灾害后,易沿沟运动冲出,堵塞河道形成灾害链。
(3)针对凉山州不同致灾类型的地质灾害,在常态防灾减灾过程中应采取针对性防范措施,以达到精准防控的目的,如加强库区地质灾害的排查、监测和防治,特别是加强移民安置区地质灾害的防治,避免库岸型滑坡的产生;规范采煤采矿行为、科学合理的堆放废石弃渣等,避免发生含煤层型滑坡和矿渣型泥石流;严防森林火灾,火烧迹地应采取生物措施及时恢复植被生态并采取必要的治理措施,防止发生群发性火后泥石流;修路建房等工程活动应科学合理切坡,避免诱发崩滑灾害。后续还需深入开展不同致灾类型的地质灾害的形成机理、防治措施、风险管控等方面的研究。
-
图 2 席芨滩滑坡概况图
注:a为席芨滩滑坡位置图;b为席芨滩滑坡分期图;c为席芨滩滑坡剖面图[30];d为次级滑坡航拍图;e、f、g为席芨滩滑坡分期发育特征。
Figure 2. Overview of the location of Xijitan landslide
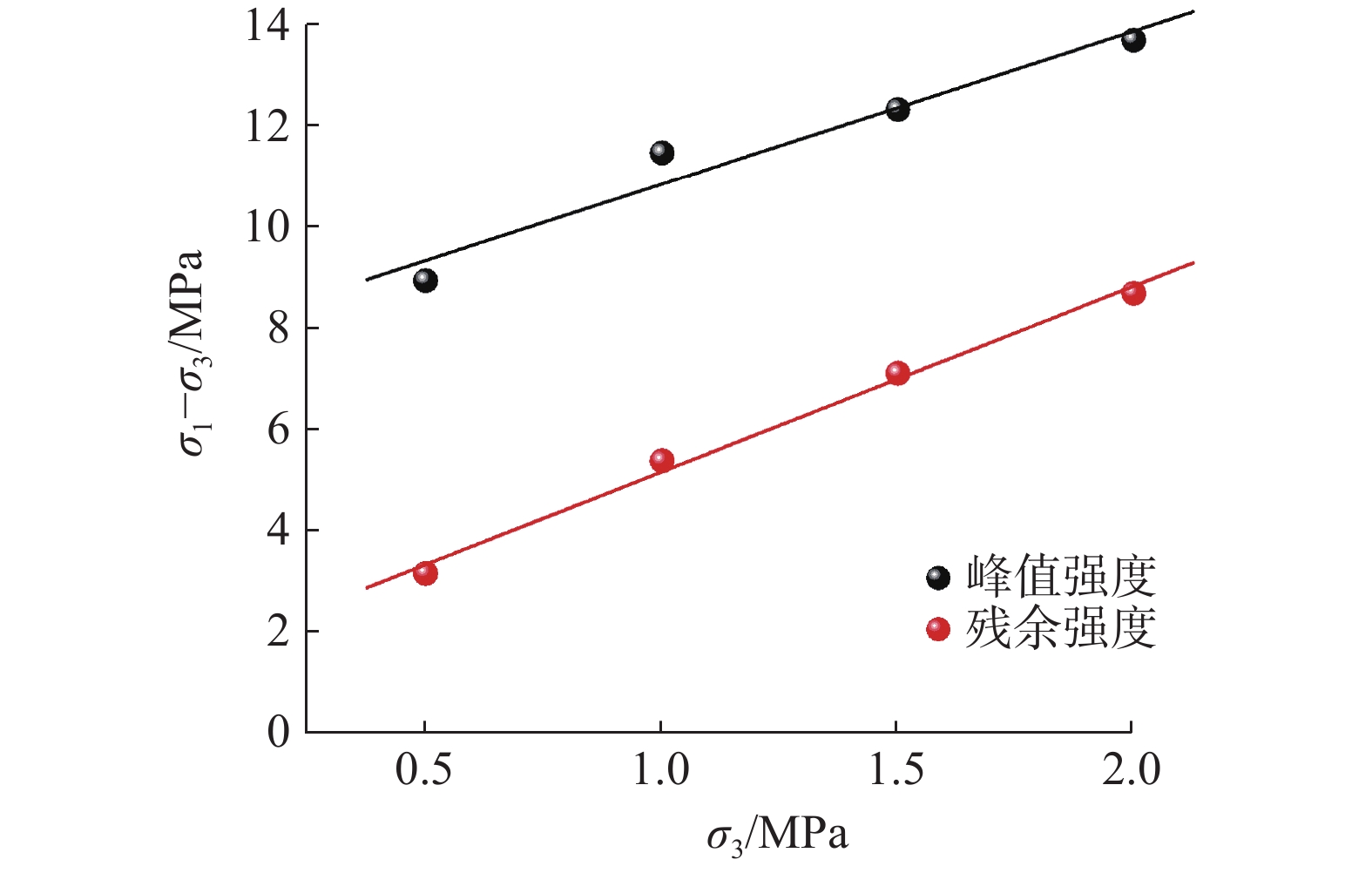
表 1 泥岩峰值强度和残余强度拟合参数
Table 1 Fitting parameters for peak strength and residual strength of mudstone
a b R2 峰值强度 3.028 ± 0.479 7.835 ± 0.656 0.9523 残余强度 3.663 ± 0.209 1.517 ± 0.287 0.9935 -
[1] 殷跃平, 高少华. 高位远程地质灾害研究: 回顾与展望[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(1):1 − 18. [YIN Yueping, GAO Shaohua. Research on high-altitude and long-runout rockslides: review and prospects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(1):1 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping, GAO Shaohua. Research on high-altitude and long-runout rockslides: review and prospects[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(1): 1 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 兰恒星,彭建兵,祝艳波,等. 黄河流域地质地表过程与重大灾害效应研究与展望[J]. 中国科学:地球科学,2022,52(2):199 − 221. [LAN Hengxing,PENG Jianbing,ZHU Yanbo,et al. Research and prospect of geological surface processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Science Chinese:Earth Science,2022,52(2):199 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LAN Hengxing, PENG Jianbing, ZHU Yanbo, et al. Research and prospect of geological surface processes and major disaster effects in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Science Chinese: Earth Science, 2022, 52(2): 199 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] YIN Z,QIN X,YIN Y,et al. Landslide developmental characteristics and response to climate change since the last glacial in the upper reaches of the Yellow River,NE Tibetan Plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica‐English Edition,2014,88(2):635 − 646. DOI: 10.1111/1755-6724.12219
[4] 胡贵寿. 青海省特大型滑坡发育分布规律[D]. 北京:中国地质大学,2013. [HU Guishou. Development and distribution patterns of large-scale landslides in Qinghai Province [D]. Beijing:China University of Geosciences,2013 (in Chinese with English abstract)] HU Guishou. Development and distribution patterns of large-scale landslides in Qinghai Province [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences, 2013 (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 崔之久,伍永秋,刘耕年,等. 关于“昆仑-黄河运动”[J]. 中国科学(D辑),1998,28(1):53 − 59. [CUI Zhijiu,WU Yongqiu,LIU Gengnian,et al. On the Kunlun Yellow River Movement[J]. Science In Chinese (Series D),1998,28(1):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CUI Zhijiu, WU Yongqiu, LIU Gengnian, et al. On the Kunlun Yellow River Movement[J]. Science In Chinese (Series D), 1998, 28(1): 53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张春山. 黄河上游地区地质灾害形成条件与风险评价研究[D]. 北京:中国地质科学院,2003. [ZHANG Chunshan. Study on the formation conditions and risk assessment about geological hazards in the upper reaches of the Yellow River [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences,2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Chunshan. Study on the formation conditions and risk assessment about geological hazards in the upper reaches of the Yellow River [D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2003. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 贾润幸,方维萱,张建国,等. 山西清徐——太谷地区地裂缝形成机理[J]. 地质通报,2022,41(7):1282 − 1290. [JIA Runxing,FANG Weixuan,ZHANG Jianguo,et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in the Qingxu Taigu area of Shanxi Province[J]. Geolgical Bulletin of China,2022,41(7):1282 − 1290. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIA Runxing, FANG Weixuan, ZHANG Jianguo, et al. The formation mechanism of ground fissures in the Qingxu Taigu area of Shanxi Province[J]. Geolgical Bulletin of China, 2022, 41(7): 1282 − 1290. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 范宣梅,方成勇,戴岚欣,等. 地震诱发滑坡空间分布概率近实时预测研究——以2022年6月1日四川芦山地震为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2022,30(3):729 − 739. [FAN Xuanmei,FANG Chengyong,DAI Lanxin,et al. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides: Take the Lushan Earthquake on June 1,2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2022,30(3):729 − 739. (in Chinese with English abstract)] FAN Xuanmei, FANG Chengyong, DAI Lanxin, et al. Near real time prediction of spatial distribution probability of earthquake-induced landslides: Take the Lushan Earthquake on June 1, 2022 as an example[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2022, 30(3): 729 − 739. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 殷跃平,王文沛,张楠,等. 强震区高位滑坡远程灾害特征研究——以四川茂县新磨滑坡为例[J]. 中国地质,2017,44(5):827 − 841. [YIN Yueping,WANG Wenpei,ZHANG Nan,et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area:A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County,Sichuan Province[J] Geology in China,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YIN Yueping, WANG Wenpei, ZHANG Nan, et al. Long runout geological disaster initiated by the ridge-top rockslide in a strong earthquake area: A case study of the Xinmo landslide in Maoxian County, Sichuan Province[J] Geology in China, 2017, 44(5): 827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 杨琴,范宣梅,许强,等. 北川唐家湾滑坡变形历史与形成机制研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(2):136 − 141. [YANG Qin,FAN Xuanmei,XU Qiang,et al. A study of the deformation history and mechanism of the Tangjiawan landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2017,44(5):827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Qin, FAN Xuanmei, XU Qiang, et al. A study of the deformation history and mechanism of the Tangjiawan landslide[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2017, 44(5): 827 − 841. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] CHEN G,JIN JC,MENG X,et al. Influence of tectonic effects on the formation and characteristics of landslide dams on the NE Tibetan Plateau:A case study in the Bailong River Basin,China[J]. Landslides,2024:1 − 19.
[12] YU H,LI A,et al. "Present-day crustal deformation and strain transfer in northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters,487(2018):179 − 189.
[13] 周保,马涛,魏正发,等. 黄河上游曲哇加萨滑坡“9•20”动力学过程模拟与分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):9 − 15. [ZHOU Bao,MA Tao,WEI Zhengfai,et al. Dynamic simulation and analysis of “9•20” sliding process of Quwajiasa landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):9 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHOU Bao, MA Tao, WEI Zhengfai, et al. Dynamic simulation and analysis of “9•20” sliding process of Quwajiasa landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 9 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 魏刚,殷志强,马吉福,等. 黄河上游阿什贡滑坡群发育期次及演化过程分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(6):133 − 140. [WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,MA Jifu,et al. An analysis of forming stages and evolution process of the Ashigong landslide cluster in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(6):133 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, MA Jifu, et al. An analysis of forming stages and evolution process of the Ashigong landslide cluster in the upper reaches of the Yellow River[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(6): 133 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 李小林,郭小花,李万花. 黄河上游龙羊峡—刘家峡河段巨型滑坡形成机理分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2011,19(4):516 − 529. [LI Xiaolin,GUO Xiaohua,LI Wanhua. Mechanism of giant landslides from Longyangxia Vally to Liujiaxia Vally along upper Yellow River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2011,19(4):516 − 529. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.013 LI Xiaolin, GUO Xiaohua, LI Wanhua. Mechanism of giant landslides from Longyangxia Vally to Liujiaxia Vally along upper Yellow River[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2011, 19(4): 516 − 529. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2011.04.013
[16] 张永双,杜国梁,姚鑫,等. 塔吉克斯坦MS7.2级地震滑坡危险性快速评估及其对中国西部边疆山区巨灾风险防控的启示[J]. 地质学报,2023,97(5):1371 − 1382. [ZHANG Yongshuang,DU Guoliang,YAO Xin,et al. Rapid assessment of landslide risk during the MS7.2 earthquake in Tajikistan inspiration on disaster risk prevention and control in the mountainous regions of western China's border regions[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2023,97(5):1371 − 1382. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.05.001 ZHANG Yongshuang, DU Guoliang, YAO Xin, et al. Rapid assessment of landslide risk during the MS7.2 earthquake in Tajikistan inspiration on disaster risk prevention and control in the mountainous regions of western China's border regions[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 2023, 97(5): 1371 − 1382. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2023.05.001
[17] 邓威,肖世国. 含裂隙近水平红层软岩边坡渗透稳定性模型试验[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2024,51(1):57 − 68. [DENG Wei,XIAO Shiguo. Model test on stability of soft rock slopes composed of nearly horizontal redbeds with cracks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2024,51(1):57 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DENG Wei, XIAO Shiguo. Model test on stability of soft rock slopes composed of nearly horizontal redbeds with cracks[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2024, 51(1): 57 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 刘建强,许强,郑光,等. 贵州省鸡场滑坡地下水化学特征反映的水-岩(土)作用[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):132 − 140. [LIU Jianqiang,XU Qiang,ZHENG Guang,et al. Water-rock /soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Jianqiang, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Water-rock /soil interaction reflected by the chemical characteristics of groundwater of Jichang landslide in Guizhou Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 132 − 140. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] KONG Lingwei,ZENG Zhixiong,BAI Wei,et al. Engineering geological properties of weathered swelling mudstones and their effects on the landslides occurrence in the Yanji section of the Jilin-Hunchun high-speed railway[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2018,77(4):1491 − 1503. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-017-1096-2
[20] ZHOU Zhe,CHEN Shanxiong,WANG Yinhui,et al. Crack evolution characteristics and cracking mechanism of red beds in central Sichuan during seepage and swelling[J]. Geofluids,2021,Article ID 9981046:1 − 19.
[21] WANG H J,SUN P,ZHANG S,et al. Rainfall-induced landslide in loess area,Northwest China:A case study of the Changhe landslide on September 14,2019,in Gansu Province[J]. Landslides,2020,17(9):2145 − 2160 DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01460-0
[22] LIU Y J,CHIU Y Y,TSAI F T C,et al. Analysis of landslide occurrence time via rainfall intensity and soil water index ternary diagram[J]. Landslides,2022,19(12):2823 − 2837. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-022-01944-1
[23] 魏刚,殷志强,罗银飞,等. 黄河上游康杨滑坡堆积体特征及形成机理分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(2):1 − 8. [WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,LUO Yinfei,et al. Analysis on the accumulation deposits characteristics and formation mechanism of Kangyang landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(2):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, LUO Yinfei, et al. Analysis on the accumulation deposits characteristics and formation mechanism of Kangyang landslide in the upper reaches of Yellow River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(2): 1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[24] CHEN L,YANG H,SONG K,et al. Failure mechanisms and characteristics of the Zhongbao landslide at Liujing Village,Wulong,China[J]. Landslides,2021,18(4):1445 − 1457. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-020-01594-1
[25] 万飞鹏,杨为民,邱占林,等. 甘肃岷县纳古呢沟滑坡-泥石流灾害链成灾机制及其演化[J]. 中国地质,2023,50(3):911 − 925. [WAN Feipeng,YANG Weimin,QIU Zhanlin,et al. Disaster mechanism and evolution of Nagune Gully landslide-debris flow disaster chain in Minxian County,Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China,2023,50(3):911 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WAN Feipeng, YANG Weimin, QIU Zhanlin, et al. Disaster mechanism and evolution of Nagune Gully landslide-debris flow disaster chain in Minxian County, Gansu Province[J]. Geology in China, 2023, 50(3): 911 − 925. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[26] GRABER A,SANTI P,MEZA Arestegui P. Constraining the critical groundwater conditions for initiation of large,irrigation-induced landslides,Siguas River Valley,Peru[J]. Landslides,2021,18(12):3753 − 3767. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-021-01767-6
[27] 史立群,魏刚,殷志强,等. 青海尖扎盆地寺门村滑坡发育特征及成因分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):15 − 21. [SHI Liqun,WEI Gang,YIN Zhiqiang,et al. Characteristics and formation of Simencun landslides in Jianzha Basin of Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):15 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SHI Liqun, WEI Gang, YIN Zhiqiang, et al. Characteristics and formation of Simencun landslides in Jianzha Basin of Qinghai Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(5): 15 − 21. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[28] 冉林,马鹏辉,彭建兵,等. 甘肃黑方台“10•5”黄土滑坡启动及运动特征分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(6):1 − 9. [RAN Lin,MA Penghui,PENG Jianbing,et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10•5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform,Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(6):1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)] RAN Lin, MA Penghui, PENG Jianbing, et al. The initiation and motion characteristics of the “10•5” loess landslide in the Heifangtai platform, Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(6): 1 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[29] 潘保田. 贵德盆地地貌演化与黄河上游发育研究[J]. 干旱区地理,1994(3):43 − 50. [PAN Baotian. Study on the landform evolution of the Guide Basin and the development of the upper Yellow River[J]. Arid Area Geography,1994(3):43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.13826/j.cnki.cn65-1103/x.1994.03.006. PAN Baotian. Study on the landform evolution of the Guide Basin and the development of the upper Yellow River[J]. Arid Area Geography, 1994(3): 43 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.13826/j.cnki.cn65-1103/x.1994.03.006.
[30] 赵无忌,殷志强,马吉福,等. 黄河上游贵德盆地席芨滩巨型滑坡发育特征及地貌演化[J]. 地质论评,2016,62(3):709 − 721. [ZHAO Wuji,YIN Zhiqiang,MA Jifu,et al. Development characteristics and geomorphological evolution of the Xijitan giant landslide in the Guide Basin of the Upper Yellow River[J]. Geological Review,2016,62(3):709 − 721. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.16509/j.georeview.2016.03.013. ZHAO Wuji, YIN Zhiqiang, MA Jifu, et al. Development characteristics and geomorphological evolution of the Xijitan giant landslide in the Guide Basin of the Upper Yellow River[J]. Geological Review, 2016, 62(3): 709 − 721. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.16509/j.georeview.2016.03.013.
[31] 赵无忌. 黄河上游贵德盆地滑坡泥石流扇发育特征及地貌演化过程[D]. 北京:中国地质大学(北京),2015. [ZHAO Wuji. The formation characteristics and geomorphical evolution of the landslides and debris flow fans in Guide Basin,the upper Yellow River [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing),2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Wuji. The formation characteristics and geomorphical evolution of the landslides and debris flow fans in Guide Basin, the upper Yellow River [D]. Beijing: China University of Geosciences (Beijing), 2015. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[32] CRADDOCK W H, KIRBY E, HARKINS N W, et al. Rapid fluvial incision along the Yellow River during headward basin integration[J]. Nature Geoscience,2010(3):209 − 213.
[33] ZHANG H, ZHANG P, CHAMPAGNAC J D, et al. Pleistocene drainage reorganization driven by the isostatic response to deep incision into the northeastern Tibetan Plateau[J]. Geology, 2014, 42(4): 303-306.
[34] 周保. 黄河上游(拉干峡—寺沟峡段)特大型滑坡发育特征与群发机理研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学, 2010. [ZHOU Bao. Study on the development characteristics and mass mechanism of super-large landslide in the upper reaches of the Yellow River (Laganxia-Sigouxia section)[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHOU Bao. Study on the development characteristics and mass mechanism of super-large landslide in the upper reaches of the Yellow River (Laganxia-Sigouxia section)[D]. Xi’an: Chang’an University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] National Earth System Science Data Center,National Science & Technology Infrastructure of China (http://www.geodata.cn).
[36] 刘佑荣,唐辉明. 岩体力学[M]. 北京:化学工业出版社,2009. [LIU Yourong,TANG Huiming. Rock mass mechanics[M]. Beijing:Chemical Industry Press,2009. (in Chinese)] LIU Yourong, TANG Huiming. Rock mass mechanics[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2009. (in Chinese)





 下载:
下载:

























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS