A review of earthquake-induced loess landslides research and future prospects
-
摘要:
黄土地区地貌形态复杂,地震频发,地震滑坡灾害严重。黄土地震滑坡受多种因素影响,包括黄土边坡地形地貌、地层岩性、动力响应,黄土强度和动力特性,水文地质条件等。目前,黄土地震滑坡研究主要采用室内试验、物理与数值模型试验、野外调研、遥感与监测等手段,研究内容包括黄土地震滑坡成因机理、发育特征与分布、滑坡动力响应和稳定性等方面。文章阐述了黄土地震滑坡国内外研究现状,介绍了一种考虑地震波动特性的拟动力评价方法,并对基于拟动力法开展黄土地震滑坡研究进行了展望。通过分析黄土地震滑坡力学成因机制、研究黄土滑坡地震液化现象、讨论黄土地震滑坡失稳特征,提出能够精确评价黄土地震滑坡稳定性的计算方法,可以为黄土地区防震减灾提供理论依据,也是今后研究的重点。
Abstract:The loess region is characterized by complex geomorphological patterns. This region is prone to frequent earthquakes with serious seismic landslide disasters. Loess seismic landslides are affected by a variety of factors, including the topography and geomorphology of loess slopes, stratigraphic lithology, dynamic responses, strength and dynamic characteristics of loess, and hydrogeological conditions. Current research on loess seismic landslides primarily involves laboratory experiments, physical and numerical simulations, field investigations, and remote sensing and monitoring techniques. The research focuses on the mechanisms, development characteristics, distribution, dynamic responses, and stability of loess seismic landslides. This paper reviews the current state of both domestic and international research on loess seismic landslides, introduces the pseudo-dynamic method that considers seismic wave propagation characteristics, and outlines future research prospects based on this method. By analyzing the mechanics mechanisms of loess seismic landslide, investigating the seismic liquefaction phenomena of loess landslides, and discussing the instability characteristics of these landslides, this study proposes a calculation method to accurately evaluate the stability of loess seismic landslides. This research can provide a theoretical basis for earthquake disaster prevention and mitigation in loess areas, and it represents a key focus for future studies.
-
Keywords:
- pseudo-dynamic method /
- loess /
- earthquake /
- landslide /
- slope
-
0. 引言
凉山州地处横断山系东北缘、川滇构造带南段,受活动构造、地形地貌、河流切割等作用,地质灾害发育且频发,时常造成群死群伤和巨大经济损失,如2003年普格县“6•20”泥石流[1]、2004年德昌县“8•24”群发型泥石流[2]、2015年雷波县碉楼沟泥石流[3]、2017年普格县荞窝镇8·8泥石流[4]、2019年甘洛县群发性山洪泥石流[5]、2019年甘洛县“8•14”埃岱村滑坡[6]等。
近年来,许多学者对凉山州突发重大地质灾害的发育特征、成灾机理、破坏模式、防治措施等方面进行了研究:在滑坡灾害研究方面,以会理县老营盘村[7]、美姑县火洛村滑坡[8]、美姑县洛渣滑坡[9]、普格县姚家山滑坡[10]、宁南县水塘村滑坡[11]、西昌市太和矿北采场滑坡[12]为研究对象,开展了滑坡的形成机理和稳定性研究;在古滑坡复活研究方面,以木里县卡基娃滑坡[13]、雷波县马湖古滑坡群[14]、美姑县拉马阿觉滑坡[15]、金阳县城区古滑坡[16]、盐源县玻璃村滑坡[17]为研究对象,开展了古滑坡复活特征、成因机制、影响因素研究;在火后泥石流研究方面,以木里县黄泥巴沟泥石流[18]和项脚沟泥石流[19]、西昌市响水沟泥石流[20]和电池厂沟泥石流[21]、喜德县中坝村泥石流[22]为研究对象,开展了火后泥石流发育特征、成灾机理研究;在暴雨诱发泥石流研究方面,以2004年德昌县群发泥石流[23]、2009年金阳县地洛电站泥石流[24]等为研究对象,开展了泥石流成灾过程、特征成因、形成机理研究;在链式灾害研究方面,以白沙村滑坡-碎屑流[25]、埃岱村滑坡-碎屑流[6]、阿坡洛滑坡-堰塞湖[26]和采书组滑坡-堰塞湖[27]为研究对象,开展了滑坡发育特征、成灾机理和运动过程研究。但是,对于凉山州地质灾害的整体发育特征、灾情特征、主要致灾类型等方面缺乏系统性总结与研究。
本文基于凉山州地质灾害数据和资料,分析了凉山州地质灾害整体发育特征和灾情特征,总结提炼了7种主要致灾类型,通过实例逐一分析了灾害发育特征,以期对凉山州地质灾害的防灾减灾工作提供数据支撑和科学参考。
1. 地质环境背景
凉山彝族自治州,位于四川省西南部,地势西北高,东南低,北部高,南部低。地处杨子古陆块西缘,川滇构造带南段,境内构造发育,主要构造体系有:安宁河构造带、小江构造带、青藏川“歹”字形构造带、玉树—甘孜构造带、龙门山构造带、雷波—马边构造带。地处中国南北地震带中段,是构造地震活动强烈地区之一。位于扬子和巴颜喀拉秦岭两大地层区,金矿—木里深大断裂,以东属扬子地层区,以西的木里县和冕宁县西缘属巴颜喀拉秦岭地层区,地层复杂,变化较大。
位于川西南横断山系东北缘,界于四川盆地和云南高原之间,地形地貌复杂,地势西北高、东南低,主要山系有大凉山山系、小相岭—鲁南山山系、大雪山山系。地貌按成因分为河谷堆积地貌、中山地貌和构造剥蚀高山地貌;中山地貌占全州面积的78%,山势相对陡峭,河谷宽阔,多呈“U”型,岸坡平缓;构造剥蚀高山地貌主要分布在凉山州西北部的木里县,占全域面积的20%,切割剧烈,山高谷深,呈狭窄“V”型。
属亚热带季风气候,四季不明显,但干湿分明。全州年平均气温4.6 °C,年均降水量为995.5 mm,7月份的月均降水量最高,达274.1 mm,5—9月份降雨量约占全年总量的79.24%。金沙江干热河谷年降水量600 mm左右,气候炎热少雨,植被稀少,水土流失严重,生态十分脆弱,物理风化作用强烈,干旱易发生森林火灾,自然灾害特别突出,如木里县(2019年、2020年)、西昌市(2020年)、冕宁县(2021年)都曾发生规模较大的森林火灾,火灾造成植被和土壤不同程度的破坏,为火后泥石流等地质灾害的发生提供了丰富的物源。境内河流众多,由金沙江、雅砻江和大渡河三大水系组成。大于
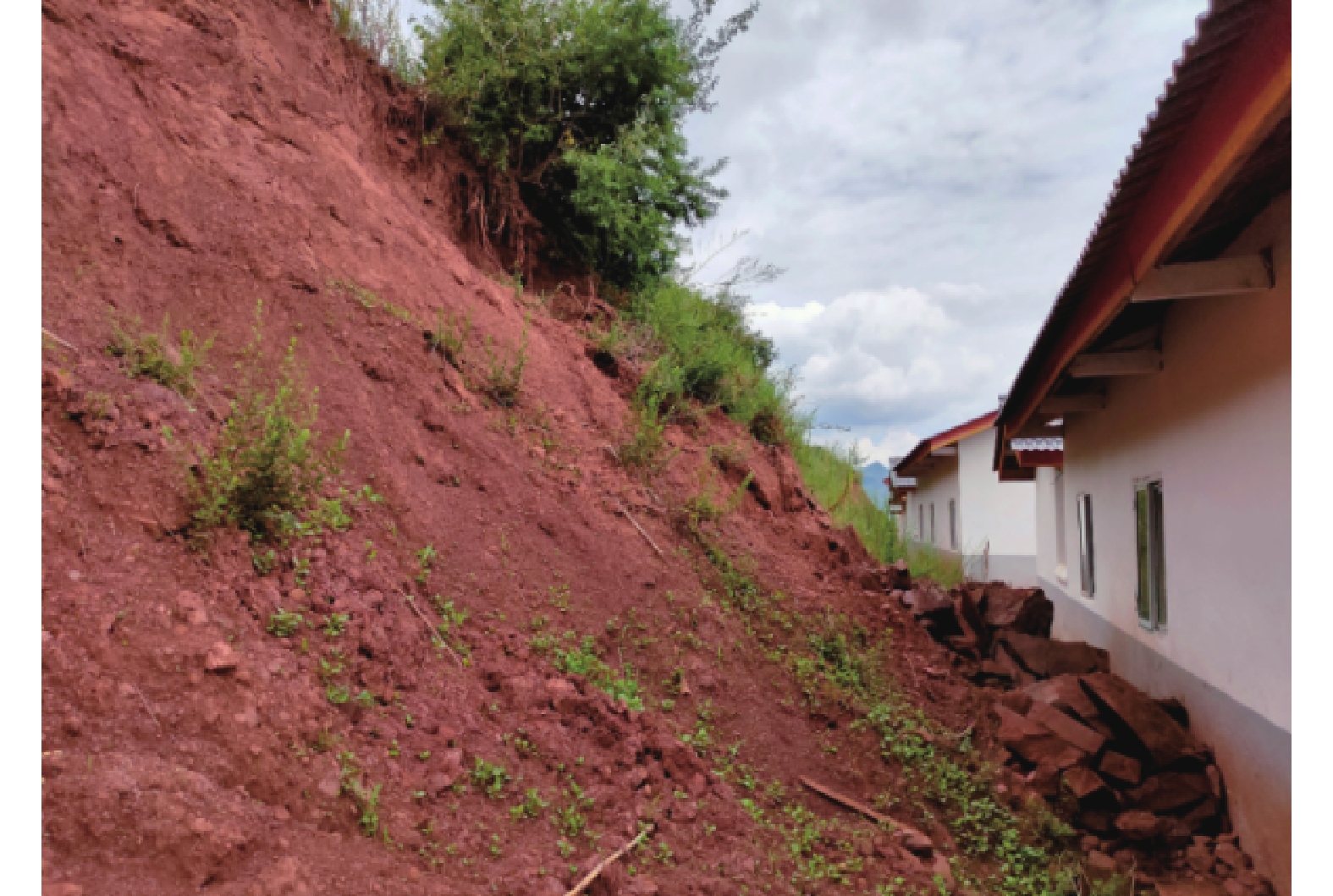
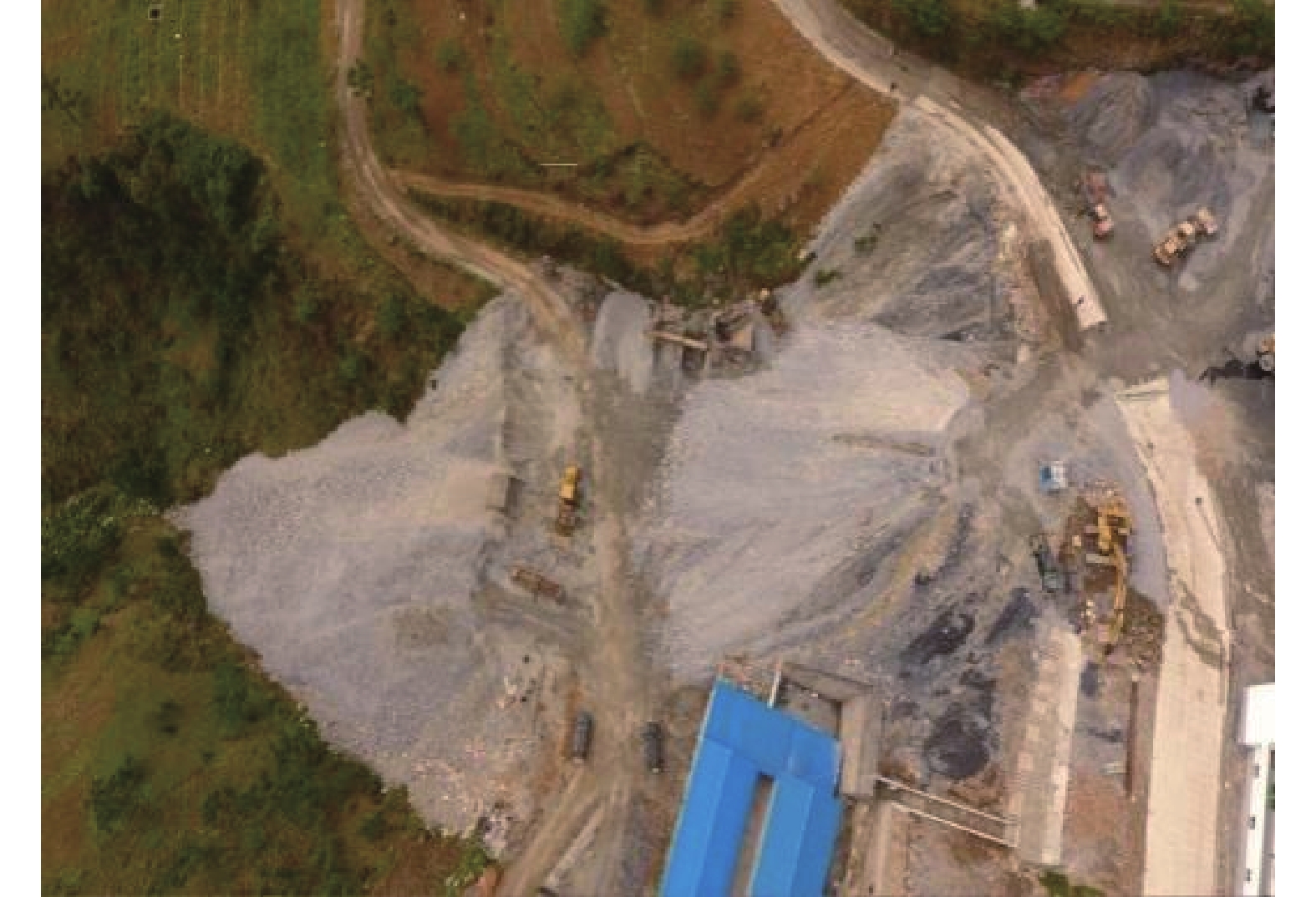
1000 km2的河流11条,还有邛海、马湖、泸沽湖等23个内陆淡水湖泊。水力资源极为丰富,有溪洛渡(1.26 ×106 kW)、白鹤滩(1.305 ×106 kW)等14座在建和规划的大型水电站。人类工程活动对原有地质环境的改造,是诱发凉山州地质灾害的重要因素之一。道路建设、切坡建房等人类活动(图1—2),对边坡不合理的开挖,破坏斜坡体稳定性,在降雨、地震等诱发因素下更容易发生滑坡灾害。凉山州矿产资源丰富,矿区内废石、弃渣的不合理堆放(图3),会造成弃渣斜坡的失稳滑动,也为矿渣型泥石流的形成提供丰富物源。
2. 凉山州地质灾害发育特征
2.1 地质灾害类型
四川省是西南地区地质灾害点数量最多的省份[28],数量达30239处;凉山州所处的川西地区共发育地质灾害
16411 处[29]。依据《四川省凉山州(1∶100 000)地质灾害风险调查评价成果报告》中数据显示,凉山州地质灾害总数4016 处(截至2021年底)(图4、表1),约占全省灾害总数量的13.4%,其中滑坡2674 处、泥石流1087 处、崩塌249处、地面塌陷6处,分别占全州总数的66.6%、27.1%、6.2%、0.15%。从灾害类型和规模等级看,滑坡以中小型为主,数量达2565 处,占滑坡总数的95.9%;崩塌以中小型为主,数量达245处,占崩塌总数的98.4%;泥石流以中小型为主,数量达1061 处,占泥石流总数的97.6%。如表2所示,滑坡按物质组成统计,以土质滑坡为主,数量达2950 处,占比98.4%;崩塌按物质组成统计,以岩质崩塌为主,数量达305处,占比95.91%;泥石流按流域形态统计,以沟道型泥石流为主,数量达1177 处,占比96.55%。表 1 凉山州地质灾害发育类型及数量Table 1. Development types and quantities of geological hazards in Liangshan Prefecture规模 崩塌 滑坡 泥石流 地面塌陷 合计 占比/% 特大型 2 3 4 0 9 0.22 大型 2 106 22 0 130 3.24 中型 76 830 258 0 1164 28.98 小型 169 1735 803 6 2713 67.55 合计 249 2674 1087 6 4016 100 占比/% 6.20 66.58 27.07 0.15 100 表 2 凉山州不同类型地质灾害发育特征统计Table 2. Statistical analysis of development characteristics of different types of geological hazards in Liangshan Prefecture灾害类型 发育特征 数量/处 占比/% 滑坡 土质 2950 98.40 岩质 48 1.60 崩塌 土质 13 4.09 岩质 305 95.91 泥石流 沟道型 1177 96.55 坡面型 42 3.45 2.2 地质灾害人员伤亡及经济损失
收集和梳理凉山州各县有记录以来的历史重大地质灾害资料得到(表3),凉山州共计发生24起死亡10人以上的地质灾害,灾害类型以泥石流为主;造成伤亡最严重的灾害为1850年发生在西昌的7.5级地震,据记载地震及诱发的地质灾害造成约2.79万户人受灾,2.7万人死亡,2.6万余间房屋倒塌。
表 3 凉山州历史重大地质灾害灾情简表(死亡10人以上)Table 3. Summary of major historical significant geological disasters in Liangshan Prefecture (with 10 or more fatalities)序号 位置 发生日期 灾害类型 规模
/104 m3受灾对象 受灾人口/人 死亡/人 直接经济
损失/万元具体成因 1 西昌城区及周边乡镇 1850-09-12 7.5级地震 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 2.79万户 约27 000 不详 7.5级地震 2 会东县小田坝村下坝老街 1881-02-06 滑坡 不详 人、畜和房屋 不详 约30 不详 不详 3 喜德县东河 1891-07-05 泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 约1000 不详 暴雨 4 西昌市东河、西河 1942-06-16 山洪、泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 约120 不详 暴雨 5 西昌沿安宁河19个乡 1951-08-24 山洪、泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 15 不详 暴雨 6 西昌市东河 1955-07-14 山洪、泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 68 不详 暴雨 7 喜德县中沟 1957-06-29 泥石流 不详 居民、房屋、道路等 不详 84 不详 暴雨 8 冕宁县泸沽镇洛瓦村4组 1970-05-26 泥石流 530 原铁道部第二工程处食堂、
仓库和工棚500 104 不详 矿山开采 9 喜德县红莫镇司金沟3社 1972-08-01 泥石流 不详 村落、房屋 不详 200 3000 暴雨 10 甘洛县乌史大桥乡利子依达沟 1981-07-09 泥石流 30万 成昆铁路利子依达大桥、
旅客列车不详 240 2000 余万暴雨 11 会东县溜姑乡三家村 1988-06-01 泥石流 不详 公路大桥桥墩、工棚 26 13 不详 暴雨及冰雹 12 冕宁县漫水湾镇二村沟1组 1989-09-04 泥石流 不详 居民点、农田 3000 51 不详 暴雨 13 冕宁县漫水湾镇胜利村 1989-09-04 泥石流 不详 居民点、农田 500 12 不详 暴雨 14 德昌县永郎镇蒲坝村 1995-07-11 泥石流 2.5 聚集区 63 10 800 暴雨 15 普格县五道箐镇采阿咀沟 2003-06-20 泥石流 70 公路、房屋、通信光缆 58 10 100 暴雨 16 盐源县平川镇骡马铺村2组 2006-07-14 泥石流 100 聚集区 168 16 500 暴雨 17 冕宁县彝海乡勒帕村 2011-06-16 泥石流 不详 聚集区 不详 17 不详 暴雨 18 宁南县白鹤滩镇和平村
1组矮子沟2012-06-27 泥石流 8 分散农户、白鹤滩水
电站施工区不详 38 530 暴雨 19 雷波县岩脚乡金沙村 2013-07-27 滑坡-涌浪 不详 金沙江航道船只、对岸码头 不详 约20 不详 暴雨 20 普格县荞窝镇耿底村
4、5组桐子林沟2017-08-08 泥石流 1.03 通村公路、房屋 577 26 16000 暴雨 21 冕宁县棉沙镇许家坪村
1、2组下草坪子滑坡2012-07-12 滑坡 不详 公路、房屋 95 13 400 持续降雨 22 德昌县茨达镇新华村 2004-08-23 滑坡、泥石流 不详 聚集区 4960 17 不详 暴雨 23 德昌县乐跃镇乐跃沟村 2004-09-24 泥石流 不详 聚集区 不详 11 不详 暴雨 24 盐源县洼里乡手爬村二组北沟段 2012-08-30 泥石流、滑坡 不详 聚集区 241 13 520 暴雨 根据2006—2020年地质灾害灾情资料,凉山州共发生46起因灾伤亡的地质灾害(表4),包括泥石流30起、滑坡9起、崩塌7起,共计死亡156人,失踪66人,受伤77人,直接经济损失
29200 万元。按照灾情等级划分,特大型2起、大型4起、中型17起、小型23起。其中2起特大型灾情分别是:2017年8月8日凌晨4点至4点30分,普格县荞窝镇耿底村4组和5组桐子林沟发生泥石流灾害,导致25人死亡,71间房屋损毁,1.6亿元经济损失;2012年6月28日,宁南县白鹤滩镇矮子沟暴发特大山洪泥石流灾害,造成白鹤滩镇1540 户6151 人受灾,白鹤滩电站水电四局施工人员20人失踪、20人遇难、13人受伤的严重后果。表 4 凉山州各县市灾情统计表(2006—2020年)Table 4. Statistical table of disaster situation for each county and city in Liangshan Prefecture (2006—2020)县/市 灾情数量/起 死亡失踪/人 经济损失/万元 县/市 灾情数量/起 死亡失踪/人 经济损失/万元 德昌县 2 3 410 冕宁县 2 20 520 甘洛县 3 4 111 木里县 3 16 220 会东县 1 2 15 宁南县 8 52 6850 会理市 2 1 75 普格县 4 31 17470 金阳县 4 13 170 喜德县 1 6 100 雷波县 7 25 745 盐源县 3 30 1470 美姑县 2 8 546 越西县 2 1 118 昭觉县 2 10 380 合计 46 222 29200 3. 主要致灾类型
梳理分析凉山州发生的重大突发地质灾害数据,总结提炼了凉山州7种地质灾害主要致灾类型,分别是红层滑坡、复活型古滑坡、库岸型滑坡、含煤层型滑坡、矿渣型泥石流、火后型泥石流、链式灾害。
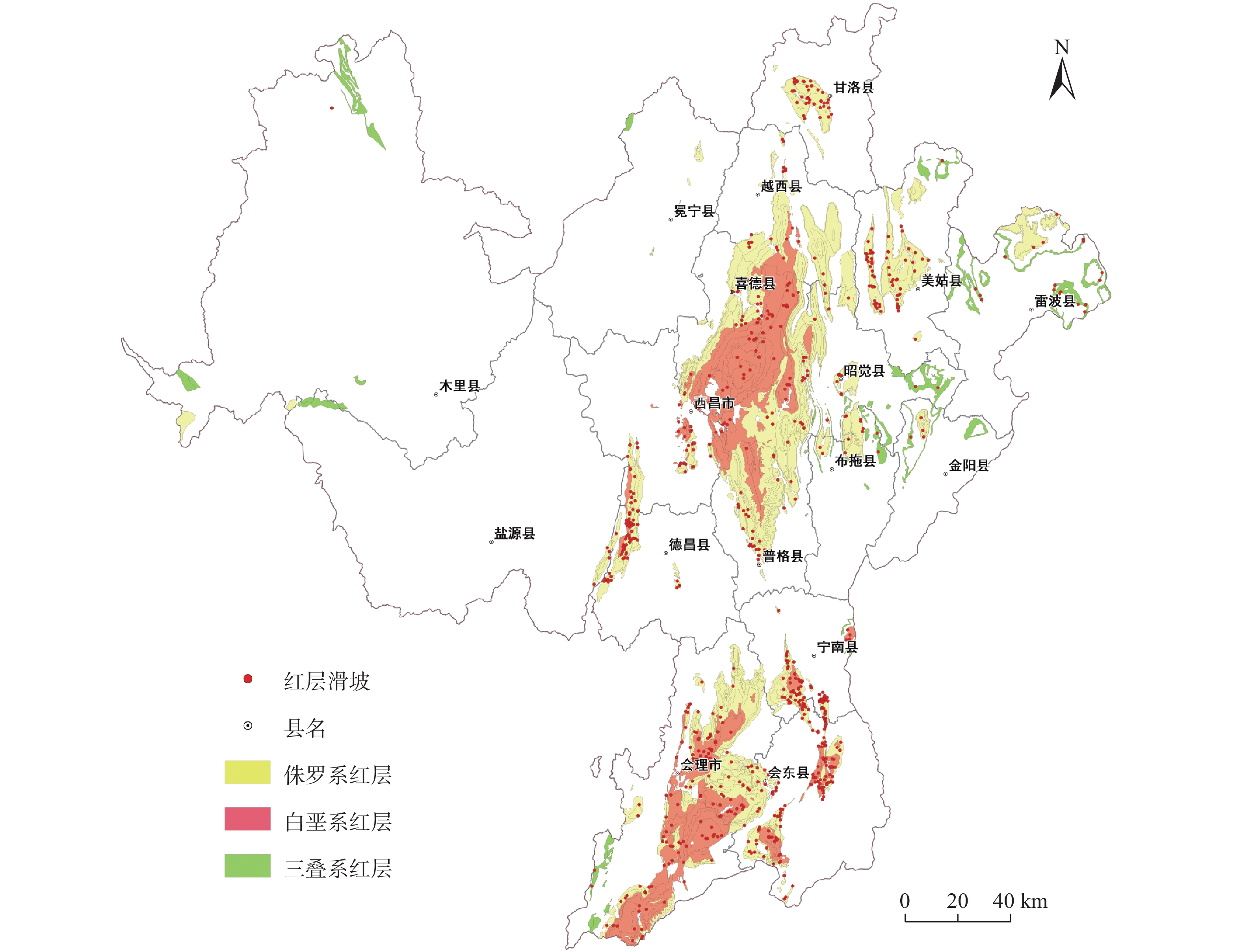
3.1 红层滑坡
凉山州发育红层滑坡729处,占滑坡总数的27.3%(图5),红层地层主要发育在凉山州南部的中低山区;统计红层滑坡发育的地层年代(表5),发育在侏罗系地层的红层滑坡数量最多,占红层滑坡总数的70.6%,发育在白垩系、三叠系地层的红层滑坡数量占比分别为26.1%、3.3%。红层边坡自稳能力差,不及时治理会发生变形破坏,进而诱发滑坡、崩塌、落石等地质灾害[30]。
表 5 凉山州红层红层滑坡统计Table 5. Statistical analysis of red-bed landslide in Liangshan Prefecture红层地层 面积/km2 数量/处 灾害密度
/(处·km−2)占比/% 侏罗系 5778 515 0.089 70.6 白垩系 3177 190 0.06 26.1 三叠系 837 24 0.029 3.3 会理市新发镇铜厂村1组老包滑坡(图6),出露岩性为第四系全新统残坡积层($ \mathrm{Q}\mathrm{h}^{el+dl} $)碎石土,下覆基岩为下震旦统澄江组(Z1c)粗粒长石石英砂岩夹紫红色含砾砂泥岩,岩层产状185°∠35°,岩体易风化破碎,遇水极易软化解体。滑坡附近有一条近南北走向逆断层通过,大致沿红沙沟延伸。老包滑坡所在红沙沟位置,均为断层破碎带,岩体异常破碎,地质条件脆弱,断层是滑坡形成的主要原因之一。同时,滑坡区地层遇水易软化解体,降雨入渗使岩土体饱水,造成自重加大和软弱结构面润滑,加之良好的临空面,最终在陡坡段形成滑坡。
3.2 复活型古滑坡
古滑坡在凉山州多有分布,如普格县螺髻山镇—扯扯街一线仍保留10处大型地震古滑坡,雷波县金沙江两岸古滑坡发育,由于人类工程活动、河流冲刷等因素,易引发古滑坡变形和复活。
金阳县天地坝镇老营盘村城北滑坡,顺层牵引式深层特大型滑坡(图7)。出露地层为含碎石粉质黏土、碎石土。主滑方向106°,平均宽度570 m,纵向长约630 m,滑体平均厚度35 m,总体积约
1.253 ×106 m3,滑坡平面形态呈舌型,滑体物质组成主要为碎石土、角砾土,局部夹块石、黏土,由于滑坡年代久远,滑体物质胶结良好。下覆基岩主要为下奥陶统湄潭组(O1m)页岩、灰岩及上寒武统二道水组($\in_3 e $)白云岩。由于金阳河的不断切割,致使前缘临空面不断加大,最终导致古滑坡的发生,近年来古滑坡未出现整体变形迹象。但由于人类工程活动的加剧,新建房屋大量填方、生活污水排放、降雨入渗等原因,古滑坡体局部区域出现了变形和次级滑动,滑坡左侧中部区域变形破坏较为强烈,地表可见发育有多条明显拉裂缝,房屋变形破坏较严重,形成体积约1.368×106 m3复活体。3.3 库岸型滑坡
库岸型滑坡主要发育在凉山州的白鹤滩、溪洛渡、乌东德、官地、锦屏二级、锦屏一级等水电站库区内。受库水位消落带影响,斜坡坡脚常发生滑塌现象,进而影响坡体稳定性,如木里县锦屏库区尾库段的后所乡、列瓦镇一带,发育有23处库岸型滑坡;布拖县金沙江沿岸合井—牛角湾一带,地处溪洛渡库区库尾,受库水位影响发育有大滩滑坡,麻地湾滑坡,贾沙田滑坡等库岸型滑坡;宁南县白鹤滩电站2021年水位抬升后,发育有17处塌岸隐患,多数为土质边坡(图8)。
木里县瓦厂镇纳子店村店扎组滑坡位于木里县瓦厂镇纳子店村店扎组(图9),木里河左岸。平面形态呈舌形,坡面形态呈折线形,相对高差约120 m,宽160 m,长330 m,主滑方向270°,平均厚10.0 m,体积约为52.8×104 m3,属中型土质滑坡。滑体物质主要为全新统的滑坡堆积($ Q\mathrm{h}_{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{\mathrm{ }}}\mathrm{\mathrm{ }}}}}^{\ del} $)的碎石土,下覆基岩为下奥陶统组瓦厂组(O1w)青灰色砂岩。受木里河立州水电站蓄水影响,在水位升降及斜坡土体饱水等作用下滑坡出现变形,2019、2020两年变形较剧烈,后部G227国道路面出现拉裂、下错,房屋墙体出现裂缝。
3.4 含煤层型滑坡
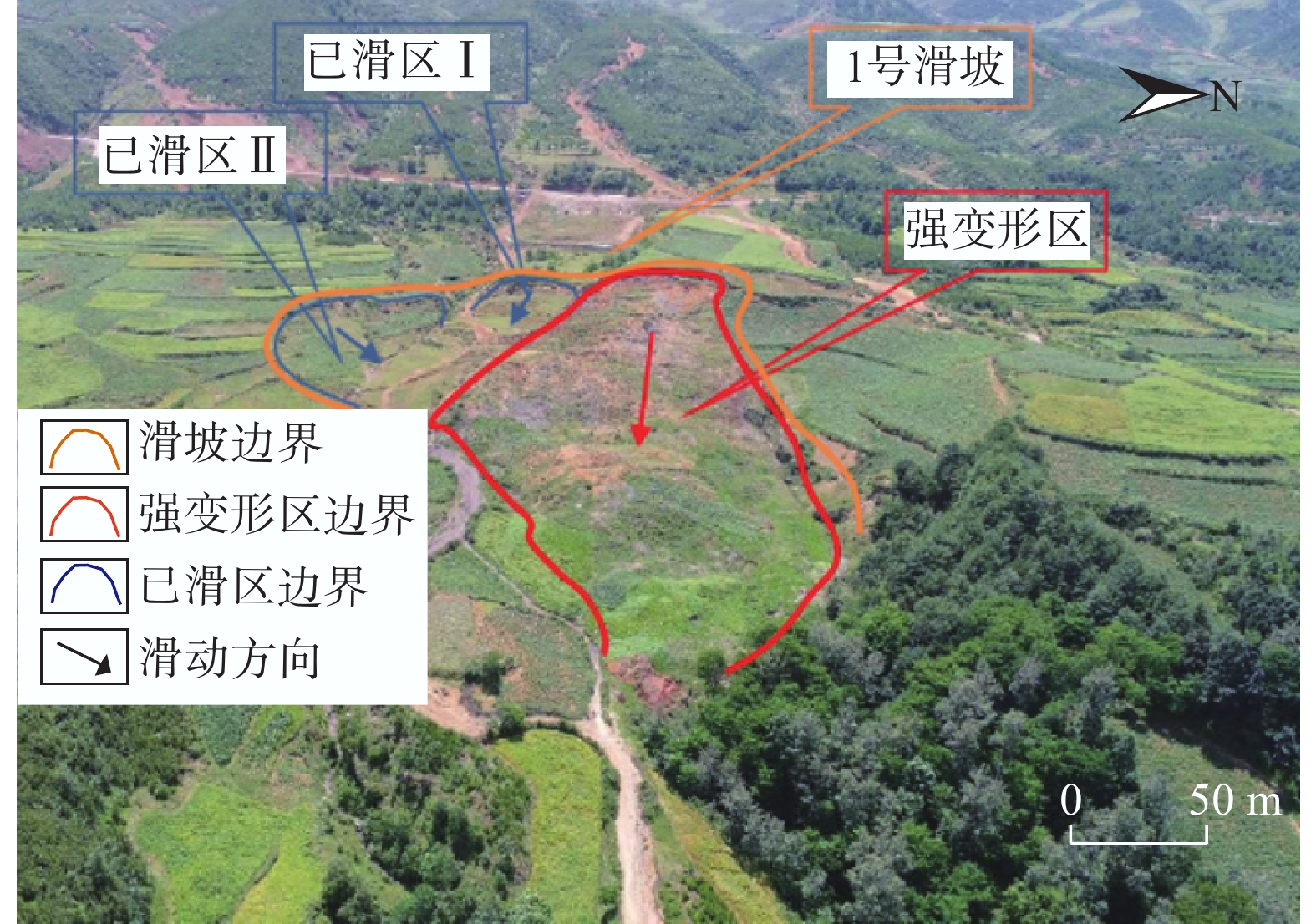
煤系地层主要发育在凉山州南部的中低山区,上三叠统白果湾组、须家河组、宝顶组等地层为主要产煤地层。布拖县勒吉村4组约坡吉乃滑坡,位于布拖县北部(图10),为一处沿基覆界面滑动的中型土质滑坡。20世纪80年代,滑坡前缘底部发现褐煤层,每到冬季当地村民集中开挖褐煤取暖,到2004年形成一高5~8 m近垂直人工边坡,2004年受强降雨影响,该人工边坡开始出现滑塌现象,边坡后缘出现贯通拉裂缝,2010年7月滑坡前缘整体垮塌,同年9月发生整体滑动。滑坡可分为强变形区、已滑区Ⅰ区、已滑区Ⅱ区。强变形区微地貌主要为陡坡、陡坎,横宽95~130 m,纵长约270 m,主滑方向89°,面积约2.45×104 m2,平均厚约12 m,总体积约29.4×104 m3,坡体基本解体,剖面形态呈三级平台,滑坡后壁坡度近垂直,相对高差约12 m,2015—2017年向右前侧滑动7~9 m;已滑区Ⅰ区位于1号滑坡体中右侧,横宽约60 m,纵向长约55 m,主滑方向99°后缘滑壁陡峭,中前部形成相对较缓的坡体,形成“上陡下缓”形态,体积约1.2×104 m3;已滑区Ⅱ区位于1号滑坡体右后侧,横向宽40~50 m,纵向长60~70 m,主滑方向59°,滑坡后壁高差约1.5 m,体积约2.57×104 m3。坡体含碎石黏土,下覆基岩为昔格达组砂质泥岩。
3.5 矿渣型泥石流
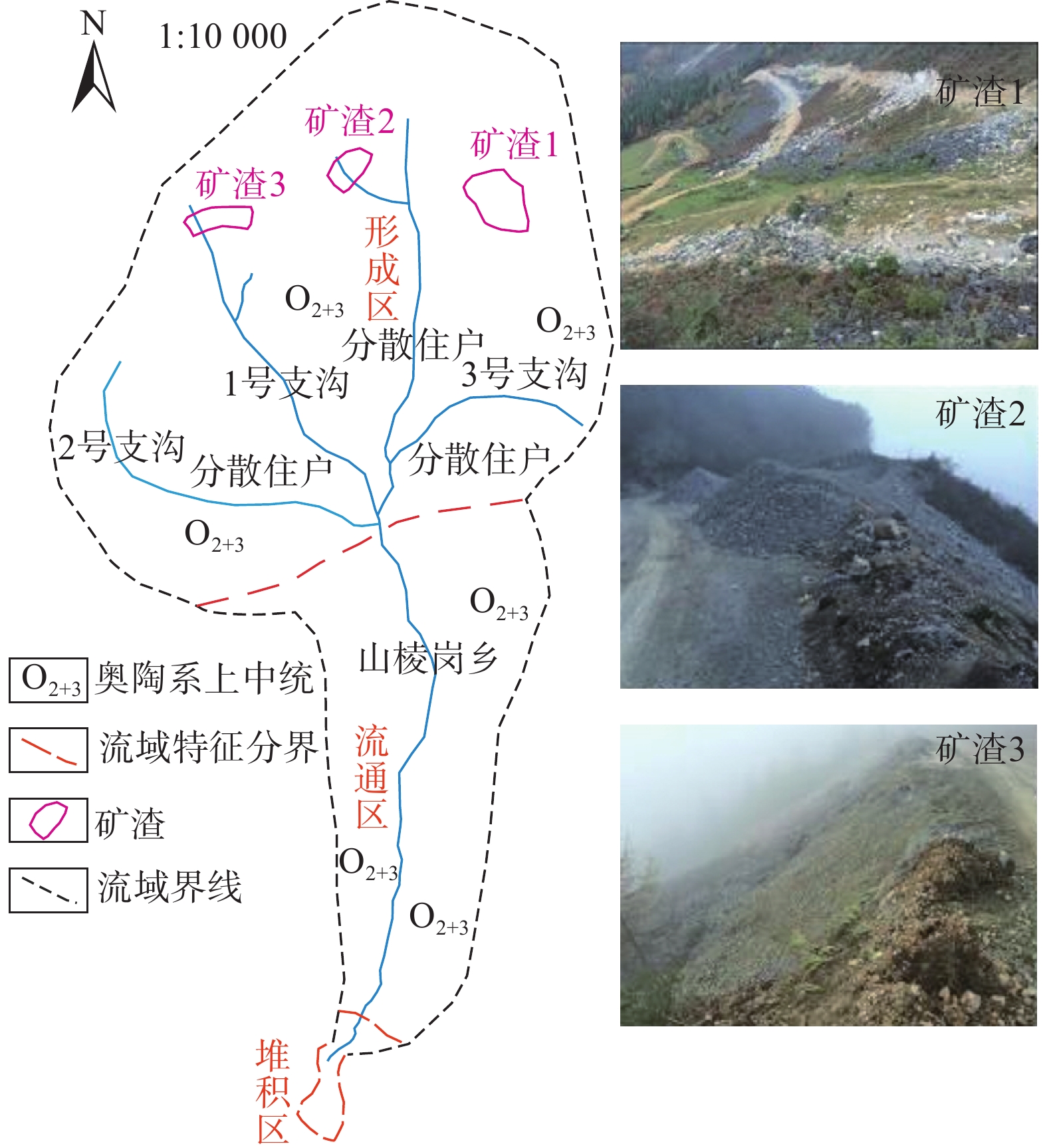
凉山州矿产资源丰富,矿山开采的矿渣、剥离废石、尾砂等废物,不合理的堆放,为泥石流灾害提供了丰富物源。雷波县西苏角河流域日格尔泥石流,位于山棱岗乡田坝村3、6组,沟口位于西苏角河(图11)。在1972年、2013年和2014年规模性暴发过,属于暴雨激发的中—高频中型稀性泥石流。单次冲淤堆积体积约0.72×104 m3,现沟内可参与泥石流活动的固体物源动储量达37.13×104 m3,2016年对该泥石流进行了排导槽治理。沟域高程差约为
1800 m,流域面积16.39 km2,主沟沟道长6.92 km,主沟呈“U”字型。由四条支沟交汇形成,汇水条件好,支沟多呈狭窄“V”字型,暴雨形成的地表径流是引发泥石流的主要水源。在流域的中上部为铅锌矿私挖开采地,采矿分选后大量的矸石沿沟道、公路堆积,成为了该沟的重要物源,现该私挖矿场已经关闭,其他物源来自于沟床侵蚀物源(沟床内松散堆积体)及坡面侵蚀物源。3.6 火后型泥石流
森林火灾是凉山州林区常见自然灾害,林火后根-土复合体的抗剪强度降低,土壤的黏聚力出现明显下降[31],火烧迹地在降雨条件下,极易发生火后泥石流,具有发生概率大幅提高、暴发所需降雨阈值明显降低等特点。冕宁县从2016年以来,每年均有火灾发生,仅2021年就发生了3次火灾,在安宁河流域集中发育有15处火后泥石流隐患点;西昌市经久乡一带2020年3月发生特大森林火灾,同年8月遭遇多次暴雨,诱发多条火后泥石流,经过火后次生灾害排查,确定了63条潜在泥石流沟。
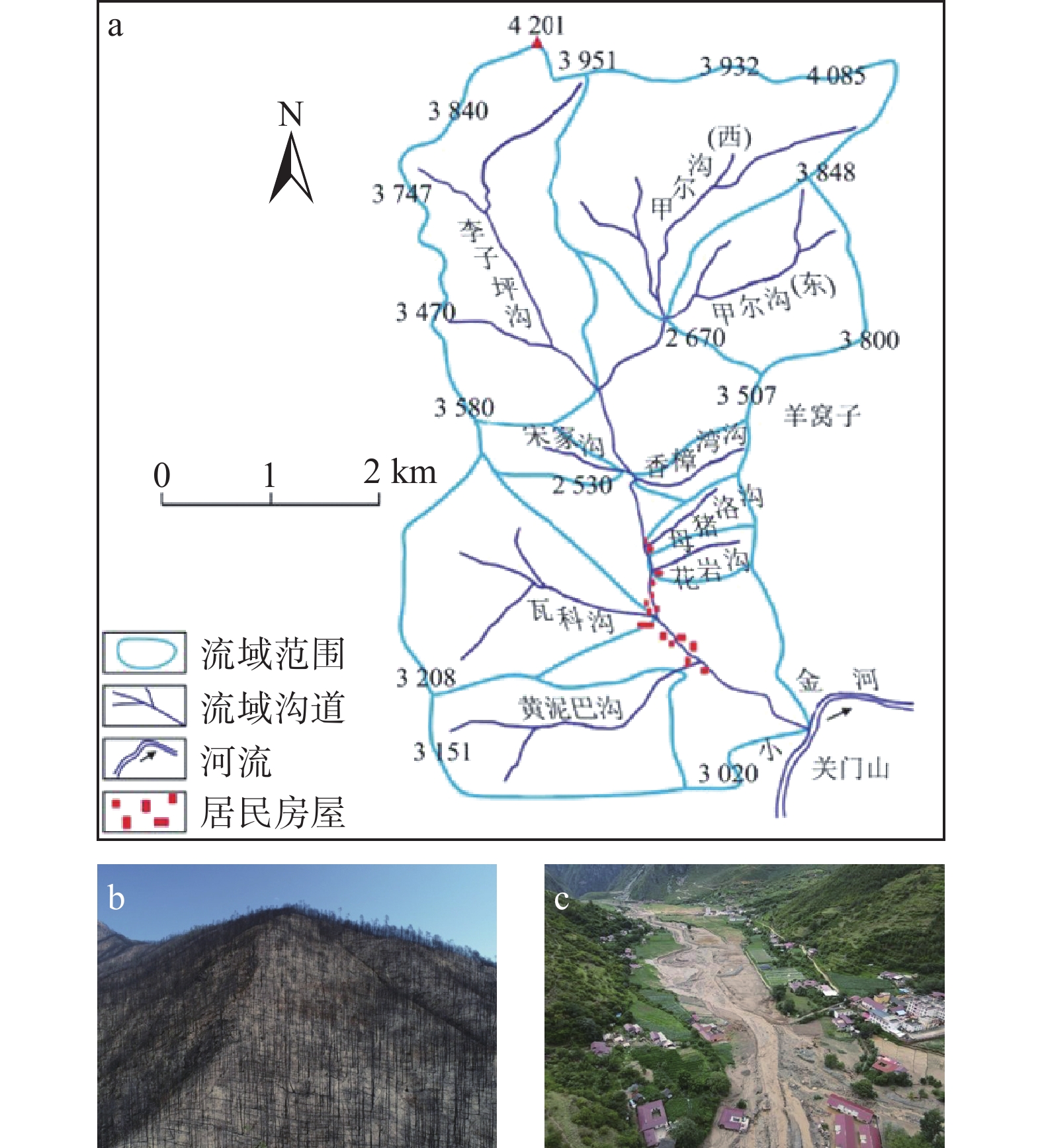
木里县项脚乡项脚沟流域火后泥石流就是此类泥石流的典型(图12)。2020年3月28日,木里县项脚乡及其毗邻乡镇发生森林火灾,其中项脚乡项脚沟流域的中、上部火灾导致植被遭受严重破坏,过火面积约37.97 km2,中度及重度火烈度区面积占比65.81%。自6月9日山顶附近局地短时强降雨激发甲尔沟暴发火后泥石流灾害以来,项脚沟主沟及宋家沟、香樟湾沟、母猪洛沟、花岩沟、黄泥巴沟等多条支沟于6月、7月先后7次发生不等规模火后泥石流,冲出固体物质10余万方,导致沟口22户居民建筑物被淤埋,直接经济损失超
2600 万元。2021年7月5日,短时强降雨导致项脚沟流域7条支沟再次相继发生泥石流灾害,携带大量粗大树木,冲出沟口物源达1.62×106 m3,沟道内分布有大量漂石,岩性以灰岩为主,其中最大颗粒直径为3.2 m×3.1 m×1.9 m。灾害造成186间房屋和乡道2 km受损,撤离避险251户1042 人,无人员伤亡。项脚沟流域面积77.12 km2,主沟长14.95 km,平均纵比降为110‰,流域最高海拔
4130 m,沟口最低海拔1820 m,最大高差2310 m,主沟沟道以宽“U“型谷为主。中上游呈“树枝状”水系,下游呈“掌状”水系,各级支流共计30余条,其中一级支沟13条。支沟多以”V”型谷为主,山体平均坡度多在40°以上,基岩出露较多。地层以三叠系西康群及上二叠统地层为主,岩性主要为变质砂岩、砂板岩、板岩、大理岩及结晶灰岩夹层、变质玄武岩,及少量千枚岩。流域内不良地质现象发育,松散固体物质2216.4 ×104 m3,动储量为2.928×106 m3,主要为早期崩滑堆积物源、坡面侵蚀物源、历史泥石流沟道堆积物源及火灾形成的灰烬及土壤结构扰动层等物源,火烧区物源主要分布于沟域顶部。3.7 链式灾害
按照诱发因素划分,地质灾害链包括内动力地质灾害链、外动力地质灾害链、人为活动地质灾害链和复合型地质灾害链[32],在高山峡谷、高地应力场、频繁的地震活动、暴雨及人类活动等复杂的内外动力耦合作用下,河谷地段往往造成大型的崩滑堵江断流形成堰塞湖的事件,从而使得灾害范围及灾害种类进一步扩大,形成灾害链[33]。
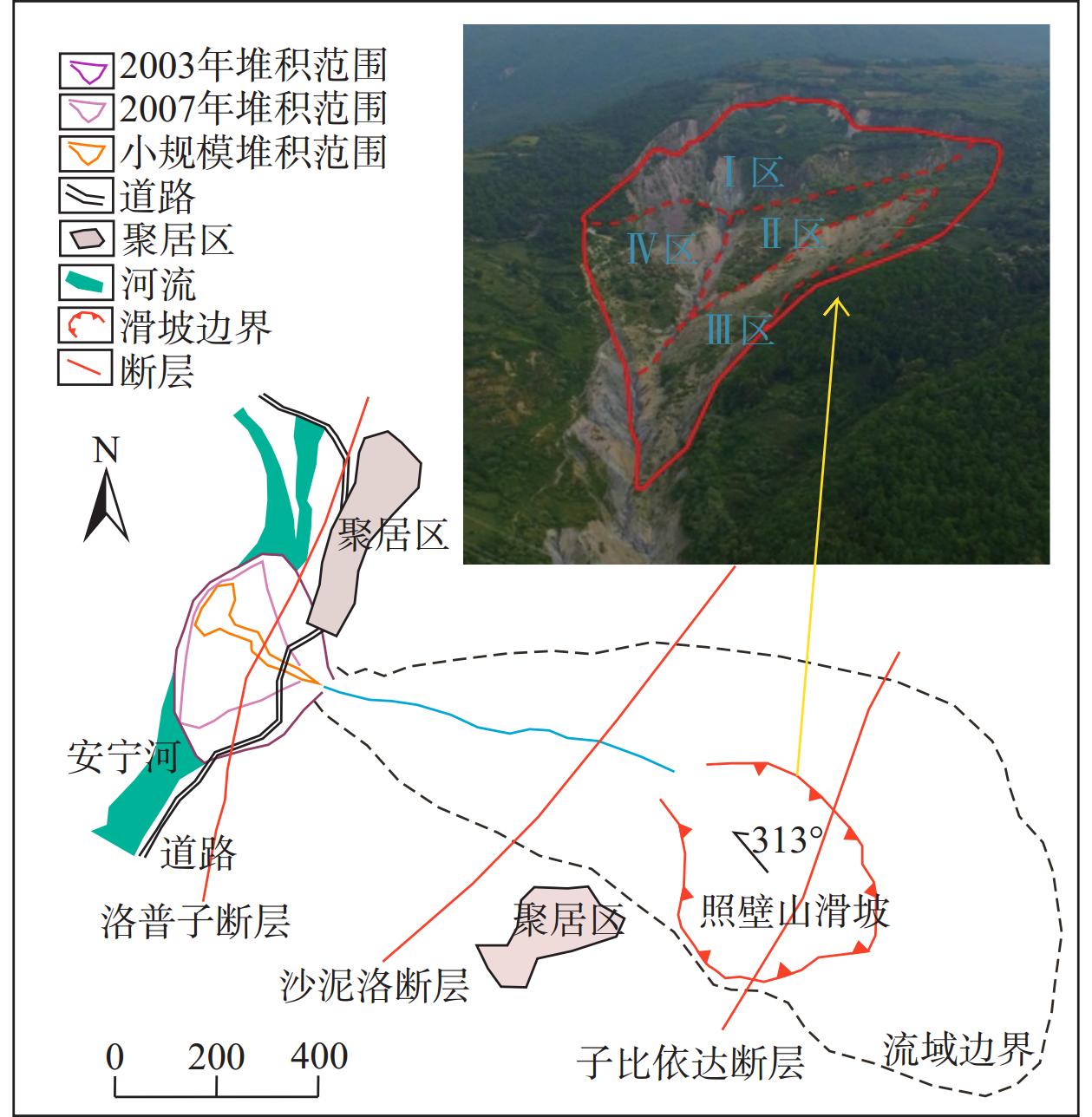
冕宁县照壁山滑坡位于冷渍沟上游(图13),滑坡呈“圈椅状”,主滑方向为313°,滑坡区地层主要为早震旦世苏雄组一段(Z1S1)变流纹、变英安岩,三叠系白果湾群(T3bg)砂岩、页岩,以及第四系残坡积物。大规模发生于2000年7月18日,滑坡发生时体积约337×104 m3,形成的碎屑流冲出冷渍沟口约30×104 m3,堵塞安宁河河道;剩余滑坡体堆积于冷渍沟中,此后雨季冷渍沟均发生规模不等的泥石流。2003年7月19日,冕宁县遭遇50年一遇暴雨(日降雨量达218.6 mm),冷渍沟暴发大规模泥石流,约30×104 m3固体物质冲出沟口,造成堆积扇上1人死亡,3辆汽车被掩埋,同时冲入安宁河造成河道堵塞,河水淤高翻越右岸防护堤,冲毁右岸部分房屋、耕地。2007年8月7日,冷渍沟再次暴发泥石流堵塞安宁河河道。2007年8月7日,冷渍沟再次暴发泥石流堵塞安宁河河道。
4. 结 论
(1)查明了凉山州地质灾害整体发育特征和灾情特征。凉山州地质灾害以滑坡、泥石流为主,分别占全州总数的66.6%、27.1%;滑坡以中小型土质滑坡为主,泥石流以中小型沟谷泥石流为主。统计分析凉山州有记录以来的灾情发现,凉山州共计发生24起死亡10人以上的地质灾害。2006—2020年,凉山州共发生46起因灾伤亡的地质灾害,以泥石流为主,数量达30起,灾情规模以中小型为主,分别达17起、23起。
(2)通过系统梳理凉山州地质灾害的发育特征,结合实例总结提炼7种主要致灾类型:①红层滑坡,是凉山州滑坡主要类型之一,遇水易软化解体,降雨入渗使岩土体饱水,自稳能力差;②复活型古滑坡,在凉山州多有分布,由于人类工程活动、河流冲刷等因素,易引发古滑坡变形和复活;③库岸型滑坡,主要发育在木里县、布拖县、宁南县的水电站库区内,受库水位消落带影响,斜坡坡脚滑塌,坡体稳定性降低形成滑坡;④含煤层型滑坡,多发育在主要发育在凉山州南部的煤系地层区域,对斜坡前缘不合理的采煤开挖,易诱发前缘滑塌并造成整体滑动;⑤矿渣型泥石流,是凉山州泥石流主要类型之一,矿山开采的矿渣、废石、尾砂等不合理堆放,为泥石流灾害提供了丰富物源,叠加良好汇水条件和暴雨等因素,易引发泥石流;⑥火后型泥石流,凉山州常发生森林火灾,火灾形成的灰烬及土壤结构扰动层等为泥石流提供了物源条件,火烧迹地遭遇暴雨后,易诱发火后泥石流;⑦链式灾害,由于凉山州构造活动强烈,山势陡峭,沟谷发育,在沟谷上游发生崩滑灾害后,易沿沟运动冲出,堵塞河道形成灾害链。
(3)针对凉山州不同致灾类型的地质灾害,在常态防灾减灾过程中应采取针对性防范措施,以达到精准防控的目的,如加强库区地质灾害的排查、监测和防治,特别是加强移民安置区地质灾害的防治,避免库岸型滑坡的产生;规范采煤采矿行为、科学合理的堆放废石弃渣等,避免发生含煤层型滑坡和矿渣型泥石流;严防森林火灾,火烧迹地应采取生物措施及时恢复植被生态并采取必要的治理措施,防止发生群发性火后泥石流;修路建房等工程活动应科学合理切坡,避免诱发崩滑灾害。后续还需深入开展不同致灾类型的地质灾害的形成机理、防治措施、风险管控等方面的研究。
-
-
[1] 唐辉明. 重大滑坡预测预报研究进展与展望[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(6):1 − 13. [TANG Huiming. Advance and prospect of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(6):1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TANG Huiming. Advance and prospect of major landslides prediction and forecasting[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(6): 1 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 铁永波,张宪政,卢佳燕,等. 四川省泸定县Ms 6.8级地震地质灾害发育规律与减灾对策[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2022,49(6):1 − 12. [TIE Yongbo,ZHANG Xianzheng,LU Jiayan,et al. Characteristics of geological hazards and it’s mitigations of the Ms 6.8 earthquake in Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2022,49(6):1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TIE Yongbo, ZHANG Xianzheng, LU Jiayan, et al. Characteristics of geological hazards and it’s mitigations of the Ms 6.8 earthquake in Luding County, Sichuan Province[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2022, 49(6): 1 − 12. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 黄润秋,李为乐. “5•12” 汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(12):2585 − 2592. [HUANG Runqiu,LI Weile. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May,2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(12):2585 − 2592. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 HUANG Runqiu, LI Weile. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May, 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(12): 2585 − 2592. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028
[4] 国务院抗震救灾总指挥部. 汶川特大地震抗震救灾总结报告[R]. 2008. [State Council Earthquake Relief Headquarters. Wenchuan earthquake relief summary report[R]. 2008. (in Chinese)] State Council Earthquake Relief Headquarters. Wenchuan earthquake relief summary report[R]. 2008. (in Chinese)
[5] 殷跃平. 汶川八级地震地质灾害研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2008,16(4):433 − 444. [YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake,Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2008,16(4):433 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.04.001 YIN Yueping. Researches on the geo-hazards triggered by Wenchuan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2008, 16(4): 433 − 444. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2008.04.001
[6] 张倬元. 工程地质分析原理[M]. 4版. 北京:地质出版社,2016. [ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Principles of engineering geological analysis[M]. 4th ed. Beijing:Geological Publishing House,2016. (in Chinese)] ZHANG Zhuoyuan. Principles of engineering geological analysis[M]. 4th ed. Beijing: Geological Publishing House, 2016. (in Chinese)
[7] 王椿镛,段永红,吴庆举,等. 华北强烈地震深部构造环境的探测与研究[J]. 地震学报,2016,38(4):511 − 549. [WANG Chunyong,DUAN Yonghong,WU Qingju,et al. Exploration on the deep tectonic environment of strong earthquakes in North China and relevant research findings[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica,2016,38(4):511 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Chunyong, DUAN Yonghong, WU Qingju, et al. Exploration on the deep tectonic environment of strong earthquakes in North China and relevant research findings[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 2016, 38(4): 511 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 孙金龙,徐辉龙,詹文欢,等. 南海北部陆缘地震带的活动性与发震机制[J]. 热带海洋学报,2012,31(3):40 − 47. [SUN Jinlong,XU Huilong,ZHAN Wenhuan,et al. Activity and seismogenic mechanism of the continental margin seismic belt in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography,2012,31(3):40 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SUN Jinlong, XU Huilong, ZHAN Wenhuan, et al. Activity and seismogenic mechanism of the continental margin seismic belt in the northern South China Sea[J]. Journal of Tropical Oceanography, 2012, 31(3): 40 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 徐杰,周本刚,计凤桔,等. 华北渤海湾盆地区大震发震构造的基本特征[J]. 地震地质,2012,34(4):618 − 636. [XU Jie,ZHOU Bengang,JI Fengju,et al. Features of seismogenic structures of great earthquakes in the Bohai Bay Basin area,North China[J]. Seismology and Geology,2012,34(4):618 − 636. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.008 XU Jie, ZHOU Bengang, JI Fengju, et al. Features of seismogenic structures of great earthquakes in the Bohai Bay Basin area, North China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2012, 34(4): 618 − 636. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2012.04.008
[10] 陈祥熊,袁定强,吴长江. 台湾海峡南部Ms 7.3地震震源破裂特征及东南沿海地震形势分析[J]. 地震学报,1996(2):145 − 155. [CHEN Xiangxiong,YUAN Dingqiang,WU Changjiang. Focal rupture characteristics of the Ms 7.3 earthquake in the south of Taiwan strait and analysis of seismic situation along the southeast coast[J]. Acta Seismological Sinica,1996(2):145 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Xiangxiong, YUAN Dingqiang, WU Changjiang. Focal rupture characteristics of the Ms 7.3 earthquake in the south of Taiwan strait and analysis of seismic situation along the southeast coast[J]. Acta Seismological Sinica, 1996(2): 145 − 155. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 王卫民,赵连锋,李娟,等. 四川汶川8.0级地震震源过程[J]. 地球物理学报,2008,51(5):1403 − 1410. [WANG Weimin,ZHAO Lianfeng,LI Juan,et al. Rupture process of the M 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake of Sichuan,China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2008,51(5):1403 − 1410. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.013 WANG Weimin, ZHAO Lianfeng, LI Juan, et al. Rupture process of the M 8.0 Wenchuan earthquake of Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2008, 51(5): 1403 − 1410. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0001-5733.2008.05.013
[12] 李锦轶,刘建峰,曲军峰,等. 中国东北地区主要地质特征和地壳构造格架[J]. 岩石学报,2019,35(10):2989 − 3016. [LI Jinyi,LIU Jianfeng,QU Junfeng,et al. Major geological features and crustal tectonic framework of Northeast China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica,2019,35(10):2989 − 3016. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.04 LI Jinyi, LIU Jianfeng, QU Junfeng, et al. Major geological features and crustal tectonic framework of Northeast China[J]. Acta Petrologica Sinica, 2019, 35(10): 2989 − 3016. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.18654/1000-0569/2019.10.04
[13] 潘桂棠,肖庆辉,陆松年,等. 中国大地构造单元划分[J]. 中国地质,2009,36(1):1 − 28. [PAN Guitang,XIAO Qinghui,LU Songnian,et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China,2009,36(1):1 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.01.001 PAN Guitang, XIAO Qinghui, LU Songnian, et al. Subdivision of tectonic units in China[J]. Geology in China, 2009, 36(1): 1 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2009.01.001
[14] 李锦轶,张进,刘建峰,等. 中国大陆主要变形系统[J]. 地学前缘,2014,21(3):226 − 245. [LI Jinyi,ZHANG Jin,LIU Jianfeng,et al. Major deformation systems in the Mainland of China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2014,21(3):226 − 245. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Jinyi, ZHANG Jin, LIU Jianfeng, et al. Major deformation systems in the Mainland of China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2014, 21(3): 226 − 245. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 王涛,吴树仁,石菊松,等. 历史强震对渭河中游群发大型滑坡的诱发效应反演[J]. 地球学报,2015,36(3):352 − 360. [WANG Tao,WU Shuren,SHI Jusong,et al. Inversion of the inducing effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslides around the middle reaches of the Weihe River[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica,2015,36(3):352 − 360. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Tao, WU Shuren, SHI Jusong, et al. Inversion of the inducing effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslides around the middle reaches of the Weihe River[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 2015, 36(3): 352 − 360. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 徐岳仁,张伟恒,李文巧,等. 1556年华县地震同震黄土滑坡密集区的发现及意义[J]. 地震地质,2018,40(4):721 − 737. [XU Yueren,ZHANG Weiheng,LI Wenqiao,et al. Distribution characteristics of the AD 1556 Huaxian earthquake triggered disasters and its implications[J]. Seismology and Geology,2018,40(4):721 − 737. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Yueren, ZHANG Weiheng, LI Wenqiao, et al. Distribution characteristics of the AD 1556 Huaxian earthquake triggered disasters and its implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2018, 40(4): 721 − 737. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张振中. 黄土地震灾害预测[M]. 北京:地震出版社,1999. [ZHANG Zhenzhong. Earthquake disaster prediction of loess[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press,1999. (in Chinese)] ZHANG Zhenzhong. Earthquake disaster prediction of loess[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1999. (in Chinese)
[18] 王亚强,王兰民,张小曳. GIS支持下的黄土高原地震滑坡区划研究[J]. 地理科学,2004,24(2):170 − 176. [WANG Yaqiang,WANG Lanmin,ZHANG Xiaoye. GIS based seismic landslide zonation of the Loess Plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2004,24(2):170 − 176. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.02.007 WANG Yaqiang, WANG Lanmin, ZHANG Xiaoye. GIS based seismic landslide zonation of the Loess Plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2004, 24(2): 170 − 176. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2004.02.007
[19] 王海科. 重大工程影响下黄土渗透特性与入渗机理研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2023. [WANG Haike. Study on seepage characteristics and infiltration mechanism of loess under the influence of major projects[D]. Xi’an:Changan University,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Haike. Study on seepage characteristics and infiltration mechanism of loess under the influence of major projects[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 王兰民,蒲小武,陈金昌. 黄土高原地震诱发滑坡分布特征与灾害风险[J]. 城市与减灾,2019(3):33 − 40. [WANG Lanmin,PU Xiaowu,CHEN Jinchang. Distribution characteristics and disaster risk of earthquake-induced landslides in Loess Plateau[J]. City and Disaster Reduction,2019(3):33 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2019.03.009 WANG Lanmin, PU Xiaowu, CHEN Jinchang. Distribution characteristics and disaster risk of earthquake-induced landslides in Loess Plateau[J]. City and Disaster Reduction, 2019(3): 33 − 40. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2019.03.009
[21] 王绅皓,谢婉丽,常一伦,等. 浸水作用下湿陷性黄土微观结构及分形特征研究[J]. 高校地质学报,2023,29(2):280 − 288. [WANG Shenhao,XIE Wanli,CHANG Yilun,et al. Microstructures and fractal characteristics of collapsible loess subjected to water immersion[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities,2023,29(2):280 − 288. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Shenhao, XIE Wanli, CHANG Yilun, et al. Microstructures and fractal characteristics of collapsible loess subjected to water immersion[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2023, 29(2): 280 − 288. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[22] 李维光,张继春. 地震作用下顺层岩质边坡稳定性的拟静力分析[J]. 山地学报,2007,25(2):184 − 189. [LI Weiguang,ZHANG Jichun. Equivalent static stability study on rock mass bedding slope under blasting[J]. Mountain Research,2007,25(2):184 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.02.009 LI Weiguang, ZHANG Jichun. Equivalent static stability study on rock mass bedding slope under blasting[J]. Mountain Research, 2007, 25(2): 184 − 189. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.02.009
[23] 邓东平,李亮,罗伟. 地震荷载作用下土钉支护边坡稳定性拟静力分析[J]. 岩土力学,2012,33(6):1787 − 1794. [DENG Dongping,LI Liang,LUO Wei. Stability analysis of slope protected by soil nailing under earthquake loads based on pseudo static method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2012,33(6):1787 − 1794. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.06.029 DENG Dongping, LI Liang, LUO Wei. Stability analysis of slope protected by soil nailing under earthquake loads based on pseudo static method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2012, 33(6): 1787 − 1794. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2012.06.029
[24] 李泊良,张帆宇. 降雨和地震条件下浅层黄土滑坡三维稳定性评价[J]. 工程科学学报,2022,44(3):440 − 450. [LI Boliang,ZHANG Fanyu. Three-dimensional stability evaluation of shallow loess landslides under rainfall and earthquake conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering,2022,44(3):440 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.3.bjkjdxxb202203013 LI Boliang, ZHANG Fanyu. Three-dimensional stability evaluation of shallow loess landslides under rainfall and earthquake conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Engineering, 2022, 44(3): 440 − 450. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn.1001-053X.2022.3.bjkjdxxb202203013
[25] 赵振明,唐亚明,徐永,等. 山西大宁县典型滑坡体地貌特征与降雨和强震关系[J]. 地震工程学报,2020,42(6):1641 − 1649. [ZHAO Zhenming,TANG Yaming,XU Yong,et al. Geomorphic characteristics of typical landslides in Daning County,Shanxi Province,China,and its relationship with rainfall and strong earthquakes[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2020,42(6):1641 − 1649. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.06.1641 ZHAO Zhenming, TANG Yaming, XU Yong, et al. Geomorphic characteristics of typical landslides in Daning County, Shanxi Province, China, and its relationship with rainfall and strong earthquakes[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2020, 42(6): 1641 − 1649. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.06.1641
[26] CLOSE U,MCCORMICK E. Where the mountains walked[J]. National Geographic Magazine,1922,41(5):445 − 464.
[27] 王兰民. 黄土动力学[M]. 北京:地震出版社,2003. [WANG Lanmin. Loess dynamics[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press,2003. (in Chinese)] WANG Lanmin. Loess dynamics[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 2003. (in Chinese)
[28] 李昭淑,崔鹏. 1556年华县大地震的次生灾害[J]. 山地学报,2007(4):425 − 430. [LI Zhaoshu,CUI Peng. The secondary disasters of great Huaxian earthquake in 1556[J]. Journal of Mountain science,2007(4):425 − 430. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.04.007 LI Zhaoshu, CUI Peng. The secondary disasters of great Huaxian earthquake in 1556[J]. Journal of Mountain science, 2007(4): 425 − 430. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-2786.2007.04.007
[29] 吕艳,董颖,冯希杰,等. 1556年陕西关中华县特大地震地质灾害遗迹发育特征[J]. 工程地质学报,2014,22(2):300 − 308. [LYU Yan,DONG Ying,FENG Xijie,et al. Characteristics of geological relics due to 1556 Huaxian great earthquake in Guanzhong area of Shaanxi Province,China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2014,22(2):300 − 308. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LYU Yan, DONG Ying, FENG Xijie, et al. Characteristics of geological relics due to 1556 Huaxian great earthquake in Guanzhong area of Shaanxi Province, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2014, 22(2): 300 − 308. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[30] WANG T,WU S R,SHI J S,et al. Assessment of the effects of historical strong earthquakes on large-scale landslide groupings in the Wei River midstream[J]. Engineering Geology,2018,235:11 − 19. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2018.01.020
[31] 徐岳仁,杜朋,李文巧,等. 1718年通渭M 7.5地震滑坡特征分析——黄土高原历史强震触发滑坡数据库的应用[J]. 地球物理学报,2020,63(3):1235 − 1248. [XU Yueren,DU Peng,LI Wenqiao,et al. A case study on AD 1718 Tongwei M 7.5 earthquake triggered landslides:Application of landslide database triggered by historical strong earthquakes on the Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics,2020,63(3):1235 − 1248. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.6038/cjg2020N0146 XU Yueren, DU Peng, LI Wenqiao, et al. A case study on AD 1718 Tongwei M 7.5 earthquake triggered landslides: Application of landslide database triggered by historical strong earthquakes on the Loess Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2020, 63(3): 1235 − 1248. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.6038/cjg2020N0146
[32] ZHUANG Jianqi,PENG Jianbing,XU Chong,et al. Distribution and characteristics of loess landslides triggered by the 1920 Haiyuan Earthquake,Northwest of China[J]. Geomorphology,2018,314:1 − 12. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2018.04.012
[33] 王磊,李孝波,苏占东,等. 高密度电法在黄土-泥岩接触面滑坡勘察中的应用[J]. 地质力学学报,2019,25(4):536 − 543. [WANG Lei,LI Xiaobo,SU Zhandong,et al. Application of high-density electrical method in loess-mudstone interface landslide investigation[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2019,25(4):536 − 543. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.052 WANG Lei, LI Xiaobo, SU Zhandong, et al. Application of high-density electrical method in loess-mudstone interface landslide investigation[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2019, 25(4): 536 − 543. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12090/j.issn.1006-6616.2019.25.04.052
[34] 冯卫,毕银强,唐亚明,等. 甘肃礼县至罗家堡断裂带沿线地质灾害分布规律及断层效应研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2021,30(2):183 − 190. [FENG Wei,BI Yinqiang,TANG Yaming,et al. Research on the distribution law of geological disasters and fault effect along the Lixian-Luojiabu fault zone in Gansu[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2021,30(2):183 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract)] FENG Wei, BI Yinqiang, TANG Yaming, et al. Research on the distribution law of geological disasters and fault effect along the Lixian-Luojiabu fault zone in Gansu[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters, 2021, 30(2): 183 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[35] 王兰民,吴志坚. 岷县漳县6.6级地震震害特征及其启示[J]. 地震工程学报,2013,35(3):401 − 412. [WANG Lanmin,WU Zhijian. Earthquake damage characteristics of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms6.6 earthquake and its lessons[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2013,35(3):401 − 412. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.03.0401 WANG Lanmin, WU Zhijian. Earthquake damage characteristics of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms6.6 earthquake and its lessons[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2013, 35(3): 401 − 412. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.03.0401
[36] 许冲,吴熙彦,徐锡伟. 黄土高原及邻区的地震滑坡[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,26(增刊):260 − 273. [XU Chong,WU Xiyan,XU Xiwei. Earthquake-triggered landslides in the loess plateau and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,26(Sup):260 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Chong, WU Xiyan, XU Xiwei. Earthquake-triggered landslides in the loess plateau and its adjacent areas[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2016, 26(Sup): 260 − 273. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[37] 黄雅虹. 地震作用下黄土斜坡的稳定性分析预测[J]. 西北地震学报,1998(3):53 − 59. [HUANG Yahong. Analysis and prediction for stability of loess slope under the effect of earthquakes[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,1998(3):53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Yahong. Analysis and prediction for stability of loess slope under the effect of earthquakes[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1998(3): 53 − 59. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[38] 马学宁. 地震作用下黑方台黄土滑坡稳定性分析及治理措施[J]. 湖南工程学院学报(自然科学版),2013,23(1):77 − 81. [MA Xuening. Stability analysis and control measures of earthquake-induced loess landslides in Heifangtai[J]. Journal of Hunan Institute of Engineering (Natural Science Edition),2013,23(1):77 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MA Xuening. Stability analysis and control measures of earthquake-induced loess landslides in Heifangtai[J]. Journal of Hunan Institute of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 23(1): 77 − 81. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[39] 张振中,郑恒利,王兰民. 黄土随机振动强度参数在地震滑坡分析中的应用[J]. 西北地震学报,1991(3):45 − 49. [ZHANG Zhenzhong,ZHEGN Hengli,WANG Lanmin. Application of loess strength parameters under random vibration in analysis of seismic landslides[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal,1991(3):45 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Zhenzhong, ZHEGN Hengli, WANG Lanmin. Application of loess strength parameters under random vibration in analysis of seismic landslides[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 1991(3): 45 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[40] 邹谨敞,邵顺妹. 海原地震滑坡及其分布特征探讨[J]. 内陆地震,1996(1):1 − 6. [ZHOU Jinchang,ZHAO Shunmei. Characteristics of Haiyuan earthquake landslide and its distribution[J]. Inland Earthquake,1996(1):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHOU Jinchang, ZHAO Shunmei. Characteristics of Haiyuan earthquake landslide and its distribution[J]. Inland Earthquake, 1996(1): 1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[41] 谢定义. 试论我国黄土力学研究中的若干新趋向[J]. 岩土工程学报,2001,23(1):3 − 13. [XIE Dingyi. Exploration of some new tendencies in research of loess soil mechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2001,23(1):3 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.01.002 XIE Dingyi. Exploration of some new tendencies in research of loess soil mechanics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2001, 23(1): 3 − 13. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2001.01.002
[42] 陈存礼,杨鹏,何军芳. 饱和击实黄土的动力特性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2007,28(8):1551 − 1556. [CHEN Cunli,YANG Peng,HE Junfang. Research on dynamic characteristics of saturated compacted loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2007,28(8):1551 − 1556. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.08.005 CHEN Cunli, YANG Peng, HE Junfang. Research on dynamic characteristics of saturated compacted loess[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2007, 28(8): 1551 − 1556. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2007.08.005
[43] CHEN Huie,JIANG Yaling,NIU Cencen,et al. Dynamic characteristics of saturated loess under different confining pressures:A microscopic analysis[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2019,78(2):931 − 944. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-017-1101-9
[44] WANG Qian,WANG Yan,MA Wenguo,et al. Dynamic characteristics of post-cyclic saturated loess[J]. Applied Sciences,2022,13(1):306. DOI: 10.3390/app13010306
[45] CAREY J M,MCSAVENEY M J,PETLEY D N. Dynamic liquefaction of shear zones in intact loess during simulated earthquake loading[J]. Landslides,2017,14(3):789 − 804. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-016-0746-y
[46] WU Zhijian,XU Shiming,CHEN Dawei,et al. An experimental study of the influence of structural parameters on dynamic characteristics of loess[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2020,132:106067. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106067
[47] WANG Ping,WANG Jun,CHAI Shaofeng,et al. Experimental study on dynamic strength regional characteristics of undisturbed loess based on the mohr-coulomb failure criterion[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2013,700:111 − 118. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.700.111
[48] QIAO Feng,CHANG Chaoyu,BO Jingshan,et al. Study on the dynamic characteristics of loess[J]. Sustainability,2023,15(6):5428. DOI: 10.3390/su15065428
[49] WEI Tingting,WU Zhijian,CHEN Yanping,et al. Three-dimensional characterization and quantitative research of Malan loess microstructure under seismic loading[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science,2023,10:1106168. DOI: 10.3389/feart.2022.1106168
[50] WANG N Q,LIU X L,LUO,et al. Study on Dynamic Strength Characteristics of Malan Loess. Applied Mechanics and Materials[C]. 2nd International Conference on Civil Engineering,Architecture and Building Materials (CEABM 2012),2012,Yantai,PEOPLES R CHINA.
[51] WANG N Q,LIU X L,BO H,et al. Test of Dynamic Strength Characteristics of Lishi Loess. Applied Mechanics and Materials [C]. International Conference on Sensors,Measurement and Intelligent Materials (ICSMIM 2012),2012,Guilin,PEOPLES R CHINA.
[52] LIU Wei,WANG Qian,LIN Gaochao,et al. Effect of pre-dynamic loading on dynamic liquefaction of undisturbed loess[J]. Bulletin of Earthquake Engineering,2020,18(13):5779 − 5806. DOI: 10.1007/s10518-020-00917-w
[53] WANG Haojie,SUN Ping,LIU Enlong,et al. Dynamic properties of Tianshui saturated remolded loess:A laboratory study[J]. Engineering Geology,2020,272:105570. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105570
[54] CHENG Xuansheng,LI Xinlei,NIE Jun,et al. Research on the dynamic parameters of loess[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering,2019,37(1):77 − 93. DOI: 10.1007/s10706-018-0592-x
[55] 颜灵勇,李孝波,欧阳刚垒. 黄土地震滑坡形成机理研究的若干进展[J]. 防灾科技学院学报,2021,23(2):46 − 53. [YAN Lingyong,LI Xiaobo,OUYANG Ganglei. Research progress in formation mechanism of loess coseismic landslides[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention,2021,23(2):46 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2021.02.006 YAN Lingyong, LI Xiaobo, OUYANG Ganglei. Research progress in formation mechanism of loess coseismic landslides[J]. Journal of Institute of Disaster Prevention, 2021, 23(2): 46 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8047.2021.02.006
[56] 刘魁. 固原市原州区地震诱发黄土滑坡形成机理研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2012. [LIU Kui. Study on formation mechanism of loess landslide induced by earthquake in Yuanzhou District of Guyuan City[D]. Xi’an:Changan University,2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Kui. Study on formation mechanism of loess landslide induced by earthquake in Yuanzhou District of Guyuan City[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2012. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[57] CHEN Jinchang,WANG Lanmin,WANG Ping,et al. Failure mechanism investigation on loess-mudstone landslides based on the Hilbert-Huang transform method using a large-scale shaking table test[J]. Engineering Geology,2022,302:106630. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2022.106630
[58] 王明轩,倪万魁. 喜家湾地震黄土滑坡形成机理[J]. 华北地震科学,2018,36(1):54 − 58. [WANG Mingxuan,NI Wankui. Study on the formation mechanism of Xijiawan loess landslide induced by earthquake[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences,2018,36(1):54 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2018.01.009 WANG Mingxuan, NI Wankui. Study on the formation mechanism of Xijiawan loess landslide induced by earthquake[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 2018, 36(1): 54 − 58. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1375.2018.01.009
[59] 徐舜华,吴志坚,孙军杰,等. 岷县漳县6.6级地震典型滑坡特征及其诱发机制[J]. 地震工程学报,2013,35(3):471 − 476. [XU Shunhua,WU Zhijian,SUN Junjie,et al. Study of the characteristics and inducing mechanism of typical earthquake landslides of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms 6.6 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2013,35(3):471 − 476. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.03.0471 XU Shunhua, WU Zhijian, SUN Junjie, et al. Study of the characteristics and inducing mechanism of typical earthquake landslides of the Minxian-Zhangxian Ms 6.6 earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2013, 35(3): 471 − 476. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2013.03.0471
[60] 王鼐,王兰民. 河谷地区黄土地震滑坡特征与影响因素分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2013,35(增刊1):434 − 438. [WANG Nai,WANG Lanmin. Characteristics and influencing factors of seismic loess slopes in valley areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2013,35(Sup 1):434 − 438. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Nai, WANG Lanmin. Characteristics and influencing factors of seismic loess slopes in valley areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2013, 35(Sup 1): 434 − 438. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[61] 王立朝,侯圣山,董英,等. 甘肃积石山Ms 6.2级地震的同震地质灾害基本特征及风险防控建议[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2024,35(3):108 − 118. [WANG Lichao,HOU Shengshan,DONG Ying,et al. Basic characteristics of co-seismic geological hazards induced by Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake and suggestions for their risk control[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2024,35(3):108 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Lichao, HOU Shengshan, DONG Ying, et al. Basic characteristics of co-seismic geological hazards induced by Jishishan Ms 6.2 earthquake and suggestions for their risk control[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2024, 35(3): 108 − 118. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[62] 段玉石,薄景山,彭达,等. 地震诱发黄土滑坡分布特征分析——以1920年海原特大地震为例[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报,1 − 17. [DUAN Yushi,BO Jingshan,PENG Da,et al. Distribution characteristics of earthquake-induced loess landslides:A case study of the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,1 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DUAN Yushi, BO Jingshan, PENG Da, et al. Distribution characteristics of earthquake-induced loess landslides: A case study of the 1920 Haiyuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 1 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[63] 钱紫玲. 基于统计模型的黄土地震滑坡危险性评价[D]. 兰州:中国地震局兰州地震研究所,2023. [QIAN Ziling. Risk assessment of loess earthquake landslide based on statistical model[D]. Lanzhou:China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology,2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)] QIAN Ziling. Risk assessment of loess earthquake landslide based on statistical model[D]. Lanzhou: China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, 2023. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[64] 程小杰,杨为民,向灵芝,等. 基于Newmark模型的天水市北山地震黄土滑坡危险性评价[J]. 地质力学学报,2017,23(2):296 − 305. [CHENG Xiaojie,YANG Weimin,XIANG Lingzhi,et al. Risk assessment of seismic loess landslide based on newmark model in Beishan,Tianshui City[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2017,23(2):296 − 305.(in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.013 CHENG Xiaojie, YANG Weimin, XIANG Lingzhi, et al. Risk assessment of seismic loess landslide based on newmark model in Beishan, Tianshui City[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 2017, 23(2): 296 − 305.(in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-6616.2017.02.013
[65] 邓龙胜. 强震作用下黄土边坡的动力响应机理和动力稳定性研究[D]. 西安:长安大学,2010. [DENG Longsheng. Study on dynamic response mechanism and dynamic stability of loess slope under strong earthquake[D]. Xi’an:Changan University,2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DENG Longsheng. Study on dynamic response mechanism and dynamic stability of loess slope under strong earthquake[D]. Xi’an: Changan University, 2010. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[66] 赵文琛. 强震作用下黄土斜坡动力响应特征与稳定性分析[D]. 兰州:中国地震局兰州地震研究所,2016. [ZHAO Wenchen. Dynamic response characteristics and stability analysis of loess slope under strong earthquake[D]. Lanzhou:China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology,2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHAO Wenchen. Dynamic response characteristics and stability analysis of loess slope under strong earthquake[D]. Lanzhou: China Earthquake Administration Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, 2016. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[67] 车福东,王涛,辛鹏,等. 近远震作用下黄土滑坡动力响应与变形——以甘肃天水震区黎坪村滑坡为例[J]. 地质通报,2020,39(12):1981 − 1992. [CHE Fudong,WANG Tao,XIN Peng,et al. Dynamic response and deformation of loess landslide under near and far earthquakes:A case study of Liping Village landslide in Tianshui earthquake area,Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2020,39(12):1981 − 1992. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.012 CHE Fudong, WANG Tao, XIN Peng, et al. Dynamic response and deformation of loess landslide under near and far earthquakes: A case study of Liping Village landslide in Tianshui earthquake area, Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2020, 39(12): 1981 − 1992. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.12097/j.issn.1671-2552.2020.12.012
[68] 常晁瑜,徐久欢,薄景山,等. 基于颗粒流的地震液化型滑坡运动学特征分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2022,42(6):153 − 161. [CHANG Chaoyu,XU Jiuhuan,BO Jingshan,et al. Kinematic characteristics analysis of seismic liquefaction landslide based on particle flow[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics,2022,42(6):153 − 161. ((in Chinese with English abstract)] CHANG Chaoyu, XU Jiuhuan, BO Jingshan, et al. Kinematic characteristics analysis of seismic liquefaction landslide based on particle flow[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics, 2022, 42(6): 153 − 161. ((in Chinese with English abstract)
[69] 张子东,张晓超,任鹏,等. 非饱和黄土动力液化研究 ——以党家岔滑坡为例[J]. 地震工程学报,2021,43(5):1228 − 1237. [ZHANG Zidong,ZHANG Xiaochao,REN Peng,et al. Dynamic liquefaction of unsaturated loess:A case study of Dangjiacha landslide[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2021,43(5):1228 − 1237. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2021.05.1228 ZHANG Zidong, ZHANG Xiaochao, REN Peng, et al. Dynamic liquefaction of unsaturated loess: A case study of Dangjiacha landslide[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2021, 43(5): 1228 − 1237. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2021.05.1228
[70] 吴志坚,陈豫津,王谦,等. 岷县漳县6.6级地震永光村滑坡致灾机制分析[J]. 岩土工程学报,2019,41(S2):165 − 168. [WU Zhijian,CHEN Yujin,WANG Qian,et al. Disaster-causing mechanism of Yongguang landslide under Minxian-Zhangxian Ms 6.6 Earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019,41(S2):165 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.11779/CJGE2019S2042 WU Zhijian, CHEN Yujin, WANG Qian, et al. Disaster-causing mechanism of Yongguang landslide under Minxian-Zhangxian Ms 6.6 Earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2019, 41(S2): 165 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11779/CJGE2019S2042
[71] 张晓超,裴向军,张茂省,等. 强震触发黄土滑坡流滑机理的试验研究——以宁夏党家岔滑坡为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1219 − 1226. [ZHANG Xiaochao,PEI Xiangjun,ZHANG Maosheng,et al. Experimental study on mechanism of flow slide of loess landslides triggered by strong earthquake:A case study in Dangjiacha,Ningxia Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1219 − 1226. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Xiaochao, PEI Xiangjun, ZHANG Maosheng, et al. Experimental study on mechanism of flow slide of loess landslides triggered by strong earthquake: A case study in Dangjiacha, Ningxia Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2018, 26(5): 1219 − 1226. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[72] 国家地震局兰州地震研究所宁夏回族自治区地震队. 一九二〇年海原大地震[M]. 北京:地震出版社,1980. [Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Seismological Team, Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, National Seismological Bureau. Haiyuan earthquake in 1920[M]. Beijing:Seismological Press,1980. (in Chinese)] Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region Seismological Team, Lanzhou Institute of Seismology, National Seismological Bureau. Haiyuan earthquake in 1920[M]. Beijing: Seismological Press, 1980. (in Chinese)
[73] 彭建兵,王启耀,门玉明,等. 黄土高原滑坡灾害[M]. 北京:科学出版社,2019. [PENG Jianbing,WANG Qiyao,MEN Yuming,et al. Landslide disaster in Loess Plateau[M]. Beijing:Science Press,2019. (in Chinese)] PENG Jianbing, WANG Qiyao, MEN Yuming, et al. Landslide disaster in Loess Plateau[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2019. (in Chinese)
[74] 张振中,张冬丽,刘红玫. 黄土震陷灾害典型震例的综合研究(英文)[J]. 西北地震学报,2005,27(1):36 − 41. [ZHANG Zhenzhong,ZHANG Dongli,LIU Hongmei. Comprehensive study on seismic subsidence of loess under earthquake[J]. Northwestern seismological Journal,2005,27(1):36 − 41. (in English with Chinese abstract)] ZHANG Zhenzhong, ZHANG Dongli, LIU Hongmei. Comprehensive study on seismic subsidence of loess under earthquake[J]. Northwestern seismological Journal, 2005, 27(1): 36 − 41. (in English with Chinese abstract)
[75] 王兰民. 黄土地层大规模地震液化滑移的机理与风险评估[J]. 岩土工程学报,2020,42(1):1 − 19. [WANG Lanmin. Mechanism and risk evaluation of sliding flow triggered by liquefaction of loess deposit during earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2020,42(1):1 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.11779/CJGE202001001 WANG Lanmin. Mechanism and risk evaluation of sliding flow triggered by liquefaction of loess deposit during earthquakes[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(1): 1 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11779/CJGE202001001
[76] SHANG H,NI W K,NIU F J,et al. Development characteristics and causes of seismic loess landslides in north-west China [J]. Disaster Advances,2013,6:24-38.
[77] ZHONG Xiumei,XU Xiaowei,CHEN Wenkai,et al. Characteristics of loess landslides triggered by the 1927 Mw8.0 earthquake that occurred in Gulang County,Gansu Province,China[J]. Frontiers in Environmental Science,2022,10:973262. DOI: 10.3389/fenvs.2022.973262
[78] LI Xiaobo,YAN Lingyong,WU Yiwen,et al. Distribution and characteristics of loess landslides induced by the 1654 Tianshui earthquake,Northwest of China[J]. Landslides,2023,20(12):2775 − 2790. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-023-02128-1
[79] 陈永明,石玉成,刘红玫,等. 黄土地区地震滑坡的分布特征及其影响因素分析[J]. 中国地震,2005,21(2):235 − 243. [CHEN Yongming,SHI Yucheng,LIU Hongmei,et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors analysis of seismic loess landslides[J]. Earthquake Research in China,2005,21(2):235 − 243. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2005.02.011 CHEN Yongming, SHI Yucheng, LIU Hongmei, et al. Distribution characteristics and influencing factors analysis of seismic loess landslides[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2005, 21(2): 235 − 243. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4683.2005.02.011
[80] 王兰民,郭安宁,王平,等. 1920年海原大地震震害特征与启示[J]. 城市与减灾,2020(6):43 − 53. [WANG Lanmin,GUO Anning,WANG Ping,et al. The characteristics and revelation of the Great Haiyuan Earthquake in 1920[J]. City and Disaster Reduction,2020(6):43 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2020.06.007 WANG Lanmin, GUO Anning, WANG Ping, et al. The characteristics and revelation of the Great Haiyuan Earthquake in 1920[J]. City and Disaster Reduction, 2020(6): 43 − 53. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0495.2020.06.007
[81] 王尚,梁庆国,乔向进,等. 基于小波包和反应谱的黄土边坡动力特征研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2023,45(1):94 − 102. [WANG Shang,LIANG Qingguo,QIAO Xiangjin,et al. Dynamic characteristics of loess slopes based on wavelet packet and response spectrum[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2023,45(1):94 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Shang, LIANG Qingguo, QIAO Xiangjin, et al. Dynamic characteristics of loess slopes based on wavelet packet and response spectrum[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2023, 45(1): 94 − 102. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[82] 张兴臣,梁庆国,孙文,等. 地震作用下黄土边坡动力响应的时频特征分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2022,44(5):1090 − 1099. [ZHANG Xingchen,LIANG Qingguo,SUN Wen,et al. Time-frequency characteristics of dynamic responses of loess slopes under earthquake action[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2022,44(5):1090 − 1099. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Xingchen, LIANG Qingguo, SUN Wen, et al. Time-frequency characteristics of dynamic responses of loess slopes under earthquake action[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2022, 44(5): 1090 − 1099. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[83] 张彬,邵帅,邵生俊,等. 黄土丘陵区边坡动力响应及震陷变形分析方法[J]. 岩土工程学报,2023,45(4):869 − 875. [ZHANG Bin,SHAO Shuai,SHAO Shengjun,et al. Dynamic response of slopes in hilly regions of loess and analysis method for their seismic subsidence deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2023,45(4):869 − 875. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Bin, SHAO Shuai, SHAO Shengjun, et al. Dynamic response of slopes in hilly regions of loess and analysis method for their seismic subsidence deformation[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2023, 45(4): 869 − 875. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[84] 孙文,梁庆国,乔向进,等. 不同失稳形态黄土边坡的动力响应研究[J]. 铁道学报,2022,44(6):123 − 130. [SUN Wen,LIANG Qingguo,QIAO Xiangjin,et al. Study on dynamic response of loess slopes with different failure patterns[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society,2022,44(6):123 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.06.015 SUN Wen, LIANG Qingguo, QIAO Xiangjin, et al. Study on dynamic response of loess slopes with different failure patterns[J]. Journal of the China Railway Society, 2022, 44(6): 123 − 130. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8360.2022.06.015
[85] 孙文,梁庆国,乔向进,等. 黄土边坡动力失稳的振动台试验研究[J]. 兰州交通大学学报,2021,40(2):15 − 22. [SUN Wen,LIANG Qingguo,QIAO Xiangjin,et al. Research on dynamic failure of loess slope by shaking table test[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University,2021,40(2):15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2021.02.003 SUN Wen, LIANG Qingguo, QIAO Xiangjin, et al. Research on dynamic failure of loess slope by shaking table test[J]. Journal of Lanzhou Jiaotong University, 2021, 40(2): 15 − 22. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4373.2021.02.003
[86] 田欣欣,严武建,郑海忠,等. 地震作用下含暗穴高边坡黄土路基稳定性分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2022,44(1):72 − 78. [TIAN Xinxin,YAN Wujian,ZHENG Haizhong,et al. Stability analysis of high-slope loess subgrade with hidden holes under earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2022,44(1):72 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TIAN Xinxin, YAN Wujian, ZHENG Haizhong, et al. Stability analysis of high-slope loess subgrade with hidden holes under earthquake[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2022, 44(1): 72 − 78. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[87] 万金侠,施艳秋,陈小云. 基于动土压力响应特性的黄土滑坡振动台试验研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2021,41(3):586 − 593. [WAN Jinxia,SHI Yanqiu,CHEN Xiaoyun. Shaking table experiment of loess landslide based on dynamic earth pressure response characteristics[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2021,41(3):586 − 593. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WAN Jinxia, SHI Yanqiu, CHEN Xiaoyun. Shaking table experiment of loess landslide based on dynamic earth pressure response characteristics[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2021, 41(3): 586 − 593. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[88] 邵帅,邵生俊,李宁,等. 地震作用下黄土边坡震陷破坏的动力离心模型试验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2021,43(2):245 − 253. [SHAO Shuai, SHAO Shengjun, LI Ning, et al. Dynamic centrifugal model tests on seismic subsidence of loess slopes under earthquake action[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2021,43(2):245 − 253. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SHAO Shuai, SHAO Shengjun, LI Ning, et al. Dynamic centrifugal model tests on seismic subsidence of loess slopes under earthquake action[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2021, 43(2): 245 − 253. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[89] 施艳秋,谢显龙,张玘恺,等. 基于小波变换的黄土滑坡动土压力响应及其频谱特性研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(12):2570 − 2581. [SHI Yanqiu,XIE Xianlong,ZHANG Qikai,et al. Study on spectrum characteristics of dynamic earth pressure of loess landslides based on wavelet transform[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(12):2570 − 2581. (in Chinese with English abstract)] SHI Yanqiu, XIE Xianlong, ZHANG Qikai, et al. Study on spectrum characteristics of dynamic earth pressure of loess landslides based on wavelet transform[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(12): 2570 − 2581. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[90] 陈金昌,王兰民,王平,等. 基于振动台试验的纯黄土边坡动力响应研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2020,42(2):529 − 535. [CHEN Jinchang,WANG Lanmin,WANG Ping,et al. Dynamic response of loess slopes based on the shake table test[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2020,42(2):529 − 535. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.02.529 CHEN Jinchang, WANG Lanmin, WANG Ping, et al. Dynamic response of loess slopes based on the shake table test[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2020, 42(2): 529 − 535. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2020.02.529
[91] 夏坤,董林,蒲小武,等. 黄土塬地震动响应特征分析[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(1):295 − 304. [XIA Kun,DONG Lin,PU Xiaowu,et al. Earthquake response characteristics of loess tableland[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(1):295 − 304. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XIA Kun, DONG Lin, PU Xiaowu, et al. Earthquake response characteristics of loess tableland[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(1): 295 − 304. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[92] 张泽林,吴树仁,王涛,等. 地震波振幅对黄土-泥岩边坡动力响应规律的影响[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(7):2403 − 2412. [ZHANG Zelin,WU Shuren,WANG Tao,et al. Influence of seismic wave amplitude on dynamic response of loess-mudstone slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(7):2403 − 2412. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Zelin, WU Shuren, WANG Tao, et al. Influence of seismic wave amplitude on dynamic response of loess-mudstone slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2018, 39(7): 2403 − 2412. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[93] 芮雪莲,裴向军,张晓超. 强震触发黄土滑坡发生机制试验[J]. 实验室研究与探索,2016,35(1):23 − 26. [RUI Xuelian,PEI Xiangjun,ZHANG Xiaochao. Laboratory study of the mechanism of loess landslide caused by violent earthquake[J]. Research and Exploration In Laboratory,2016,35(1):23 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2016.01.007 RUI Xuelian, PEI Xiangjun, ZHANG Xiaochao. Laboratory study of the mechanism of loess landslide caused by violent earthquake[J]. Research and Exploration In Laboratory, 2016, 35(1): 23 − 26. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7167.2016.01.007
[94] 张晓超,黄润秋,许模,等. 石碑塬滑坡黄土液化特征及其影响因素研究[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(3):801 − 810. [ZHANG Xiaochao,HUANG Runqiu,XU Mo,et al. Loess liquefaction characteristics and its influential factors of Shibeiyuan landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(3):801 − 810. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Xiaochao, HUANG Runqiu, XU Mo, et al. Loess liquefaction characteristics and its influential factors of Shibeiyuan landslide[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(3): 801 − 810. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[95] PEI Xiangjun,ZHANG Xiaochao,GUO Bin,et al. Experimental case study of seismically induced loess liquefaction and landslide[J]. Engineering Geology,2017,223:23 − 30. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2017.03.016
[96] 胡成,卢坤林,朱大勇,等. 三维边坡拟静力抗震稳定性分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(增刊1):2904 − 2912. [HU Cheng,LU Kunlin,ZHU Dayong,et al. Analysis of pseudo-static seismic stability for three-dimensional slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering. 2011,30(Sup 1):2904 − 2912. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HU Cheng, LU Kunlin, ZHU Dayong, et al. Analysis of pseudo-static seismic stability for three-dimensional slope[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering. 2011, 30(Sup 1): 2904 − 2912. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[97] 郑颖人,叶海林,黄润秋,等. 边坡地震稳定性分析探讨[J]. 地震工程与工程振动,2010,30(2):173 − 180. [ZHEGN Yingren,YE Hailin,HUANG Runqiu,et al. Study on the seismic stability analysis of a slope[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration,2010,30(2):173 − 180. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHEGN Yingren, YE Hailin, HUANG Runqiu, et al. Study on the seismic stability analysis of a slope[J]. Journal of Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 2010, 30(2): 173 − 180. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[98] 刘春玲,祁生文,童立强,等. 利用FLAC3D分析某边坡地震稳定性[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004(16):2730 − 2733. [LIU Chunling,QI Shengwen,TONG Liqiang,et al. Stability analysis of slope under earthquake with FLAC3D[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004(16):2730 − 2733. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.014 LIU Chunling, QI Shengwen, TONG Liqiang, et al. Stability analysis of slope under earthquake with FLAC3D[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004(16): 2730 − 2733. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2004.16.014
[99] NEWMARK N M. Effects of earthquakes on dams and embankments[J]. Geotechnique,1965,15(2):139 − 160. DOI: 10.1680/geot.1965.15.2.139
[100] STEEDMAN R S,ZENG X. The influence of phase on the calculation of pseudo-static earth pressure on a retaining wall[J]. Géotechnique,1990,40(1):103 − 112.
[101] 李亮,褚雪松,庞峰,等. 地震边坡稳定性分析的拟静力方法适用性探讨[J]. 世界地震工程,2012,28(2):57 − 63. [LI Liang,CHU Xuesong,PANG Feng,et al. Discussion on suitability of pseudo-static method in seismic slope stability analysis[J]. World Earthquake Engineering,2012,28(2):57 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2012.02.010 LI Liang, CHU Xuesong, PANG Feng, et al. Discussion on suitability of pseudo-static method in seismic slope stability analysis[J]. World Earthquake Engineering, 2012, 28(2): 57 − 63. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6069.2012.02.010
[102] KARRAY M,HUSSIEN M N,DELISLE M C,et al. Framework to assess pseudo-static approach for seismic stability of clayey slopes[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,2018,55(12):1860 − 1876. DOI: 10.1139/cgj-2017-0383
[103] MENDEZ B,TASTAN E O,GUTIERREZ J. Performance-based slope stability analysis and the pseudo-static factor of safety[C]//Geotechnical Frontiers 2017. Orlando,Florida. Reston,VA:American Society of Civil Engineers,2017,278:390 − 399.
[104] UTILI S,ABD A H. On the stability of fissured slopes subject to seismic action[J]. International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,2016,40(5):785 − 806. DOI: 10.1002/nag.2498
[105] TERZAGHI K. Mechanisms of landslide[M]. Engineering Geology (Berdey) volume,1950,Geological Society of America.
[106] KRAMER S L. Geotechnical earthquake engineering[M]. Upper Saddle River,NJ:Prentice Hall,1996.
[107] SEED H B. Considerations in the earthquake-resistant design of earth and rockfill dams[J]. Géotechnique,1979,29(3):215 − 263.
[108] SEED H B. Stability of earth and rock-fill dams during earthquake[J]. Embankment-Dam Eng. 1973. Casagrande.
[109] 中华人民共和国国家经济贸易委员会. 水工建筑物抗震设计规范:DL 5073—2000[S]. 北京:中国电力出版社,2001. [State Economic and Trade Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for seismic design of hydraulic structures:DL 5073—2000[S]. Beijing:China Electric Power Press,2001. (in Chinese)] State Economic and Trade Commission of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications for seismic design of hydraulic structures: DL 5073—2000[S]. Beijing: China Electric Power Press, 2001. (in Chinese)
[110] 中华人民共和国国家标准编写小组. 铁路工程抗震设计规范:GB 50111—2006[S]. 北京:中国计划出版社, 2009. [The National Standards Compilation Group of People’s Republic of China. Code for seismic design of railway engineering:GB 50111—2006[S].Beijing: China Plan Press, 2009. (in Chinese)] The National Standards Compilation Group of People’s Republic of China. Code for seismic design of railway engineering: GB 50111—2006[S].Beijing: China Plan Press, 2009. (in Chinese)
[111] 中华人民共和国交通部. 公路工程抗震设计规范:JTJ 004—1989[S]. 北京:人民交通出版社,1990. [Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications of earthquake resistant design for highway engineering:JTJ 004—1989[S]. Beijing:China Communications Press,1990. (in Chinese)] Ministry of Transport of the People’s Republic of China. Specifications of earthquake resistant design for highway engineering: JTJ 004—1989[S]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 1990. (in Chinese)
[112] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部, 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局.建筑抗震设计规范(2016版):GB 50011—2010[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社,2016. [Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Code for seismic design of buildings (2016 edition):GB 50011—2010[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016. (in Chinese)] Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China, General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Code for seismic design of buildings (2016 edition): GB 50011—2010[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2016. (in Chinese)
[113] 梁承龙,刘芳. 地震作用下双层土裂缝边坡稳定性分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2022,44(5):1050 − 1058. [LIANG Chenglong,LIU Fang. Stability analysis of two-layered cracked slopes subjected to seismic excitation[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2022,44(5):1050 − 1058. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIANG Chenglong, LIU Fang. Stability analysis of two-layered cracked slopes subjected to seismic excitation[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2022, 44(5): 1050 − 1058. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[114] FARSHIDFAR N, KESHAVARZ A, MIRHOSSEINI S M. Pseudo-static seismic analysis of reinforced soil slopes using the horizontal slice method[J]. Arabian Journal of Geosciences,2020,13(7):283.
[115] 袁中夏,李德鹏,叶帅华. 地震和降雨条件下黄土高填方边坡稳定性分析[J]. 兰州理工大学学报,2022,48(4):119 − 125. [YUAN Zhongxia,LI Depeng,YE Shuaihua. Stability analysis of high fill slope with loess under earthquake and rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology,2022,48(4):119 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2022.04.018 YUAN Zhongxia, LI Depeng, YE Shuaihua. Stability analysis of high fill slope with loess under earthquake and rainfall infiltration[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University of Technology, 2022, 48(4): 119 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5196.2022.04.018
[116] 李旭东,王平,王丽丽,等. 强震作用下坡顶建筑荷载对边坡稳定性影响研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2021,43(5):1220 − 1227. [LI Xudong,WANG Ping,WANG Lili,et al. Influence of top building on the slope stability under strong earthquakes[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2021,43(5):1220 − 1227. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2021.05.1220 LI Xudong, WANG Ping, WANG Lili, et al. Influence of top building on the slope stability under strong earthquakes[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2021, 43(5): 1220 − 1227. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2021.05.1220
[117] 刘畅,张平松,杨为民,等. 税湾地震黄土滑坡的岩土动力特性及其稳定性评价[J]. 西北地质,2020,53(4):176 − 185. [LIU Chang,ZHANG Pingsong,YANG Weimin,et al. Geotechnical dynamic characteristics and stability evaluation of loess landslides in Shuiwan earthquake,Tianshui,Gansu[J]. Northwestern Geology,2020,53(4):176 − 185. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Chang, ZHANG Pingsong, YANG Weimin, et al. Geotechnical dynamic characteristics and stability evaluation of loess landslides in Shuiwan earthquake, Tianshui, Gansu[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2020, 53(4): 176 − 185. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[118] 陈亚光. 宝兰客专天水市王家墩滑坡地震稳定性分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2019,41(6):1607 − 1614. [CHEN Yaguang. Stability analysis of Wangjiadun landslide in Tianshui City under earthquake load[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2019,41(6):1607 − 1614. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.06.1607 CHEN Yaguang. Stability analysis of Wangjiadun landslide in Tianshui City under earthquake load[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2019, 41(6): 1607 − 1614. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.06.1607
[119] 闫东晗,薄景山,李孝波,等. 海原特大地震红土川滑坡拟静力强度折减法模拟分析[J]. 科学技术与工程,2019,19(28):50 − 55. [YAN Donghan,BO Jingshan,LI Xiaobo,et al. Simulation analysis of Hongtuchuan landslide in Haiyuan earthquake quasi-static strength reduction method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2019,19(28):50 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.28.006 YAN Donghan, BO Jingshan, LI Xiaobo, et al. Simulation analysis of Hongtuchuan landslide in Haiyuan earthquake quasi-static strength reduction method[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2019, 19(28): 50 − 55. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2019.28.006
[120] 孙萍,祝恩珍,张帅,等. 地震作用下甘肃天水地区黄土-泥岩接触面滑坡机理[J]. 现代地质,2019,33(1):218 − 226. [SUN Ping,ZHU Enzhen,ZHANG Shuai,et al. Mechanism of earthquake-triggered loess-mudstone interface landslide in Tianshui Area,Gansu Province[J]. Geoscience,2019,33(1):218 − 226.(in Chinese with English abstract)] SUN Ping, ZHU Enzhen, ZHANG Shuai, et al. Mechanism of earthquake-triggered loess-mudstone interface landslide in Tianshui Area, Gansu Province[J]. Geoscience, 2019, 33(1): 218 − 226.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[121] ZENG X,STEEDMAN R S. On the behaviour of quay walls in earthquakes[J]. Géotechnique,1993,43(3):417 − 431.
[122] CHOUDHURY D,NIMBALKAR S. Seismic passive resistance by pseudo-dynamic method[J]. Géotechnique,2005,55(9):699 − 702.
[123] CHOUDHURY D,NIMBALKAR S S. Pseudo-dynamic approach of seismic active earth pressure behind retaining wall[J]. Geotechnical & Geological Engineering,2006,24(5):1103 − 1113.
[124] CHOUDHURY D,NIMBALKAR S. Seismic rotational displacement of gravity walls by pseudo-dynamic method:Passive case[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2007,27(3):242 − 249. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2006.06.009
[125] BAZIAR M H,SHAHNAZARI H,RABETI MOGHADAM M. Sliding stability analysis of gravity retaining walls using the pseudo-dynamic method[J]. Proceedings of the Institution of Civil Engineers - Geotechnical Engineering,2013,166(4):389 − 398. DOI: 10.1680/geng.10.00036
[126] YAN Zuofei,DENG Yahong,HE Jia,et al. A pseudodynamic approach of seismic active pressure on retaining walls based on a curved rupture surface[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering,2020,2020:6462034.
[127] GANESH R,KHUNTIA S,SAHOO J P. Seismic uplift capacity of shallow strip anchors:A new pseudo-dynamic upper bound limit analysis[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2018,109:69 − 75. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2018.03.004
[128] ZHAO Lianheng,YU Chenghao,LI Liang,et al. Rock slope reliability analysis using Barton-Bandis failure criterion with modified pseudo-dynamic approach[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2020,139:106310. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2020.106310
[129] MUNWAR BASHA B,SIVAKUMAR BABU G L. Reliability assessment of internal stability of reinforced soil structures:A pseudo-dynamic approach[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2010,30(5):336 − 353. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2009.12.007
[130] BASHA B M,BABU G L S. Seismic reliability assessment of internal stability of reinforced soil walls using the pseudo-dynamic method[J]. Geosynthetics International,2011,18(5):221 − 241. DOI: 10.1680/gein.2011.18.5.221
[131] ZHOU X P,CHENG H. Stability analysis of three-dimensional seismic landslides using the rigorous limit equilibrium method[J]. Engineering Geology,2014,174:87 − 102. DOI: 10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.03.009
[132] CHAKRABORTY D,CHOUDHURY D. Pseudo-static and pseudo-dynamic stability analysis of tailings dam under seismic conditions[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,India Section A:Physical Sciences,2013,83(1):63 − 71. DOI: 10.1007/s40010-013-0069-5
[133] 阮晓波,孙树林,刘文亮. 锚固岩石边坡地震稳定性拟动力分析[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(增刊1):293 − 300. [RUAN Xiaobo,SUN Shulin,LIU Wenliang. Seismic stability of anchored rock slope using pseudo-dynamic method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(Sup 1):293 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)] RUAN Xiaobo, SUN Shulin, LIU Wenliang. Seismic stability of anchored rock slope using pseudo-dynamic method[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2013, 34(Sup 1): 293 − 300. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[134] RUAN Xiaobo,SUN Shulin,LIU Wenliang. Effect of the amplification factor on seismic stability of expanded municipal solid waste landfills using the pseudo-dynamic method[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University SCIENCE A,2013,14(10):731 − 738. DOI: 10.1631/jzus.A1300041
[135] ZHOU Xiaoping,QIAN Qihu,CHENG Hao,et al. Stability analysis of two-dimensional landslides subjected to seismic loads[J]. Acta Mechanica Solida Sinica,2015,28(3):262 − 276. DOI: 10.1016/S0894-9166(15)30013-6
[136] 卢玉林,薄景山,陈晓冉,等. 考虑渗流和地震时的砂土边坡稳定性计算[J]. 重庆大学学报,2017,40(1):65 − 75. [LU Yulin,BO Jingshan,CHEN Xiaoran,et al. Calculation of sand slope stability with considering seepage and earthquake[J]. Journal of Chongqing University,2017,40(1):65 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LU Yulin, BO Jingshan, CHEN Xiaoran, et al. Calculation of sand slope stability with considering seepage and earthquake[J]. Journal of Chongqing University, 2017, 40(1): 65 − 75. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[137] 邓亚虹,徐召,孙科,等. 一种考虑波动效应的拟动力地震边坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 地球科学与环境学报,2019,41(5):623 − 630. [DENG Yahong,XU Zhao,SUN Ke,et al. Pseudo-dynamic seismic slope stability analysis method considering wave propagation effects[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment,2019,41(5):623 − 630. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2019.05.010 DENG Yahong, XU Zhao, SUN Ke, et al. Pseudo-dynamic seismic slope stability analysis method considering wave propagation effects[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 2019, 41(5): 623 − 630. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6561.2019.05.010
[138] 杨楠,邓亚虹,慕焕东,等. 一种基于拟动力法和剩余推力法的地震边坡稳定性分析新方法[J]. 工程地质学报,2023,31(2):607 − 616. [YANG Nan,DENG Yahong,MU Huandong,et al. A new method of seismic slope stability analysis based on pseudo-dynamic method and residual thrust method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2023,31(2):607 − 616. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Nan, DENG Yahong, MU Huandong, et al. A new method of seismic slope stability analysis based on pseudo-dynamic method and residual thrust method[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2023, 31(2): 607 − 616. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[139] 蒋青江,邓亚虹,杨楠,等. 基于严格条分法的拟动力地震边坡稳定性分析方法研究[J]. 地震工程学报,2023,45(3):716 − 723. [JIANG Qingjiang,DENG Yahong,YANG Nan,et,al. Pseudo-dynamic seismic slope stability analysis based on rigorous slice method[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2023,45(3):716 − 723. (in Chinese with English abstract)] JIANG Qingjiang, DENG Yahong, YANG Nan, et, al. Pseudo-dynamic seismic slope stability analysis based on rigorous slice method[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2023, 45(3): 716 − 723. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[140] 宋桂锋,杜江梅,柯鉴,等. 基于拟动力法的顺层岩质边坡稳定性极限分析[J]. 地震工程学报,2019,41(4):931 − 938. [SONG Guifeng,DU Jiangmei,KE Jian,et al. Stability limit analysis of bedding rock slopes based on pseudo-dynamic method[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal,2019,41(4):931 − 938. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.04.931 SONG Guifeng, DU Jiangmei, KE Jian, et al. Stability limit analysis of bedding rock slopes based on pseudo-dynamic method[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 2019, 41(4): 931 − 938. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0844.2019.04.931
[141] BELLEZZA I. A new pseudo-dynamic approach for seismic active soil thrust[J]. Geotechnical and Geological Engineering,2014,32(2):561 − 576. DOI: 10.1007/s10706-014-9734-y
[142] CHANDA N,GHOSH S,PAL M. Seismic stability of slope using modified pseudo-dynamic method[J]. International Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2019,13(6):548 − 559. DOI: 10.1080/19386362.2017.1372056
[143] PAIN A,CHOUDHURY D,BHATTACHARYYA S K. Effect of dynamic soil properties and frequency content of harmonic excitation on the internal stability of reinforced soil retaining structure[J]. Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2017,45(5):471 − 486. DOI: 10.1016/j.geotexmem.2017.07.003
[144] QIN Changbing,CHIAN S C. Impact of earthquake characteristics on seismic slope stability using modified pseudodynamic method[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2019,19(9):04019106. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0001489
[145] 李雨浓,赵巍,刘畅,等. 基于修正拟动力法的抗滑桩加固边坡三维地震稳定性分析[J]. 中国公路学报,2024,37(1):44 − 54. [LI Yunnong,ZHAO Wei,LIU Chang,et al. 3D seismic stability analysis of slopes reinforced with stabilizing piles based on a modified pseudo-dynamic method[J]. China J. Highw. Transp,2024,37(1):44 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Yunnong, ZHAO Wei, LIU Chang, et al. 3D seismic stability analysis of slopes reinforced with stabilizing piles based on a modified pseudo-dynamic method[J]. China J. Highw. Transp, 2024, 37(1): 44 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[146] CHEN Guanghui,ZOU Jinfeng,SHENG Yuming,et al. Three-dimensional seismic bearing capacity assessment of heterogeneous and anisotropic slopes[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2022,22(9):04022148. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0002493
[147] 张磊,孙树林,储浩,等. 基于改进拟动力法的主动土压力分析研究[J]. 河北工程大学学报(自然科学版),2017,34(3):32 − 37. [ZHANG Lei,SUN Shulin,CHU Hao,et al. Active earth pressure of retaining wall based on modified pseu-do-dynamic method[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition),2017,34(3):32 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2017.03.007 ZHANG Lei, SUN Shulin, CHU Hao, et al. Active earth pressure of retaining wall based on modified pseu-do-dynamic method[J]. Journal of Hebei University of Engineering (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 34(3): 32 − 37. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9469.2017.03.007
[148] 陈立伟,安彦勇,赵靓,等. 基于改进拟动力法的沿河岩石边坡地震抗倾覆稳定性分析[J]. 水道港口,2023,44(5):819 − 827. [CHEN Liwei,AN Yanyong,ZHAO Jing,et al. Analysis of seismic anti overturning stability of rock slope along the river based on improved pseudo dynamic method[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor,2023,44(5):819 − 827. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Liwei, AN Yanyong, ZHAO Jing, et al. Analysis of seismic anti overturning stability of rock slope along the river based on improved pseudo dynamic method[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor, 2023, 44(5): 819 − 827. (in Chinese with English abstract)





 下载:
下载:









 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS