Analysis of monitoring and treatment effect of anti-sliping piles for the landslide at Jiangdingya, Zhouqu County
-
摘要:
为研究白龙江流域舟曲段堆积体滑坡治理中抗滑桩的承载特性及其治理效果,以舟曲江顶崖滑坡治理工程为对象,在滑坡前缘中部和两侧的3根抗滑桩迎滑面和背滑面的中部与角部分别布置钢筋应力计,获取现场3 a的动态数据,并通过ABAQUS对治理后的滑坡体进行数值模拟分析。结果表明:(1)当前桩身钢筋的应力增长速率较施工结束时明显减缓,低于抗拉强度设计值,且钢筋仍处于弹性工作状态,这表明抗滑桩对滑坡的治理效果较好;(2)江顶崖滑坡多级滑面的滑动导致抗滑桩不仅受到滑坡推力的作用,其表面还受到了岩土体的摩擦力作用,具体表现为3根试验桩的迎滑面与背滑面两侧的钢筋在5 m、10 m、20 m深度处均主要表现为拉应力,这与现行规范抗滑桩设计时截面前后两侧拉压应力状态相反的情况不符,是因为应力具有叠加效应,当摩擦力对桩产生的拉应力大于弯曲压应力时,会使得该侧的钢筋应力整体表现为拉应力,从而出现抗滑桩前后两侧钢筋均受拉的应力状态;(3)治理工程完工后,通过数值模拟对滑坡的水平位移进行分析,发现滑坡的最大水平位移为33.93 mm,表明滑坡支护结构加固作用较好,滑坡体在经过加固后处于基本稳定状态,且桩土之间形成了新的变形协调。研究成果可为该区域堆积体滑坡治理工程的设计提供科学依据。
Abstract:In order to study the bearing characteristics and treatment effects of anti-sliping piles in the treatment of accumulation landslides in the Bailong River Basin, Zhouqu section, Zhouqu Jiangdingya landslide treatment project was taken as the object. Steel bar stress gauges were arranged at the middle and corners of the upstream and downstream sliding surfaces of the three anti-sliping piles at the front edge of the landslide, and dynamic data from three years were obtained on site. Numerical simulation analysis was conducted on the treated landslide using ABAQUS. The results show that: (1) The stress growth rate of pile reinforcement has significantly slowed down compared to the end of construction, which is lower than the design value of tensile strength, and the rebar is still in an elastic working state, indicating that the treatment effect of anti-sliding piles on the landslide control is good; (2) The multi-level sliding of Jiangdingya landslide causes the anti-sliding piles to not only be effected by the landslide thrust, but also by the frictional force of the rock and soil body. Specifically, the steel bars on both sides of the sliding and backing surfaces of the three test piles is mainly tensile stress at depths of 5 m, 10 m and 20 m, which is opposite to the stress state of tension and compression on both sides of the section when designing anti-sliding piles according to current standards. This discrepancy is due to the superposition effect of stress. When the tensile stress generated by friction force on the pile is greater than the bending compressive stress, the overall stress of the steel bar on that side will be tensile stress. (3) After the completion of the treatment project, the horizontal displacement of the landslide is analyzed by numerical simulation. It was found that the maximum horizontal displacement of the landslide was 33.93 mm, indicating that the reinforcement of the landslide support structure is good. The landslide body is in a stable state after reinforcement, and a new deformation coordination between piles and soil has been formed. The research results can provide scientific basis for the design of accumulation landslide control project in this area.
-
0. 引言
白龙江流域舟曲段地处青藏高原东北缘,北接黄土高原,东望秦岭,向南为四川盆地,区域内地质构造强烈、地形起伏大、沟深坡陡,是典型的高山峡谷地貌,堆积体滑坡十分发育[1]。该地区的堆积体滑坡上覆土体结构松散,通常规模巨大,十分容易发生滑动,造成堵江等灾害,每年造成的人员伤亡和经济损失巨大[2 − 3]。抗滑桩在该区域的滑坡治理工程中已经得到广泛应用,但有关抗滑桩承载特性研究十分匮乏[4 − 5]。
现场监测是研究抗滑桩的承载特性的有效手段[6 − 10],目前对于抗滑桩的内力监测分析已有了较多的研究成果,各种监测技术和分析理论不断完善。张会远等[11]监测了抗滑桩靠山侧最中部位置钢筋的应力,通过单筋矩形截面受弯模型得到桩身弯矩分布曲线。任伟中等[12]通过在抗滑桩迎滑面中部沿长度方向上钻孔埋设测斜仪,根据弹性地基梁法由桩身变形来分析桩身承载特性。王秀丽等[13]长期监测了锁儿头滑坡矩形抗滑桩四个角部的钢筋应力,同侧钢筋应力取平均值进行计算,得出了抗滑桩在使用过程中的内力变化特征曲线;黄雪峰等[14]通过监测悬臂桩在不同开挖工况条件下拉压两侧钢筋应力,研究了其内力和土体水平应力分布特点。上述学者将抗滑桩受力状态简化为仅受到弯曲作用,认为全桩的应力状态均为迎滑面受拉、背滑面受压,桩截面内力计算误差较大且无法进行优化,因此,需要通过现场监测进一步研究堆积体滑坡中抗滑桩的承载特性。
有限元强度折减法是常用的边坡稳定性分析方法,也被用于计算滑坡支挡结构内力和分析边坡加固机制等研究。张怡颖等[15]通过FLAC3D数值模拟软件,分析了扎马古滑坡体在不同工况下的变形情况,发现在暴雨与强震耦合作用工况下,易产生贯通滑动面,会导致滑坡失稳滑动。Galeandro等[16]通过数值模拟,研究了在不同降雨工况下的边坡稳定性,短时强降雨作用下滑坡引发地表变形更大。陈冲等[4]提出了一种采用结构单元和实体单元相结合的复合抗滑桩模型,能在真实模拟抗滑桩性能的同时快速提取桩身内力。陈伟志[17]等依托林织铁路滑坡案例,提出了框架式抗滑支挡结构加固巨型古滑坡的设计方法与施工技术,并通过数值模拟计算了支挡结构的内力,分析了加固机制。郑颖人等[18]认为强度折减法既可以考虑锚索抗滑桩与岩土之间的相互作用关系,又能够算出极限状态下锚索抗滑桩中的内力,相比于传统分析方法有较大的优越性。
综上所述,本文依托舟曲江顶崖大型堆积体滑坡治理工程,对主剖面位置处的抗滑桩布置钢筋应力计,通过现场监测获取3 a的动态数据,对桩身承载特性与进行深入研究。此外,通过ABAQUS对治理后的滑坡体进行数值模拟分析,以评价其治理后的稳定性。
1. 滑坡概况
1.1 工程地质条件
江顶崖滑坡体位于白龙江左岸,该区域谷道狭窄、陡坡流急,属于构造侵蚀山地。滑坡区位于舟曲—武都地震亚带,属于坪定—化马断裂带,新构造运动强烈,大型断裂带滑坡发育。据2017年收集的舟曲县气象站统计资料,白龙江流域舟曲段降雨主要在夏季,日最大降雨量为96.7 mm。
受汛期连续强降雨及白龙江冲刷坡脚的影响,2018年7月12日,舟曲县南峪乡江顶崖发生山体滑坡,造成堵江,致使原本宽约36 m的江面最窄处仅有5 m。滑坡灾害的发生导致上游江水水位上升,最高可达7~8 m,导致上游村庄被淹,滑坡前缘国道被冲毁,造成严重经济损失,并严重威胁下游居民的生命财产安全。本次发生滑动的主要为H1滑体(图1),长462 m,平均宽度210 m,体积338.1×104 m3,属特大型地质灾害。
江顶崖滑坡为南峪滑坡群的一部分,南峪滑坡历史上发生多次滑动,因此江顶崖滑坡土体为老滑坡堆积体。其中滑体土为松散的碎石土,土体多呈黄褐色,粒径大小悬殊,结构松散,呈干燥—稍湿状,其力学性质差,渗水性强,稳定性差。滑带土为含砾黏土及炭质板岩碎屑,结构较为致密,呈灰黑色,含水量较高,手搓后呈粉末状或泥状,强度较低,属易滑地层。根据前期研究成果可知,滑坡机理为前期地震作用改变土体物理力学性质,然后在汛期连续强降雨的渗透作用以及白龙江冲刷坡脚条件下所诱发[19 − 21]。
1.2 滑坡破坏
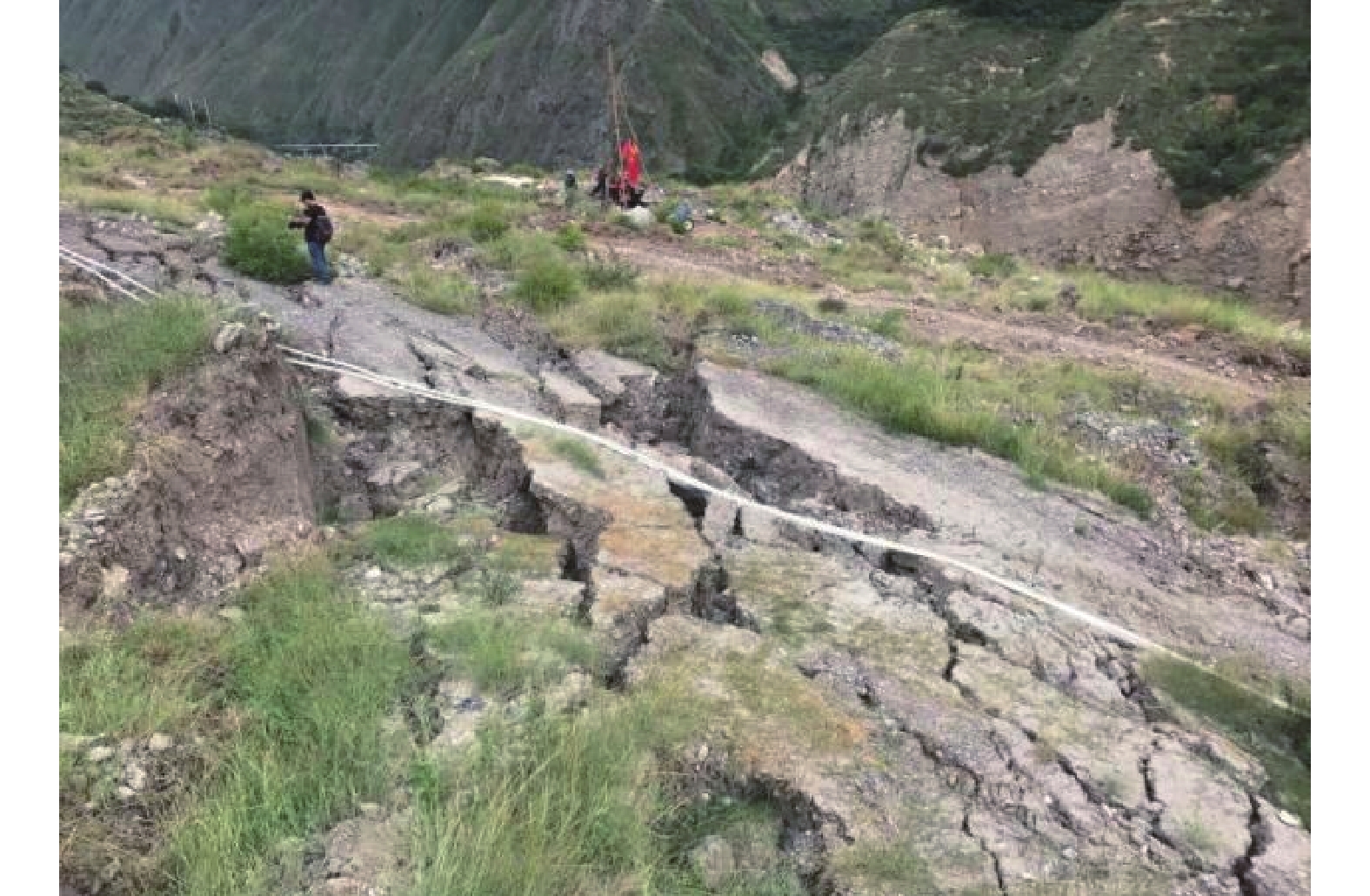
滑坡发生后,对滑坡进行现场勘察,发现滑体后缘及侧缘拉裂形成了高陡的后壁,在后壁出现了大量弧形、走向与后壁一致的裂缝,两侧侧壁沿滑坡滑动方向也出现了大量的裂缝,致使滑坡后缘及两侧侧缘分别形成了影响变形区。滑坡体变形迹象明显,由于滑坡体蠕动下滑后,上部土体推挤中前部土体,在滑坡中下部形成了百余条剪切裂缝,如图2所示。
2. 滑坡治理工程现场监测方案
2.1 滑坡治理工程概况
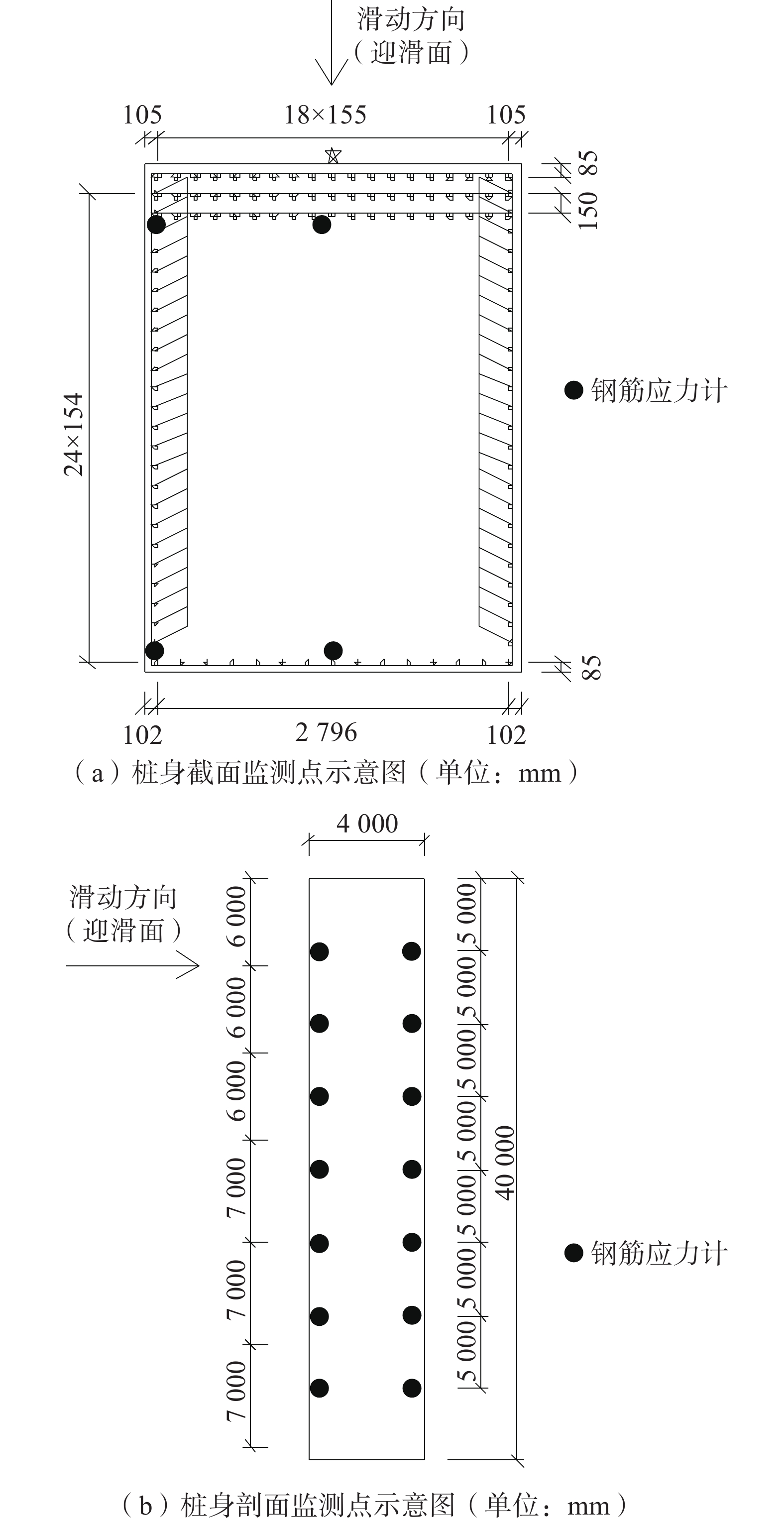
为防止H1堆积体滑坡继续滑动,首先对滑坡后缘及侧壁进行削方处理,在后缘采用钢筋混凝土框架预应力锚索进行支护,并且在滑坡前缘布置抗滑桩。其中,前缘治理抗滑桩为主要的抗滑桩支护结构,抗滑桩截面尺寸3.0 m×4.0 m,开挖桩孔尺寸为3.7 m×4.7 m,抗滑桩桩长为40 m,桩心距为5.5 m,总共布置39根。迎滑面钢筋布置三排直径为32 mm的HRB400级钢筋,共170根。背滑面采用单排布筋,每两根一组,共30根。江顶崖H1滑坡治理工程的布置情况如图3(a)所示。
2.2 监测试验传感器布置
为了研究白龙江流域舟曲段堆积体滑坡中大口径抗滑桩的承载特性,选取滑坡前缘主剖面位置处的抗滑桩为试验桩,见图3(a),对其钢筋应力进行监测。在抗滑桩施工过程中安装现场监测传感器,分别在抗滑桩迎滑面、背滑面的中部和角部布置钢筋应力计,其竖向间距为5m,每个竖向监测方向上布设7个测点,共布设了28个钢筋应力计。图4为抗滑桩传感器布置图。
按照前述监测方案在江顶崖滑坡现场埋设监测传感器,自2019年8月开始每日于0:00和12:00收集2次监测数据,对滑坡治理抗滑桩的应力应变进行持续监测,并通过无线远程监测系统进行数据采集。现场监测传感器安装见图5。
3. 抗滑桩监测承载特性结果分析
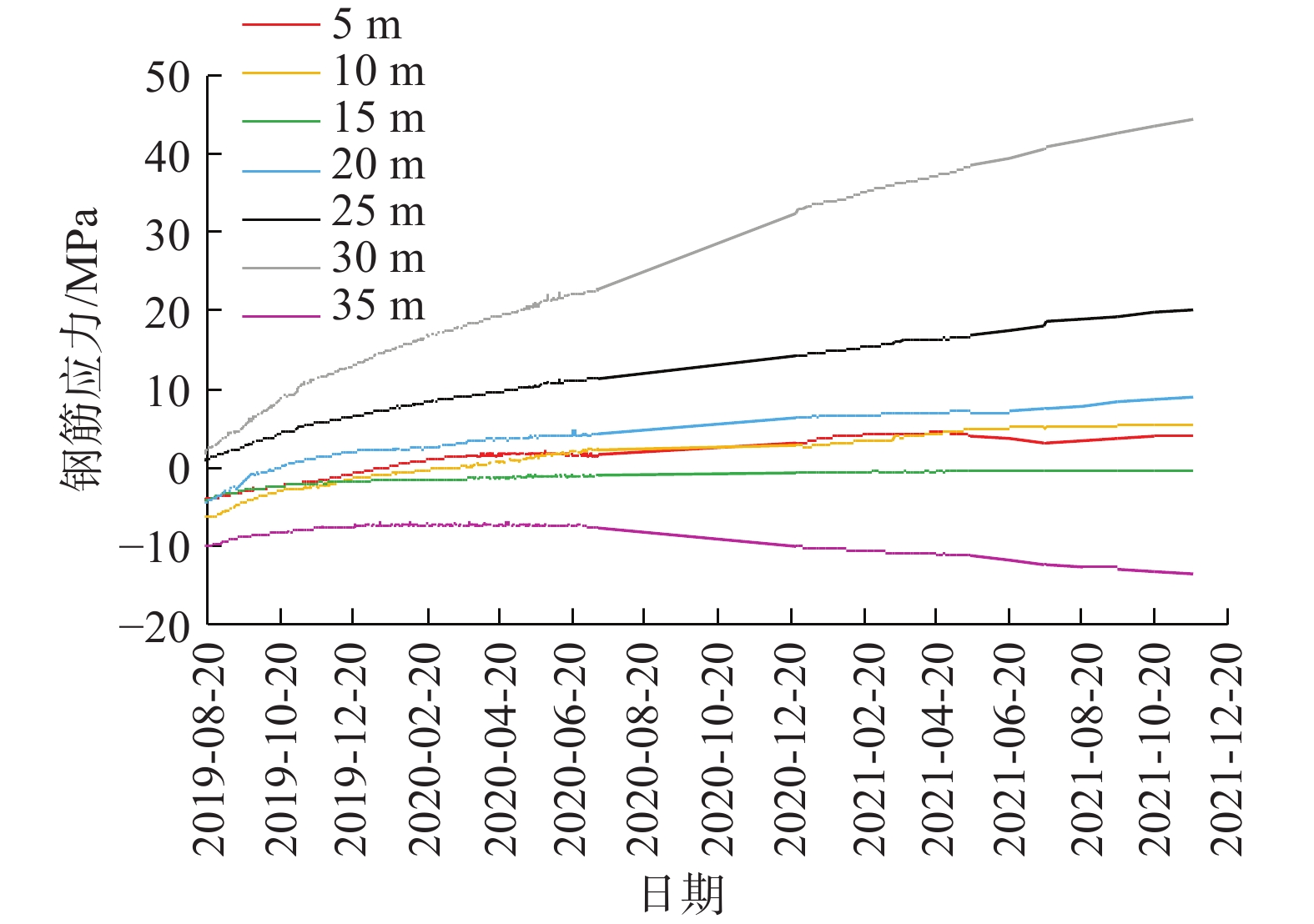
试验桩靠江侧角部的监测钢筋应力随时间变化曲线如图6所示。由图可知,监测抗滑桩钢筋应力还在缓慢增加,且当前桩身钢筋的应力增长速率较施工结束时明显减缓。截至2021年12月20日,钢筋单根最大拉应力在30 m深处为44.5 MPa,最大压应力的绝对值在35 m深处约为13.5 MPa。支护抗滑桩的钢筋应力值均低于钢筋抗拉强度设计值,处于弹性工作状态。
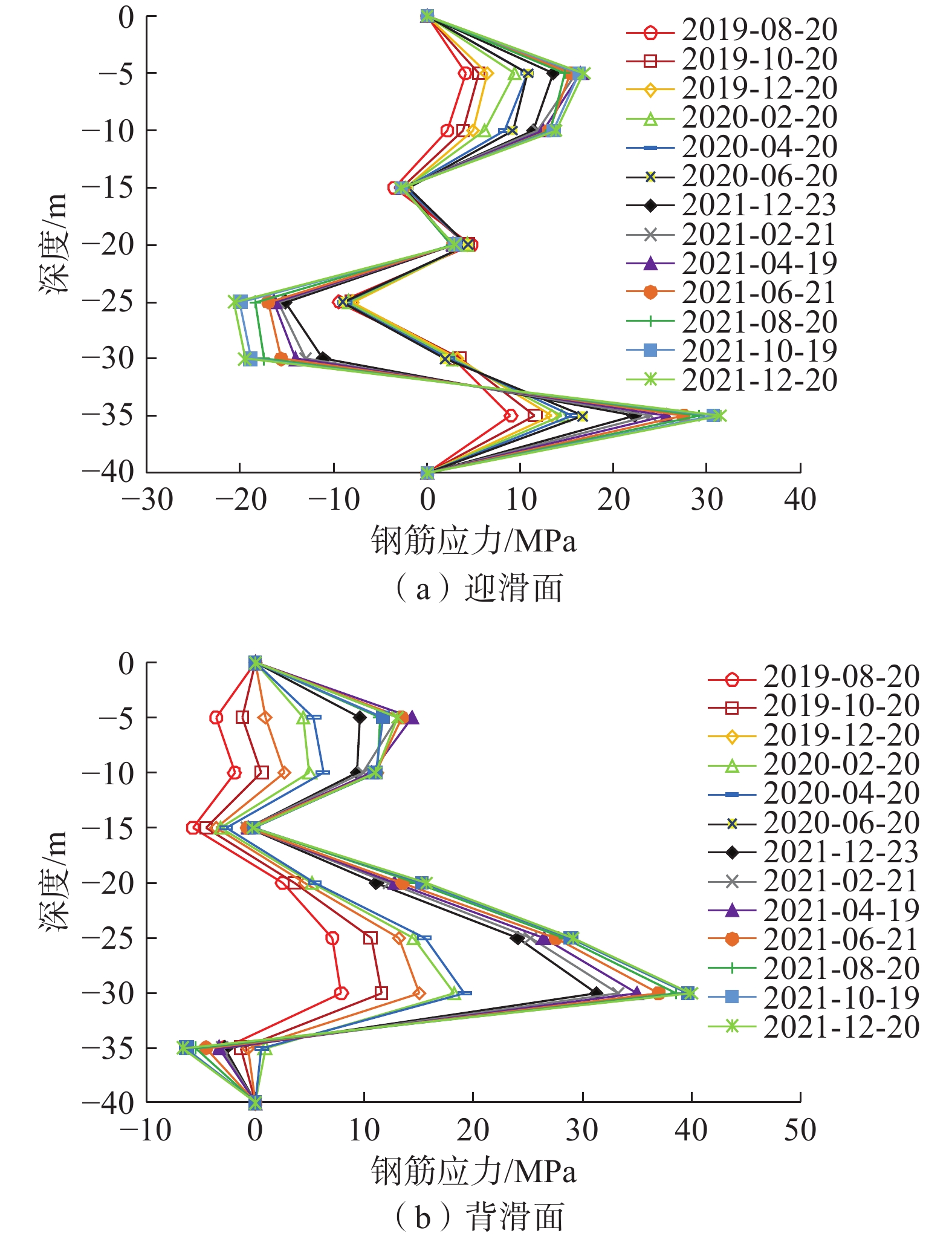
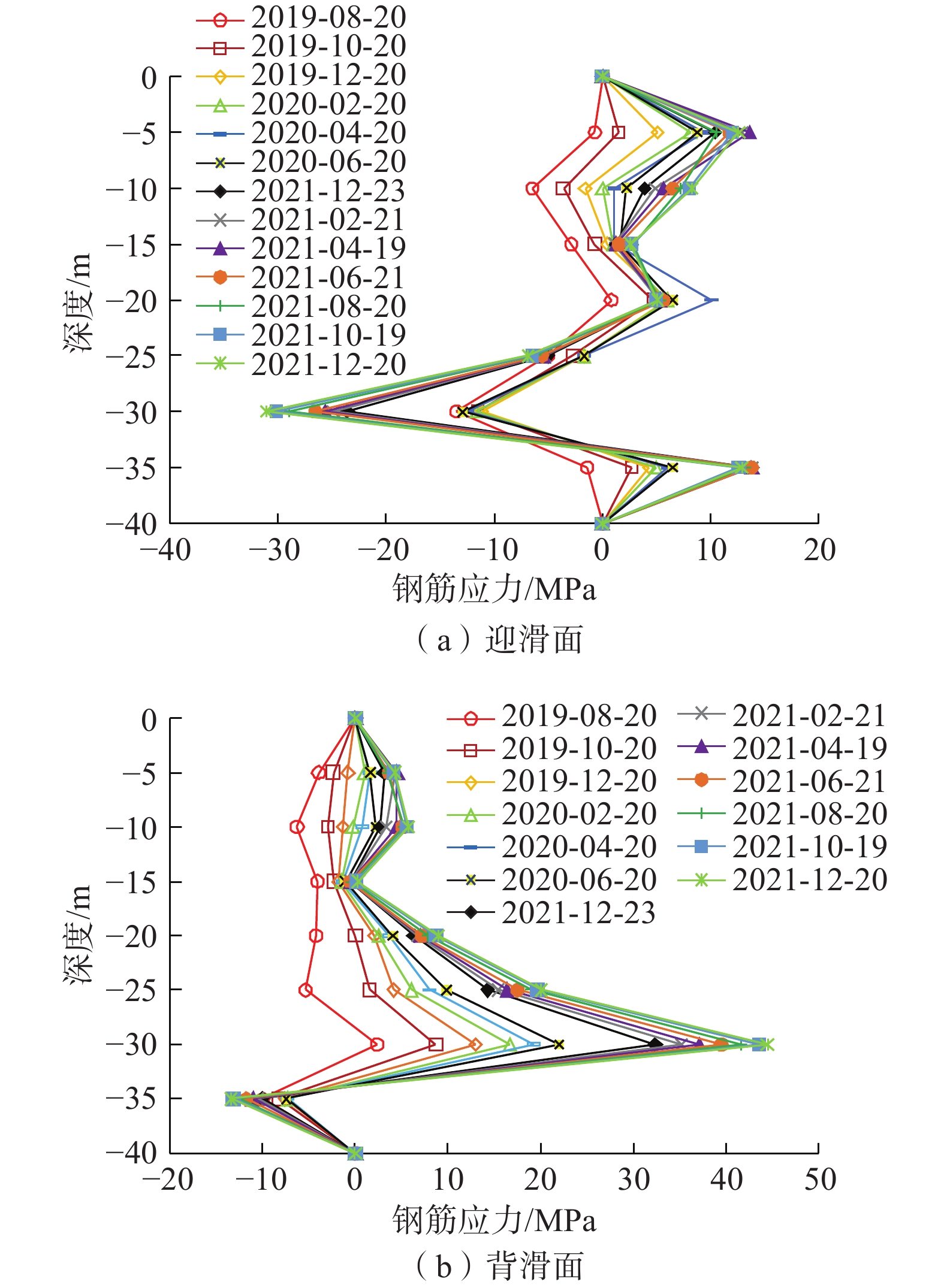
抗滑桩中部各深度钢筋应力分布曲线见图7。由图7(a)迎滑面中部钢筋应力曲线可知,试验桩在5 m至10 m之间以及35 m深度附近钢筋拉应力增长幅度较大,在25 m至30 m之间钢筋压应力增长明显。此外,迎滑面中部钢筋应力曲线均出现多个极值,试验桩迎滑面中部的钢筋拉应力存在5 m、20 m、35 m共3个极值,最大拉应力在约35 m深处,为31.4 MPa。抗滑桩迎滑面中部钢筋在25 m深度出现压应力最大值,其绝对值为20.6 MPa。由图7(b)背滑面中部钢筋应力曲线可知,试验桩在5 m和30 m处存在拉应力极值,最大拉应力在约30 m深处,为39.9 MPa;最大压应力出现在15 m深处,其绝对值为5.7 MPa。抗滑桩在35 m深度以下的背滑面中部钢筋应力均为压应力,对应的迎滑面中部钢筋拉应力数值较大,表明此深度范围内的抗滑桩受到较大的弯曲作用。滑坡工程地质剖面图,见图3(b),中的滑动面深度位置也在地下约20 m和约35 m深度处,这与图7中钢筋应力极值点位置相符合,证明抗滑桩的受力效果较好。
抗滑桩角部监测钢筋应力如图8所示。由图8可知,抗滑桩迎滑面角部的钢筋单根拉应力在5 m、20 m、35 m深度处出现极值,这与迎滑面中部监测钢筋应力曲线变化趋势一致;迎滑面角部钢筋最大压应力在30 m深处的绝对值约为31.1 MPa。背滑面角部的钢筋应力曲线分布形式与图7(b)所示背滑面中部基本一致,最大拉应力在30 m深处约为44.5 MPa,最大压应力在35 m深处的绝对值约为13.5 MPa。
对比图7与图8可知,试验桩的迎滑面与背滑面两侧的钢筋在5 m、10 m、20 m深度处均主要表现为拉应力,这种现象在3根监测试验桩上均出现,这与现行规范抗滑桩设计时截面前后两侧拉压应力状态相反的情况不符。由此可知,传统抗滑桩弯矩分析中仅考虑横力弯曲作用属于过度简化,抗滑桩沿长度方向上还受到较大的拉力作用。分析上述现象出现的原因,当滑坡发生蠕滑时滑带土体相对滑动,抗滑桩表面受到沿桩身长度方向上的土体摩擦力作用,表现为拉拔力。这表明抗滑桩主筋的拉应力并非全部由桩身弯曲所提供,还有部分来自于桩身受拉;应力具有叠加效应,当摩擦力对桩产生的拉应力大于弯曲压应力时,会使得该侧的钢筋应力整体表现为拉应力,从而出现抗滑桩前后两侧钢筋均受拉的应力状态。因此,抗滑桩在复活堆积体滑坡中所受到的摩擦力导致拉拔作用,比现行规范中抗滑桩仅为受弯状态的假定更为复杂,采用规范法设计抗滑桩时需要进行修正。
4. 基于数值模拟的滑坡治理效果评价
4.1 建立滑坡模型
采用ABAQUS工程模拟有限元软件,建立滑坡的三维模型对其稳定性进行分析,模型尺寸及参数与原型一致。滑坡模型从上至下主要有滑体、滑带以及滑床共3层土体,土体的材料属性采用摩尔-库仑本构模型,参数取值参照地勘以及室内试验结果[19 − 20];支护结构均为混凝土结构,材料属性采用弹性材料,滑坡土体与支护结构材料参数见表1。边界条件设置时,支护结构与土体之间的接触采用摩擦接触,摩擦系数为0.3。最不利工况为地震和降雨耦合作用,降雨计算工况将土层参数中黏聚力和内摩擦角折减,地震工况选择峰值加速度0.21g地震波进行数值模拟。
表 1 材料物理力学参数Table 1. Physical and mechanical parameters of materials材料 弹性模量
/MPa泊松比 重度
/(kN·m−3)黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)滑体土 18 0.32 21 12 22 滑带土 12 0.35 20.5 9 18 滑床 100 0.26 26 18 36 混凝土 3×104 0.2 25 − − 4.2 基于数值模拟的滑坡水平位移分析
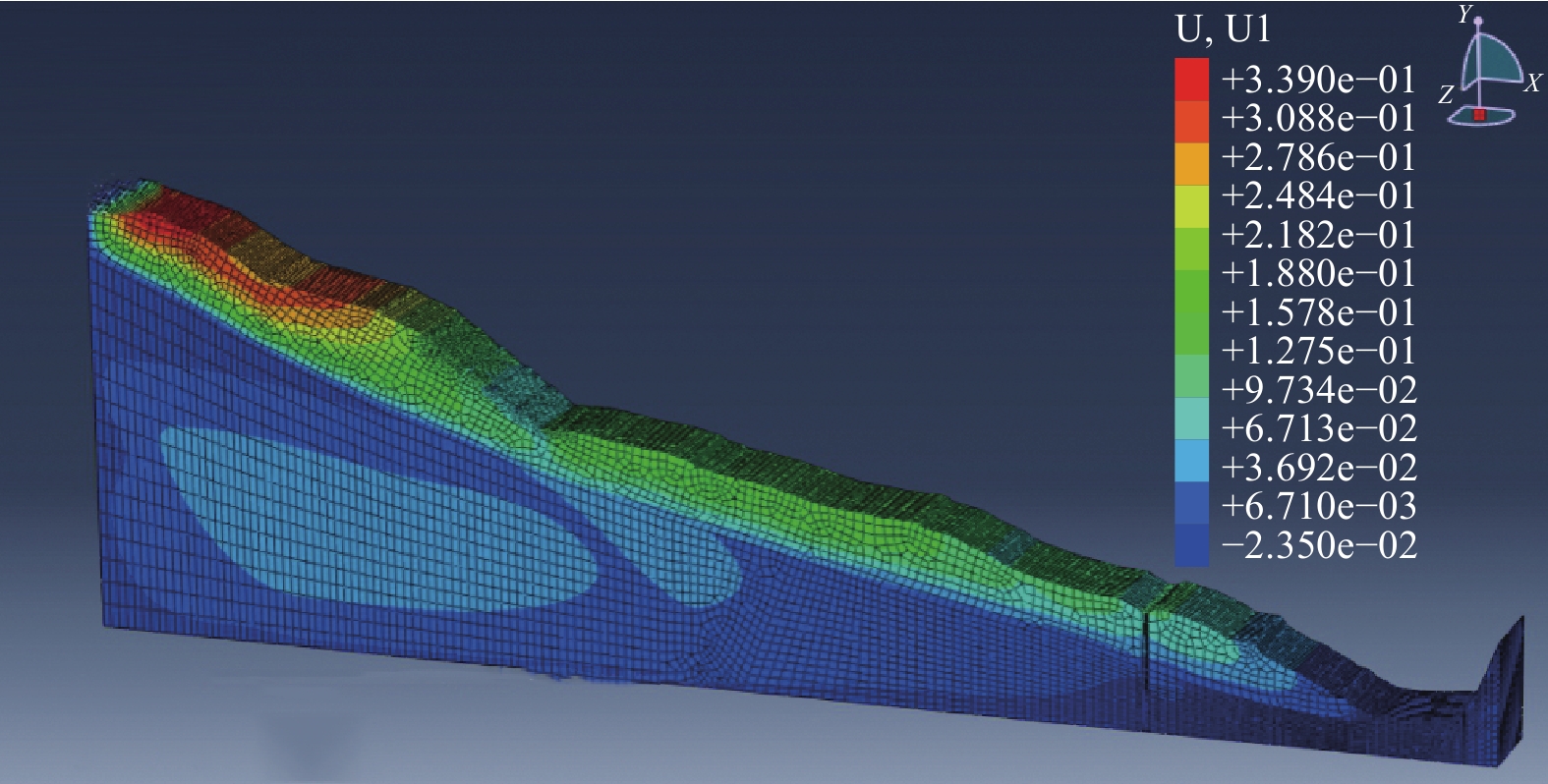
江顶崖滑坡在治理工程完工后最不利工况下的位移云图如图9所示。由图9可知,滑坡的最大水平位移出现在滑坡体的后部未支护位置,为33.93 mm。而本次滑动的H1滑体在治理后的位移值很小,表明滑坡支护结构发挥作用,滑坡体处于基本稳定状态。从抗滑桩附近的水平位移云图(图10)可以看出该区域的土体水平位移很小,说明在治理工程施工完成后,前缘支护抗滑桩可有效控制滑坡的变形。并且,桩前土体的水平位移较桩后土体的水平位移大。
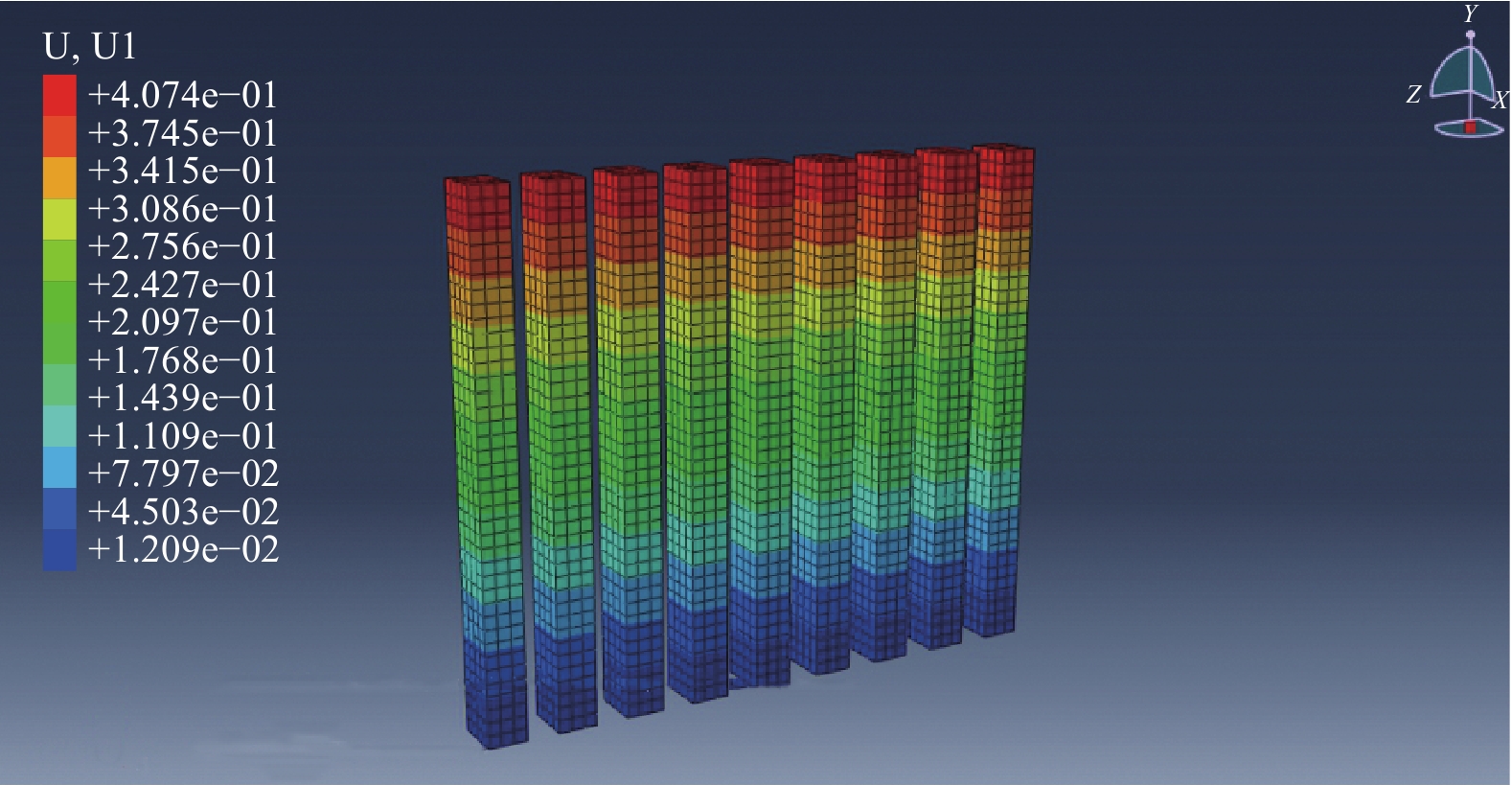
抗滑桩的桩身水平侧移云图及桩身侧移见图11。从图11中可以看出抗滑桩顶端在施工完成后发生了4.07 mm的水平位移,然而桩身下部位移值很小,结合桩身内力监测结果分析所得抗滑桩承载特性可知,抗滑桩在经过一定的弯曲变形之后,与土体之间形成了新的变形协调,证明了其对边坡整体加固效果的有效性。
5. 讨论
5.1 滑坡中可能存在的多级滑面
根据前文监测结果分析可知,试验桩迎滑面中部的钢筋拉应力存在5 m、20 m、35 m共3个极值,抗滑桩迎滑面角部的钢筋单根拉应力在5 m、20 m、35 m深度处也出现了极值,这与迎滑面中部监测钢筋应力曲线变化趋势一致,而抗滑桩在35 m深度以下的背滑面中部钢筋应力均为压应力,对应的迎滑面中部钢筋拉应力数值较大,表明此深度范围内的抗滑桩受到较大的弯曲作用。这些都与《滑坡防治设计规范》GB/T 38509—2020基于单滑面简化计算模型不符,说明该堆积体滑坡内部有较为明显的分层,可能存在新老不同的多级岩土体,即该滑坡可能存在多级滑面,后续应该对该滑坡是否具有多级滑面的特性进行进一步的研究。
5.2 抗滑桩的受力模式及承载特性探讨
试验桩在5~10 m以及35 m深度附近钢筋拉应力增长幅度较大,在25~30 m钢筋压应力增长明显。由图7和图8相互对比可知,3根监测试验桩的迎滑面与背滑面两侧的钢筋在5 m、10 m、20 m深度处均主要表现为拉应力,而现行规范抗滑桩设计时截面前后两侧拉压应力状态相反。
推测两侧钢筋均表现为拉应力的原因可能是:由于受到滑坡推力作用,桩身发生了一定的弯曲变形和桩土间的相对运动,迎滑侧的土体相对桩身向上运动,造成桩土摩擦,表现为桩身在土体作用下向上“受拉”;背滑侧桩身弯曲,导致桩土间摩擦,总体也表现为受拉,其本质都是桩身与岩土体的相对运动。因此,抗滑桩主筋的拉应力并非全部由桩身弯曲所提供,还有部分来自于桩身受拉;应力具有叠加效应,当摩擦力对桩产生的拉应力大于弯曲压应力时,会使得该侧的钢筋应力整体表现为拉应力,从而出现抗滑桩前后两侧钢筋均受拉的应力状态。
6. 结论
(1)2018年1月21日江顶崖滑坡形变量最大为16 mm,到2018年7月8日滑坡发生前,累计形变量达到最大值41 mm,而数值模拟分析显示,经过治理后的抗滑桩顶端在施工完成后仅发生了4.07 mm的水平位移,监测结果表明使用抗滑桩对该滑坡进行治理取得了较好的效果。
(2)由数值模拟可知,在地震和降雨耦合作用下江顶崖滑坡的最大水平位移出现在滑坡体的后部未支护位置,为33.93 mm。在治理工程施工完成后,桩前土体的水平位移较桩后土体的水平位移大,前缘支护抗滑桩可有效控制滑坡的变形。在加入抗滑桩后,抗滑桩顶端发生了4.07 mm的水平位移,相较于未治理的江顶崖滑坡变形明显减小,数值模拟分析结果表明抗滑桩治理效果较好。
(3)3根试验桩的迎滑面与背滑面两侧的钢筋在5 m、10 m、20 m深度处均主要表现为拉应力,说明抗滑桩两侧沿长度方向上受到较大的拉力作用,其原因可能是当滑坡发生蠕滑时滑带土体相对滑动,抗滑桩表面受到沿桩身长度方向上的土体摩擦力作用,这表明抗滑桩主筋的拉应力并非全部由桩身弯曲所提供,还有部分来自于桩身受拉,建议在按照规范设计该类抗滑桩时进行一定的修正。
-
表 1 材料物理力学参数
Table 1 Physical and mechanical parameters of materials
材料 弹性模量
/MPa泊松比 重度
/(kN·m−3)黏聚力
/kPa内摩擦角
/(°)滑体土 18 0.32 21 12 22 滑带土 12 0.35 20.5 9 18 滑床 100 0.26 26 18 36 混凝土 3×104 0.2 25 − − -
[1] QI Tianjun,MENG Xingmin,QING Feng,et al. Distribution and characteristics of large landslides in a fault zone:A case study of the NE Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Geomorphology,2021,379:107592. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2021.107592
[2] YANG Xiaohui,JIANG Yuanwen,ZHU Junchuan,et al. Deformation characteristics and failure mechanism of the Moli landslide in Guoye Town,Zhouqu County[J]. Landslides,2023,20(4):789 − 800. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-022-02019-x
[3] 郭一兵,姜鑫,郭富赟,等. 甘肃舟曲县果耶镇磨里滑坡成因及堵江危险性预测分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(3):58 − 68. [GUO Yibing,JIANG Xin,GUO Fuyun,et al. Analysis on the formation of the Moli landslide and river blockage risk in Guoye Town, Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(3):58 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)] GUO Yibing, JIANG Xin, GUO Fuyun, et al. Analysis on the formation of the Moli landslide and river blockage risk in Guoye Town, Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(3): 58 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 陈冲,王卫,吕华永. 基于复合抗滑桩模型加固边坡稳定性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2019,40(8):3207 − 3217. [CHEN Chong,WANG Wei,LYU Huayong. Stability analysis of slope reinforced with composite anti-slide pile model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2019,40(8):3207 − 3217. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Chong, WANG Wei, LYU Huayong. Stability analysis of slope reinforced with composite anti-slide pile model[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2019, 40(8): 3207 − 3217. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 高子雁,李瑞冬,石鹏卿,等. 基于长短期记忆网络的甘肃舟曲立节北山滑坡变形预测[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(6):30 − 36. [GAO Ziyan,LI Ruidong,SHI Pengqing,et al. Deformation prediction of the Northern Mountain landslide in Lijie Town of Zhouqu, Gansu Province based on long-short term memory network[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(6):30 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)] GAO Ziyan, LI Ruidong, SHI Pengqing, et al. Deformation prediction of the Northern Mountain landslide in Lijie Town of Zhouqu, Gansu Province based on long-short term memory network[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(6): 30 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 张明熠,吕兆华,杨建波. 软土弯剪作用下大直径刚性桩水平承载性能试验[J]. 同济大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(8):1166 − 1172. [ZHANG Mingyi,LYU Zhaohua,YANG Jianbo. Experiment on lateral load capacities of large-diameter rigid pile against toppling moment and shear forces under soft soil site conditions[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science),2016,44(8):1166 − 1172. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Mingyi, LYU Zhaohua, YANG Jianbo. Experiment on lateral load capacities of large-diameter rigid pile against toppling moment and shear forces under soft soil site conditions[J]. Journal of Tongji University (Natural Science), 2016, 44(8): 1166 − 1172. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 张敏, 周灵, 谭超, 等. 复杂地层方形抗滑桩旋挖成孔工艺及工程应用[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2023,34(1):85 − 93. [ZHANG Min,ZHOU Ling,TAN Chao,et al. Techniques of rotary hole-drilling for square anti-slide piles in complex formation and its application[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2023,34(1):85 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Min, ZHOU Ling, TAN Chao, et al. Techniques of rotary hole-drilling for square anti-slide piles in complex formation and its application[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2023, 34(1): 85 − 93. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 王文沛,殷跃平,王立朝,等. 排水抗滑桩技术研究现状及展望[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2023,50(2):73 − 83. [WANG Wenpei,YIN Yueping,WANG Lichao, et al. Studies on status and prospects of anti-slide shaft technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2023,50(2):73 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Wenpei, YIN Yueping, WANG Lichao, et al. Studies on status and prospects of anti-slide shaft technology[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2023, 50(2): 73 − 83. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 邓时容,肖世国. 嵌固段顶部拓宽型抗滑桩计算方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):84 − 91. [DENG Shirong,XIAO Shiguo. Calculation method of stabilizing piles with broadened top at the built-in section[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):84 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)] DENG Shirong, XIAO Shiguo. Calculation method of stabilizing piles with broadened top at the built-in section[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 84 − 91. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 毛正君,于海泳,梁伟,等. 基于无人机倾斜摄影测量三维建模的区域黄土滑坡识别及特征分析[J]. 中国地质,2024,51(2):561 − 576. [MAO Zhengjun,YU Haiyong,LIANG Wei,et al. Identification and feature analysis of regional loess landslides based on UAV tilt photogrammetry 3D modeling[J]. Geology in China,2024,51(2):561 − 576. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MAO Zhengjun, YU Haiyong, LIANG Wei, et al. Identification and feature analysis of regional loess landslides based on UAV tilt photogrammetry 3D modeling[J]. Geology in China, 2024, 51(2): 561 − 576. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 张会远,吴锐,靳喆菲,等. 某滑坡抗滑桩治理效果监测分析[J]. 煤田地质与勘探,2015,43(5):69 − 73. [ZHANG Huiyuan,WU Rui,JIN Zhefei,et al. Monitoring and analysis of reinforcement effect of anti-slide piles of a slop[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration,2015,43(5):69 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Huiyuan, WU Rui, JIN Zhefei, et al. Monitoring and analysis of reinforcement effect of anti-slide piles of a slop[J]. Coal Geology & Exploration, 2015, 43(5): 69 − 73. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 任伟中,陈浩,唐新建,等. 运用钻孔测斜仪监测滑坡抗滑桩变形受力状态研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(增刊2):3667 − 3672. [REN Weizhong,CHEN Hao,TANG Xinjian,et al. Study on monitoring deformation and stress state of landslide anti-slide pile by borehole inclinometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(Sup 2):3667 − 3672. (in Chinese)] REN Weizhong, CHEN Hao, TANG Xinjian, et al. Study on monitoring deformation and stress state of landslide anti-slide pile by borehole inclinometer[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2008, 27(Sup 2): 3667 − 3672. (in Chinese)
[13] 王秀丽,金兆鑫,董文燕,等. 舟曲锁儿头滑坡抗滑桩监测及分析[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(5):123 − 128. [WANG Xiuli,JIN Zhaoxin,DONG Wenyan,et al. Monitoring and analysis of anti-slide pile of the Suo’ertou large landslide in Zhouqu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(5):123 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WANG Xiuli, JIN Zhaoxin, DONG Wenyan, et al. Monitoring and analysis of anti-slide pile of the Suo’ertou large landslide in Zhouqu[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(5): 123 − 128. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 黄雪峰,张蓓,覃小华,等. 悬臂式围护桩受力性状与土压力试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2015,36(2):340 − 346. [HUANG Xuefeng,ZHANG Bei,QIN Xiaohua,et al. Experimental investigation on force behavior and earth pressure of cantilever fender pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2015,36(2):340 − 346. (in Chinese with English abstract)] HUANG Xuefeng, ZHANG Bei, QIN Xiaohua, et al. Experimental investigation on force behavior and earth pressure of cantilever fender pile[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2015, 36(2): 340 − 346. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 杨校辉,朱鹏,窦晓东,等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖古滑坡复活变形特征与稳定性分析[J]. 地质通报,2024,43(6):947 − 957. [YANG Xiaohui,ZHU Peng,DOU Xiaodong,et al. Resurrection deformation characteristics and stability of Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China,2024,43(6):947 − 957. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Xiaohui, ZHU Peng, DOU Xiaodong, et al. Resurrection deformation characteristics and stability of Jiangdingya ancient landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 2024, 43(6): 947 − 957. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] GALEANDRO A,DOGLIONI A,SIMEONE V,et al. Analysis of infiltration processes into fractured and swelling soils as triggering factors of landslides[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences,2014,71(6):2911 − 2923. DOI: 10.1007/s12665-013-2666-7
[17] 陈伟志,李安洪,胡会星,等. 横穿古滑坡框架式抗滑支挡结构工程技术研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(增刊1):2861 − 2875. [CHEN Weizhi,LI Anhong,HU Huixing,et al. Study on engineering technology of frame anti-sliding retaining structure across ancient landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(Sup 1):2861 − 2875. (in Chinese)] CHEN Weizhi, LI Anhong, HU Huixing, et al. Study on engineering technology of frame anti-sliding retaining structure across ancient landslide[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(Sup 1): 2861 − 2875. (in Chinese)
[18] 郑颖人,赵尚毅. 用有限元强度折减法求边(滑)坡支挡结构的内力[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2004,23(20):3552 − 3558. [ZHENG Yingren,ZHAO Shangyi. Calculation of inner force of support structure for landslide/slope by using strength reduction fem[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2004,23(20):3552 − 3558. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHENG Yingren, ZHAO Shangyi. Calculation of inner force of support structure for landslide/slope by using strength reduction fem[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2004, 23(20): 3552 − 3558. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[19] 张卫雄,翟向华,丁保艳,等. 甘肃舟曲江顶崖滑坡成因分析与综合治理措施[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(5):7 − 14. [ZHANG Weixiong,ZHAI Xianghua,DING Baoyan,et al. Causative analysis and comprehensive treatment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(5):7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Weixiong, ZHAI Xianghua, DING Baoyan, et al. Causative analysis and comprehensive treatment of the Jiangdingya landslide in Zhouqu County of Gansu Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2020, 31(5): 7 − 14. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[20] 张卫雄,丁保艳,张文纶,等. 舟曲江顶崖大型滑坡成因及破坏机制分析[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2022,42(4):714 − 722. [ZHANG Weixiong,DING Baoyan,ZHANG Wenlun,et al. Analysis on the cause and failure mechanism of the jiangdingya large landslide in Zhouqu,Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2022,42(4):714 − 722. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Weixiong, DING Baoyan, ZHANG Wenlun, et al. Analysis on the cause and failure mechanism of the jiangdingya large landslide in Zhouqu, Gansu Province[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering, 2022, 42(4): 714 − 722. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[21] 窦晓东,贾 强,刘心彪,等. 舟曲县南峪乡江顶崖滑坡灾害应急治理工程勘查报告[R]. 甘肃省地质环境监测院,2018. [DOU Xiaodong,JIA Qiang,LIU Xinbiao,et al. Exploration report of Jiangdingya landslide disaster emergency management project in Nanyu Township,Zhouqu County[R]. Gansu Province Geological Environment Monitoring Institute,2018. (in Chinese)] DOU Xiaodong, JIA Qiang, LIU Xinbiao, et al. Exploration report of Jiangdingya landslide disaster emergency management project in Nanyu Township, Zhouqu County[R]. Gansu Province Geological Environment Monitoring Institute, 2018. (in Chinese)





 下载:
下载:




 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS