Research on risk early warning for rainfall-induced shallow landslides in Guangdong Province based on a dynamic slope instability model
-
摘要:
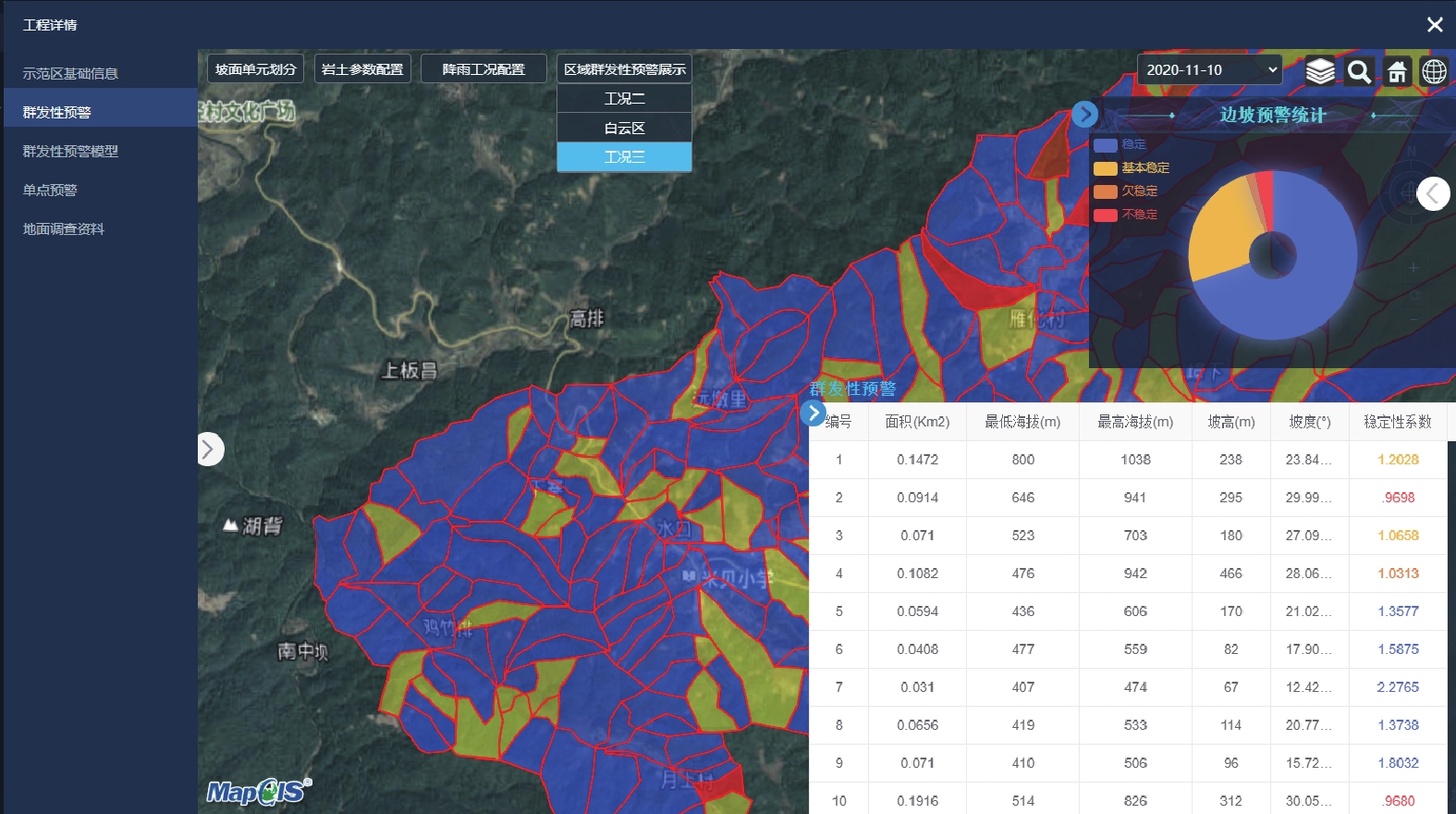
针对县级地质灾害气象风险预警面临的精度及模型建设问题,根据广东省地质灾害主要发生在坡面残坡积浅表层的突出特点,通过对典型地质灾害进行物理模拟试验和数值模拟,研究广东省浅表层斜坡失稳发生机理。研究表明:边坡在暴雨条件下,斜坡岩土体容易在浅表层首先造成失稳,影响因素主要有降雨量、降雨历时、土体类别和坡体结构等因素。由此,对研究区划分斜坡单元,按各斜坡单元的坡长、坡度、岩土类型、分层及其关键物理力学参数开展斜坡单元概化分类,并将Green-Ampt降雨入渗模型和无限边坡稳定性评价方法相结合,优化构建了动力学斜坡稳定性评价模型。结合龙川县贝岭镇流域应用实例,初步探索了坡面单元尺度下地质灾害气象风险预警斜坡失稳动力学预警技术,可为广东省开展以斜坡单元预警为主要方式的县级地质灾害气象风险预警提供支撑。
Abstract:In light of the accuracy and model construction challenges in county-level meteorological risk early warning for geo-hazards, and considering the prominent characteristics that these geo-hazards mainly occur on the shallow surface of residual slopes, the mechanism of shallow surface slope instability in Guangdong Province was studied through physical simulation experiments and numerical simulations of typical geo-hazards. The results show that the slope is easy to lose stability in the shallow surface layer under the condition of rainstorm, and the main factors are rainfall, rainfall duration, soil type and slope structure. Subsequently, by dividing the study area into slope units, we developed a generalized classification and numerical modeling of these units based on parameters such as slope length, slope gradient, rock and soil type, stratification, and key physical and mechanical parameters of each slope unit, and by combining the Green-Ampt rainfall infiltration model with the infinite slope stability evaluation method, the slope instability dynamics warning model was then constructed. Through the application in the basin of Beiling Town in Longchuan County, and the application of dynamic early-warning technology for slope instability in meteorological risk early warning for geological hazards was preliminarily explored at the scale of slope units, which can provide support for county-level geo-hazards meteorological risk early-warning based on slope unit early-warning in Guangdong Province.
-
0. 引言
森林火灾是林区常见自然灾害,其不仅对生态环境质量和人类健康安全构成严重威胁,且火烧迹地在降雨条件下,极易发生泥石流灾害,这种与林火密切相关的泥石流通常被称为“火后泥石流”(post-fire debris flow)[1-3]。火烧迹地发生泥石流的概率会大幅度提高,CANNON等[4]2000年对加利福尼亚南部86个火烧迹地调查发现,约35%的火烧迹地会发生火后泥石流灾害,CANNON等[5]2001年得出约40%(37/95)的火烧迹地发生了泥石流灾害。与常规泥石流相比,火后泥石流呈现集中高频暴发[6]、降雨阈值极低[7-8]、受到火烧严重程度[9]的影响等特点[10],且起动机理也有显著区别,SANTI等[11]2008年发现火后泥石流主要由地表径流引发,GABET等[12]2008年也指出森林植物灰烬具有提高地表径流容积和运输能力的作用,任云[13]2018年基于Fuzzy-AHP建立了适用于火后泥石流的危险性评价模型。由于火后泥石流独特的发育特征与成灾机理,常规泥石流的危险性评价模型和预警避险方案适用性较差,因此建立针对火烧区火后泥石流的降雨阈值,在此基础上形成基于火后泥石流暴发降雨阈值、实时雨量监测数据与群测群防于一体的预警避险方案,对火后泥石流科学防灾具有重要意义。
1. 喜德县中坝村火烧区概况
1.1 地质环境特征
喜德县地处川西高原南段,属典型亚热带西南季风和高原气候,呈现出既有高原干燥气候、又有充沛降雨的特点。区内年平均气温约14.1 ℃,多年平均降雨量1000 mm,日最大降雨量164.3 mm。5—10月为雨季,降水过程多为强降雨、连阴雨、多夜雨,雨季降雨量占全年总降雨量的93%左右,且山区气候垂直分带十分明显,海拔每增高100 m,降雨量增加约30 mm。
发生于2020年5月7日森林火灾区位于凉山州喜德县鲁基乡中坝村一组(图1),地势北高南低,山岭海拔2050~3505 m,山区地形切割深度较浅,属构造侵蚀低中山地貌区。岩性主要为花岗岩为主,第四系全新统残坡积层主要为含块(碎)石的粉质黏土。区内因白昼以及垂直高度不同气温变化较大,地表风蚀作用强烈,岩石风化十分严重。
1.2 火烈度特征及空间分布
火烧区植被类型以云南松和常绿阔叶林为主,火灾后火烧迹地植被遭受严重破坏,覆盖率明显降低,采用多光谱遥感数据中两个波段所构建的监测指数如dNBR(the delta Normalized Burn Ratio)可以准确检算森林火烧地区的过火面积、边界及火烧程度[14-16]。本文通过Envi软件对事发地火烧前后(分别是2020年4月1日及2020年5月12日)多光谱卫星遥感图像(20 m精度)进行解译,并结合现场调查情况判断火烧面积、边界及不同区域的火烧强烈程度。火烈度遥感解译后的图像通过软件处理,可统计出火烧迹地范围内不同火烈度区面积占比,以及每条沟道流域内高烈度火烧区(中度及重度火烈度区)的面积占比。
基于PERSON等[17]提出的不同强度火烧判别特征表1,对中坝村后山火烧迹地不同火烈度区域通过遥感图像解译并结合现场实地调查,根据火烧迹地植被被烧毁程度、灰烬层厚度等特征,将火烧迹地的林火烈度分为重度、中度、轻度与未火烧四个等级。
表 1 中坝村后山火烧迹地不同强度火烈度判别特征Table 1. Distinguishing characteristics of fire intensity of different intensity in Zhongba Village burned area火强度 特点 未火烧 火烧前后地表覆盖物无变化 轻度火烧 超过50%的枯枝落叶未完全燃烧 中度火烧 大部分枯枝落叶被烧毁,但是大部分粗可燃物未完全燃烧 严重火烧 枯枝落叶和粗可燃物均被完全烧毁,地表为灰烬覆盖 根据火烈度判别标准,中坝村后山火烧迹地不同火烈度分区及相应重度、中度、轻度与未火烧区,各分区见图2、图3。
结果表明,中坝村后山森林火灾总过火面积约6.7 km2,其中重度火烧区占比65.93%、中度火烧区占比19.76%、轻度火烧区占比14.31%,中坝村后山1#~4#沟流域内中度及重度火烧区面积占比均超过90%(表2)。
表 2 中坝村森林火烧区不同火烈度面积占比数据统计Table 2. Statistics on the proportion of different fire intensity areas in the forest fire area of Zhongba Village/% 火烧区 轻度火烈度区面积占比 中度火烈度区面积占比 重度火烈度区面积占比 中度及重度火烈度区面积占比 整个火烧迹地 14.31 19.76 65.93 85.69 1#沟 2.11 26.56 69.41 95.97 2#沟 3.69 16.94 78.37 95.32 3#沟 3.18 18.51 74.78 93.28 4#沟 7.36 26.52 63.82 90.33 2. 火后泥石流发育特征
2.1 2020年“6·4”火后泥石流致灾情况
2020年6月4日下午,四川省凉山州喜德县鲁基乡突降暴雨,十分钟最大降雨量11.7 mm,小时最大降雨量15.4 mm,日降雨量26.3 mm,短时强降雨导致中坝村后山季节性冲沟沟道水位暴涨,暴发山洪,进而引发泥石流灾害。泥石流沿着沟谷冲出,冲毁农田并淤埋沟口房屋。此次中坝村共4条沟道暴发火后泥石流,自西向东分别为1#、2#、3#、4#泥石流沟,冲出总规模3.26×104 m3,造成直接经济损失70万元,土地受损4.99×104 m2,房屋受损4户12间,其中1户受损严重(图4),受灾人口41户164人。由于驻村第一书记及时预警,泥石流发生前10分钟,受威胁农户在帮扶队员和乡、村、组干部的组织下迅速疏散转移,得以成功避险,未造成人员伤亡。
2.2 火后泥石流形成条件
2.2.1 地形特征
中坝村4条火后泥石流沟道均为窄陡型,沟底平均宽度2.5~3.0 m,两侧岸坡较陡多为35°~50°,沟谷形态呈“V”字型,沟道平均纵坡降较大,且沟域中上游区段地势较陡,跌水陡坎发育,下游区段地势较缓。清水区汇水区面积约占整个沟域的80%,下游段汇水区域较小,整体流域形态呈“叶片状”(表3)。上宽下窄、上陡下缓的沟道特征,使得降雨过程中极易呈现“漏斗状”汇流,以极快的速度席卷沟道内丰富的物源形成泥石流灾害。
表 3 火烧区4条泥石流沟形态特征统计Table 3. Morphological characteristics statistics of 4 debris flow ditches in burned area沟道编号 流域面积/km2 主沟长/km 主沟纵坡比降/‰ 相对高差/m 岸坡坡度/(°) 沟谷形状 1# 0.13 0.652 450 244 40~50 “V”形 2# 0.23 0.893 429 317 40~50 “V”形 3# 0.36 1.040 360 326 35~45 “V”形 4# 0.73 2.090 311 395 35~45 “V”形 2.2.2 物源特征
现场调查显示,中坝村后山1#~4#流域内物源主要分为三类:坡面侵蚀物源、崩滑物源、沟道堆积物源。坡面侵蚀物源主要分布于沟道中上游,其中因植被烧毁堆积于坡面的灰烬层是火后泥石流的标志性物源之一,见图5(a),也是构成首次火后泥石流的主要补给物源,由于坡面汇流条件及火烧迹地土体性质的改变,大量坡面侵蚀物源在坡面径流作用下运移堆积,则成为第二次、第三次火后泥石流的主要启动物源。沟道物源主要分布于流域中上游区段,以碎块石、残枝树干以及灰烬松散物为主,见图5(b),块石粒径一般10~30 cm,较大者粒径达1.0~1.5 m,巨石堆积于沟道中,造成过流断面减小,易堵塞沟道,堵塞溃决后放大泥石流规模。崩滑物源主要分布在沟道中下游两岸,由于沟道下切作用,水流冲刷坡脚,造成两侧岸坡失稳,形成小范围滑塌堆积于沟道。统计显示(表4),1#沟物源静储量约4.5×104 m3,动储量约0.71×104 m3;2#沟物源静储量约10.23×104 m3,动储量约1.65×104 m3;3#沟物源静储量约15.57×104 m3,动储量约2.47×104 m3;4#沟物源静储量约35.95×104 m3,动储量约5.08×104 m3。
表 4 火烧区各泥石流沟动、静储量统计Table 4. Statistics of dynamic and static reserves of debris flow gully in burned area/(×104 m3) 沟号 物源储量 崩滑物源 沟道物源 坡面侵蚀物源 总计 1#沟 静储量 1.10 0.20 3.20 4.50 动储量 0.33 0.06 0.32 0.71 2#沟 静储量 1.60 0.23 8.40 10.23 动储量 0.48 0.07 1.10 1.65 3#沟 静储量 1.32 0.25 14.00 15.57 动储量 0.39 0.08 2.00 2.47 4#沟 静储量 0.75 0.20 35.00 35.95 动储量 0.22 0.06 4.80 5.08 从物源分布看,各物源无明显集中分布的趋势。从物源数量看(图6),4条沟道坡面侵蚀物源均为主要物源,1#~4#沟坡面侵蚀物源占各沟总物源比例分别为71.1%、82.1%、89.9%、97.4%。森林过火后坡面侵蚀物源的急剧增加,残枝树干及巨石等沟道堆积物造成的堵塞溃决,沟道侧蚀导致岸坡失稳提供物源补给,都为中坝村“6·4”泥石流的孕育和发生提供了有利条件。
2.2.3 水源条件
根据《中国暴雨参数统计图集》(2006年版),中坝村区域10 min、60 min、6 h、24 h年最大暴雨量平均值
$ \bar{H} $ 分别为15.0 mm、35.0 mm、66.0 mm、70.0 mm,变差系数Cv分别为0.40,0.45,0.47,0.42。通过计算中坝村区域不同频率降雨强度见表5。表 5 中坝村不同频率降雨强度值Table 5. Rainfall intensity values of different design frequencies in Zhongba Village降雨时段/h 设计频率/% 20 10 5 3.33 2 1 H1/6P 19.23 23.02 26.63 28.69 31.23 34.63 H1P 45.70 55.95 65.86 71.55 78.64 88.14 H6P 86.73 107.16 127.01 138.45 152.72 171.89 H24P 90.43 109.23 127.25 137.54 150.32 167.40 对照中坝村附近所设自动监测雨量计数据(表6),实测10分钟降雨量为11.7 mm,1小时降雨量为15.4 mm,结合表3可知,此次激发泥石流的降雨强度远小于该区域5年一遇降雨强度。对照喜德县附近的冕宁县彝海镇盐井村泥石流(2020年6月12日)暴发时,其小时降雨量达36.6 mm,且据调查中坝村区域近20年内未发生泥石流,由此可以推测相对于火烧前,火后泥石流暴发所需的降雨阈值急剧降低,10 min及1 h激发降雨阈值分别至少降低了55.62%与76.62%。
表 6 中坝村2020年“6·4”泥石流暴发实时降雨量监测数据Table 6. Real-time rainfall monitoring data of 6·4 debris flow outbreak in Zhongba Village in 2020雨量站位置 距中坝村距离/
km10 min雨量/
mm1 h雨量/
mm漫水湾镇松林村1-4组 4.5 11.7 15.4 3. 火后泥石流运动学特征
迄今为止尚未建立一套适用于火后泥石流特征参数的计算模型,本文参照常规泥石流特征参数计算模型对该区火后泥石流流速、流量等进行计算[18-21]。
采用现场配浆法,得出中坝村火后泥石流容重平均值为1.98 t/m3,属于黏性泥石流。
中坝村火后泥石流为黏性,根据规范,流速计算可采用通用公式计算。基于1#~4#沟沟床粗糙,凹凸不平,沟道中块碎石较多,部分区段沟道弯曲且发育有跌水现象,沟床纵坡降较陡,根据规范,沟床糙率系数取10,选取各沟道沟口断面进行计算,计算结果见表7。
本次泥石流峰值流量采用形态调查法计算,经现场踏勘,选取沟口附近、沟道相对顺直、断面变化不大、无阻塞回流、上下沟槽无明显冲淤变化且具有清晰泥痕的沟段,经实地测量确定泥位及过流断面面积等参数,计算结果见表8。
表 7 中坝村火后泥石流各沟道沟口平均流速计算结果Table 7. Calculation results of the average flow velocity of each channel gully of post-fire debris flow in Zhongba Village沟道编号 1# 2# 3# 4# 泥深/m 1.3 1.4 1.6 1.0 主沟纵坡降/‰ 450 429 360 311 平均流速/(m·s−1) 7.85 7.28 8.04 7.03 表 8 中坝村2020年6·4火后泥石流峰值流量计算结果Table 8. Calculation results of peak flow of 6·4 post-fire debris flow in Zhongba Village in 2020沟道编号 1# 2# 3# 4# 平均流速/(m·s−1) 7.85 7.28 8.04 7.03 计算断面面积/m2 5.88 11.56 11.31 2.75 峰值流量/(m3·s−1) 46.17 74.19 90.92 19.33 4. 火后泥石流危险性评价及预警避险方案
4.1 中坝村火后泥石流危险性评价
本文采用常规泥石流危险度评价模型对中坝村泥石流危险度进行相应评价,为沟口居民安全的预警避险提供参考。采用刘希林、唐川提出的单沟泥石流危险性评价模型[19]对中坝村泥石流沟进行危险度评价:
$$\begin{split} {H}_{\text{单}}=&0.29M+0.29F+0.14{S}_{1}+0.09{S}_{2}\\ &+0.06{S}_{3}+0.11{S}_{6}+0.03{S}_{9} \end{split}$$ (1) 该方法一共包含7个评价因子,即泥石流规模M (103 m3)、暴发频率F (次/100年)、流域面积S1(km2)、主沟长度S2(km)、流域相对高差S3(km)、流域切割密度S6(km−1)、不稳定沟床比例S9(%)。其中,泥石流规模及发生频率为主要因子,泥石流规模M通常根据史料记载,取历史上已暴发泥石流一次堆积量的最大值即可,对于无相关记录的泥石流,可根据式(2)计算其规模,泥石流暴发频率f可根据史料记载获取,也可采用式(3)计算。除泥石流规模与暴发频率外,其余5个因子均为次要因子,其中流域切割密度一般取泥石流流域范围内冲沟长度之和与流域面积比值(式(4)),不稳定沟床比例即泥沙沿程补给的沟道长度占比,可结合野外考察和航拍分析确定。
$$ m=-2+0.26{s}_{1}+0.41{s}_{6}+0.0021w $$ (2) 式中:
$ w $ ——松散固体物储量/(104 m3)。$$ f=-80.6596-2.8302{s}_{1}+12.13{s}_{6}+0.0209w $$ (3) $$ {s}_{6}=l_i/{s}_{1} $$ (4) 式中:
$ {l}_{i} $ —流域内冲沟总长度/m,${l}_{i}={l}_{1}+{l}_{2}+ $ $ {l}_{3}+\cdots {+l}_{n}$ 。上述计算公式中,M、F、S1、S2、S3、S6、S9使用的数值均为基础数据m、f、s1、s2、s6、s9的转换值,使各个因子数值无量纲化[22]。各沟道基础数据见表9,将7个评价指标进行转换加权后可得各沟道危险度评价结果。
表 9 中坝村1#~4#沟道沟域基础数据Table 9. Basic data of 1#~4# trench trench area in Zhongba Village沟道编号 泥石流规模m/
(103 m3)暴发频率f/
(次·100年−1)流域面积s1/
km2主沟长度s2/
km流域相对高差s3/
km流域切割密度s6/
km不稳定沟床比例s9/
%1# 6.30 32.43 0.130 0.652 0.244 9.33 76 2# 11.40 28.73 0.230 0.893 0.317 9.04 85 3# 12.30 27.98 0.360 1.040 0.326 9.00 80 4# 2.60 56.15 0.730 2.090 0.395 11.40 65 由表10计算结果可知,中坝村1#沟道危险度为0.42,2#沟道危险度为0.45,3#沟道危险度为0.46,4#沟道危险度为0.48,将其与单沟泥石流危险度分级标准对照(表11),4条沟道均属于中度危险。
表 10 中坝村泥石流1#~4#沟危险度评价Table 10. Evaluation of dangerous degree of ditch 1#~4# in Zhongba Village沟道编号 1# 2# 3# 4# 泥石流规模M/103 m3 0.266 0.352 0.363 0.138 暴发频率F/(次·100年−1) 0.756 0.729 0.723 0.875 流域面积S1/km2 0.085 0.130 0.160 0.225 主沟长度S2/km 0.175 0.285 0.296 0.416 流域相对高差S3/km 0.163 0.211 0.217 0.379 流域切割密度S6/km 0.466 0.452 0.450 0.570 不稳定沟床比例S9/% 1 1 1 1 评价结果 0.42 0.45 0.46 0.48 表 11 单沟泥石流危险度分级标准Table 11. Classification standard of danger degree of single ditch debris flow单沟泥石流危险度 0.0~0.2 0.2~0.4 0.4~0.6 0.6~0.8 0.8~1.0 危险度分级 极低危险 低危险度 中危险度 高危险度 极高危险 4.2 中坝村火后泥石流预警避险方案及体会
上述分析结果显示,中坝村后山沟4条冲沟流域面积较小(均小于1 km2)、主沟平均纵坡降大、中度及重度火烧区面积占比高(均大于90%)、沟域内物源丰富,火后泥石流启动降雨阈值低,流速快、暴发迅猛且一次冲出规模较大,且均属于中度危险。尽管如此,由于基于已有火后泥石流暴发降雨量阈值研究成果对当地基层人员的普及,以及火烧区周边可以实时提供雨量监测数据,当地村干部(第一书记)工作到位,及时预警提醒沟口居民尽早做好避险避让准备工作,因此未造成人员伤亡,避灾效果极为显著。总结喜德县基鲁乡中坝村成功避让泥石流灾害主要得益于以下三个方面工作的落实(图7)。
(1)省、州、县、乡党委政府高度重视,责任落实;自然资源等部门履职尽责,工作到位,措施得当。森林火灾后及时组织专业技术队伍对过火区域及其周边开展次生地质灾害隐患排查,对火烧迹地植被烧毁情况及物源条件进行详细调查,通过泥石流危险度计算,确定中坝村后山所有潜在泥石流沟道发生火后泥石流的危险性等级,锁定危险区域保护对象,并加强对居民关于火后泥石流危险性的宣传教育。
(2)准确划定危险区域范围,设置警戒标志,安排监测人员在降雨时段进行实时监测巡查预警。同时预先选择安全地段,规划好紧急撤离路线,组织居民反复进行避险演练,并实现各村民小组之间、村民之间信息互通、信息共享,在最短时间内将预警信息快速传递,最大限度缩短撤离避让时间。
(3)实时获取火烧区附近雨量监测站的降雨监测资料(间隔5 min传送一次雨量数据),一旦发生强降雨,立即启动泥石流预警,并迅速组织居民撤离至安全地段。
5. 结论
(1)发生于2020年5月7的凉山喜德县森林火灾,总过火面积约6.73 km2,其中重度、中度和轻度火烧区占比分别为65.93%、19.76%和14.31%,中坝村后山1#~4#沟流域内中度及重度火烧区面积占比分别为95.97%、95.32%、93.28%、90.33%。
(2)中坝村后山沟火后泥石流激发降雨强度远小于该区域5年一遇降雨强度,相对于火烧前,火后泥石流10 min及1 h激发降雨阈值分别至少降低了55.62%与76.62%。
(3)中坝村后山1#沟与4#沟冲出固体物质小于1×104 m3,属小型泥石流,而2#沟与3#沟泥石流冲出固体物质均大于1×104 m3,属于中等规模泥石流。
(4)火后泥石流危险度评价结果显示,中坝村1#、2#、3#和4#和沟道危险度分别为0.42,0.45,0.46,0.48,均属于中度危险。
(5)林火发生后立即制定科学预警避险方案,并得到有效落实,泥石流暴发前10分钟紧急预警,居民迅速、有序、安全撤离,未造成人员伤亡,避灾效果显著。
-
表 1 天然及暴雨状态下斜坡岩土体计算参数
Table 1 Calculation parameters of rock and soil mass of the slope under natural and rainstorm conditions
名称 弹性模量
/MPa孔隙比 天然状态 饱水状态 γ/(kN·m−3) c/kPa ϕ/(°) γsat/(kN·m−3) c/kPa ϕ/(°) 砂质黏性土①-1 8.0 0.99 18.0 19.1 18.0 18.5 18.1 17.0 砂质黏性土①-2 8.5 0.88 18.1 20.2 19.2 18.7 19.3 18.3 砂质黏性土①-3 9.2 0.83 19.1 28.3 22.5 19.6 26.2 21.1 全风化花岗岩 50.0 0.71 21.0 38.0 35.0 21.5 − − 中风化花岗岩 100.0 0.65 22.0 50.0 45.0 22.5 − − 表 2 河源市龙川县地质灾害数值模拟(部分示例)
Table 2 Numerical simulation of geo-hazards in Longchuan County, Heyuan City (some examples)
灾害体特征 二/三维数值模拟 稳定系数 

1.25
(自然状态)1.01
(饱和状态)

1.22
(自然状态)0.80
(饱和状态) -
[1] 张君霞,黄武斌,李安泰,等. 甘肃省主要地质灾害精细化气象风险预警预报[J]. 干旱区地理,2023,46(9):1443 − 1452. [ZHANG Junxia,HUANG Wubin,LI Antai,et al. Fine meteorological risk early warning forecast of main geological disasters in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography,2023,46(9):1443 − 1452. (in Chinese with English abstract)] ZHANG Junxia, HUANG Wubin, LI Antai, et al. Fine meteorological risk early warning forecast of main geological disasters in Gansu Province[J]. Arid Land Geography, 2023, 46(9): 1443 − 1452. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 刘艳辉,刘传正,连建发,等. 基于显式统计原理的地质灾害区域预警方法初步研究[J]. 中国地质,2008,35(2):344 − 350. [LIU Yanhui,LIU Chuanzheng,LIAN Jianfa,et al. Method of regional early warning of geohazards based on the explicit statistical theory[J]. Geology in China,2008,35(2):344 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Yanhui, LIU Chuanzheng, LIAN Jianfa, et al. Method of regional early warning of geohazards based on the explicit statistical theory[J]. Geology in China, 2008, 35(2): 344 − 350. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[3] 魏平新,李秀娟. 广东省突发性地质灾害气象预警实践[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2015,26(1):138 − 144. [WEI Pingxin,LI Xiujuan. The meteorologic early warning research of sudden geo-hazard in Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2015,26(1):138 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)] WEI Pingxin, LI Xiujuan. The meteorologic early warning research of sudden geo-hazard in Guangdong Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2015, 26(1): 138 − 144. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 李朝奎,陈建辉,魏振伟,等. 显式统计预警模型下地质灾害预警方法及应用[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版),2019,44(7):1020 − 1026. [LI Chaokui,CHEN Jianhui,WEI Zhenwei,et al. Method and application of geological hazard early warning based on explicit statistical principle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University,2019,44(7):1020 − 1026. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Chaokui, CHEN Jianhui, WEI Zhenwei, et al. Method and application of geological hazard early warning based on explicit statistical principle[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2019, 44(7): 1020 − 1026. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 李秀娟,魏平新. 广东省典型降雨型滑坡自动监测点变形分析[J]. 西部探矿工程,2019,31(2):5 − 10. [LI Xiujuan,WEI Pingxin. Deformation analysis of automatic monitoring points of typical rainfall landslides in Guangdong Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering,2019,31(2):5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Xiujuan, WEI Pingxin. Deformation analysis of automatic monitoring points of typical rainfall landslides in Guangdong Province[J]. West-China Exploration Engineering, 2019, 31(2): 5 − 10. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 童纪伟. 广东省“十三·五” 期间地质灾害发育特征及影响因素分析[J]. 现代矿业,2021,37(10):219 − 221. [TONG Jiwei. Analysis of development characteristics and influencing factors of geological hazards during the “thirteenth five-year plan” period in Guangdong Province[J]. Modern Mining,2021,37(10):219 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)] TONG Jiwei. Analysis of development characteristics and influencing factors of geological hazards during the “thirteenth five-year plan” period in Guangdong Province[J]. Modern Mining, 2021, 37(10): 219 − 221. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 陈伟,莫海鸿,陈乐求. 非饱和土边坡降雨入渗过程及最大入渗深度研究[J]. 矿冶工程,2009,29(6):13 − 16. [CHEN Wei,MO Haihong,CHEN Leqiu. Study on rainfall infiltration process and the biggest infiltration depth for unsaturated soil slope[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2009,29(6):13 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)] CHEN Wei, MO Haihong, CHEN Leqiu. Study on rainfall infiltration process and the biggest infiltration depth for unsaturated soil slope[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2009, 29(6): 13 − 16. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 刘贤, 揭鸿鹄, 蒋水华, 等. 融合历史降雨下斜坡稳定性观测信息的可靠度分析[J]. 地球科学,2023,48(5):1865 − 1874. [LIU Xian, JIE Honghu, JIANG Shuihua, et al. Slope reliability analysis incorporating observation of stability performance under A past rainfall event[J]. Earth Science,2023,48(5):1865 − 1874. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Xian, JIE Honghu, JIANG Shuihua, et al. Slope reliability analysis incorporating observation of stability performance under A past rainfall event[J]. Earth Science, 2023, 48(5): 1865 − 1874. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 许旭堂, 鲜振兴, 杨枫, 等. 水-力耦合及干湿循环效应对浅层残积土斜坡稳定性的影响[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2022,33(4):28 − 36. [XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2022,33(4):28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)] XU Xutang, XIAN Zhenxing, YANG Feng, et al. Influence of hydraulic-mechanical coupling and dry-wet cycle effect on surficial layer stability of residual soil slopes[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2022, 33(4): 28 − 36. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 李诚诚. 强降雨作用下基于Green-Ampt入渗模型的边坡稳定性分析[D]. 长沙:湖南大学,2019. [LI Chengcheng. Stability analysis of slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under heavy rainfall[D]. Changsha:Hunan University,2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LI Chengcheng. Stability analysis of slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under heavy rainfall[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 马世国. 强降雨条件下基于Green-Ampt入渗模型的无限边坡稳定性研究[D]. 杭州:浙江大学,2014. [MA Shiguo. Study on the stability of infinite slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under intense rainfall[D]. Hangzhou:Zhejiang University,2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MA Shiguo. Study on the stability of infinite slope based on green-ampt infiltration model under intense rainfall[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2014. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 袁畅,宋雁,李慧生,等. 基于降雨监测的群发性滑坡灾害预警技术研究[J]. 广州建筑,2022,50(4):29 − 32. [YUAN Chang,SONG Yan,LI Huisheng,et al. Research on early warning technology of regional mass shallow landslide based on rainfall monitoring[J]. Guangzhou Architecture,2022,50(4):29 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YUAN Chang, SONG Yan, LI Huisheng, et al. Research on early warning technology of regional mass shallow landslide based on rainfall monitoring[J]. Guangzhou Architecture, 2022, 50(4): 29 − 32. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 荣广智,张继权,李天涛,等. 极端降水诱发地质灾害链风险评估研究——以贵州省水城县为例[J]. 灾害学,2022,37(4):201 − 210. [RONG Guangzhi,ZHANG Jiquan,LI Tiantao,et al. Risk assessment of extreme precipitation-induced geological disaster chain:A case study of Shuicheng County,Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2022,37(4):201 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract)] RONG Guangzhi, ZHANG Jiquan, LI Tiantao, et al. Risk assessment of extreme precipitation-induced geological disaster chain: A case study of Shuicheng County, Guizhou Province[J]. Journal of Catastrophology, 2022, 37(4): 201 − 210. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 刘正华,余丰华,夏跃珍,等,基于斜坡单元的地质灾害气象预警系统建设初探[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2015,42(6):131-136. [LIU Zhenghua,YU Fenghua,XIA Yuezhen,et al. Primary exploration of the geological hazard meteorological warning system based on slope unit[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2015,42(6):131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Zhenghua, YU Fenghua, XIA Yuezhen, et al. Primary exploration of the geological hazard meteorological warning system based on slope unit[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2015, 42(6): 131-136. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 刘艳辉,苏永超. 四川青川县区域地质灾害气象风险预警模型研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2019,27(1):134 − 143. [LIU Yanhui,SU Yongchao. Early-warning model of regional geological disasters based on meteorological factor in Qingchuan County,Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2019,27(1):134 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao. Early-warning model of regional geological disasters based on meteorological factor in Qingchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2019, 27(1): 134 − 143. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 罗鸿东,李瑞冬,张勃,等. 基于信息量法的地质灾害气象风险预警模型:以甘肃省陇南地区为例[J]. 地学前缘,2019,26(6):289 − 297. [LUO Hongdong,LI Ruidong,ZHANG Bo,et al. An early warning model system for predicting meteorological risk associated with geological disasters in the Longnan area,Gansu Province based on the information value method[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2019,26(6):289 − 297. (in Chinese with English abstract)] LUO Hongdong, LI Ruidong, ZHANG Bo, et al. An early warning model system for predicting meteorological risk associated with geological disasters in the Longnan area, Gansu Province based on the information value method[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 2019, 26(6): 289 − 297. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 阳帅, 谭泽颖, 陈宏信, 等. 基于修正Green-Ampt模型的降雨诱发区域浅层斜坡失稳灾害分析[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):219 − 227. [YANG Shuai, TAN Zeying, CHEN Hongxin, et al. Analysis of instability disaster of rainfall induced shallow landslides at the regional scale based on the modified Green Ampt model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):219 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract)] YANG Shuai, TAN Zeying, CHEN Hongxin, et al. Analysis of instability disaster of rainfall induced shallow landslides at the regional scale based on the modified Green Ampt model[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 219 − 227. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 缪海波, 王功辉. 风振影响下乔木坡地暴雨型浅层滑坡演化机制[J]. 地质科技通报,2022,41(2):60 − 70. [MIAO Haibo, WANG Gonghui. Evolution mechanism of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides on slopes covered by arbors considering the influence of wind-induced vibration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology,2022,41(2):60 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)] MIAO Haibo, WANG Gonghui. Evolution mechanism of rainstorm-induced shallow landslides on slopes covered by arbors considering the influence of wind-induced vibration[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 2022, 41(2): 60 − 70. (in Chinese with English abstract)





 下载:
下载:
























 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS