Analysis on deformation characteristics of a cutting high bedding rock slope with multiple weak layers based on physical model tests
-
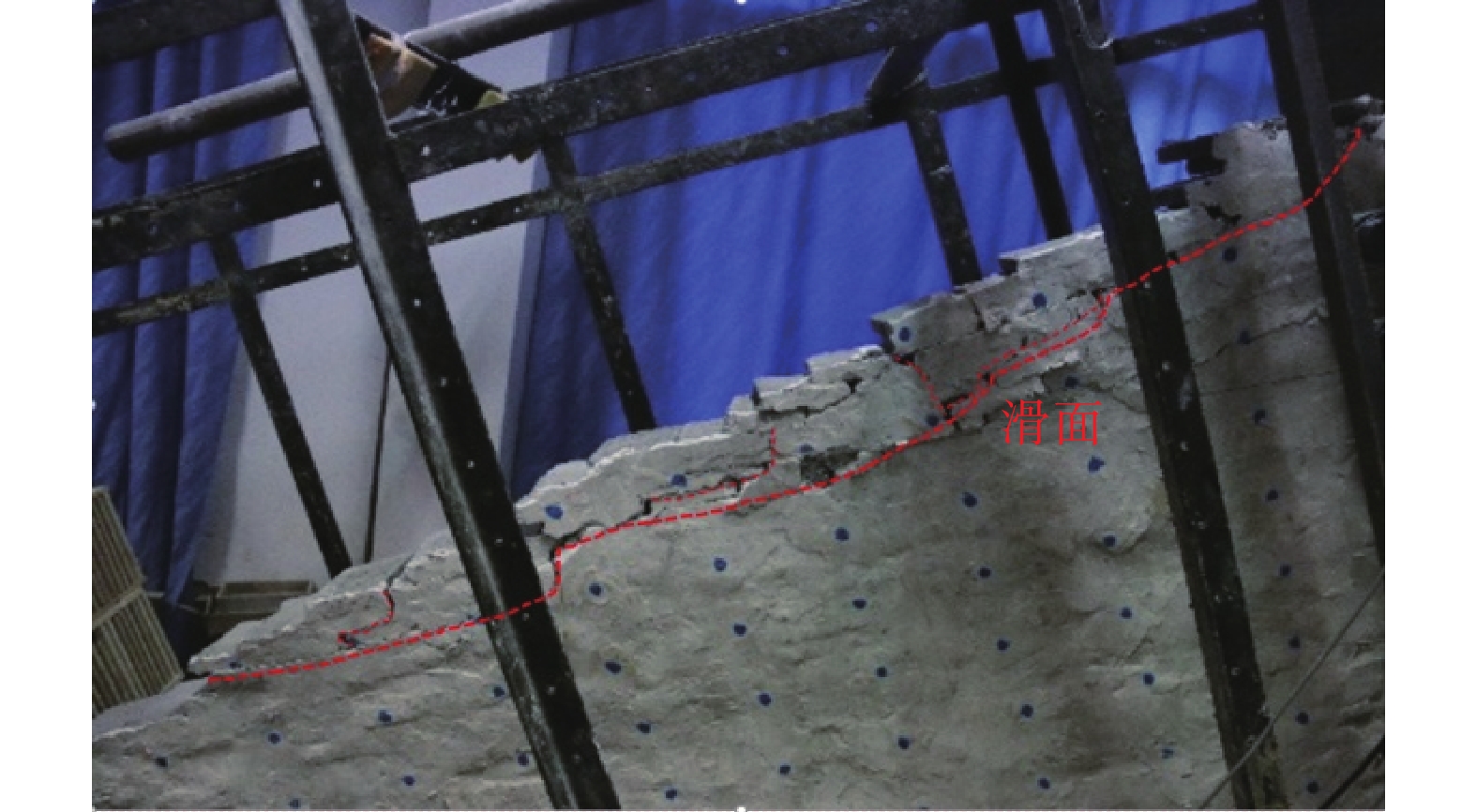
摘要: 含有多层软弱夹层的开挖边坡具有坡体结构复杂、稳定性评价及治理难度大的特点。以黔西地区现场开挖高边坡为研究对象,建立室内物理试验模型,通过不同的工况开挖,呈现变形破坏演化过程,分析变形破坏模型及形成机理,确定失稳破坏范围。结果显示:开挖边坡裂隙产生由表及里,由上及下,由最初的陡倾短小裂隙扩展延伸,最终贯通,形成近似平行岩层的长大裂缝;缓坡度开挖变形破坏为浅表层,整体稳定性较好,失稳范围及规模较小;陡坡度开挖变形破坏规模大,稳定性较差,以滑移-拉裂深层失稳为主;浅层滑坡滑面以层间泥化夹层剪切为主,基本呈直线状;深层滑坡滑面以层间泥化夹层剪切以及陡倾裂隙组合形成阶梯状。该研究成果对于黔西地区的顺层开挖高边坡设计、稳定性评价、治理措施选择等具有重要的指导意义。Abstract: The excavated slope with multi-layer weak interlayer has the characteristics of complex slope structure and difficult stability evaluation and treatment. Based on the on-site excavation of high slope in western Guizhou, an indoor physical test model is carried out. Through excavation under different working conditions, the evolution process of deformation and failure is presented. The deformation and failure model and formation mechanism are analyzed to determine the instability and failure range. The results show that the fissures in the excavated slope extend from the surface to the inside, from top to bottom, from the initial steep short fissures, and finally through to form a long fissure approximately parallel to the rock layer; the deformation and failure of gentle slope excavation is shallow surface, the overall stability is good, and the instability range and scale are small; the excavation deformation and failure scale of steep slope is large, and the stability is poor, mainly in the deep instability of slip tensile fissure; the slip surface of shallow landslide is mainly sheared by interlayer argillaceous interlayer, which is basically linear; the sliding surface of deep landslide is stepped by the combination of interlayer argillaceous interlayer shear and steep inclined fractures. The research results have important guiding significance for the design, stability evaluation and treatment measures of bedding excavation high slope in western Guizhou.
-
0. 引言
强震是人类所面临的最危险的自然灾害之一[1]。在强切割山区,山体在地震作用下往往发生震裂松动,其完整性、强度大幅度降低,诱发一系列的崩、滑灾害[2-3]。崩滑灾害堆积物又会为泥石流的发生提供物源[4-5]。上述“崩滑流”灾害造成的人员伤亡和财产损失往往不亚于地震本身[6]。随着对地震滑坡研究的深入,一些学者认为,山体在地震作用的失稳机理与山体的地震放大效应存在耦合关系。罗永红等[7]对汶川地震次生地质灾害展开调查后,结合灾害区域地貌单元,认为特殊地形尺寸与地震波长的耦合作用导致地震放大效应。范刚[8]基于自贡西山公园台站记录的地震数据,分析了地形对峰值加速度、峰值位移等地震动参数的影响规律,认为地形因素仅对水平向的地震响施加影响,而在垂直向不明显。VALAGUSSA等[9]通过对1993年Papua New Guinea地震、1999年ChiChi地震、1994年Northridge地震、2004年Niigata–Chuetsu地震、2008年Iwate–Miyagi Nairiku地震和2008年汶川地震后造成的地貌改观展开分析,探讨了地震震级和震中距与山体失稳规模的耦合关系。CROISSANT等[10]通过2D数值模拟,发现地震作用下断层作为一种不稳定结构面会对山体的稳定性产生不利影响。GUAN等[11]通过物理模拟,发现隧道深处即山体内部的水平向峰值加速度要小于同一高程山体表面处。HARZTEL等[12]对1989年Loma Prieta地震展开研究后表明,体波在山脊内的多向反射和散射以及瑞利波与勒夫波的相互作用是导致Robinwood山脊受震灾破坏严重的重要原因。CELEBI[13]通过对1976年Guatemala地震和1989年Loma Prieta地震数据展开分析,发现山脊处的地震放大效应与地震波入射角度存在耦合关系。SU等[14]通过对地震波进行小波变换,讨论了地震波不同频率段的地面运动属性。2014年康定地震后,王运生等[15]对冷竹关地震台阵所记录到的数据进行分析,发现山体内部的地震动放大效应要弱于同高程山体表面,且山体表面傅立页谱图较山体内部,成分更为复杂。刘峡等[16]利用小波变换的方法,对地震信号进行了时域特征上的分析。
地震波是一种复杂的非稳定波型,其携带的能量在时域上和频率域上分布极不均匀[16],一旦某时刻能量突然集中会对受震物体的结构稳定产生不利影响。目前针对地震动响应的研究多侧重于傅立页谱分析,而傅立页谱仅能表明频率域上能量分布,而忽略掉了相应频率出现的时间。小波分析作为数学放大镜,突破了傅立页变换和短时傅立页变换局限,可以清楚地表明地震波能量、时域、频率域之间的关系,以及地震波成分的演变。因此基于连续小波变换深入探讨地震在特殊山地单元下的地震动响应规律,对揭示地震致灾机理和开展防灾减灾工作意义重大。
1. 监测数据来源与地震动响应分析
1.1 强震监测点概况
据中国地震台网,2019年6月17日22时55分,四川省宜宾市长宁县发生Ms6.0级地震,震中位于长宁县双河镇附近,震源深度16 km。云南,四川和重庆等多地均有明显震感。成都理工大学地质灾害防治与地质环境保护国家重点实验室依托中国地震局“川西深切河谷斜坡地震动评价技术研究”项目,在雅安市石棉县南桠河两岸设立的3个地震监测点记录到了此次Ms6.0级地震。其中南桠河右岸鸡公山上放置有两台强震监测仪,左岸陈家包山上放置有一台强震监测仪器,其监测点分布位置如图1所示。鸡公山上两台站置于前震旦纪晋宁期具碎裂结构的弱风化花岗岩平硐内,陈家包台站置于坡残积厚覆盖层之上,下伏前震旦纪晋宁期花岗岩,在南桠河左岸坡脚有部分出露。红色剖面线所代表的地质剖面图见图2。三台站仪器放置场地稳定,无外界因素干扰。其场地属性如表1所示。用于地震监测的仪器则由中国地震局工程力学研究所研制的G01NET-3结构与斜坡震动监测仪,采样时间间隔为0.00512 s。同时,四川省地震局也提供了石棉县先锋台阵记录到Ms6.0级地震监测数据作为参照基准。
表 1 各监测点所在位置场地属性Table 1. Properties of monitoring sites监测点编号 绝对高程/m 震中距/km 监测点所在部位 场地类型 1# 1150 265 山体平坡处 基岩(花岗岩) 2# 1060 265 山脊处 基岩(花岗岩) 3# 1102 267 山脊处 厚覆盖层 参照点(石棉先锋) × × × 薄覆盖层 1.2 石棉县南桠河两岸山体地震动响应综述
山体的地震动响应主要表现在峰值加速度(Peak Ground Acceleration, PGA)和阿里亚斯强度(Arias Intensity, AI)的放大[17]。对3个监测点以及1个参照点所记录到Ms6.0级地震的数据进行低通30 Hz滤波处理后,通过软件SeismoSignal处理后可以读出其地震动响应的基本参数属性。其4个点的峰值加速度、阿里亚斯强度以及峰值加速度放大倍数如表2所示。
表 2 各监测点地震动响应参数Table 2. Ground motion response parameters at each monitoring site监测点编号 峰值加速度/gal 阿里亚斯强度/(cm·s−1) EW SN UD EW SN UD 1# 1.22 2.94 2.23 0.36 1.22 0.89 2# 2.13 3.64 2.35 0.55 1.80 0.81 3# 7.42 10.18 2.94 15.09 13.26 2.75 *参照点 1.74 3.36 1.88 0.88 2.70 0.87 注:1 gal=1 cm/s2 罗永红[17]、贺建先等[18]、祁生文等[19]结合大量实测地震数据分析发现,山体的山脊处,山体转折部位以及第四纪覆盖层会对山体的地震动响应起控制作用,具体表现为上述部位的峰值加速度放大,在地震来临时候更加强烈的震动响应会导致山体发生失稳。由表2可见,同位于鸡公山上的1#及2#监测点,位于山脊处的2#监测点其峰值加速度要大于1#监测点。而3#监测点场地类型为厚覆盖层,其水平向峰值加速度远远大于1#和2#监测点,而垂直向峰值加速度放大效应则弱于水平向,但也有一定程度的放大。可以明显看出,峰值加速度的放大效应在水平和垂直方向上具有显著的差异。
2. 地震信号的时频分析
傅立页变换作为一种良好的信号分析手段,在世界范围内被广泛应用[16]。但对于非稳定信号,傅立页变换只能体现出信号的频域特性,而隐略了随机信号中的时域特性。小波变换自1986年被发明以来,因其具有良好的时频分析能力,在信号处理领域内发展迅速[20]。小波变换分析不仅可以描述非稳定信号的局部变化特征,而且可以通过尺度变换,从不同频域上观察信号的演变特征。因此,相较于使用传统手段傅立页变换对地震信号频率域上展开解析,利用小波变换分析地震信号,可以反映地震信号的时频特性,明确地震时频演变规律。
2.1 连续小波变换
将四台强震监测仪记录到的地震数据做小波变换处理。所选用的变换方式为连续小波变换(Continuous Wavelet Transform),小波基函数为Mexh,其中心频率(Centre Frequency)为0.25。选择矢量尺度为1至140,由140至1作公差为−0.5的递减。由尺度-频率换算公式计算可得,其覆盖频率范围0.35~50 Hz。
地震数据进行连续小波变换后,可以三维的方式呈现,其中x轴表示时间,单位为s;y轴表示频率,单位为Hz;z轴表示地震加速度幅值,单位为20 gal。3个监测点的地震时频图如表3所示。地震信号经过连续小波变换之后,透过传统时程图增加了频率信息,做到了时域和频率域上的结合。
表 3 监测点3分量连续小波分解图Table 3. Three-component continuous wavelet decomposition东西方向 南北方向 垂直方向 2.2 地震信号时频成分统计
地震信号经过连续小波变换后,其时域频域的结合有助与对地震信号成分的分析。4处监测点的3分量地震信号时频图中,随着时间增加,有两个波峰,其中峰值较低先到达的为P波,而后到达的峰值较大的则为S波。在S波后面则为一段由体波激发的面波。S波在到达受震地表后,分异为高频和低频两种成分:形状尖锐、变化剧烈的低频成分与光滑平顺、平稳降低的高频成分。地震发生时,受震物体的破坏主要依靠S波和体波交会激发的面波[21]。P波主要为垂直方向上的振动,且幅值小于S波,对受震物体结构破坏较小[6],因此本文分析重点为S波成分变化。现对各监测点三分量上P波和S波波峰空间坐标进行测量,其结果如表4所示,其中第一行表示波峰出现的时间位置,第二行表示波峰出现的频率位置,第三行表示波峰幅值绝对值。
表 4 监测点波峰成分统计表Table 4. Statistical table of signal peak at each site方向 S波高频波峰 S波低频波峰 1# 2# 3# 参照点 1# 2# 3# 参照点 东西 27.23 s 37.67 s × 32.02 s 27.00 s 37.76 s 36.03 s 31.70 s 2.8 Hz 3.9 Hz × 3.2 Hz 1.4 Hz 1.4 Hz 1.3 Hz 1.1 Hz 0.045 0.078 × 0.076 0.063 0.072 0.630 0.068 南北 26.50 s 36.52 s × 32.00 s 27.09 s 36.41 s 35.09 s 32.27 s 2.8 Hz 3.5 Hz × 2.5 Hz 1.1 Hz 1.1 Hz 1.1 Hz 1.1 Hz 0.120 0.183 × 0.188 0.110 0.115 0.656 0.138 垂直 26.77 s 37.73 s 34.85 s 32.88 s 27.19 s 38.13 s 35.28 s 32.36 s 3.5 Hz 3.5 Hz 2.8 Hz 3.2 Hz 1.1 Hz 1.1 Hz 1.1 Hz 1.1 Hz 0.086 0.107 0.150 0.076 0.090 0.068 0.089 0.068 3. 放大效应分析
3.1 山脊部位放大效应分析
历史地震监测表明,地震作用下山脊部位往往放大效应更为显著[17-18]。根据表2的时程数据分析结果来看,2#监测点所处的山脊部位,其水平向上PGA和AI数值要高于同在山腰部位的1#监测点。其中PGA放大系数(2#/1#)在东西南北和垂直向上分别为1.74、1.23和1.05;AI放大系数(2#/1#)在三个方向上则分别为1.52、1.47和0.91。这说明2#监测点所在山体部位地震动力响应更为强烈。由表4可以看到地震成分的演变,1#与2#监测点的S波低频部分,其波峰在频域上的发生位置完全相同,这可能与两处监测点位于一座山体有关。相较于1#监测点,2#监测点的东西向、南北向和垂直向S波高频成分,波峰幅值放大倍数分别为1.73、1.53和1.16,而S波低频部分的放大倍数则分别为1.14、1.04和0.76。2#监测点三分量S波高频波峰幅值全部高于低频部分,而1#监测点则相反。即在基岩场地下,山脊相较于山腰,地震放大效应主要体现为高频成分能量的增加,低频部分有小幅增大,但远不如高频部分。此外,放大效应还存在显著的方向性,无论是在PGA、AI放大系数上还是地震波峰成分演变上,水平方向的放大效应要更为显著。受地震作用,在2#点所在的山脊处,落石与斜坡变形较其他地方更为发育(图3)。
3.2 覆盖层场地放大效应分析
3#监测点的场地条件为厚覆盖层,下伏同晋宁期花岗岩,仅在南桠河左岸边坡支护剖面上有所出露。通过表3可以看到,3#监测点水平向时频三维图上高频成分衰减剧烈,其低频波峰幅值在东西向和南北向更是分别高达0.630和0.656,相较于同在山脊部位的2#监测点S波最大幅值,其放大倍数达8.08和3.53。但在垂直向,依然可以清楚地看到S波的高频和低频成分,低频成分在时间序列上出现的次数更多。此外,参照点场地条件为薄覆盖层,下伏同套岩组。同样可以看到,薄覆盖层场地的低频部分相较于基岩场地,其低频部分已经有所发育。而PGA放大系数(3#/2#)在东西、南北和垂直向上的放大系数为3.48、2.79和1.25;AI放大系数(3#/2#)则分别为27.4、7.36和3.39。地震时,震感更加强烈。
现有研究表明,当成层厚覆盖层接收来自基岩传来的剪切波时,在地震波向地表传播的过程中,会发生多次反射与折射,波能量发生叠加而进一步增强,尤其为长周期波更为显著,这与表征能量的AI显著放大相吻合[21-22]。此外,覆盖层土体对入射剪切波具有吸收和放大作用。当剪切波由基岩入射到覆盖层后,其中短周期成分被吸收,而长周期成分由于与土体自身振动周期相近,极易发生共振作用[22]。为了探究3#厚覆盖层场地的S波低频部分剧烈变化是否为共振效应引起,现在对3#监测数据进行加速度反应谱分析。加速度反应谱即在某一阻尼比的作用下,反应一系列单质点在振动时,其最大响应绝对值与场地结构周期的关系的频谱图。现采用0.05,0.1,0.2的阻尼比[20],对3#监测点三分量加速度反应谱展开计算,用于评价场地的特征周期。其三分量反应谱图如表5所示。加速度反应谱中有多个波峰,表明覆盖层成分不均匀。其最高点所代表的时间即为场地的特征周期[20],分析后其特征周期如表6。同时,由同样方法求得基岩场地特征周期如表7。
表 5 3#监测点场地3分量反应图谱Table 5. Three-component response spectrum of monitoring site No.3东西向 南北向 垂直向 表 6 3#监测点三分量特征周期/频率表Table 6. Dominant period / frequency of site 3#东西向 南北向 垂直向 特征周期/s 0.74 0.88 0.36 特征频率/Hz 1.35 1.13 2.77 表 7 1#与2#监测点三分量特征周期Table 7. Dominant period of site 1# and 2#监测点编号 特征周期/s 东西向 南北向 垂直向 1# 0.26 0.26 0.25 2# 0.26 0.26 0.28 由表6和表7可知,基岩场地特征周期远小于厚覆盖层场地。3#监测点东西向和南北向特征频率分别为1.35 Hz和1.13 Hz,即场地的特征频率十分接近于S波低频成分波峰峰值处频率,频率差值分别为0.05 Hz和0.03 Hz。而垂直向特征频率则与水平向有较大差异。在水平方向上,由于频率接近,地震发生时,S波中低频成分振动与场地自振交汇,产生强烈的共振效应,导致频率域上其特征周期附近区间内振动峰值显著增加。加之厚覆盖层土体对短周期波成分的吸收效应和长周期波成分的折射叠加效应,3#监测点的S波高频部分衰减显著[21-22]。厚覆盖层对地震波显著放大,地震时其震感更加强烈,加重震害损失,这一现象在震中长宁灾害调查中得以体现。3#点所在村落多为刚度大,结合性差的低矮砖混结构房屋和土坯房,此次地震由于震中距较大,震级较小,未对3#点所在村落建筑物造成严重损害。但如果震级加大,受到山脊放大效应和覆盖层放大效应的双重影响,震感强烈,相较于基岩场地这里会遭受更加严重地表震害。
4. 结论
基于连续小波变换的信号处理手段,对石棉县城南桠河两岸强震监测点所记录到的长宁Ms6.0级地震数据,作三维时频图谱,并结合时域和频域对地震信号成分进行分析。现有结论如下:
(1)通过连续小波变换所呈的三维时频图,可以清楚看到S波到达地表时分为高频和低频两种成分。其中高频成分主频在3.5 Hz附近,而低频成分主频在1.1 Hz附近,两种成分在时域上近乎同时出现。
(2)地震时山脊部分的地震动响应更加强烈。山脊部位场地类型为基岩,通过时频分析结果可知,放大效应主要体现为S波高频成分能量的增加,而低频部分则无明显变化。
(3)覆盖层场地对S波具有显著的低频放大和高频衰减效应。S波在厚覆盖层的折射和反射作用,以及3#覆盖层场地水平方向的自振与S波低频成分交汇产生共振效应,是导致覆盖层场地低频放大效应显著的原因。地震发生时,3#场地震感强烈,地表震害将更加严重。
(4)地震动响应规律具有极强的方向差异性,从时程分析结果和时频分析结果可以看出,其差异性主要体现在水平向和垂直向上,其水平向的放大效应相较于垂直向要更为显著。
-
表 1 试验主要物理量相似比取值
Table 1 The ratios of main physical quantities in tests
物理量 相似比符号 相比取值 几何相似 Cl 60 重度相似 Cr 1 泊松比相似 Cμ 1 摩擦系数相似 Cf 1 黏聚力相似 CC 60 摩擦角相似 Cφ 1 应变相似 Cε 60 时间相似 Ct=(Cl)1/2 7.75 表 2 边坡变形破坏分析与评价
Table 2 Comprehensive analysis and evaluation of slope deformation and failure
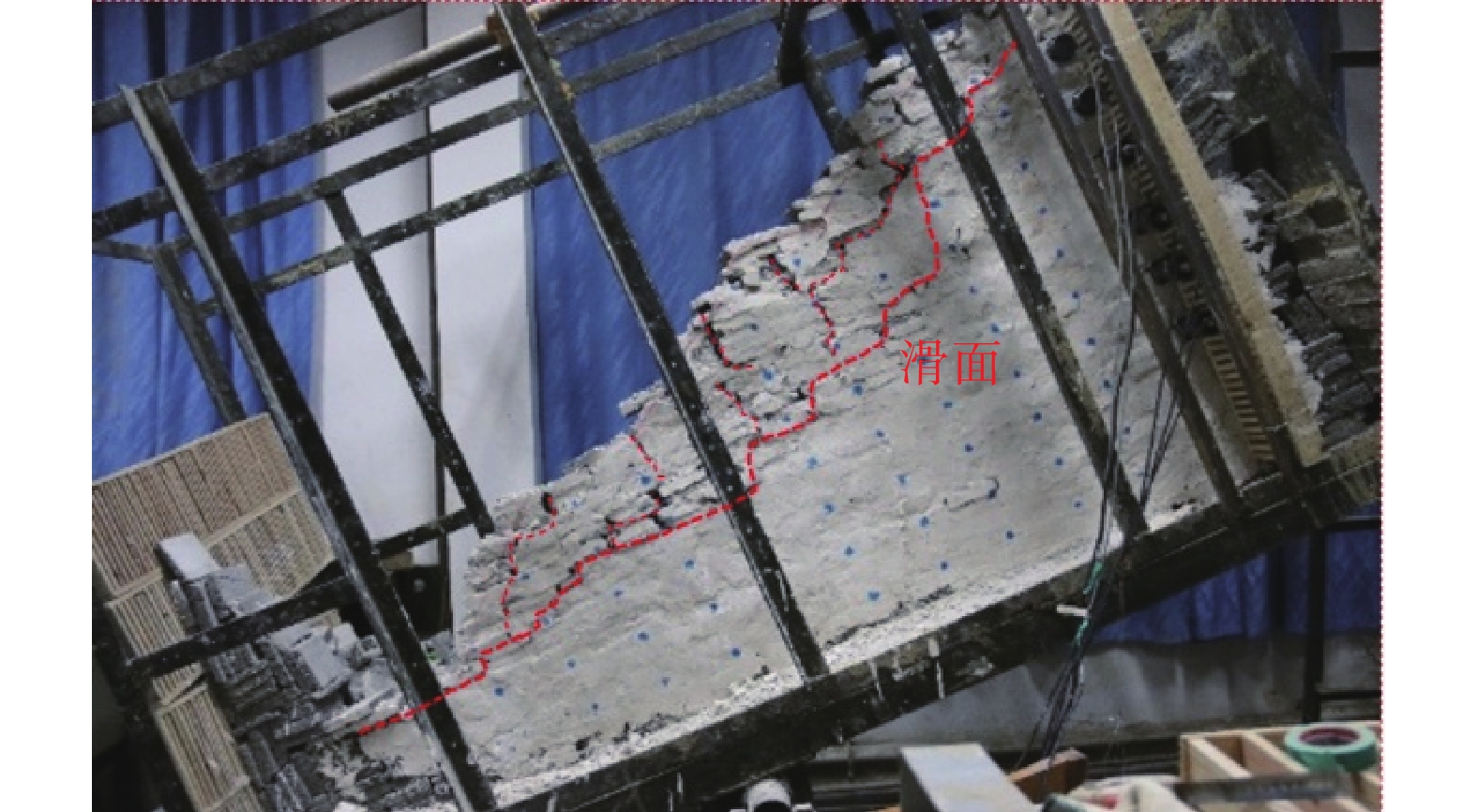
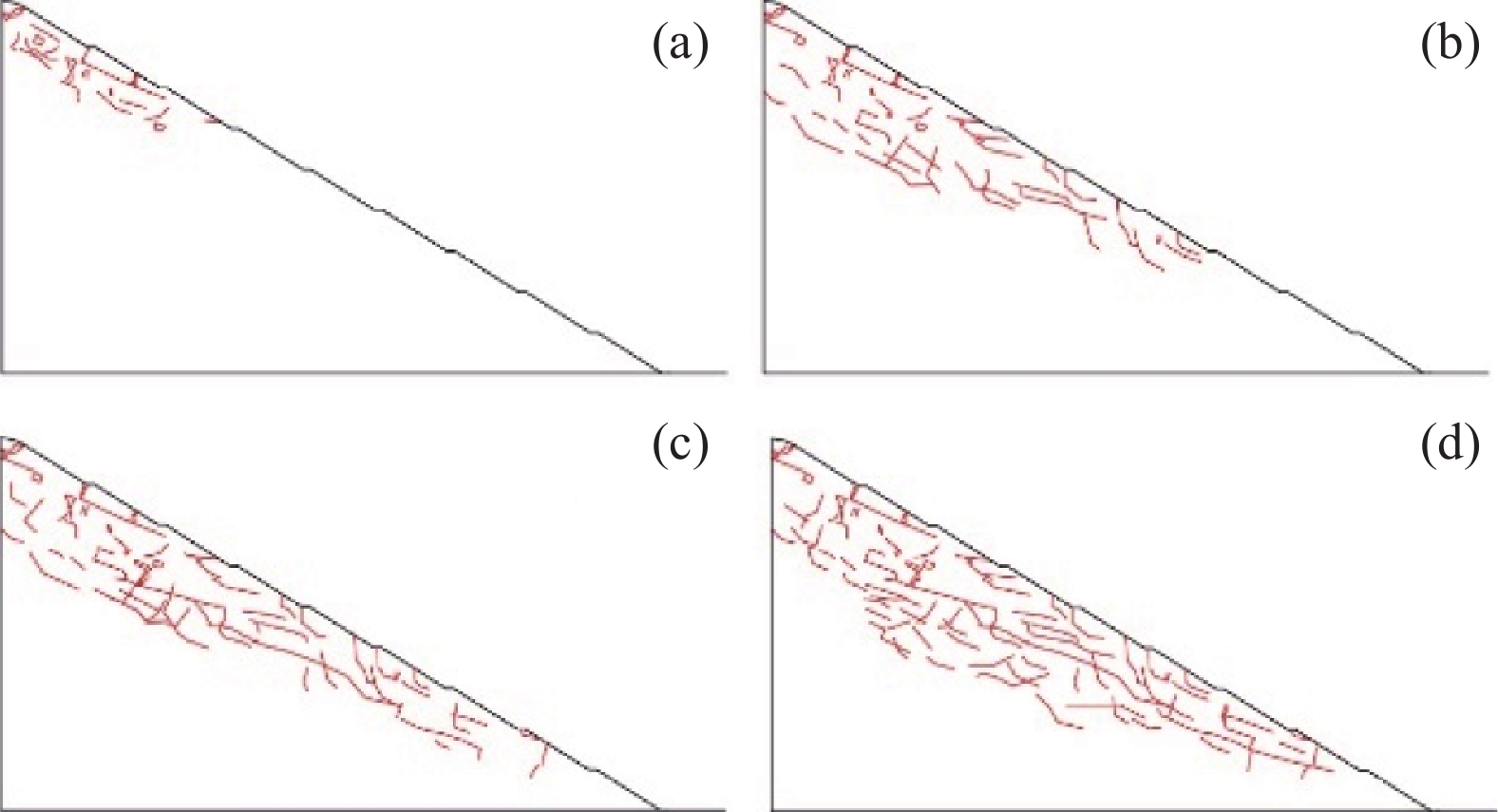
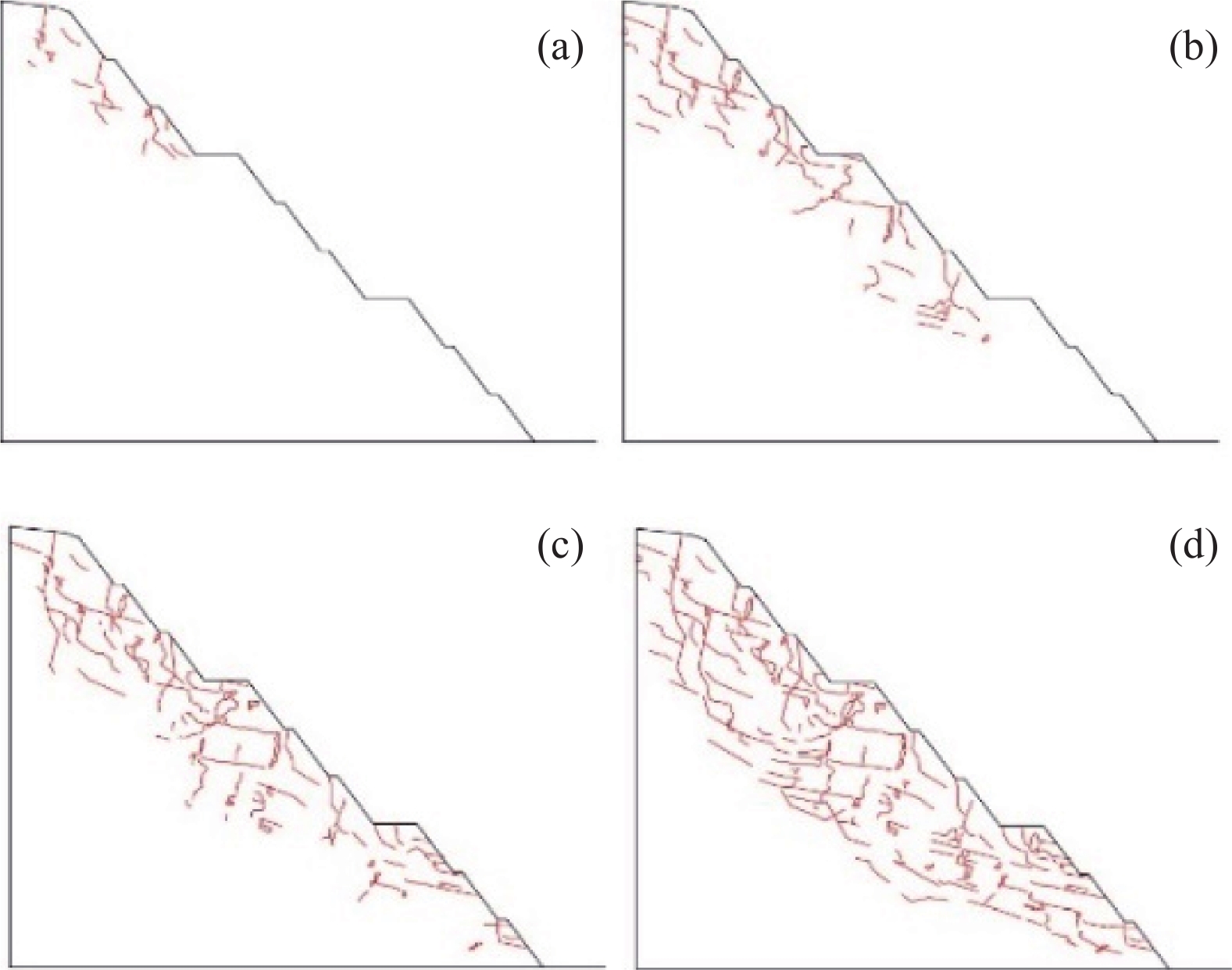
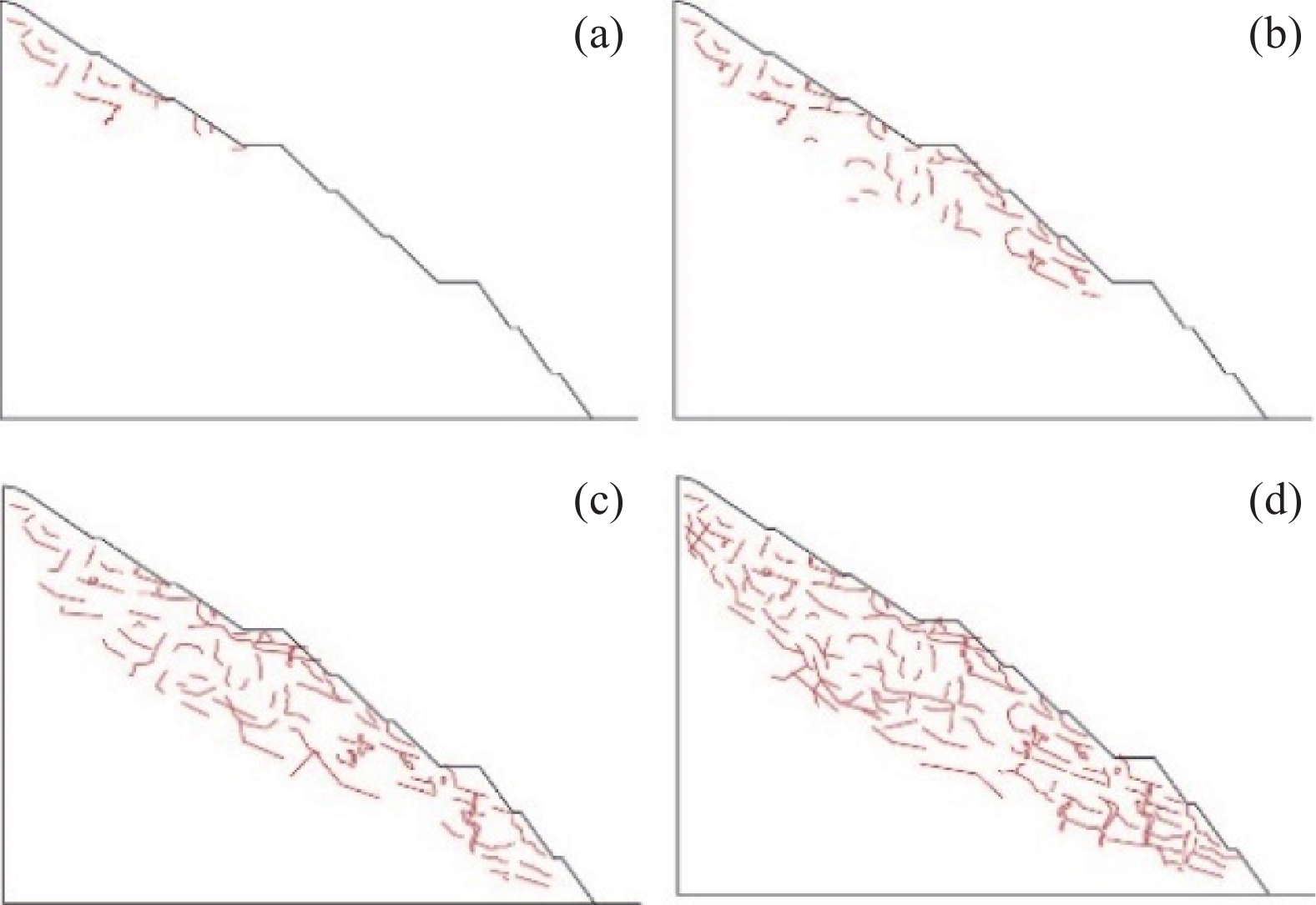
工况 变形破坏特征 稳定性及评价复杂性 失稳规模及范围 失稳模式及机理 工况一 变形破坏特征以滑移-拉裂为主。裂缝产生由表及里,通常先产生竖向或垂直坡面的陡倾短小裂缝,然后裂缝进一步扩展延伸形成近似平行坡面的长大裂缝,最终贯通引起变形破坏。缓坡度开挖,滑面最终呈现沿软弱夹层剪切的平直滑面;陡坡度开挖则形成分级变形破坏、滑面呈现折线、台阶形态。 稳定性相对较好,滑面短小,最终贯通后整体呈折线型,局部出现台阶,易于识别,评价简单。 规模较小,最大深度为一般4.0~8.0 m,位于3~4级坡面,易形成多级失稳。支护方便、简单。占地面积大,不利于工程建设规划。 缓坡度开挖条件下,坡体沿层面剪切滑移,变形破坏模式为渐进牵引式的滑移-拉裂。重力和开挖临空面是形成失稳破坏的主要影响因素,陡倾裂缝及软弱夹层剪切滑移是形成机理的重要条件。 工况二 稳定性差,滑面长大,形状连续多变,以阶梯状、直线状或混合状为主。变形失稳演化过程复杂,评价难度较大。 规模较大,最大深度为一般为20.0~50.0 m,位于4~5级边坡。易形成1~2级失稳。支护复杂,难度大。占地面积小,利于工程建设规划。 陡坡度开挖条件下,坡体呈现多级变形破坏,通常是上部滑移-拉裂坡体对下部坡体形成一定的推力,整体变形破坏模式为渐进推移式。边坡开挖后,在重力和临空面的作用下,首先沿着层间软弱夹层剪切滑移,由于滑面埋深较大,同时竖向裂隙发育,在滑移错动过程中形成折线、台阶式滑面。 工况三 稳定性较差,滑面长大,形状多变,阶梯状、直线状或混合状,以台阶形态为主。变形破坏演化过程复杂,评价难度大。 规模较大,最大深度为一般为30.0~60.0 m,位于4~5级边坡。易形成1~2级失稳。支护复杂,难度大。占地面积较小,较利于工程建设规划。 陡-缓相结合的开挖条件下,坡体上部坡体沿层间软弱夹层剪切滑移形成滑移-拉裂变形破坏,下部则在上部失稳坡体推力以及自身重力作用下,产生渐进推移式变形失稳。而坡体中部变形破坏则兼含了牵引式和推移式,形成机理复杂。 -
[1] MÜLLER-SALZBURG L. The Vajont catastrophe—A personal review[J]. Engineering Geology,1987,24(1/2/3/4):423 − 444.[LinkOut
[2] 杨海平, 王金生. 长江三峡工程库区千将坪滑坡地质特征及成因分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2009,17(2):233 − 239. [YANG Haiping, WANG Jinsheng. Geological features and cause analysis of Qianjiangping landslide of July 13, 2003 on Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2009,17(2):233 − 239. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.013 YANG Haiping, WANG Jinsheng. Geological features and cause analysis of Qianjiangping landslide of July 13, 2003 on Three Gorges Reservoir[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology, 2009, 17(2): 233-239. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2009.02.013
[3] 许强, 邓茂林, 李世海, 等. 武隆鸡尾山滑坡形成机理数值模拟研究[J]. 岩土工程学报,2018,40(11):2012 − 2021. [XU Qiang, DENG Maolin, LI Shihai, et al. Numerical simulation for formation of Jiweishan landslide in Wulong County, Chongqing City of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2018,40(11):2012 − 2021. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Qiang, DENG Maolin, LI Shihai, et al. Numerical simulation for formation of Jiweishan landslide in Wulong County, Chongqing City of China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2018, 40(11): 2012-2021. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[4] 穆成林. 顺层岩质高边坡开挖过程变形失稳演化机制及预测评价研究——以织金石化场区边坡为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2017 MU Chenglin. Study on deformation instability evolution mechanism and prediction during excavating process of bedded rock slope: A case of slope as the studied object in the gasoline construction site[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2017. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[5] 张社荣, 谭尧升, 王超, 等. 多层软弱夹层边坡岩体破坏机制与稳定性研究[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(6):1695 − 1702. [ZHANG Sherong, TAN Yaosheng, WANG Chao, et al. Research on deformation failure mechanism and stability of slope rock mass containing multi-weak interlayers[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(6):1695 − 1702. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHANG Sherong, TAN Yaosheng, WANG Chao, et al. Research on deformation failure mechanism and stability of slope rock mass containing multi-weak interlayers[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2014, 35(6): 1695-1702. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[6] 许宝田, 钱七虎, 阎长虹, 等. 多层软弱夹层边坡岩体稳定性及加固分析[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(增刊 2):3959 − 3964. [XU Baotian, QIAN Qihu, YAN Changhong, et al. Stability and strengthening analyses of slope rock mass containing multi-weak interlayers[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(Sup 2):3959 − 3964. (in Chinese with English abstract) XU Baotian, QIAN Qihu, YAN Changhong, et al. Stability and strengthening analyses of slope rock mass containing multi-weak interlayers[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2009, 28(Sup 2): 3959-3964. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[7] 龙建辉, 任杰, 曾凡桂, 等. 双软弱夹层岩质滑坡的滑动模式及变形规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2019,44(10):3031 − 3040. [LONG Jianhui, REN Jie, ZENG Fangui, et al. Sliding mode and deformation law of double weak interlayer rock landslide[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2019,44(10):3031 − 3040. (in Chinese with English abstract) LONG Jianhui, REN Jie, ZENG Fangui, et al. Sliding mode and deformation law of double weak interlayer rock landslide[J]. Journal of China Coal Society, 2019, 44(10): 3031-3040. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[8] 唐朝晖, 余小龙, 柴波, 等. 顺层岩质滑坡渐进破坏进入加速的能量学判据[J]. 地球科学,2021,46(11):4033 − 4042. [TANG Zhaohui, YU Xiaolong, CHAI Bo, et al. Energetic criterion of entering acceleration in progressive failure process of bedding rockslide: A case study for Shanshucao landslide[J]. Earth Science,2021,46(11):4033 − 4042. (in Chinese with English abstract) TANG Zhaohui, YU Xiaolong, CHAI Bo, et al. Energetic criterion of entering acceleration in progressive failure process of bedding rockslide: A case study for Shanshucao landslide[J]. Earth Science, 2021, 46(11): 4033-4042. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[9] 泮晓华, 秦四清, 薛雷. 岩质斜坡锁固段破坏模式的物理模型试验研究[J]. 华北水利水电大学学报(自然科学版),2018,39(6):13 − 18. [PAN Xiaohua, QIN Siqing, XUE Lei. Study on failure modes of various locked segments in rock slopes based on physical model tests[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition),2018,39(6):13 − 18. (in Chinese with English abstract) PAN Xiaohua, QIN Siqing, XUE Lei. Study on failure modes of various locked segments in rock slopes based on physical model tests[J]. Journal of North China University of Water Resources and Electric Power (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 39(6): 13-18. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[10] 陶志刚, 任树林, 郝宇, 等. 层状反倾边坡破坏机制及NPR锚索控制效果物理模型试验[J]. 岩土力学,2021,42(4):976 − 990. [TAO Zhigang, REN Shulin, HAO Yu, et al. Physical model experiment on failure mechanism and NPR anchor cable control effect of layered counter-tilt slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2021,42(4):976 − 990. (in Chinese with English abstract) TAO Zhigang, REN Shulin, HAO Yu, et al. Physical model experiment on failure mechanism and NPR anchor cable control effect of layered counter-tilt slope[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2021, 42(4): 976-990. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[11] 周月, 廖海梅, 甘滨蕊, 等. 滑坡运动冲击破碎物理模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2020,39(4):726 − 735. [ZHOU Yue, LIAO Haimei, GAN Binrui, et al. Physical modeling test on impacting fragmentation during landslide moving[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2020,39(4):726 − 735. (in Chinese with English abstract) ZHOU Yue, LIAO Haimei, GAN Binrui, et al. Physical modeling test on impacting fragmentation during landslide moving[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2020, 39(4): 726-735. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[12] 黄达, 谢周州, 宋宜祥, 等. 软硬互层状反倾岩质边坡倾倒变形离心模型试验研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2021,40(7):1357 − 1368. [HUANG Da, XIE Zhouzhou, SONG Yixiang, et al. Centrifuge model test study on toppling deformation of anti-dip soft-hard interbedded rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2021,40(7):1357 − 1368. (in Chinese with English abstract) HUANG Da, XIE Zhouzhou, SONG Yixiang, et al. Centrifuge model test study on toppling deformation of anti-dip soft-hard interbedded rock slopes[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering, 2021, 40(7): 1357-1368. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 陈达, 许强, 郑光, 等. 基于离心模型试验的复杂层状软岩楔形滑坡变形演化研究[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(10):3374 − 3384. [CHEN Da, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Study on deformation evolution of wedge landslide in complex layered soft rock based on centrifugal model test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(10):3374 − 3384. (in Chinese with English abstract) CHEN Da, XU Qiang, ZHENG Guang, et al. Study on deformation evolution of wedge landslide in complex layered soft rock based on centrifugal model test[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics, 2020, 41(10): 3374-3384. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[14] 王海, 张梓钦, 杨国香, 等. 五盂高速公路顺层岩质边坡变形破坏模型试验[J]. 科学技术与工程,2021,21(9):3754 − 3762. [WANG Hai, ZHANG Ziqin, YANG Guoxiang, et al. Model tests of deformation and failure of bedding rock slope in Wuyu expressway[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2021,21(9):3754 − 3762. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.09.046 WANG Hai, ZHANG Ziqin, YANG Guoxiang, et al. Model tests of deformation and failure of bedding rock slope in Wuyu expressway[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2021, 21(9): 3754-3762. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2021.09.046
[15] 胡时友, 蔡强, 李超杰. 双排微型桩加固碎石土滑坡物理模型试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(5):114 − 120. [HU Shiyou, CAI Qiang, LI Chaojie. Physical model test study of debris landslide reinforcement with double row micro-piles[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(5):114 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) HU Shiyou, CAI Qiang, LI Chaojie. Physical model test study of debris landslide reinforcement with double row micro-piles[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2018, 45(5): 114-120. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[16] 李玉瑞, 程晓伟, 赖天文, 等. 延安北连接线黄土滑坡变形机制地质分析与模型试验研究[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(2):35 − 42. [LI Yurui, CHENG Xiaowei, LAI Tianwen, et al. Geological analysis and model test study on the deformation mechanism of loess landslide in the North connection line of Yan'an[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(2):35 − 42. (in Chinese with English abstract) LI Yurui, CHENG Xiaowei, LAI Tianwen, et al. Geological analysis and model test study on the deformation mechanism of loess landslide in the North connection line of Yan'an[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control, 2019, 30(2): 35-42. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 穆成林, 裴向军, 裴钻, 等. 基于岩体结构特征和未确知测度评价模型的岩质开挖边坡稳定性研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):150 − 158. [MU Chenglin, PEI Xiangjun, PEI Zuan, et al. A study of the stability of rock excavated slope based on rockmass structure and unascertained measure evaluation models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):150 − 158. (in Chinese with English abstract) MU Chenglin, PEI Xiangjun, PEI Zuan, et al. A study of the stability of rock excavated slope based on rockmass structure and unascertained measure evaluation models[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2019, 46(4): 150-158. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[18] 马洪生, 庄卫林, 刘阳, 等. 顺层岩质边坡静力开挖物理模拟试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2016,43(3):37 − 43. [MA Hongsheng, ZHUANG Weilin, LIU Yang, et al. Physical excavation test research on a bedding rock slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2016,43(3):37 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) MA Hongsheng, ZHUANG Weilin, LIU Yang, et al. Physical excavation test research on a bedding rock slope[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology, 2016, 43(3): 37-43. (in Chinese with English abstract)
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 易垚,林翔,雷雪霏. 不等厚互层顺层滑坡典型工程案例研究. 江西建材. 2024(01): 201-203 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 傅强. 福州市晋安区地质灾害现状及防治对策. 海峡科学. 2024(09): 76-79 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王林峰,夏万春,冉楗,张继旭,程平. 考虑库水升降和滑带弱化作用的岸坡启滑机制分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(02): 30-41 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 周亚辉,庞鑫. 广汉市红层地区滑坡地质灾害形成机制. 科学技术创新. 2022(02): 141-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 周健,刘港. 基于模糊综合评价法的凤鸣镇滑坡危险性评价. 科学咨询(科技·管理). 2022(05): 113-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 胡屿,刘勇,侯江勇. 基于GIS的贵州省丹寨县斜坡结构自动化制图方法分析. 安徽地质. 2022(02): 182-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张鹏,唐雪梅,李虎,刘思铭. 滑坡作用下X80腐蚀管道的极限宽度分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(04): 47-54 .  本站查看
本站查看
8. 胡屿,张楠,吴东燃,陈亚,何辉. 贵州金海湖新区田湾子滑坡活动特征及成因机理分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(05): 11-19 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:





 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS