Geological hazard susceptibility evaluation in Wenchuan area based on three models of multivariate instability index analysis
-
摘要: 采用多变量不安定指数分析法模型并加以改进,应用于汶川县地质灾害易发性评价。选取坡度、坡向、地层岩性、距断层距离、植被覆盖率及距水系距离六项影响因子,结合四川省自然资源厅发布的汶川县地质灾害隐患点数据,以幂次相乘、线性累加、幂次累加这三种不同的不安定指数分析法模型分别得到了研究区地质灾害易发性分区图,并用接受者操作特性曲线(Receiver Operating Characteristic curve, ROC curve)验证了各种模型的评价性能。结果表明:(1)对本案例而言,幂次相乘模型相较其它两种模型具有最高的精度;(2)汶川县地质灾害“极高”“高”“中”“低”“极低”易发区的面积占比分别为:19.3%、24.6%、19.2%、19.3%、17.6%,且研究区地质灾害易发性较高的区域多分布在断裂带附近。本研究成果可为区域地质灾害防治工作提供理论借鉴和技术参考。
-
关键词:
- GIS /
- 地质灾害易发性 /
- 汶川 /
- 多变量不安定指数分析法
Abstract: A derived model of multivariate instability index analysis method was proposed to evaluate the susceptibility of geological disasters in Wenchuan County. Based on the data of potential geological hazards in Wenchuan County released by Sichuan Provincial Department of Natural Resources, six influencing factors including slope, aspect, stratum lithology, distance from fault, vegetation coverage and distance from water system are involved. Three different methods of multivariate instability index analysis, namely power multiplication, linear accumulation and power accumulation, are used to obtain the geological disaster susceptibility zoning map of the study area Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) curve verifies the evaluation performance of various models. The results show that: (1) for this case, the power multiplication model has the highest accuracy compared with the other two models; (2) the percentages of area with different susceptibility levels, i.e. very high, high, moderate, low, and very low, are 19.3%, 24.6%, 19.2%, 19.3%, 17.6% respectively, moreover, the higher level of susceptibility, the closer to the fault zones. This research provides theoretical and technical reference for the prevention and mitigation of regional geological disasters. -
0. 引言
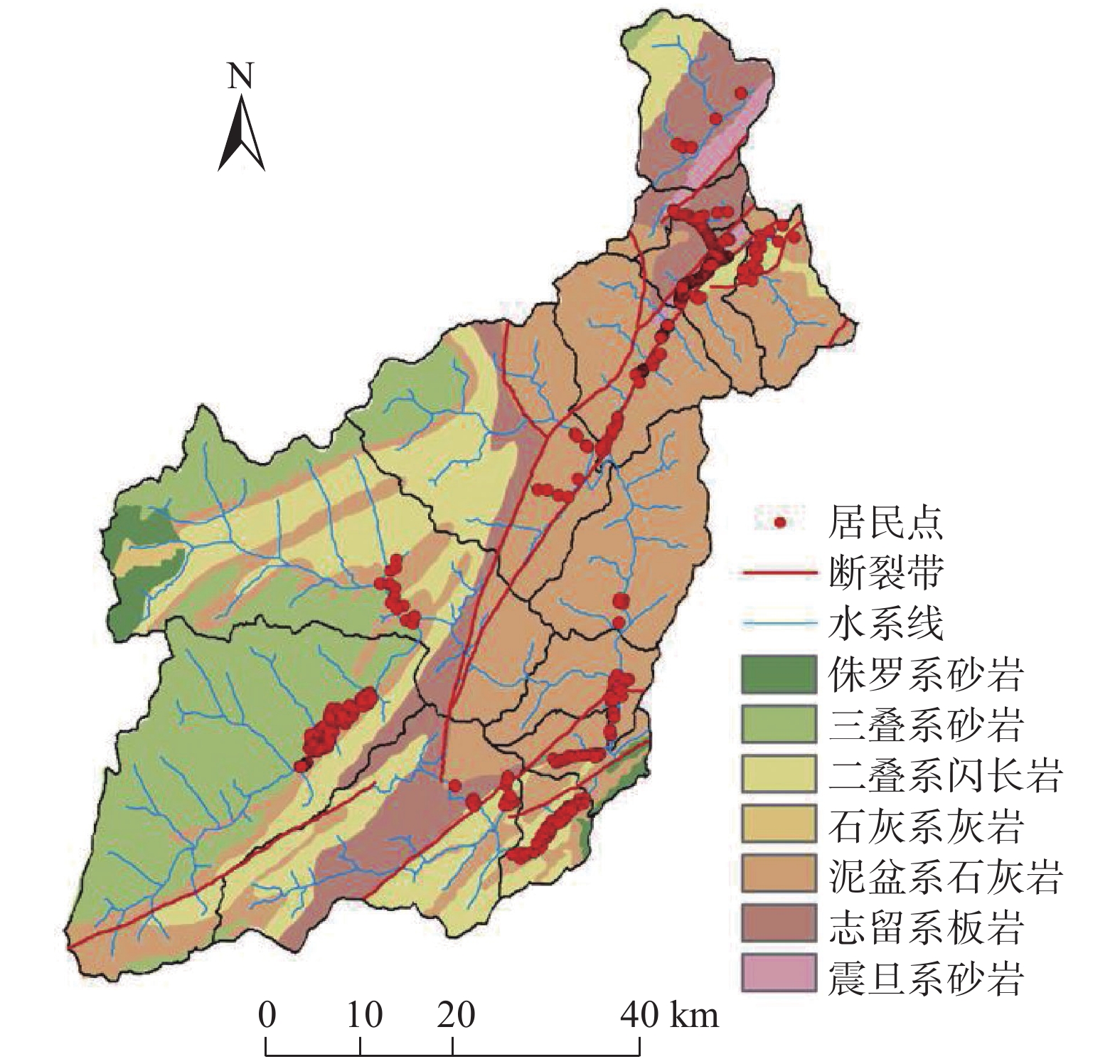
我国是地质灾害发育最为严重的国家之一,特大、重大地质灾害( 如滑坡、泥石流、崩塌等)时有发生[1]。2008年5月12日,四川省汶川县发生8.0级特大地震,汶川县地质环境遭受到了毁灭性的破坏。根据多位学者对汶川震后地质灾害发生规律的研究分析[2-6],震后汶川灾区的地质灾害将持续活跃20~25 a。2017 年“6·24”茂县特大滑坡灾害显示,特大地震对后期地质灾害的影响还将持续更长的时间[7]。根据四川省地质灾害隐患点掌上查询系统,汶川县目前存在地质灾害隐患点2152处,主要为崩塌、滑坡、泥石流和不稳定斜坡,对居民的人身财产安全存在极大的威胁。
近年来,多变量不安定指数法在地质灾害易发性评价中受到重视,该方法最早用于边坡稳定性评价研究中。1992年简李滨[8]提出将研究区域划分为网格,以不安定指数法进行区域性边坡稳定评估。多变量不安定指数分析模型以定量的对各评价因子进行赋值,排除了主观因素的影响,适应于大范围、地质条件复杂且对区域内地质灾害状况有一定了解的地区。
有许多学者以不同模型对汶川县内多种地质灾害危险性进行了研究。如许冲等[9]在GIS支持下,基于层次分析法对汶川地震区的滑坡易发性进行了评价;孟祥瑞等[10]运用因子分析法,在GIS平台下对研究区的地质灾害易发性进行评价;林虹宇等[11]在Matlab软件及GIS平台下,采用可拓模糊物元模型并结合层次分析法,对岷江上游典型泥石流进行了易发性评价。
虽然已有学者应用不同的方法对汶川县各种地质灾害易发性做出了评价,但大部分文献所使用的评价方法在评价因子的赋值方面仍然带有很大的主观性。为了弥补这一不足,本文基于多变量不安定指数分析法模型,并加以改进,开展汶川县地质灾害易发性评价,将汶川县已有的地质灾害普查数据作为数据源,实现定量地对各影响因子进行赋值,提高评估结果的合理性。
1. 多变量不安定指数分析法模型建立
1.1 多变量不安定指数分析法:标准模型
多变量不安定指数分析法是在计量统计的基础上,于一种相对关系下求出不安定指数(Dt)用以描述该研究区域发生地质灾害的危险性的高低。
在用多变量不安定指数法评价地质灾害易发性时,以诱发地质灾害的影响因子为基础建立评价指标,各个因子共同影响评价不安定指数Dt。Dt可作为判定地质灾害易发性的指标,Dt越大,则意味着该范围内发生地质灾害的可能性就越大。建立模型的具体步骤如下:
首先,确定各个致灾因子中各个等级的评分值:通过ArcGIS,利用各专题图层与已有的地质灾害分布图进行叠加分析,记录各专题地图中不同等级的地质灾害栅格数量,再求得其各自所占百分比,用式(1)计算各致灾因子中各等级的评分值:
$$ {{{d}}_i}{\text{ = }}\frac{{{\text{9(}}{X_i} - {X_{i\_}}_{\min })}}{{{X_{i\_\max }} - {X_{i\_}}_{\min }}} + 1 $$ (1) 式中:i——影响因子序号;
$ {X_{i}} $ ——各专题地图中不同等级的地质灾害点栅格数量所占总的地质灾害栅格数量的百分比;$ {X_{i\_\max }} $ ——最大百分比;$ {X_{i\_}}_{\min } $ ——最小百分比。然后,计算各个致灾因子的变异系数,式(2)为变异系数(Vi)的计算公式:
$$ {V_i} = \frac{{{\sigma _i}}}{{{\mu _i}}}{{ \times 100\% }} $$ (2) 式中:
$ {\mu _i} $ ——式(1)中$ {X_i} $ 的平均值;$ {\sigma _i} $ ——$ {X_i} $ 的标准差。再根据各个致灾因子的变异系数通过公式(3)计算其影响权重比例
$ {W_{i}} $ :$$ {W}_{i}\text=\frac{{V}_{i}}{{V}_{1}+{V}_{\text{2}}+{V}_{\text{3}}+\cdots +{V}_{n}}\text{,}i\text{=1},\cdots ,n $$ (3) 式中:i——影响因子序号;
n——影响因子个数;
$ {V_i} $ ——各个致灾因子的变异系数。最后将权重值(
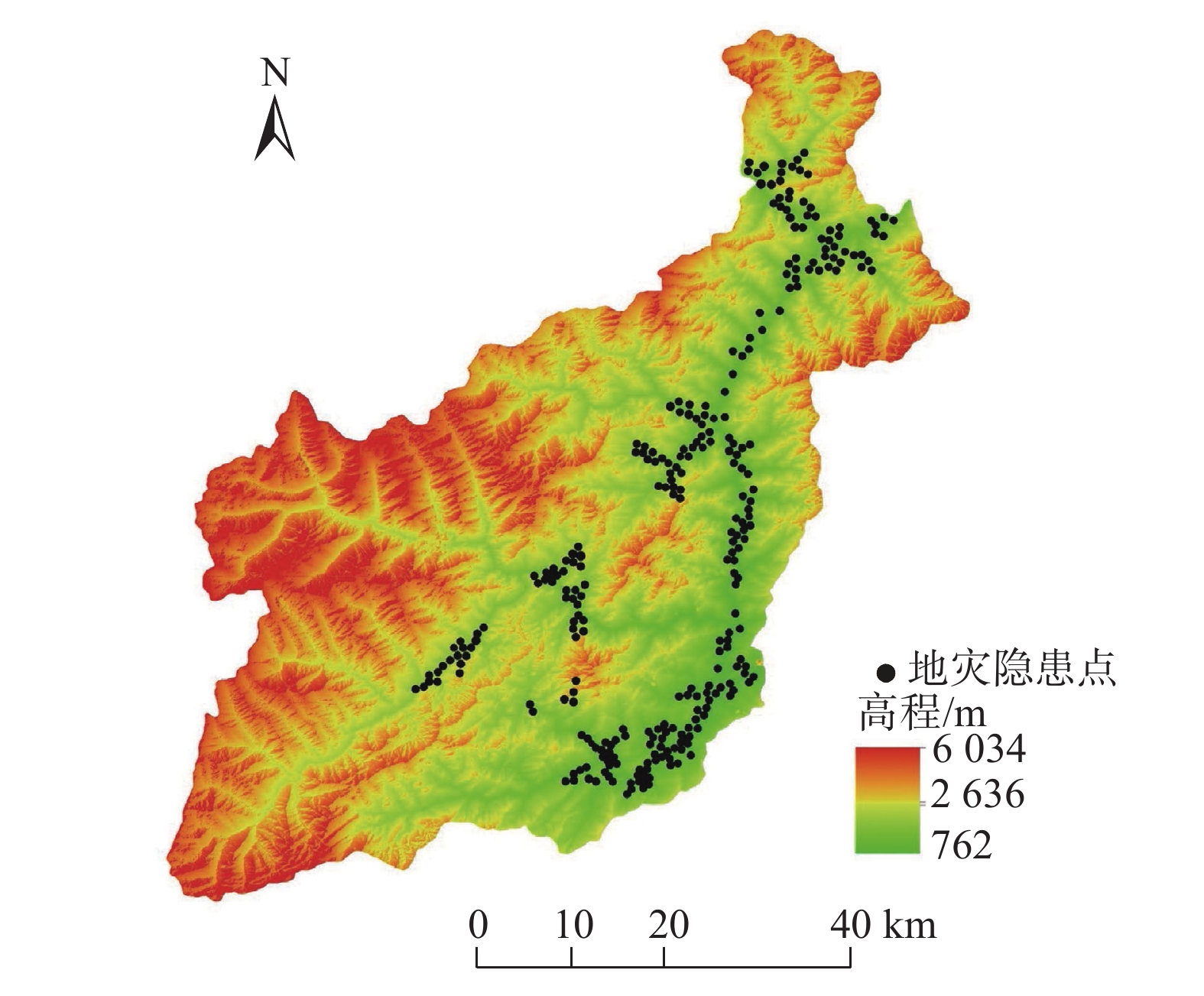
$ {W_i} $ )与评分值($ {d_i} $ )代入多变量不安定指数($ {D_t} $ )式(4)。$$ {D_t} = d_1^{{W_1}}{{ \times }}d_2^{{W_2}}{{ \times }}d_3^{{W_3}}{{ \times }} \cdots\times d_n^{{W_n}} $$ (4) 式中:n——影响因子个数;
$ {d_n} $ ——各个致灾因子各个分级的评分值;$ {W_n} $ ——各个致灾因子的权重。根据(4)式,通过GIS中的栅格计算器将各专题图层代入进行计算,即可得到研究区各区域的不安定指数
$ {D_t} $ ,用以表示区域内地质灾害易发性的大小。1.2 多变量不安定指数分析法:衍生模型
在诸多前人研究中,传统不安定指数法被广泛应用的同时,也有学者提出不同的数学模型求得不安定指数。
1.2.1 线性累加模型
各级评价因子权重值(
$ {W_i} $ )以线性累加取代幂次相乘的方式,求得不安定指数$ {D_t} $ 。如式(5)所示:$$ {D_t}{\text{ = }}\sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {W_id_i} $$ (5) 式中:i——影响因子序号;
n——影响因子个数;
${W_{i}}$ ——各个致灾因子的权重;$ {d_i} $ ——各个致灾因子各个分级的评分值。1.2.2 幂次累加模型
在吸取前人学者的研究经验后,本文提出以幂次累加方式求得
$ {D_t} $ 的模式,如公式(6)所示:$$ {D_t} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {d_i^{Wi}} $$ (6) 式中:i——影响因子序号;
n——影响因子个数;
$ {W_{\text{i}}} $ ——各个致灾因子的权重;$ {d_i} $ ——各个致灾因子各个分级的评分值。1.2.3 不同模型评价的实施过程
在地质灾害易发性评价中,分别应用式(5)或式(6)替换标准算法的式(4),通过ArcGIS中的栅格计算器将各专题图层代入进行计算,即可得到研究区各区域的不安定指数
$ {D_t} $ ,用以表示区域内地质灾害易发性的大小。在本研究中,将分别利用幂次相乘、线性累加及幂次相加三种模式求得
$ {D_t} $ ,然后对各个模式的准确性进行对比,选取准确性最高的模式对研究区地质灾害易发性进行评价。2. 研究区概况
汶川县位于四川省阿坝藏族羌族自治州东南部的岷江两岸,东西宽84 km,南北长105 km,总面积4084 km2。东北部贯穿龙门山脉,西南部为邛崃山系,地势上西北高东南低,西部多分布海拔3000 m以上的高山,其中最高的四姑娘山海拔为6250 m:东南部的岷江出口处海拔仅有780 m。汶川县降雨较多且集中、干湿季明显,雨量528.7~1332.2 mm,全县各地区降雨量差距不大[12],岷江由县北部入境,贯穿东部,长达88 km。杂谷脑河、寿江、草坡河为汶川县境内岷江三大支流,由西向东注入岷江。沿岷江及各大支流河谷、半山地带为全县主要经济活动区。汶川县地层发育比较完整,但奥陶系、志留系有大部分缺失,仅小范围出露,岩性变化较大,以第四系松散地层及强风化岩浆岩为代表的软弱岩土体分布广泛。由于汶川县处于九顶山新华夏构造带,地质构造较为复杂,断裂、褶皱较为发育。汶川县境内共有三条主要断裂带(青川-茂汶断裂带、北川-映秀断裂带、江油-灌县断裂带),三条断裂带皆呈北东-南西方向斜穿全县[13-14](图1)。汶川县境内潜在的地质灾害隐患包括崩塌、滑坡、泥石流和不稳定斜坡,共有地质灾害隐患点2152处(图2)。
3. 研究区地质灾害易发性评价
3.1 致灾因子的选取及分级
控制和影响地质灾害危险性程度的因子有多种。研究区地质灾害类型主要为滑坡、崩塌、泥石流及不稳定斜坡,因此这里选择对几种地质灾害都适用的6种评价因子:坡度、坡向、地层岩性、距水系距离、距断层带距离、植被覆盖率。
(1)坡度。坡度是影响滑坡、崩塌、泥石流和不稳定斜坡的重要影响因素。一方面坡度较缓的斜坡,会造成松散固体物质的堆积,为滑坡、泥石流的形成提供物质条件;另一方面斜坡的角度还会影响斜坡内应力的分布,当坡度较大时,会为斜坡两侧崩塌体的能量转换提供条件。因此,坡度对地质灾害的发生有较大影响。利用ArcGIS的空间分析功能对汶川县30 m分辨率的数字高程模型(Digital Elevation Model,DEM)进行空间分析,并采用自然断点法,得到坡度分级图见图3(a)。
(2)坡向。由于研究区处于高山地区,地形起伏较大,坡向不同的区域,通过太阳辐射、温度等途径造成坡面上自然地理要素的差异。并且研究区大部分范围内海拔都较高,导致上述差异在一定程度上被放大,从而加重了对岩石风化程度以及破碎程度的影响,进而影响了地质灾害的发生及规模。利用ArcGIS的空间分析功能对汶川县30 m分辨率的DEM进行空间分析,并采用自然断点法,得到坡向分级图,见图3(b)。
(3)地层岩性。岩土是地质灾害形成的基础,所以地层岩性对地质灾害的发生有着极大的影响。在致密坚硬、结构完整的岩土发育区,很少有崩塌、滑坡、泥石流活动;相反,在结构破碎或松散软弱岩土发育区,崩塌、滑坡、泥石流等地质灾害活动强烈。根据汶川县的岩土类型,可分为7类:震旦系砂岩、白云岩;志留系板岩、千枚岩;泥盆系石灰岩;石炭系灰岩;二叠系闪长岩;三叠系砂岩、千枚岩;侏罗系砂岩。地层岩性分级见图3(c)。
(4)植被覆盖率。植被起到护坡和防止水土流失的作用,并且植被根系具有加固土体,提高土体抗剪强度的能力,嵌入基岩或下部老黄土的根系还起到锚筋作用。所以植被的覆盖一定程度上可以减轻各种地质灾害发生的风险。采取归一化植被指数(Normalized Difference Vegetation Index,NDVI)来表现植被的生长状况及覆盖率,植被归一化指数是指遥感影像中,近红外波段的反射值与红光波段的反射值之差比上两者之和,可以通过ArcGIS中的栅格计算器在研究区的遥感影像中获得。如图3(d)所示,其中负值表示地面覆盖为云、水、雪等,对可见光高反射;0表示有岩石或裸土等;正值,表示有植被覆盖,且随覆盖度增大而增大,这里用自然断点法分为5级。
(5)距断层距离。断层极易诱发地质灾害,断层是岩层或岩体顺破裂面发生明显位移的构造。在地貌上,大的断层常常形成裂谷和陡崖,沿断裂带附近岩层因长期地质构造运动破坏严重,易发生崩滑现象,松散物源堆积较多后还可能造成较大规模泥石流。汶川县境内共有三条主要断裂带 (青川-茂汶断裂带、 北川-映秀断裂带、 江油-灌县断裂带 ),三条断裂带皆呈北东—南西方向斜穿全县。利用ArcGIS中的缓冲区分析功能获得研究区距断层距离分级栅格图见图3(e)。
(6)距水系距离。河流水系的冲蚀切割作用会造成更多的临空面,也会对土体斜坡的密实度造成影响,并且冲散的岩土也为滑坡、泥石流的发生提供松散物源。所以,距水系的距离也对地质灾害的发生有一定的影响作用。利用ArcGIS中的缓冲区分析功能获得研究区距水系距离分级栅格图,见图3(f)。
3.2 确定各致灾因子分级评分值及变异系数
利用ArcGIS中的叠加分析功能,将汶川县地质灾害隐患点分布图与各致灾因子分级图进行叠加分析。叠加分析后的地图中各分级的栅格数量所占总栅格量的百分比就相当于不同等级的地质灾害点数量所占总的地质灾害数量的百分比。
表 1 坡度评分值Table 1. Grading of slope坡度/(°) 出现地质灾害点的栅格数量 占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 0~14.6 8445 18.9 19.2 0.7 9.8 14.6~23.6 8576 19.2 10 23.6~30.9 7977 17.8 9.3 30.9~37.2 7096 15.8 8.3 37.2~43.4 6071 13.5 7.2 43.4~50.4 4266 9.5 5.3 50.4~60.1 2057 4.6 2.9 60.1~88.6 311 0.7 1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 2 坡向评分值Table 2. Grading of slope aspect坡向 出现地质灾害点的栅格数量 占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 北 5286 11.8 16.9 10.3 3.0 东北 4592 10.3 1 东 5299 11.8 3.0 东南 6867 15.3 7.8 南 4667 10.4 1.1 西南 5041 11.3 2.4 西 5480 12.2 3.6 西北 7563 16.9 10 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 3 地层岩性评分值Table 3. Score value of stratum lithology地层岩性 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率
/%最大/% 最小/% 评分值 震旦系砂岩、白云岩 1971 4.4 64.2 0 1.6 志留系板岩、千枚岩 4838 10.8 2.5 泥盆系石灰岩 7033 15.7 3.2 石炭系灰岩 0 0 1 二叠系闪长岩 28758 64.2 10 三叠系砂岩、千枚岩 1971 4.4 1.6 侏罗系砂岩 224 0.5 1.1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 4 植被覆盖率评分值Table 4. Score value of vegetation coverage植被归一化指数 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率
/%最大/% 最小/% 评分值 −0.16~0.03 224 0.5 51.4 0.5 1 0.03~0.11 4883 10.9 2.8 0.11~0.25 23025 51.4 10 0.25~0.39 16171 36.1 7.3 0.39~0.53 493 1.1 1.1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 5 距断裂带距离评分值Table 5. Score value of distance from fault zone距断裂带距离/km 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 0~5 36374 81.2 81.2 0 10 5~10 7346 16.4 2.8 10~15 1030 2.3 1.3 15~20 45 0.1 1 >20 0 0 1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 6 距水系距离评分值Table 6. Score value of distance from water system距水系距离/m 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 0~200 16977 37.9 37.9 7.1 10 200~600 15499 34.6 9 600~1200 9138 20.4 4.9 >1200 3181 7.1 1 合计 44795 100 — — — (2)利用式(2)计算出各致灾因子的变异系数见表7。
表 7 各致灾因子变异系数Table 7. Variation coefficient of disaster-inducing factor致灾因子 各因子分级破坏率平均值 标准差 变异系数 坡度 0.125 0.065 52 坡向 0.125 0.022 17.6 地层岩性 0.143 0.210 147.19 植被覆盖率 0.2 0.203 101.62 距断裂带距离 0.2 0.312 156 距水系距离 0.25 0.122 49 3.3 地质灾害易性区划
利用式(3)确定的各致灾因子的权重值见表8。
表 8 各致灾因子权重值Table 8. Weight value of disaster-inducing factors排名 致灾因子 变异系数 权重值 1 距断裂带距离 156 0.298 2 地层岩性 147.19 0.281 3 植被覆盖率 101.62 0.194 4 坡度 52 0.099 5 距水系距离 49 0.094 6 坡向 17.6 0.034 合计 — — 1 应用传统的多变量不安定指数分析法模型进行评价,在对各个评价因子的各分级赋值时,多为位数较多的小数,而在使用ArcGIS软件对各评价因子的各个分级进行赋值时,value值字段只接受整数,若采用四舍五入取整,则会显著影响评价模型的精度。
对模型进行改进,从而提高评价结果的精确度,选择将各评价因子各级的评分值小数点保留k位有效数字(本研究中k=1),在利用ArcGIS进行重分类时,将第3.2节获得的各影响因子的各级评分值乘以10k,记为10k
$ {d_n} $ ,将10k$ {d_n} $ 赋予各专题图层。然后利用改进后的传统多变量不安定指数($ {D_t} $ )计算式(7),及改进后的衍生多变量不安定指数($ {D_t} $ )计算式(8)和式(9)。$$ {D_t} = \frac{{{{{\text{(1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}{d_1})}^{{W_1}}} \times {{{\text{(1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}{d_2})}^{{W_2}}} \times {{{\text{(1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}{d_3})}^{{W_3}}} \times \cdots {{{\text{(1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}{d_n})}^{{W_n}}}}}{{{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{\text{k}}}}} $$ (7) $$ {D_t} = \frac{{\displaystyle\sum\limits_{i = 1}^6 {W_i{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}d_i} }}{{{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}}} $$ (8) $$ {D_t} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^6 {\frac{{{{{\text{(1}}{{\text{0}}^{{k}}}d_i{\text{)}}}^{W_i}}}}{{{\text{1}}{{\text{0}}^{{{k}}{W_i}}}}}} $$ (9) 其中,k=1, di∈[1,10]。由各公式的数学关系可以得出幂次相乘及线性累加模式下, Dt∈[1,10];幂次累加模式下, Dt>n,这里即 Dt>6。通过ArcGIS的栅格计算器,分别获得三种模式下研究区各区域的不安定指数Dt值,并分别用自然断点法将 Dt值分为5级,即将研究区地质灾害易发性分为五个等级:极低危险区、低危险区、中危险区、高危险区、极高危险区(图4)。
如果缺少科学的验证,一切预测模型及结果在一定程度上毫无科学依据[15]。文中利用接受者操作特性曲线(Receiver Operating Characteristic Curve,ROC)[16-18]分析法对本研究中三种模式下的研究区地质灾害易发性区划结果进行验证,选取准确性最高的模型作为评价该研究区地质灾害易发性的最终模型,以预测地质灾害面积百分比累加与实际地质灾害隐患点面积百分比累加分别对三种模型构建检验折线(图5)。
图中,幂次相乘模式下,ROC曲线下与坐标轴围成的面积(Area Under Curve,简称AUC值)为75.29;线性累加模式下,AUC值为67.03;幂次累加模式下,AUC值为74.87。对比显示,幂次相乘的模式下准确性最高,最适合作为该研究区地质灾害易发性评价模型。
以幂次相乘模式下对研究区地质灾害易发性的区划结果为准,对研究区地质灾害易发性进行评价分析:
(1)1≤
$ {D_t} $ <3.84,为地质灾害极低易发性区域,面积为718.5 km2,占研究区总面积17.6%,主要集中在汶川县西部的耿达、卧龙两镇内,未来几乎不会发生地质灾害。该区域距断裂带较远,水系较少,无居民,多为高山,不需要特地开展地质灾害防治工作。(2)3.84≤
$ {D_t} $ <5.42,为地质灾害低易发性区域,面积为787.6 km2,占研究区总面积19.3%,主要集中在汶川县西部及北部,主要分布在耿达、卧龙、龙溪三镇。该区域距断裂带较远,居民较少有较低可能发生地质灾害,但需要提高当地居民防范意识,及抗灾减灾意识,一旦发生地质灾害,可把损失降到最低。(3)5.42≤
$ {D_t} $ <6.76,为地质灾害中易发性区域,面积为784.8 km2,占研究区总面积19.2%,主要集中在汶川县中部及北部,该区域发生地质灾害的可能性较小。该区域距离断裂带有一定距离,有较多条水系支流,未来可能发生小规模滑坡、泥石流,可能会对该区域居民造成一定财产损失,但可以通过及时监测和一些工程措施加以避免。(4)6.76≤
$ {D_t} $ <8.24,为地质灾害高易发性区,面积为1004.3 km2占研究区总面积24.6%,主要集中在汶川县中部与东部,分布在岷江左岸及紫坪铺水库上游地区,该区域发生地质灾害可能性较高,未来可能有中等规模的地质灾害发生,该区内居民居住较密集,人类活动频繁,地质灾害产生的破坏性也会较大。因此,需要加大地质灾害防治力度。(5)8.24≤
$ {D_t} $ ≤9.96,为地质灾害极高易发性区域,面积为788.8 km2,占研究区总面积19.3%,主要集中在汶川县中部,岷江流域两岸与映秀-北川断裂带两侧,未来有极大可能发生地质灾害,且由于该区域人类活动频繁,水系复杂,岩层破碎,地质灾害的规模会较大,且该区域内以往都发生过大规模的滑坡、泥石流等,存在许多不稳定斜坡。因此,该区域内应以以防为主、防治结合、全面规划、综合治理的原则,严格开展地质灾害防治工作,以保护居民人身财产安全。4. 讨论
(1)在本研究中的各致灾因子中,距断层带距离是影响地质灾害易发性的主导因素。研究区汶川县为地震频发区,被三条断裂带贯穿,而断裂带附近地质灾害极易发生,尤其是“5·12”地震后,震发断裂带附近地质构造遭受严重破坏,近十几年来地质灾害频发,可以看出断裂带为影响该区域地质灾害易发性重要因素,而表8亦证明如此,这也就体现了对评价因子定量赋予权重的优势。
(2)在赋予6个评价因子权重时,以现有的地质灾害隐患点为基础,用定量的方法得到每个评价因子的权重值,相较于以往传统的专家打分法,更客观、准确。在权重确定过程中,由于该区域地质灾害多且大小不一,很难具体统计出各评价因子某一分级中灾害点的数量,所以这里将灾害点转化为栅格数据,以栅格数量表示灾害点数量,通过各致灾因子分级图层与现有灾害点栅格图层叠加分析,清楚的得出致灾因子各分级中灾害点的比例,相比于同样以定量方法获取各致灾因子权重的信息量法不需要繁琐的数据处理步骤。综上,多变量不安定指数分析法是一种可以对评价因子定量赋值的模型,可避免主观因素的影响,且易于操作,适用于已知研究区内部分地质灾害信息的大范围内的地质灾害易发性评价。
(3)从各影响因子权重来看,距断层带距离及地层岩性权重相似,同时为影响研究区地质灾害易发性的主要因素。分析其原因,主要是由于“5·12”震发断裂带附近大量分布着二叠系闪长岩及志留系板岩,其岩石结构在地震时受到严重破坏,所以地层也会出现与距断层带距离因子相似的现象。
(4)选用三种不同的数学模型分别获得研究区地质灾害易发性分区图,并用ROC曲线分别求得三种模式下评价结果的AUC值,比较后,选出最适合该研究区的评价模型,即以传统不安定指数分析法中的幂次相乘来求得不安定指数
$ {D_t} $ 。显然,传统的多变量不安定指数分析法模型在该研究区地质灾害易发性评价结果中较衍生出来的两种模式更为精确。5. 结论
基于多变量不安定指数分析法,选择坡度、坡向、地层岩性、距断层距离、距水系距离、植被覆盖率六项影响因子,分别采用幂次相乘、线性累加、幂次累加三种模型开展汶川县地质灾害易发性评价,结果显示:
(1)在应用多变量不安定指数分析模型求得不安定指数时,传统的幂次相乘模型较幂次累加模型及线性累加模型更为精确。
(2)幂次相乘模型下的汶川县地质灾害易发性区划结果显示:地质灾害“极高”“高”“中”“低”“极低”易发区的面积占比分别为:19.3%、24.6%、19.2%、19.3%、17.6%,且研究区地质灾害易发性较高的区域多分布在断裂带附近。
-
表 1 坡度评分值
Table 1 Grading of slope
坡度/(°) 出现地质灾害点的栅格数量 占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 0~14.6 8445 18.9 19.2 0.7 9.8 14.6~23.6 8576 19.2 10 23.6~30.9 7977 17.8 9.3 30.9~37.2 7096 15.8 8.3 37.2~43.4 6071 13.5 7.2 43.4~50.4 4266 9.5 5.3 50.4~60.1 2057 4.6 2.9 60.1~88.6 311 0.7 1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 2 坡向评分值
Table 2 Grading of slope aspect
坡向 出现地质灾害点的栅格数量 占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 北 5286 11.8 16.9 10.3 3.0 东北 4592 10.3 1 东 5299 11.8 3.0 东南 6867 15.3 7.8 南 4667 10.4 1.1 西南 5041 11.3 2.4 西 5480 12.2 3.6 西北 7563 16.9 10 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 3 地层岩性评分值
Table 3 Score value of stratum lithology
地层岩性 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率
/%最大/% 最小/% 评分值 震旦系砂岩、白云岩 1971 4.4 64.2 0 1.6 志留系板岩、千枚岩 4838 10.8 2.5 泥盆系石灰岩 7033 15.7 3.2 石炭系灰岩 0 0 1 二叠系闪长岩 28758 64.2 10 三叠系砂岩、千枚岩 1971 4.4 1.6 侏罗系砂岩 224 0.5 1.1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 4 植被覆盖率评分值
Table 4 Score value of vegetation coverage
植被归一化指数 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率
/%最大/% 最小/% 评分值 −0.16~0.03 224 0.5 51.4 0.5 1 0.03~0.11 4883 10.9 2.8 0.11~0.25 23025 51.4 10 0.25~0.39 16171 36.1 7.3 0.39~0.53 493 1.1 1.1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 5 距断裂带距离评分值
Table 5 Score value of distance from fault zone
距断裂带距离/km 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 0~5 36374 81.2 81.2 0 10 5~10 7346 16.4 2.8 10~15 1030 2.3 1.3 15~20 45 0.1 1 >20 0 0 1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 6 距水系距离评分值
Table 6 Score value of distance from water system
距水系距离/m 出现地质灾害点
的栅格数量占总数比率/% 最大/% 最小/% 评分值 0~200 16977 37.9 37.9 7.1 10 200~600 15499 34.6 9 600~1200 9138 20.4 4.9 >1200 3181 7.1 1 合计 44795 100 — — — 表 7 各致灾因子变异系数
Table 7 Variation coefficient of disaster-inducing factor
致灾因子 各因子分级破坏率平均值 标准差 变异系数 坡度 0.125 0.065 52 坡向 0.125 0.022 17.6 地层岩性 0.143 0.210 147.19 植被覆盖率 0.2 0.203 101.62 距断裂带距离 0.2 0.312 156 距水系距离 0.25 0.122 49 表 8 各致灾因子权重值
Table 8 Weight value of disaster-inducing factors
排名 致灾因子 变异系数 权重值 1 距断裂带距离 156 0.298 2 地层岩性 147.19 0.281 3 植被覆盖率 101.62 0.194 4 坡度 52 0.099 5 距水系距离 49 0.094 6 坡向 17.6 0.034 合计 — — 1 -
[1] 薛凯喜, 李炀, 多会会, 等. 地质灾害及其防治的公众认知现状探析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):113 − 121. [XUE Kaixi, LI Yang, DUO Huihui, et al. Analysis on the current situation of public perception of geological hazard and its prevention and control[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):113 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 黄润秋, 李为乐. “5·12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(12):2585 − 2592. [HUANG Runqiu, LI Weile. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May, 2008[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(12):2585 − 2592. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 [3] 崔鹏, 庄建琦, 陈兴长, 等. 汶川地震区震后泥石流活动特征与防治对策[J]. 四川大学学报(工程科学版),2010,42(5):10 − 19. [CUI Peng, ZHUANG Jianqi, CHEN Xingchang, et al. Characteristics and countermeasures of debris flow in Wenchuan area after the earthquake[J]. Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2010,42(5):10 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] CHEN M, TANG C, XIONG J, et al. The long-term evolution of landslide activity near the epicentral area of the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in China[J]. Geomorphology,2020,367:107317. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107317
[5] 高会会, 裴向军, 崔圣华, 等. 汶川震区震后地质灾害发育分布及演化特征统计分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2019,36(8):73 − 80. [GAO Huihui, PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, et al. Geological hazards after earthquake in Wenchuan earthquake area: Distribution and evolvement features[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2019,36(8):73 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20180109 [6] 王钧, 宇岩, 欧国强, 等. 岷江上游汶川地震重灾区山洪灾害危险分区研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2017,34(1):54 − 60. [WANG Jun, YU Yan, OU Guoqiang, et al. Flash flood risk zoning of areas hit by Wenchuan earthquake in the upper reach of Minjiang river[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2017,34(1):54 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20150956 [7] 温铭生, 刘传正, 刘艳辉, 等. 汶川地震高烈度区崩滑流灾害区域预警[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):10 − 19. [WEN Mingsheng, LIU Chuanzheng, LIU Yanhui, et al. Regional warning of geological hazards in high seismic intensity area of Wenchuan Earthquake[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):10 − 19. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 简李滨. 应用地理资讯系统建立坡地安定评估之计量方法[D]. 台中: 中兴大学, 1992 JIAN Libin. Establishment of measurement method for slope stability assessment using GIS. [D]. Taizhong: Zhongxing University, 1992. (in Chinese)
[9] 许冲, 戴福初, 姚鑫, 等. GIS支持下基于层次分析法的汶川地震区滑坡易发性评价[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2009,28(增刊 2):3978 − 3985. [XU Chong, DAI Fuchu, YAO Xin, et al. Gis-based landslide susceptibility assessment using analytical hierarchy process in Wenchuan earthquake region[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2009,28(Sup 2):3978 − 3985. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 孟祥瑞, 裴向军, 刘清华, 等. GIS支持下基于因子分析法的都汶路沿线地质灾害易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2016,27(3):106 − 115. [MENG Xiangrui, PEI Xiangjun, LIU Qinghua, et al. GIS-Based susceptibility assessment of geological hazards along the road from Dujiangyan to Wenchuan by factor analysis[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2016,27(3):106 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 林虹宇, 丁明涛, 佘涛, 等. 岷江上游典型泥石流活动特征及其易发性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2017,28(4):6 − 15. [LIN Hongyu, DING Mingtao, SHE Tao, et al. Characteristic analysis and susceptibility assessment of the typical debris flow in the upper reaches of Min River[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2017,28(4):6 − 15. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 胡宝荣. 基于遥感与GIS技术的汶川县地震前后生态环境质量评价[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2009 HU Baorong. Evaluation on the ecological environments before and after 5.12 Wenchuan earthquake by remote sensing and GIS[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Technology, 2009. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[13] 程思, 易加强. 四川省汶川县地质灾害的成因及防治对策[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2007,18(4):1 − 6. [CHENG Si, YI Jiaqiang. Geological hazards and their preventions in Wenchuan County, Sichuan Province[J]. Journal of Geological Hazards and Environment Preservation,2007,18(4):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2007.04.001 [14] 李明威, 唐川, 陈明, 等. 汶川震区北川县泥石流流域崩滑体时空演变特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):182 − 190. [LI Mingwei, TANG Chuan, CHEN Ming, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of landslides in debris flow catchment in Beichuan County in the Wenchuan earthquake zone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):182 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 邱海军, 曹明明, 刘闻, 等. 基于三种不同模型的区域滑坡灾害敏感性评价及结果检验研究[J]. 地理科学,2014,34(1):110 − 115. [QIU Haijun, CAO Mingming, LIU Wen, et al. The susceptibility assessment of landslide and its calibration of the models based on three different models[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica,2014,34(1):110 − 115. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] HOYER A, KUSS O. Meta-analysis of full ROC curves with flexible parametric distributions of diagnostic test values[J]. Research Synthesis Methods,2020,11(2):301 − 313. DOI: 10.1002/jrsm.1395
[17] WALKER S P. The ROC curve redefined - optimizing sensitivity (and specificity) to the lived reality of cancer[J]. The New England Journal of Medicine,2019,380(17):1594 − 1595. DOI: 10.1056/NEJMp1814951
[18] OMAR L, IVRISSIMTZIS I. Using theoretical ROC curves for analysing machine learning binary classifiers[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters,2019,128:447 − 451. DOI: 10.1016/j.patrec.2019.10.004
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 郭英,申健,刘晓晓,周亮,石向菲,王聪毅. 北京门头沟区“23·7”特大暴雨诱发地质灾害特征及分布规律研究. 中国防汛抗旱. 2025(03): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李永勤,王鹏,李琛,尉学勇,闫肖楠. 极端强降雨诱发临汾黄土地区公路灾害分布特征和影响因素分析. 公路工程. 2024(01): 112-117+130 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 顾福计,钱龙,王梦洁,沈荣辉,李朦,王立峰,闫国芹. 太行山河北段“23·7”强降雨引发的地质灾害规律研究. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(02): 55-65 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 黄莉,王芸清,王伟,宋月,石雨欣. 粤港澳大湾区复合灾害系统暴露度评估. 郑州大学学报(工学版). 2024(04): 95-101 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 王伟,石雨欣,宋月,王芸清,黄莉,杨天军. 暴雨-滑坡灾害链应急能力评估——以粤港澳大湾区为例. 自然灾害学报. 2024(04): 95-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王佳津,王皓,王春学,龙柯吉. 四川省汛期小时极端降水精细化特征. 西南大学学报(自然科学版). 2024(10): 167-176 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 曹满,王洋,陈曦,魏运芳,王传涛. 基于时空分布特征的地质灾害气象预警预报模型研究. 计算机测量与控制. 2024(11): 278-286 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 丘嘉荣,陈海燕. 广东省连山壮族瑶族自治县地质灾害分布特征及其成因分析. 四川有色金属. 2024(04): 52-56 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 次旦央宗,李鸿雁,李晓峰. 东北寒区SWAT模型融雪径流空间异质性参数率定方法及应用——以白山流域为例. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版). 2023(01): 230-240 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)




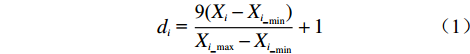
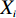
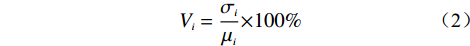

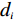
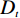
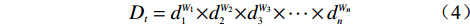
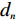
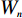
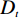
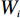
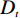
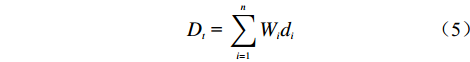
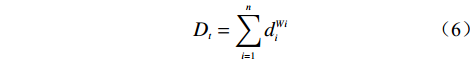
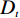
 下载:
下载:

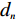
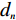
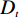
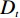
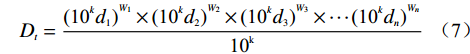
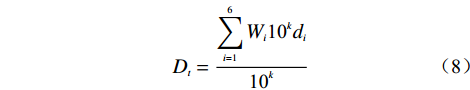
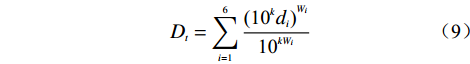

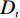
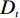
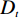
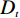
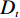
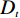
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS