Experimental study on the process of end-moraine dam failure in the middle Himalaya glacial lake: Taking the Jialongcuo glacial lake end-moraine dam as an example
-
摘要: 终碛坝广泛分布于世界各地的高山和极高山区。为了探究终碛坝的溃决过程,了解溃口的演变特征,文章以嘉龙错终碛坝的原位实验,模拟了终碛湖漫顶溃决过程。通过分析实验结果发现:(1)根据观察,将终碛坝溃决过程划分为坝体下游坡面冲刷、“溯源侵蚀”、出水口下切和溃口拓宽四个阶段。(2)上游湖区崩塌体激发的涌浪会造成溃口内的瞬时流量增加数倍,从而使得在有涌浪和无涌浪的条件下,“溯源侵蚀”过程出现陡坎和斜坡两种下切型。(3)通过分析溃口下切侵蚀过程,发现溃口的下切侵蚀发展过程主要受到坝体孔隙比和细粒含量的影响,并且溃口中点侵蚀率与水流剪应力存在一定的线性关系,符合线性侵蚀模型。通过分析发现,嘉龙错终碛坝的侵蚀系数为0.051,临界启动应力为237.64 Pa。与堰塞坝相比,可侵蚀系数比更小,而临界启动应力更大。Abstract: Moraine dams are widely distributed in high and very high mountainous areas around the world. In order to investigate the breaching process of end-moraine dams and to understand the evolution of the breaches during the breaching process of end-moraine dams, this paper designed in situ experiments for simulating the process of moraine lake overtopping breakage with the Jialongcuo as the prototype. The experimental results show that: (1) According to the phenomenon of the breach process, the moraine dam breach process is divided into four stages: downstream slope scour, “headcut erosion”, undercutting of the outlet and widening of the breach. (2) The upstream lake collapse body excited by the surge will cause the instantaneous flow in the breach to increase several times, thus making the “headcut erosion” process under the conditions of surge and no surge in two forms of undercutting, which is steep hills and slopes. (3) By analyzing the undercut erosion process of the breach, it is found that the undercut erosion process of the breach is mainly influenced by the void ratio and fines content of the dam body, and there is a linear relationship between the erosion rate at the midpoint of the breach and the water flow shear stress, which is consistent with the linear erosion model. Through the analysis found that the erodible coefficient of Jialongcuo end-moraine dam is 0.051, the critical starting stress is 237.64 Pa, compared with the landslide dams, the erodible coefficient is smaller, while the critical shear stress is larger.
-
Keywords:
- end-moraine dam /
- in situ /
- breach process /
- undercutting characteristics /
- erosion characteristics
-
0. 引言
伴随着气候变暖的过程,冰湖溃决事件不断发生,在青藏高原和科迪勒拉山系等地区造成大量的财产损失和人员伤亡[1-2]。冰湖溃决的直接原因主要有:冰崩和冰滑坡入湖所激发的涌浪、强降雨造成的终碛坝漫顶溢流、终碛坝体管涌、地震造成终碛坝瞬间垮塌和多种机制的组合[3]。冰湖溃决一般发生在气候变化较为异常的年份[4],刘建康等[5]研究发现,20世纪30年代以来,青藏高原地区已经有33个冰湖发生过溃决,我国境内的冰湖溃决灾害主要分布于喜马拉雅山中段和念青唐古拉山东段[6]。藏历1931年6月8日晚上,位于波密县的鲁姆湖发生溃决,在溃决洪水的行进过程中淹没了7处村庄,冲毁32户居民房,共造成72人死亡[6]。2013年7月5日,西藏那曲地区然则日阿错冰湖发生溃决,导致忠玉乡238户1160人不同程度受灾,经济损失2.7亿元[7]。2016年7月5日,西藏聂拉木县章藏布流域贡巴通沙错发生冰湖溃决事件,溃决洪水在尼泊尔境内摧毁了77户房屋和3座高速公路大桥[8]。2020年8月1日,西藏冲堆普流域上游的串珠状冰湖发生级联式的溃决,24小时的泄水总量达到3.00×106 m3。溃决洪水在聂拉木县城沟道内冲刷掏蚀,造成原沟道内的护岸垮塌,县政府大楼和部队营地的地基基础暴露在外,洪水汇入波曲河后,沿波曲主河向樟木镇方向前进,在曲乡边检站附近冲毁318国道,造成318国道交通中断。洪水携带的泥沙使得曲乡电站发电机组故障,造成聂拉木全县停电3天。
终碛坝属于堰塞坝的一种类型,为了解堰塞坝的溃决过程与溃决机制,国内外学者通过室内水槽实验的方法,考虑几何相似和重力相似,对沟床坡度[9]、坝体含水率[10]、上游来水流量和黏粒含量[11]、颗粒级配[12]、密实度[13]等参数,对坝体溃决过程进行了研究。但溃坝是一个土力学,水力学和泥沙运动综合作用的过程,仅仅考虑几何相似和重力相似无法准确地还原坝体真实的溃决过程,还需在此基础上满足材料的相似条件[14]。终碛坝由冰川沉积而成,磨圆度差,的沉积时间长,形成较早的冰碛物已完成固结,甚至发生了钙质或泥质胶结[15-16],其细粒含量不足10%[17]。这与堰塞坝在组成结构上有较大的差异[18]。事实上,要完全模拟终碛坝土体结构等物理力学性质是十分困难的,因此本文选择在嘉龙错冰湖的终碛坝体上进行原位实验,在实验过程中未对终碛坝进行扰动,再现了坝体的原位状态,弥补了室内试验因筑坝造成的坝体结构失真,这对于认识终碛湖溃决过程以及终碛坝溃口的演变规律具有一定的科学价值。
1. 实验原型
实验原型为嘉龙错冰湖,嘉龙错位于波曲河流域的冲堆普子流域上游,距离聂拉木县城直线距离约15.8 km(图1)。冰湖类型为终碛湖,其轴线西南方向的山腰发育有现代冰川,东南和西北方向均为侧碛垄,终碛坝位于东北方向。嘉龙错在2002年5月23日和6月29日先后两次暴发大规模泥石流灾害[19]。嘉龙错目前处于溢流状态,并且后缘冰川发生冰崩可能性较大。强降水、快速的冰川融水补给和冰崩都有可能导致嘉龙错的终碛坝漫顶破坏。基于此,考虑将嘉龙错终碛坝作为原位实验的场址,以漫顶冲刷作为溃决方式来模拟嘉龙错冰湖终碛坝的溃决过程。
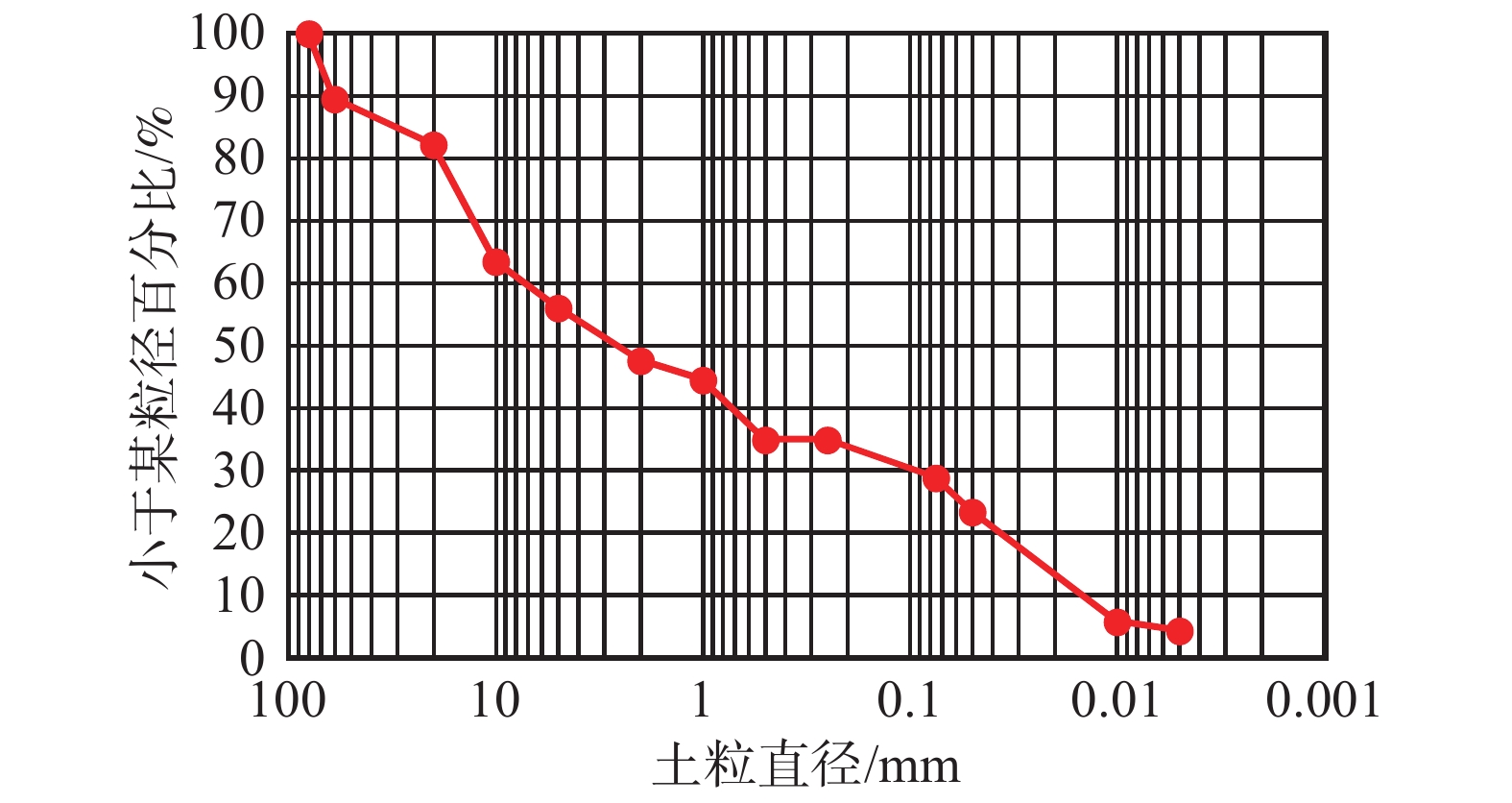
在水槽处取土密封后带回,在实验室内分别测量了坝体材料在天然含水率和饱和状态下的黏聚力和内摩擦角(表1),其中内摩擦角的值要比其他区域的冰碛土小,黏聚力介于最大值和最小值之间。堰塞坝的这两个参数变化范围较大,通过分析并参考国内的一些典型堰塞坝参数,本实验中土样黏聚力的值接近于易贡堰塞坝,内摩擦角的值接近于唐家山堰塞坝[15, 18]。坝体材料颗粒级配曲线由筛分法获得(图2),从图2中可以看出,粒径在10~20 mm的颗粒含量较多,黏粒含量为4.2%,相比于堰塞坝,终碛坝的黏粒含量偏小[18]。
表 1 实验工况参数Table 1. Experimental working conditions parameters实验
编号汇水流量
Qin
/(L·s−1)坝顶宽
WD
/m坝体下游
坡度
θ
/(°)坝高
HD
/m黏聚力
C/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)天然
含水率饱和 天然
含水率饱和 1 2.5 0.2 1∶1 1 17.43 12.17 27.97 21.85 2 0.4 3 0.6 4 0.8 2. 实验设计
2.1 实验设置
实验选取了一系列常规溃坝实验所选择的实验参数(表1),包括汇水流量、坝顶宽、坝体下游坡度和坝高。所有参数中只有坝顶宽WD
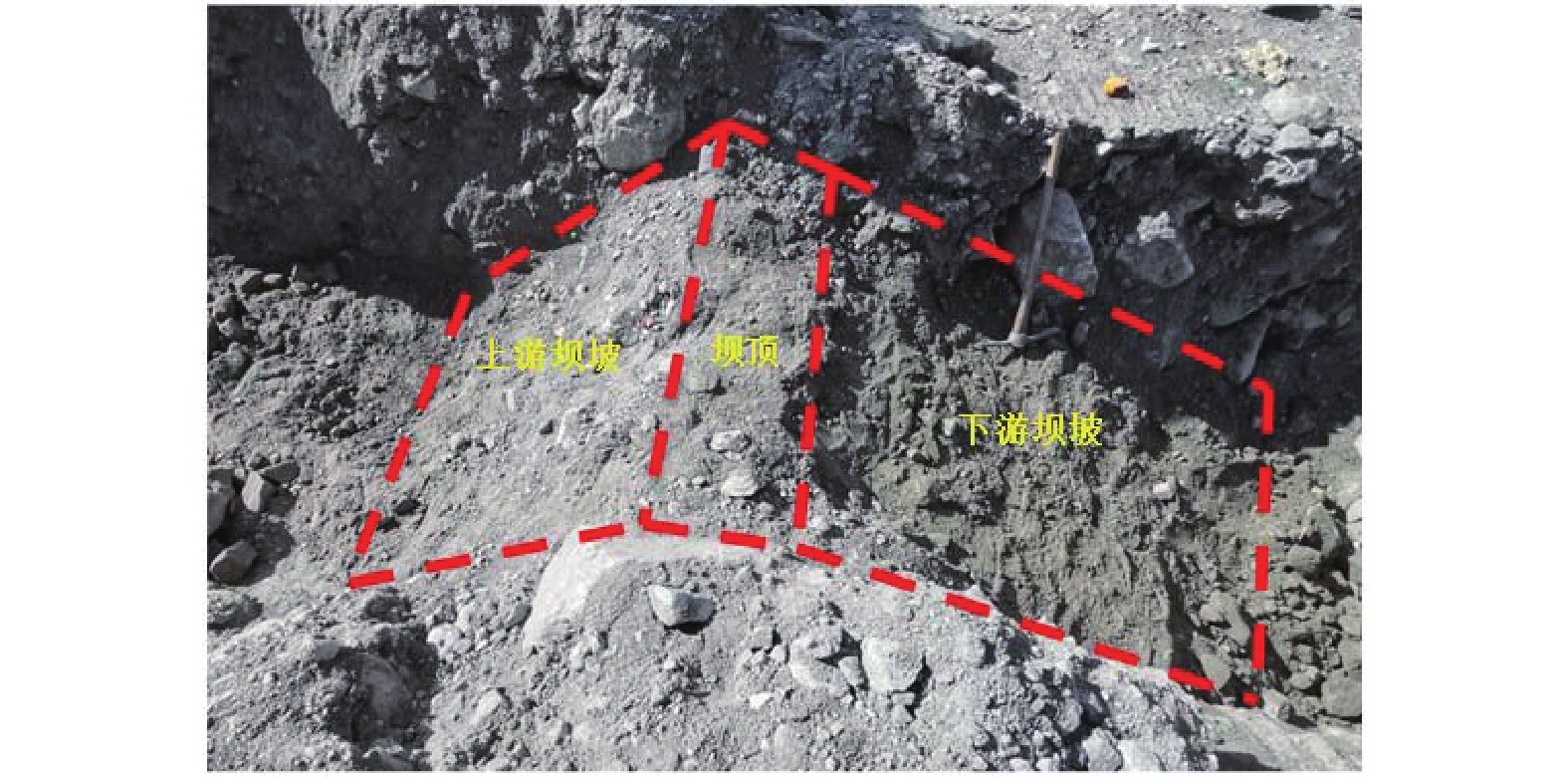
为变量,变化范围为0.2~0.8 m。 实验设计的溃决方式为漫顶冲刷,为了便于进行实验,将实验水槽设计为矩形。通过LSV软件获取了嘉龙错的轴向长度与平均宽度之比约为2.66,以宽度作为基准,实验水槽上游湖区长度与宽度的比值取为2.66。上游湖区宽度根据挖掘机挖斗的宽度设置,大小为1.5 m,计算可得上游湖区长度约为4 m。采用挖掘机对水槽进行了开挖,在开挖过程中,坝体表面不可避免地发生了轻微扰动,在挖掘机开挖后,采用人工作业去除了表面的扰动土,因此坝体依旧为原位状态。水槽系统的结构如图3所示,由上游湖区、坝体、下游蓄水池、水位计和3台摄像机组成。根据坝体尺寸的不同,水槽的总长为6.6~ 7.2 m,宽1.5 m,深1.5 m,其中上游湖区长4 m,坝体底宽2.4~3.0 m,深1 m,坝体上下游坡度均为1∶1,以坝顶宽为0.4 m为例,其坝底宽为2.6 m。实验预设了初始溃口,位于坝体中部,初始溃口宽0.2 m,深0.1 m(图3、图4)。
实验过程中水位的变化通过上游湖区底部的一个水位计(RR-1840)记录,频率为一秒一次,然后以水位计的数据为基础,通过式(1)和式(2)计算流量,计算所得流量按照一分钟一次进行平均处理,以减小数据波动带来的误差。在实验过程中也未见坝体渗流现象,因此在溃坝过程中忽略渗流的影响,认为每一秒计算所得的流量为此时刻的真实流量。三台高清摄像机(索尼FDR-AX60,GOPRO7,索尼HDR-PJ820E)分别位于蓄水区上游,坝肩一侧和坝体下游,用来捕捉溃口的演变过程。1#摄像机记录溃决过程中上游湖区的变化情况,2#摄像机用于记录溃口的下切过程,3#摄像机用于记录溃口的展宽过程和下游坝坡的变化。
$$ {Q_{{\rm{out}}}}\left( t \right) = V\left( {t - 1} \right) - V\left( t \right) + {Q_{\rm{in}}} $$ (1) $$ V\left( t \right) = 0.9H\left( t \right) + 7.2H{\left( t \right)^2} $$ (2) 式中:Qout(t)——t时刻的溃决流量;
V(t−1)、V(t)——分别表示t−1时刻、t时刻的库容;
H(t)——t时刻的的水位。
2.2 实验过程
在向水槽注水的过程中,先打开1号摄像机,记录上游湖区内发生崩塌的情况。当水位上升到距离初始溃口还有1 cm时停止向水槽注水,等待蓄水池松散土体发生崩塌。待上游湖区稳定后,放入水位计,并继续向水槽注水,当坝体快要发生溢流时,按照实验设计的要求向水槽供水,此时打开2号和3号摄像机,记录溃决的整个过程。
3. 终碛坝溃决过程分析
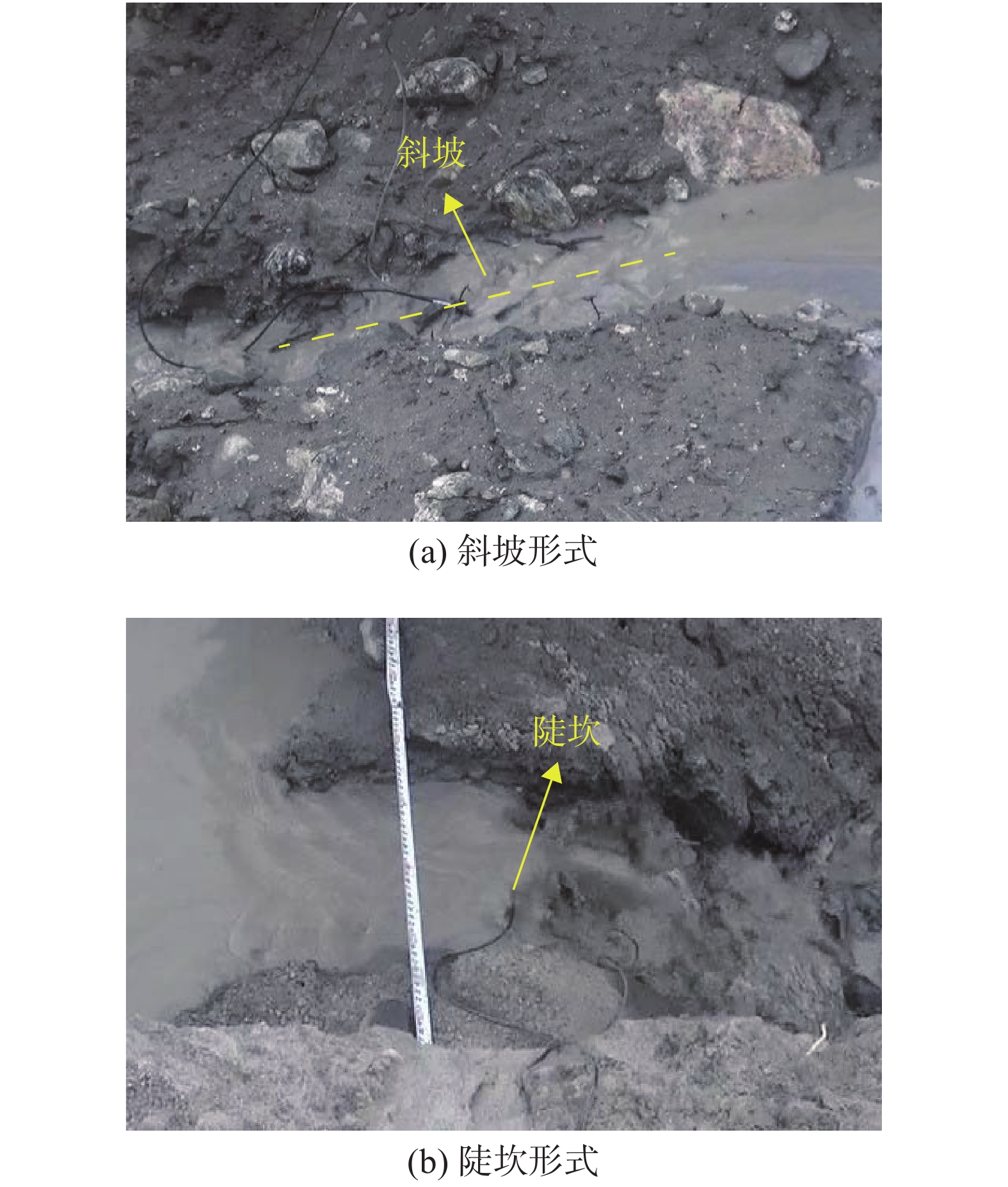
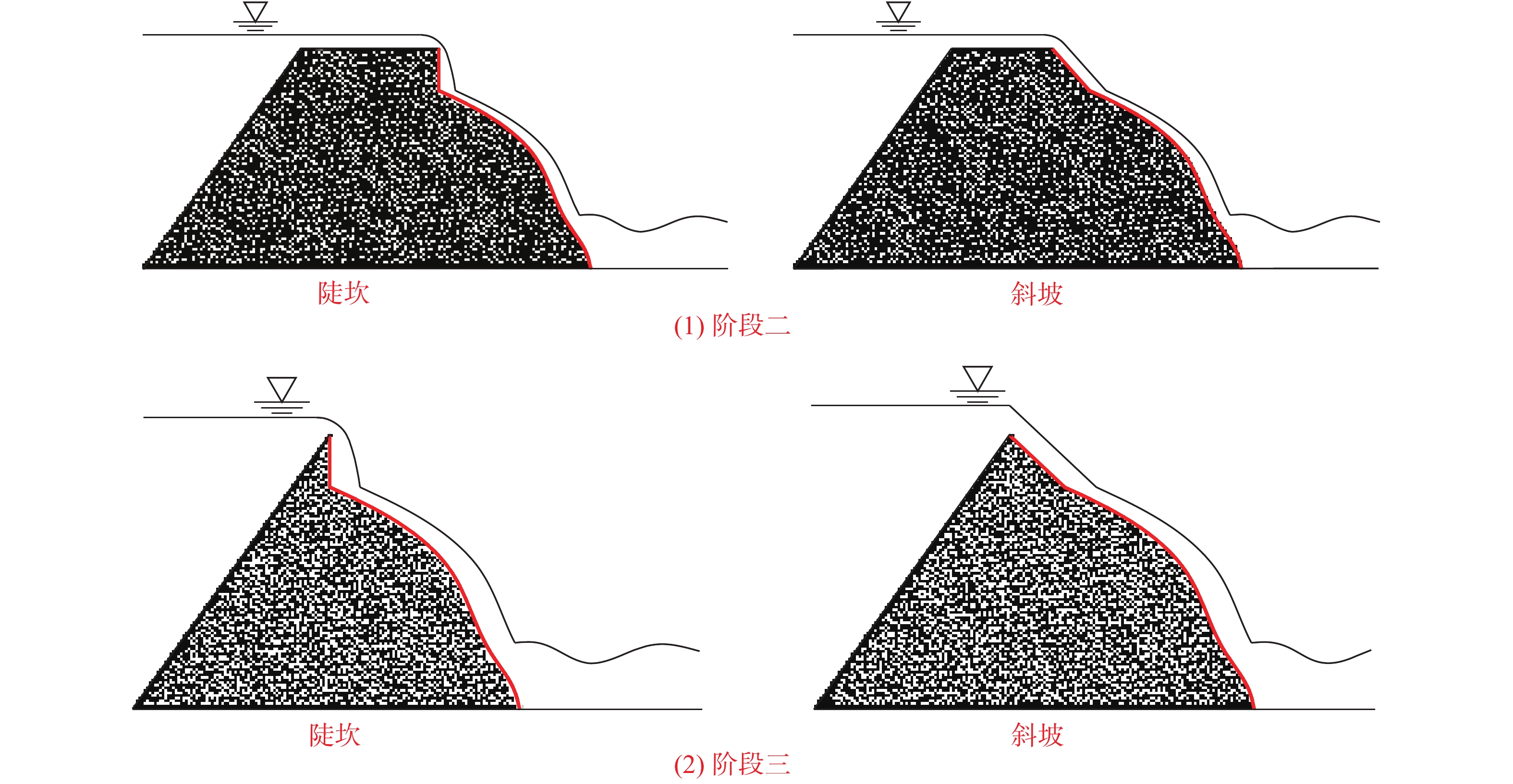
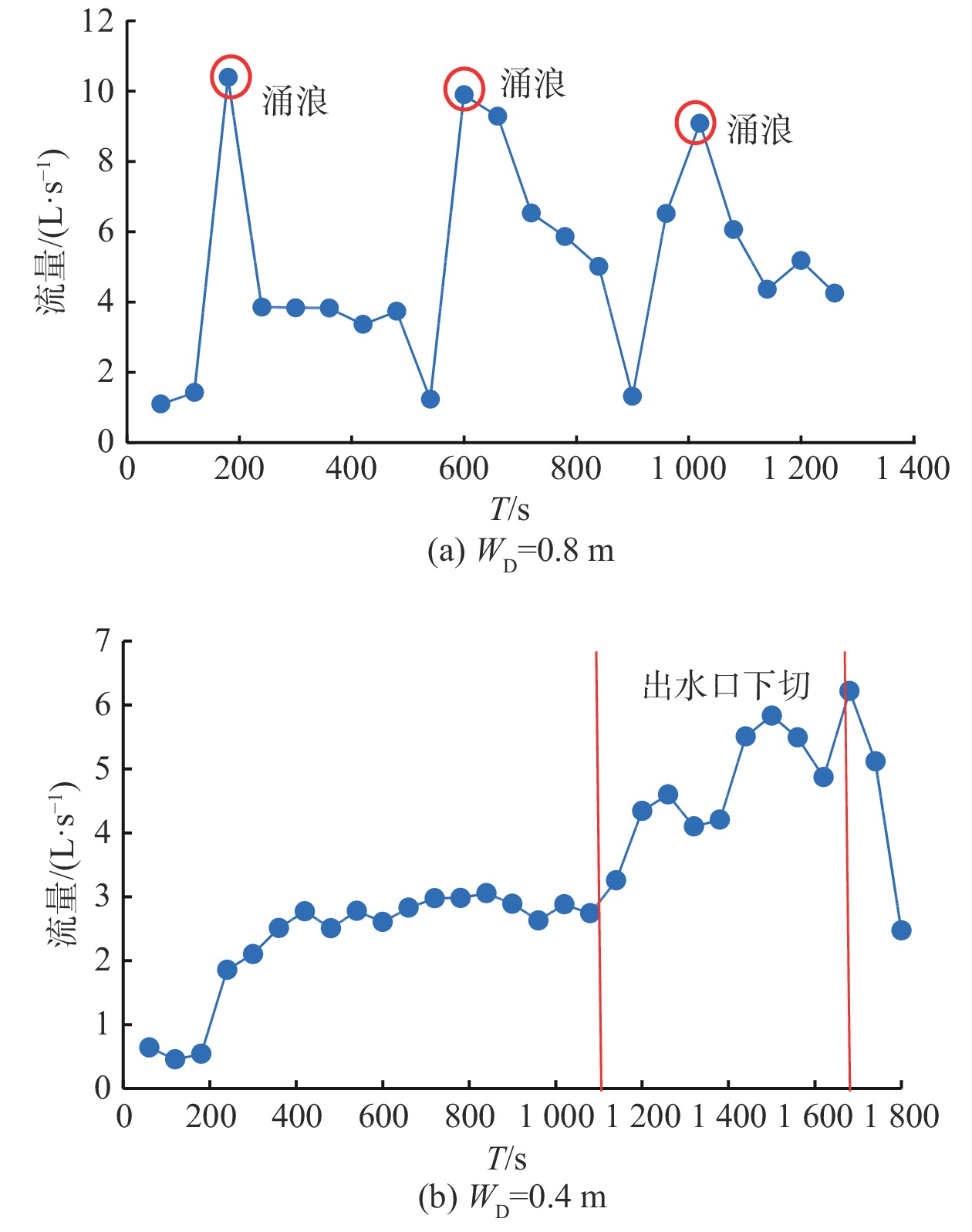
实验总共进行了4组,其中WD为0.2 m和0.4 m的实验中,上游湖区边坡没有发生崩塌现象,故而没有在湖区内激发产生涌浪。在WD为0.6 m和0.8 m的实验中,上游湖区边坡有崩塌现象产生,崩塌体在湖区内激发产生涌浪,同时由于崩塌体进入湖区内,造成湖区水位急速上升(图5),使得溃决流量激增。如图5所示,每一次水位的突变都对应着一次崩塌涌浪过程。但无论是否有涌浪,溃决过程都可以划分为四个阶段,第一个阶段为坝体下游坡面冲刷,第二阶段为溃口内的“溯源侵蚀”过程,第三阶段为出水口下切,第四阶段为溃口拓宽。在有涌浪的溃决过程中,由于崩塌入湖造成湖区水位的急速上升,因此在溃决伊始,溃决的流量较大,往往表现出以斜坡的形式进行“溯源侵蚀”(图6)。在无涌浪的溃决过程中,湖区水位没有急速上升的现象,因此溃决开始后的一段时间内,溃决流量相对较小,往往表现出以陡坎的形式进行“溯源侵蚀”(图6)。
3.1 溃决发展过程
阶段一:当库区水位达到初始溃口高程时,水流将漫过坝顶开始出现溢流现象。溢流刚开始时,由于流量和流速都较小,水流基本不具备侵蚀能力,初始溃口内不会被冲刷。当水流流出初始溃口,到达坝体下游坡面,水流开始加速,侵蚀能力显著增强,坝体下游坡面表面的土体被水流冲刷带走,表面形成一条冲沟,此时视为溃决开始。由于坡面土体被不断冲刷,坡顶处的坡度不断增大,逐渐形成一个陡坎,溃决进入下一阶段。
阶段二:在以陡坎形式进行“溯源侵蚀”的过程中,陡坎形成后,在陡坎处跌落的水流冲击陡坎底面,并形成反向旋流,在陡坎上施加一个平行于陡坎面的水流切应力[20]。陡坎上的细颗粒在持续水流剪应力作用下从陡坎上脱落,逐渐露出粗颗粒,随着时间推移,粗颗粒悬空,并在水流冲击力和重力作用下脱离陡坎,这个过程循环往复,造成陡坎向上游方向发展,产生“溯源侵蚀”现象。陡坎发展到上游湖区出水口时停止,陡坎最终在水流的冲刷下消失,下游冲沟与初始溃口连为一体,成为一条连通的泄流槽。
在以斜坡形式进行“溯源侵蚀”的过程中,当上游湖区的涌浪发生后,在涌浪和坝前水位急速上升的共同作用下,溃决流量显著增大,使得陡坎转化为斜坡。斜坡形成后,斜坡表面的泥沙颗粒随溃决水流发生输移,使得斜坡发生“溯源侵蚀”现象。当斜坡顶部发展到上游湖区出水口时,斜坡停止发展,此时进入溃决的第三阶段(图7)。
阶段三:以陡坎形式进行“溯源侵蚀”的过程中,当陡坎停止发展时,由于此时的坝体变薄,水流的冲刷作用将使溃口位于出水口的部分“快速”下切。由于坝前水位不会发生突变,因此出水口处的水流流深会快速增大,根据堰流式(3)的描述,溃决流量也会迅速增大,在WD为0.4 m时,进入第三阶段后,溃决流量从2.8 L/s上升至6.2 L/s,达到洪峰状态(图8)。以斜坡形式进行“溯源侵蚀”的过程中,当斜坡停止发展时,此时的坝体相对于陡坎形式而言更厚,因此出水口的下切速度更小,水流流深也相对较小,溃决流量的变化率也更小,这一类型的洪峰流量一般是由崩塌涌浪造成的,如WD为0.8 m时,在图8中,溃决流量在第180 s时,从1.3 L/s突然增大至10.6 L/s。由于崩塌体入湖导致坝前水位上升,使得涌浪过后,溃决流量依然较大,如WD为0.8 m时,第240 s至480 s的流量曲线。
阶段四:在出水口部分“快速”下切的过程中溃决流量迅速增大,水流掏蚀溃口边坡坡脚,使得边坡悬空,当掏蚀达到一定程度时,边坡随即发生倾倒破坏,使得溃口发生展宽现象,表现出高黏性坝和密实坝边坡失稳的特征。
$$Q = CB{\left( {H - Z} \right)^{1.5}}$$ (3) 式中:C——流量系数;
B——溃口宽度;
H——溃口内的水面高程;
Z——溃口底部高程。
3.2 溃口下切过程分析
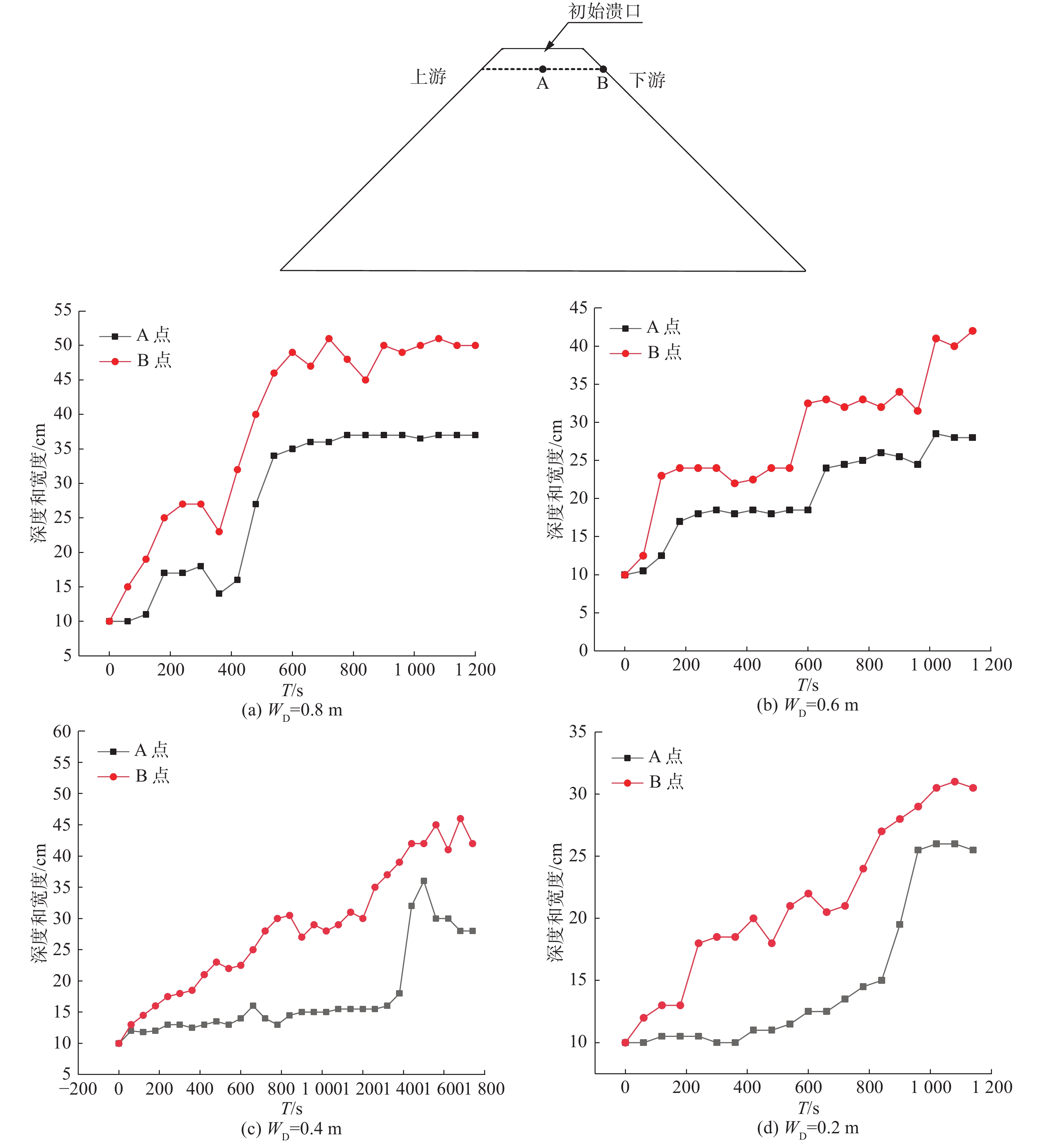
在实验过程中,每隔一分钟测量了一次A点和B点的深度,根据测量数据得到了四组实验中A点和B点的深度变化曲线(图9)。溃口的下切是水流冲刷作用和坝体物质抗冲刷作用相互抗衡的结果,主要的贡献者为“溯源侵蚀”过程。图9展示了WD从0.2 m至0.8 m的溃口深度变化曲线,从图9中可以看出,在四组实验中,A点的深度都要小于B点。当WD为0.6 m和0.8 m时,两点深度的变化趋势几乎一致。而当WD为0.2 m和0.4 m时,A点的深度在前期变化非常缓慢,分别在第860 s和第1380 s发生跳跃,变化趋势与B点完全不同。
通过对实验视频的解析发现,当WD为0.6 m和0.8 m时,上游湖区边坡有崩塌发生,崩塌体入湖后激发了涌浪,并导致坝前水位急速上升,在这两组实验中,“溯源侵蚀”过程以斜坡的形式进行(图10)。而当WD为0.2 m和0.4 m时,上游湖区边坡没有崩塌发生“溯源侵蚀”过程以陡坎的形式进行(图11)。事实上,所有组次实验在溃决刚开始时都会形成陡坎,但WD为0.6 m和0.8 m时,由于涌浪发生在溃决伊始,在涌浪冲刷和坝前水位上升双重因素的作用下,溃决流量迅速增大,水流侵蚀能力迅速增强,使得陡坎快速转化为斜坡,如图10所示,而WD为0.2 m和0.4 m时,溃决过程无涌浪,因此一直保持陡坎的形式“溯源侵蚀”。
3.3 溃口下切侵蚀分析
不同的下切形式对应了不同的侵蚀过程,这里对两种形式的溃决过程侵蚀率进行分析。侵蚀率是一个反映侵蚀快慢的物理量,其定义为[21]。
$$\varepsilon = \frac{{\Delta {\textit{z}}}}{{\Delta t}}$$ (4) 式中:Δz——溃口深度的变化量;
Δt——溃口深度变化Δz的时间,由于测量的溃口深度数据以分钟为单位,因此这里的侵蚀率表示1分钟侵蚀率。
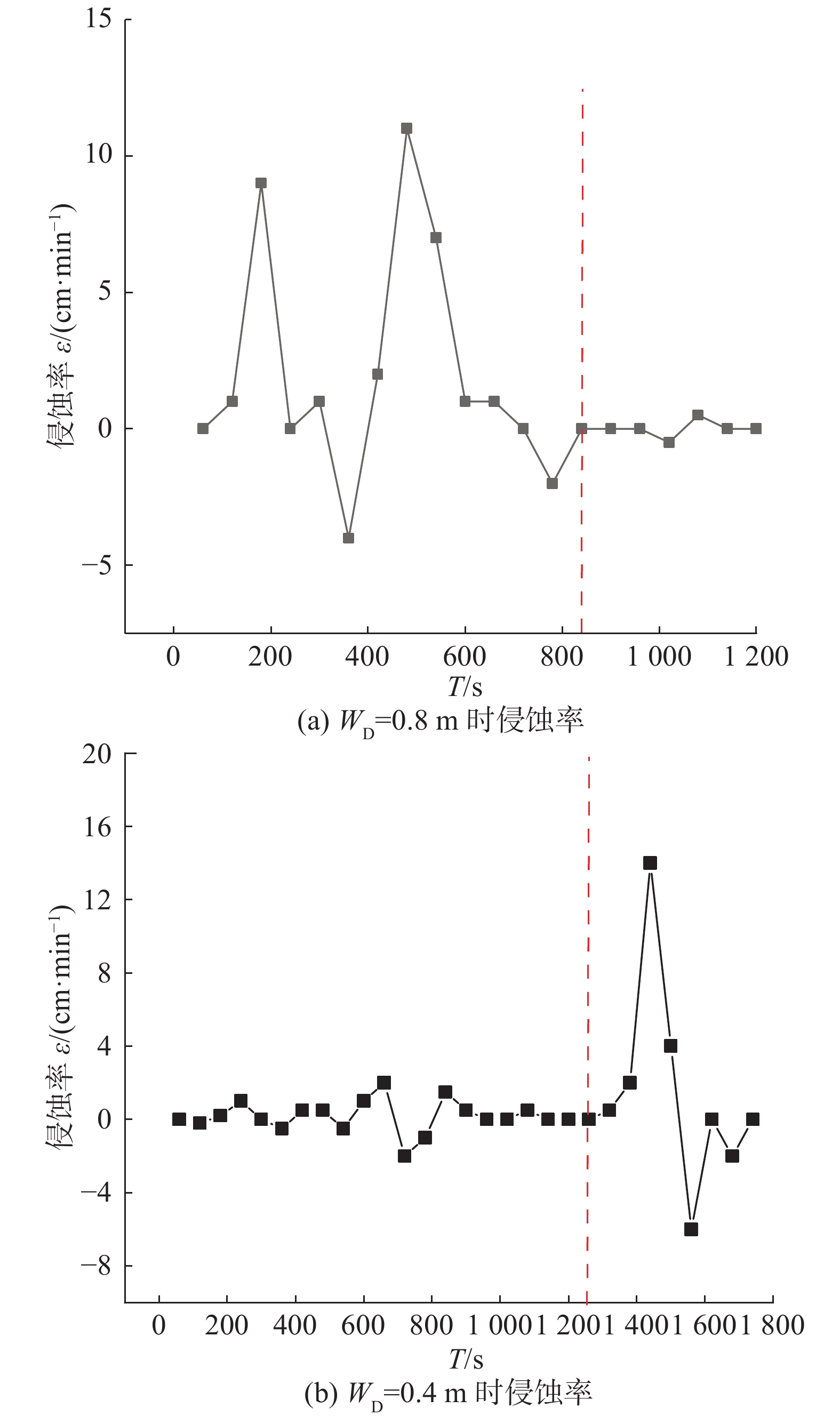
基于此,对溃决过程的侵蚀率进行了分析。将WD分别为0.8 m和0.4 m作为有涌浪和无涌浪的代表,以A点的侵蚀率为例进行说明。两组实验中A点的变化率如图11所示,图11中侵蚀率为正表示A点有下切,侵蚀率为负表示A点有沉积。从图11中可以看出,WD为0.8 m时,A点的侵蚀率在第840 s前变化较为剧烈,840 s后基本保持在0附近波动。WD为0.4 m时,A点的侵蚀率在第1260 s前虽有波动,但变化量相对于1260 s后要小得多,特别是在第1260 s发生了一次较大的突跃。
终碛坝的内部存在渗流场,当坝体温度降低时,内部的孔隙水会发生冻结,导致土颗粒之间的连接更为紧密,使得坝体的稳定性增强。但在实验开挖水槽的过程中并未发现坝体内部有冰的存在,因此可以排除由于坝体内部结冰导致坝体的强度增大这一因素,这样一来,二者侵蚀性产生差异的原因应当归结为坝体结构的影响。侵蚀性系数kd和临界启动应力τc是反映土体侵蚀难易程度的物理量,其中kd表示侵蚀的快慢,τc表示能否被侵蚀,二者共同反映土体的抗侵蚀性。CHANG等[18]通过实验得出了可侵蚀系数的计算公式:
$${k_{\rm{d}}} = 20\;075{{{e}}^{4.77}}{C_{\rm{u}}}^{ - 0.76}$$ (5) 式中:e——土体孔隙比;
Cu——不均匀系数。
从式(5)中可以看出可侵蚀系数与土体孔隙比和不均匀系数有关,通过计算可得本实验的孔隙比为0.15,不均匀系数为146,作为对比,唐家山堰塞坝10 m深度内的孔隙比为0.95,不均匀系数为610[22],白格滑坡坝的孔隙比为0.35,不均匀系数为75.4~189.1[23],易贡滑坡坝的孔隙比为0.47,不均匀系数为19.7~54.1[24]。从式(5)可以发现,孔隙比的影响程度远大于不均匀系数,因此本文认为孔隙比是终碛坝比滑坡堰塞坝更难侵蚀的原因之一。在临界起动应力方面,CHANG提出了一个经验公式:
$${\tau _c} = 6.8P{I^{0.84}}{P^{ - 1.73}}{e^{ - 0.97}}$$ (6) 式中:PI——塑性指数;
P——细粒含量。
杨安银[25]指出,塑性指数的会随着细粒含量的增加而增加,因此塑性指数和细粒含量并非相互独立的关系。在本实验的细粒含量为28.72%,唐家山堰塞坝为11.5%,白格滑坡坝为10%左右,易贡滑坡坝为12.08%[26],因此可以认为细粒含量也是导致终碛坝比滑坡堰塞坝更难侵蚀的主要因素。综上所述,本文认为孔隙比和细粒含量是终碛坝比滑坡堰塞坝更难侵蚀的其中两个原因。
目前的溃坝理论认为,当水流的剪应力τ大于土颗粒的抗剪力τc时,土体中的泥沙颗粒将发生启动,从而导致溃口下切,产生侵蚀现象。水流剪应力τ可表示为:
$$\tau = \frac{{\gamma {n^2}{v^2}}}{{{R^{\frac{1}{3}}}}}$$ (7) 式中:γ——水的重度,取值为9800 N/m3;
n——曼宁糙率系数;
v——水流的流速;
R——水力半径。
其中曼宁糙率系数是一个与土体颗粒中值粒径相关的数。
$$n = \frac{{{d_{50}}^{\frac{1}{6}}}}{{{A_n}}}$$ (8) 式中:d50——土体颗粒中值粒径;
An——一个经验系数,在实验室内取值为16,在野外实验中取值为12[21]。
水力半径R可采用式8进行计算。
$$R{\rm{ = }}\frac{{h\left( {b - h} \right)}}{b}$$ (9) 式中:h——水流的流深;
b——溃口断面宽度。
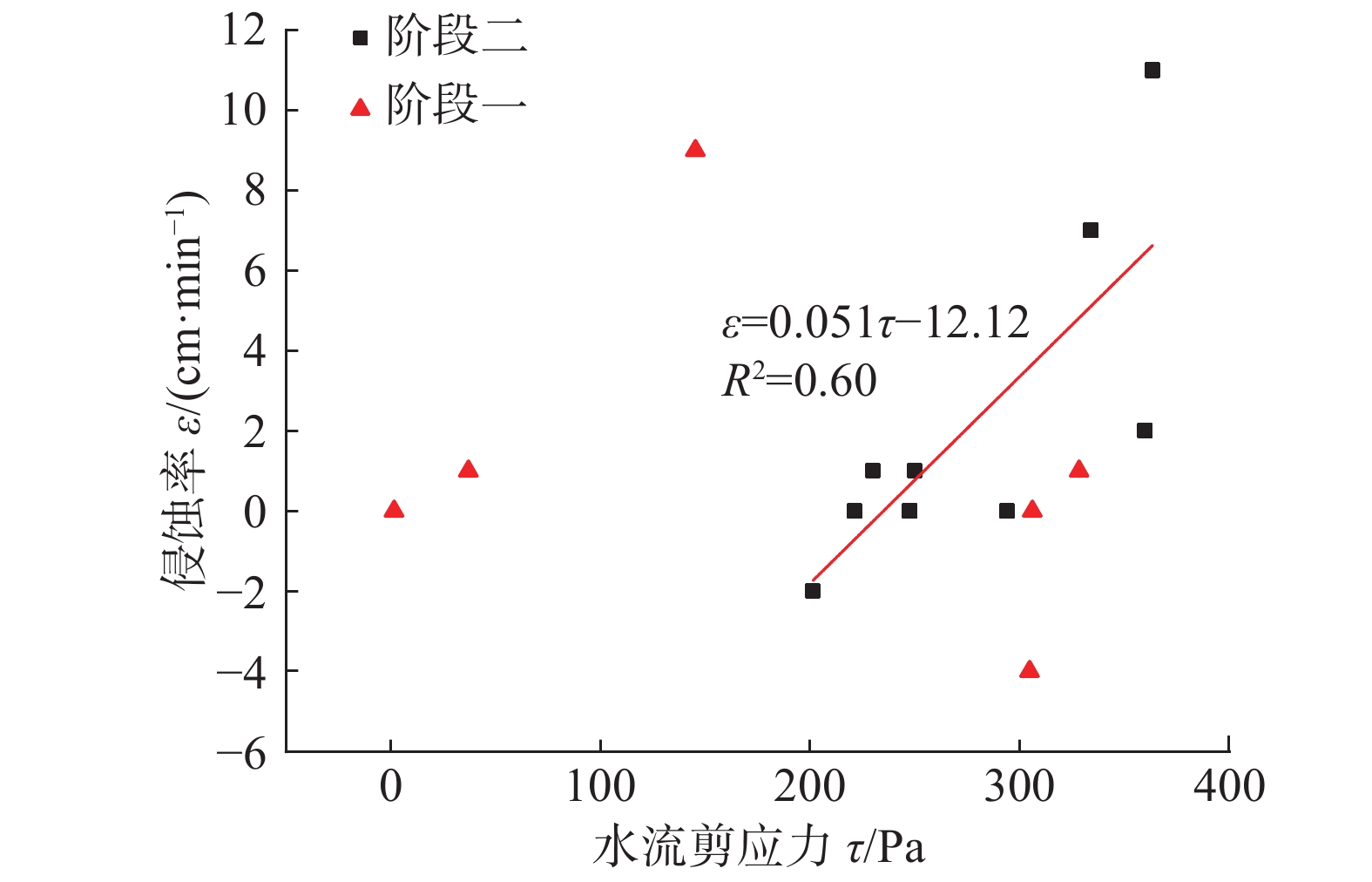
当b相对于h足够大时,可以近似用h来代替[21]。根据以获取的数据,以WD为0.8 m为例,计算了A点每一分钟末的水流剪应力。在计算某一分钟的平均剪应力时,将上一分钟末和这一分钟末的水流剪应力进行平均作为这一分钟的平均剪应力。获得水流剪应力后,拟合了水流剪应力与侵蚀率之间的关系。从图12中可以看出,侵蚀率在阶段二与水流剪应力有较好的线性关系。
对比线性侵蚀模型:
$$\varepsilon = {k_{\rm{d}}}\left( {\tau - {\tau _{\rm{c}}}} \right)$$ (10) 式中:kd——可侵蚀系数;
τc——临界启动应力。
计算可知,当坝顶宽为0.8 m时,可侵蚀系数和临界剪应力分别为0.051和237.64 Pa。与前人实验结果的对比,本实验kd偏小而τc偏大(表2)。这也意味着终碛坝要比滑坡堰塞坝更加难以侵蚀。
4. 结论
本文通过野外水槽试验,研究了漫顶溃决条件下终碛坝的溃决过程。可以得到以下结论:
(1)崩塌体入湖后会使得坝前水位急速上升并激发产生涌浪,造成溃决流量激增,水流侵蚀能力迅速增强,使得溃口内的陡坎发展为斜坡,从而使得“溯源侵蚀”过程出现斜坡和陡坎两种下切形式。
(2)根据实验过程观察到的现象,终碛坝的溃坝过程分为四个阶段,第一阶段为坝体下游坡面冲刷,第二阶段为溃口“溯源侵蚀”,第三阶段为出水口“快速”下切,第四阶段为溃口拓宽。两种“溯源侵蚀”形式下的溃决过程在阶段二和阶段三存在一定的差异,陡坎形式下的洪峰流量发生于阶段三,主要原因是出水口“快速”下切,斜坡形式下的洪峰流量主要发生于崩塌涌浪来临时。
(3)两种“溯源侵蚀”形式下的溃口中点和溃口底部与下游坝坡交线中点深度发展也不相同,在以斜坡形式进行“溯源侵蚀”的溃决过程中,溃口中点的变化趋势与溃口底部与下游坝坡交线中点几乎一致,而在以陡坎形式进行“溯源侵蚀”的溃决过程中,溃口中点在前期的变化比较缓慢,到后期发生突跃现象,在短时间内快速下切。
(4)对溃口中点侵蚀率与水流剪应力的关系进行了分析,发现二者在阶段二为线性关系,符合线性侵蚀模型。在模型中,可侵蚀系数kd和临界剪应力τc与前人对滑坡堰塞坝的研究相比,可侵蚀系数要比滑坡堰塞坝小,而临界剪应力要比滑坡堰塞坝大,这也反映出终碛坝相对于滑坡堰塞坝而言要更加难以侵蚀,并且孔隙比和细粒含量是最终导致碛坝比滑坡堰塞坝更难侵蚀的其中两个原因。
-
表 1 实验工况参数
Table 1 Experimental working conditions parameters
实验
编号汇水流量
Qin
/(L·s−1)坝顶宽
WD
/m坝体下游
坡度
θ
/(°)坝高
HD
/m黏聚力
C/kPa内摩擦角
φ/(°)天然
含水率饱和 天然
含水率饱和 1 2.5 0.2 1∶1 1 17.43 12.17 27.97 21.85 2 0.4 3 0.6 4 0.8 -
[1] 钟妍, 刘巧, 廖海军, 等. 中喜马拉雅山中—尼通道沿线冰川/冰湖变化及其相关灾害初步调查[J]. 山地学报,2020,38(2):314 − 327. [ZHONG Yan, LIU Qiao, LIAO Haijun, et al. Glaciers and glacial lakes status and their related geo-hazards along three main China-Nepal corridors[J]. Mountain Research,2020,38(2):314 − 327. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] EMMER A, HARRISON S, MERGILI M, et al. 70 years of lake evolution and glacial lake outburst floods in the Cordillera Blanca (Peru) and implications for the future[J]. Geomorphology,2020,365:107178. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2020.107178
[3] 刘晶晶, 程尊兰, 李泳, 等. 西藏终碛湖溃决形式研究[J]. 地学前缘,2009,16(4):372 − 380. [LIU Jingjing, CHENG Zunlan, LI Yong, et al. A study of the outburst form of the end-moraine lake in Tibet[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2009,16(4):372 − 380. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2009.04.037 [4] 刘晶晶, 程尊兰, 李泳, 等. 西藏冰湖溃决主要特征[J]. 灾害学,2008,23(1):55 − 60. [LIU Jingjing, CHENG Zunlan, LI Yong, et al. Characteristics of glacier-lake breaks in Tibet[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2008,23(1):55 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2008.01.013 [5] 刘建康, 张佳佳, 高波, 等. 我国西藏地区冰湖溃决灾害综述[J]. 冰川冻土,2019,41(6):1335 − 1347. [LIU Jiankang, ZHANG Jiajia, GAO Bo, et al. An overview of glacial lake outburst flood in Tibet, China[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2019,41(6):1335 − 1347. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 姚晓军, 刘时银, 孙美平, 等. 20世纪以来西藏冰湖溃决灾害事件梳理[J]. 自然资源学报,2014,29(8):1377 − 1390. [YAO Xiaojun, LIU Shiyin, SUN Meiping, et al. Study on the glacial lake outburst flood events in Tibet since the 20th Century[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2014,29(8):1377 − 1390. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11849/zrzyxb.2014.08.010 [7] 孙美平, 刘时银, 姚晓军, 等. 2013年西藏嘉黎县“7.5”冰湖溃决洪水成因及潜在危害[J]. 冰川冻土,2014,36(1):158 − 165. [SUN Meiping, LIU Shiyin, YAO Xiaojun, et al. The cause and potential hazard of glacial lake outburst flood occurred on July 5, 2013 in Jiali County, Tibet[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2014,36(1):158 − 165. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] LIU M, CHEN N S, ZHANG Y, et al. Glacial lake inventory and lake outburst flood/debris flow hazard assessment after the gorkha earthquake in the Bhote Koshi basin[J]. Water,2020,12(2):464. DOI: 10.3390/w12020464
[9] 刘邦晓, 朱兴华, 郭剑, 等. 不同沟床坡度堰塞坝溃口下切过程试验研究[J]. 长江科学院院报,2020,37(12):59 − 66. [LIU Bangxiao, ZHU Xinghua, GUO Jian, et al. Experimental research on longitudinal breaching of landslide dam under different bed slopings[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2020,37(12):59 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20190999 [10] 蒋先刚, 吴雷. 不同初始含水量条件下的堰塞坝溃决机理[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版),2020,50(1):185 − 193. [JIANG Xiangang, WU Lei. Influence of initial soil moisture on breaching mechanism of natural dam[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Earth Science Edition),2020,50(1):185 − 193. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 曹春然, 陈华勇, NEUPANE R, 等. 不同条件下泥石流堰塞坝的溃决过程[J]. 水土保持通报,2020,40(3):27 − 34. [CAO Chunran, CHEN Huayong, NEUPANE R, et al. Process of debris flow dam break under different conditons[J]. Bulletin of Soil and Water Conservation,2020,40(3):27 − 34. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 王道正, 陈晓清, 罗志刚, 等. 不同颗粒级配条件下堰塞坝溃决特征试验研究[J]. 防灾减灾工程学报,2016,36(5):827 − 833. [WANG Daozheng, CHEN Xiaoqing, LUO Zhigang, et al. Experimental research on breaking of barrier lake dam under different grading conditions[J]. Journal of Disaster Prevention and Mitigation Engineering,2016,36(5):827 − 833. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 赵高文, 姜元俊, 乔建平, 等. 不同密实条件的滑坡堰塞坝漫顶溃决实验[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2018,37(6):1496 − 1505. [ZHAO Gaowen, JIANG Yuanjun, QIAO Jianping, et al. Experimental investigation on overtopping failure of landslide dams with different conditions of compactness[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2018,37(6):1496 − 1505. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 彭铭, 王开放, 张公鼎, 等. 堰塞坝溃坝模型实验研究综述[J]. 工程地质学报,2020,28(5):1007 − 1015. [PENG Ming, WANG Kaifang, ZHANG Gongding, et al. Review of model experimental studies on break of landslide dams[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2020,28(5):1007 − 1015. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 杨栋, 王军朝, 杨东旭. 帕隆藏布流域冰碛物斜坡结构及稳定性评价方法[J]. 人民长江,2019,50(1):108 − 112. [YANG Dong, WANG Junchao, YANG Dongxu. Moraine slope structure in Parlung Zangbo River basin and its stability evaluation method[J]. Yangtze River,2019,50(1):108 − 112. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 马泽平. 川藏交通廊道冰碛物工程性质研究[D]. 成都: 西南交通大学, 2013. MA Zeping. Study on engineering properties of the moraine in Sichuan-Tibet transportation corridor[D]. Chengdu: Southwest Jiaotong University, 2013. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[17] 程强, 郭喜峰. 泸定大渡河桥冰碛土的结构及现场剪切试验研究[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(4):126 − 133. [CHENG Qiang, GUO Xifeng. Soil structure and in-site shear test of moraine soil near the Xingkang bridge over the Daduhe River in Luding[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(4):126 − 133. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] CHANG D S, ZHANG L M, XU Y, et al. Field testing of erodibility of two landslide dams triggered by the 12 May Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Landslides,2011,8(3):321 − 332. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-011-0256-x
[19] 陈晓清, 崔鹏, 杨忠, 等. 聂拉木县冲堆普2002年泥石流成因分析及防治对策[J]. 冰川冻土,2006,28(5):776 − 781. [CHEN Xiaoqing, CUI Peng, YANG Zhong, et al. Debris flows of Chongdui gully in Nyalam County, 2002: Cause and control[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2006,28(5):776 − 781. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2006.05.023 [20] HANSON G J, ROBINSON K M, COOK K R. Prediction of headcut migration using a deterministic approach[J]. Transactions of the ASAE,2001,44(3):525 − 531.
[21] ZHOU G G D, ZHOU M J, SHRESTHA M S, et al. Experimental investigation on the longitudinal evolution of landslide dam breaching and outburst floods[J]. Geomorphology,2019,334:29 − 43. DOI: 10.1016/j.geomorph.2019.02.035
[22] 石振明, 郑鸿超, 彭铭, 等. 考虑不同泄流槽方案的堰塞坝溃决机理分析: 以唐家山堰塞坝为例[J]. 工程地质学报,2016,24(5):741 − 751. [SHI Zhenming, ZHENG Hongchao, PENG Ming, et al. Breaching mechanism analysis of landslide dams considering different spillway schemes—a case study of Tangjiashan landslide dam[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2016,24(5):741 − 751. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 陈祖煜, 陈生水, 王琳, 等. 金沙江上游“11·03”白格堰塞湖溃决洪水反演分析[J]. 中国科学(技术科学),2020,50(6):763 − 774. [CHEN Zuyu, CHEN Shengshui, WANG Lin, et al. Back analysis of the breach flood of the “11·03” Baige barrier lake at the Upper Jinsha River[J]. Scientia Sinica (Technologica),2020,50(6):763 − 774. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.1360/SST-2019-0297 [24] 夏式伟. 易贡滑坡-碎屑流-堰塞坝溃决三维数值模拟研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2018. XIA Shiwei. Study on three dimensional numerical simulation of Yigong rock avalanche and it's dam breach[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2018. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[25] 杨安银. 细粒含量对尾矿动力特性的影响及坝体动力抗震研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2020. YANG Anyin. Study on the effect of fines content on the dynamic characteristics of tailings and the dynamic seismic resistance of dams[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[26] 胡明鉴, 汪发武, 程谦恭. 基于高速环剪试验易贡巨型滑坡形成原因试验探索[J]. 岩土工程学报,2009,31(10):1602 − 1606. [HU Mingjian, WANG Fawu, CHENG Qiangong. Formation of tremendous Yigong landslide based on high-speed shear tests[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2009,31(10):1602 − 1606. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2009.10.020 [27] 朱敏翔. 堰塞坝溃决动力演变过程与临界水力条件实验研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2020. ZHU Minxiang. The experiment study on dynamic evolution process and critical hydraulic conditions of barrier dams failure[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2020. (in Chinese with English abstract).
[28] CHEN Z Y, MA L Q, YU S, et al. Back analysis of the draining process of the Tangjiashan barrier lake[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2015,141(4):05014011. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)HY.1943-7900.0000965
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 余斌,杨治义,彭秋建. 冰碛湖溢流溃决实验研究. 冰川冻土. 2024(05): 1463-1480 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 路锦枝,郭新蕾,茅泽育. 泄流槽型式对涌浪激发冰碛坝溃决过程的影响. 水科学进展. 2024(06): 983-992 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)





 下载:
下载:

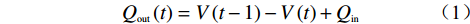



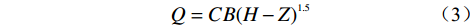

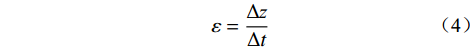

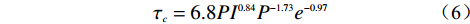
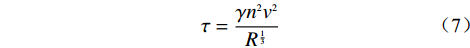
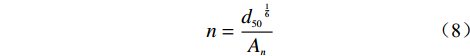
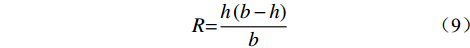
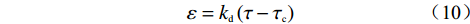
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS