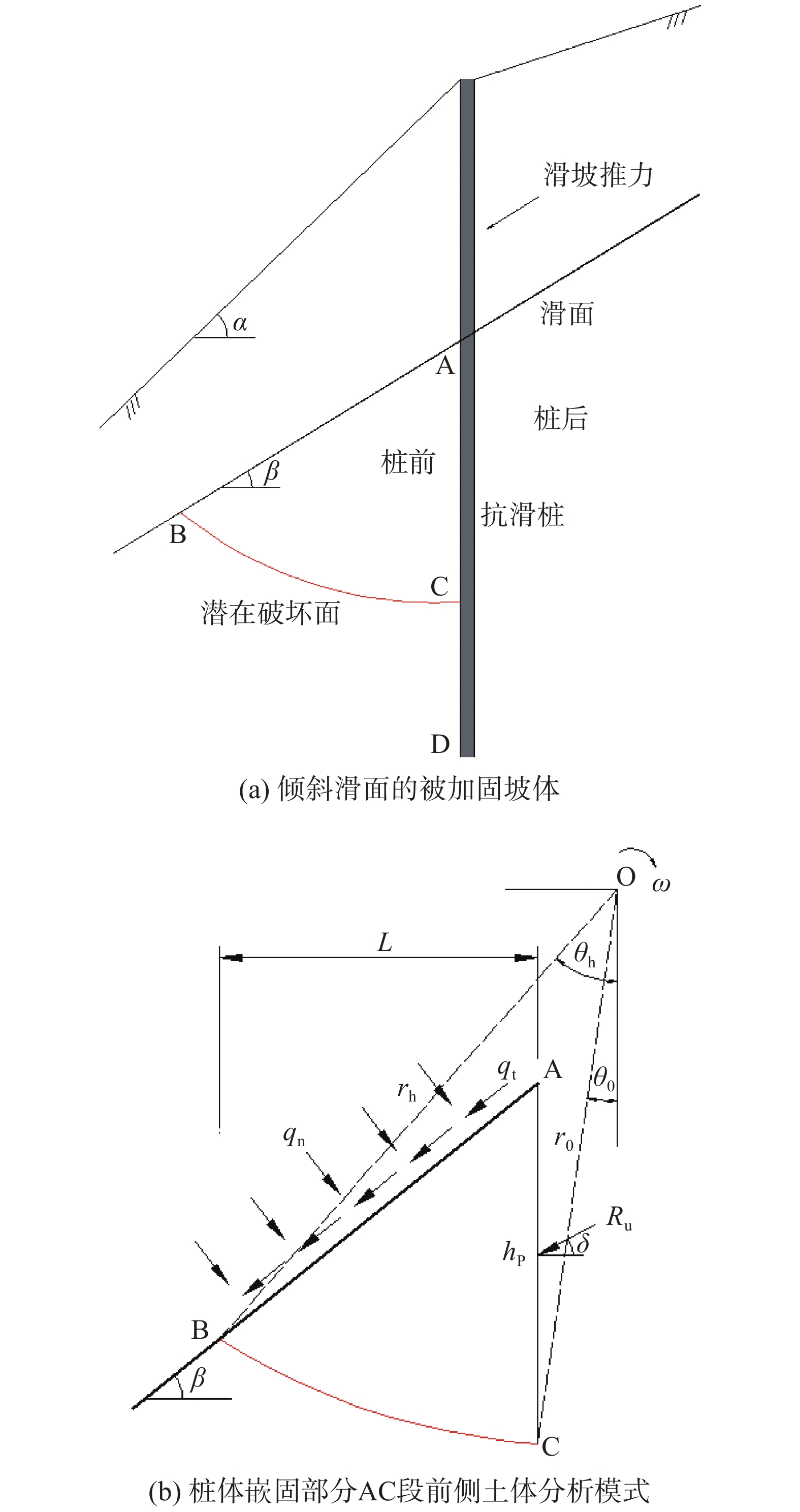
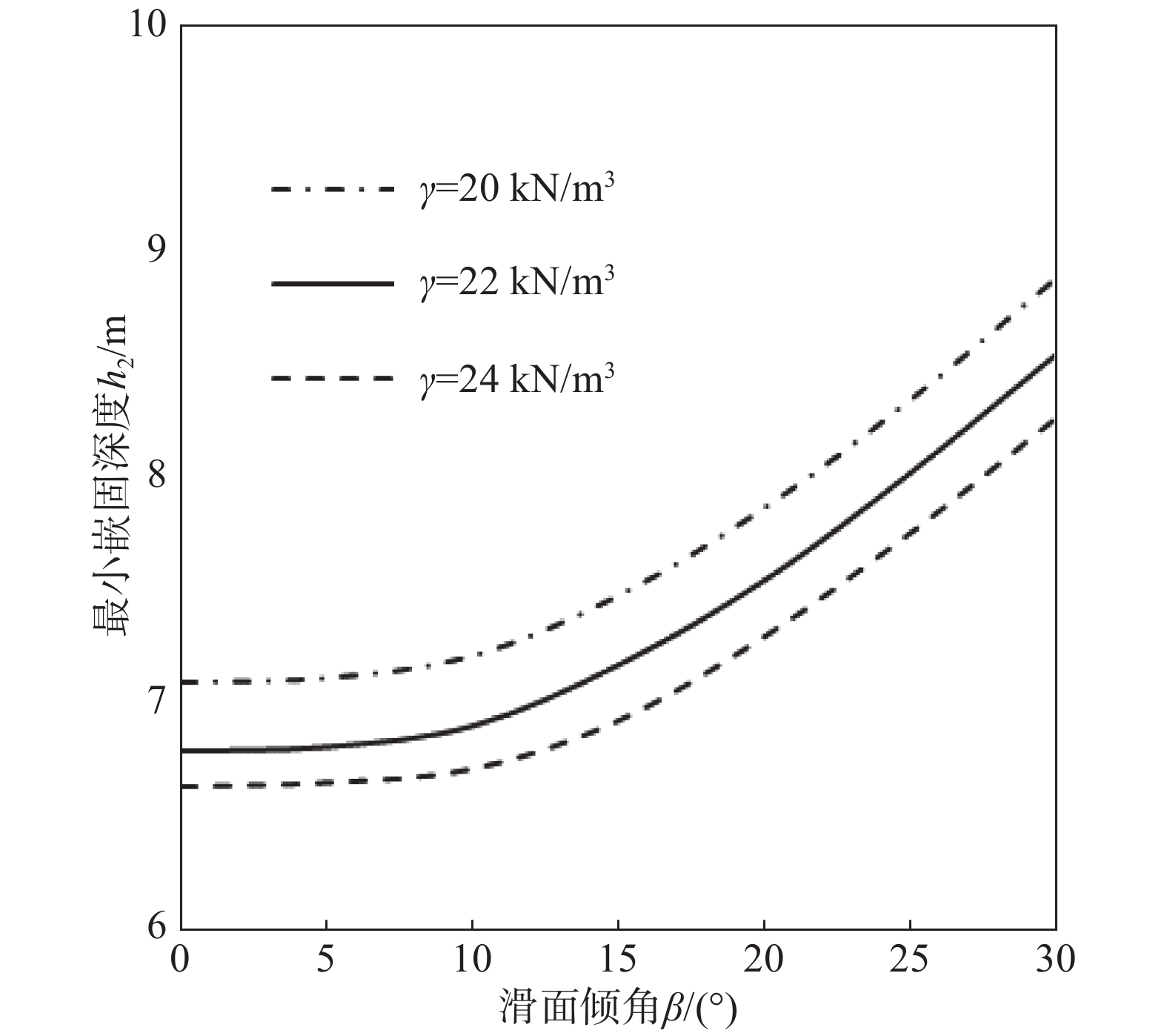
Calculation method on the minimum inserted depth of rigid anti-slide piles in the stable layer with oblique top surfaces in the downslope area
-
摘要: 为计算确定桩前滑面倾斜情况下加固边坡的抗滑桩最小嵌固深度,基于倾斜地面条件的抗滑桩计算地基系数法,确定嵌固段桩侧土层压力,同时采用塑性极限分析方法,推导与滑面倾角密切相关的嵌固段土层极限抗力,并根据桩侧地层最大压力不超过其极限抗力的条件,建立了抗滑桩最小嵌固深度计算方法,并确定了其与滑面倾角的关系。实例分析表明,抗滑桩最小嵌固深度随滑面倾角呈非线性增大,在倾角为10°~30°范围内变化显著;嵌固段地层黏聚力、内摩擦角和重度对抗滑桩最小嵌固深度均有明显影响,且呈负相关关系;本文方法所得桩体最小嵌固深度比传统考虑桩前滑面倾斜影响的方法约小18%。Abstract: In order to calculate the minimum inserted depth of rigid anti-slide piles in stable soil with oblique top surface in the downslope area of the piles in a reinforced slope under a specified factor of safety, according to elastic-foundation-coefficient method under oblique top surface of the ground to determine lateral compressive stress on the soil mass surrounding embedded segment of the pile, together with plasticity limit analysis method to compute lateral ultimate bearing capacity related to dip angle of the slip surface in the downslope area of the piles, a computation procedure for the minimum inserted depth is proposed on the basis of the limitation condition that the maximum compressive stress is not more than the ultimate bearing capacity. The relationship between the minimum inserted depth and the dip angle can be determined. Analysis results of a practical example show that the minimum inserted depth of anti-slide piles increases nonlinearly with the dip angle, and changes significantly within the range of 10°~30°; Cohesion, internal friction angle- and unit weight of the stable layer have clear effect on the minimum inserted depth, and there are negative correlations between them. The minimum inserted depth of the pile obtained by the proposed method is about 18% smaller than that obtained by the traditional method considering the oblique condition of the slip surface in the downslope area of the piles.
-
0. 引言
三峡工程是当今世界上最大的水利枢纽工程,三峡库区历来就是滑坡地质灾害隐患居多的区域。据统计,三峡水库自2003年首次蓄水以来库区发生了较大变形的滑坡有674处,其中下滑入江的有8个[1-3]。长期以来,国内学者对三峡库区一些重要滑坡的变形破坏特征进行了相关研究,如白水河滑坡、树坪滑坡、卧沙溪滑坡、千将坪滑坡、八字门滑坡、凉水井滑坡、藕塘滑坡、木鱼包滑坡等[4-10]。水土作用对水库堆积层滑坡影响甚大,主要表现为引起滑坡土体物理力学性质的改变与滑坡受力状态的变化。根据水土作用的不同方式变形成因可分为降雨型、浸泡软化型、动水压力型、浮托减重型、复合型五类[11-12]。
石榴树包滑坡是黄蜡石滑坡群中的一个重要滑坡,其长期持续变形对长江航运及人民生命财产安全造成严重威胁,一直以来备受关注。1998年罗先启等[13]采用非线性有限元方法对原石榴树包滑坡在不同运行工况下的位移、应力、塑性区进行了分析。2000年保长汉等[14]采用广义楔形体法对原石榴树包滑坡进行了稳定性计算。杨学堂等[15-16]对原石榴树包滑坡滑体滑动后的速度、滑距及涌浪进行了计算。而后一些学者采用有限元法对原石榴树包滑坡的稳定性及变形规律进行了分析[17-22]。2004年通过削方减载、设置排水等措施对滑坡进行了治理。李秀珍等[23]基于滑坡治理前10多年的变形监测资料,研究了原石榴树包滑坡的影响因素和变形演化特征和规律。钟少波等[24]基于滑坡治理后6年的监测数据,分析了石榴树包滑坡变形监测位移特征及稳定性。以上研究对石榴树包滑坡稳定性进行了分析,对滑坡变形特征分析较少,尤其对滑坡变形机制的研究几乎很少涉及。因此,本章首先通过钻探与物探资料分析石榴树包滑坡滑体的物质结构特征,再通过近两年的自动GPS表面位移、地下水位变化、降雨量等监测对该滑坡的变形特征、变形机理进行深入探讨与研究。
1. 石榴树包滑坡概况
石榴树包滑坡位于湖北省巴东县东瀼口镇黄蜡石村,长江左(北)岸。滑坡原始斜坡坡高约为500 m,斜坡倾向188°,斜坡结构类型为逆向斜坡(图1)。
石榴树包滑坡后缘高程340~350 m,前缘剪出口高程50~60 m,面积约0.25 km2,平均厚度约47.2 m,体积约11.80×106 m3。高程350~250 m间的地形坡角为32°~37°;高程200 m有一平台,为前期治理削方所致,东西长150~170 m,南北宽90~110 m;高程200 m以下地形坡角为30°~45°。石榴树包滑坡边界特征见图2。滑坡左侧边界为一冲沟,左侧边界沟外侧为一小山脊,见图2(a)。滑坡右侧边界为一冲沟,沟中树木茂密,沟外侧可见混凝土护坡,该冲沟将石榴树包滑坡与原台子角滑坡分割开来,见图2(b)。滑坡前缘大部分被江水淹没,出露部分为黏土夹紫红色泥岩、泥质砂岩与粉质砂岩块石,见图2(c)。滑坡后缘地势较为平缓,位于公路下方,与原磨盘湾滑坡的前缘相接,相对中前缘宽度变窄,见图2(d)。由于前期治理,滑坡表面分布有多条排水沟,3个排水平硐。
2. 滑坡物质组成及结构
在石榴树包滑坡建立综合观测站,主剖面上选取适当的6个位置布置钻孔,其中ZK1、ZK2、ZK4、ZK5等4个钻孔为水文孔。滑坡上安装的仪器主要有:GPS自动监测站4个(其中1个基站),地下水位监测仪器8个分布于水文孔中,库水位监测点1个,雨量监测站2个。现场仪器安装布置见图3。
2.1 钻探结果
石榴树包滑坡所处斜坡结构为逆向坡,结构复杂。根据钻孔资料综合分析,滑体物质主要为第四系崩坡积碎块石土,原岩为三叠系巴东组的岩体,经强烈滑动破坏而成,在总体上显示一定的成层性。表层覆盖少量第四系松散的崩坡积土,厚1.5~2 m,见图4(a)。浅层及后缘滑体物质主要为三叠系巴东组第四段的红色砂泥岩、粉砂岩破坏形成的碎石土;中层主要为三叠系巴东组第三段灰绿色、灰黄泥灰岩、灰岩破坏后的散裂结构块石土,从后到前厚度逐渐增大,见图4(b);下层有一层三叠系巴东组第二段紫红色泥岩和粉砂岩破坏后形成的碎石土。
滑带物质为土含碎石,位于基覆界面处,厚度一般为1~2 m,碎石含量10%~30%。土主要为灰黄、灰绿色黏土和粉质黏土。碎石以粒径2~10 mm者居多,呈次棱角-次圆状,并具有一定程度的定向排列,岩性主要为来自巴东组第三段的灰色、灰绿色灰岩、泥灰岩,见图4(c)。
滑床物质由下到上可分为三段,巴东组第一段(T2b1)为灰色、浅灰色的泥灰岩、灰岩,厚约30.30 m;巴东组第二段(T2b2)为紫红色泥岩和粉砂岩,厚度为11.07~32.65 m;巴东组第三段(T2b3)为灰绿色、灰黄色的泥灰岩,厚约11.96 m。滑床基岩岩层产状倾向山内,倾角20°~30°左右,见图4(d)。岩层总体产状70°∠20°。根据现场钻孔的工程地质剖面见图5。
2.2 物探测试结果
在三峡水库处于高水位时期(库水位为173 m),对石榴树包滑坡进行高密度电法物探工作。在滑坡体上共布设1横1纵剖面,分别为300 m和280 m,各剖面上分别布设60个电极和56个电极,电极之间间距为5 m,布设的剖面与钻孔剖面吻合,经过每个钻孔。将高密度电法结果与钻孔岩芯进行对比,见图6。
由图6可以看出:视电阻率呈块团状分布,成层性较差,视电阻率范围约0~800 Ω·m。钻探岩性及物质结构分界面与电阻率分界面较吻合。整体上表层的电阻率值较低,低至20~30 Ω·m,该处泥岩、粉砂岩颗粒粒径较小,土颗粒含量较多所致,与实际情况一致。浅层电阻率值较高的仅分布在钻孔ZK4周边的平台处,电阻率值达500~800 Ω·m,主要为浅灰色泥灰岩夹灰岩碎块石为主。由此可分析得到石榴树包滑坡体结构岩性分布,电阻率值低于50 Ω·m以下的区域主要以泥岩、粉砂岩等黏土岩形成的土石混合体为主,块状分布;电阻率值高于200 Ω·m的区域主要以泥灰岩形成的土石混合体为主,块状分布。50~200 Ω·m的区域主要为前两者的混合物。
根据钻孔资料,结合物探剖面,对石榴树包滑坡体纵剖面物质结构进行了分层,如图7所示。
3. 滑坡变形特征
3.1 历史变形特征
该滑坡为古滑坡,最早有记录的复活变形出现在1980年煤矿导洞施工,而后多次降雨以及人类工程活动出现较大变形。为此在2003年4月—2004年2月对石榴树包滑坡进行了工程治理,治理工程措施主要包含削方压脚、地下排水、地表排水。目前,前期治理工程部分失效,坡体上排水沟损坏堵塞,排水平硐内部垮塌。根据相关资料,石榴树包滑坡在治理后布置了3条监测剖面,现大部分仪器不能工作[24]。根据原监测数据分析,2004年—2009年期间滑坡变形较明显,前缘变形最大达到1.4 m,变形总体呈阶梯状持续变形,变形时间主要在每年5—8月。
3.2 近期变形特征
石榴树包滑坡3个GPS表面位移监测数据、降雨量、库水位随时间的变化曲线见图8。
由图8可以看出,在库水位下降及低水位运行期间,表面位移增加较大,在库水位升高及高水位运行期间,表面位移也在增加但增加较少。可见,石榴树包滑坡表现出动水压力型滑坡的特征,与收集的前期监测数据在变形时间上表现一致。在库水位较低时期,降雨会使滑坡各部分的位移都有小幅增大。GPS3位移量大于GPS2位移量大于GPS1位移量,可见滑坡变形主要发生在中部与后部,前缘变形较小。前缘变形较小这可能是由于前缘渗透性大,水力梯度较小的原因;中后部变形大可能是中后部渗透性小,水力梯度相对较大的原因。总体上,滑坡累计变形量最大未超过8 cm,位移随时间增加缓慢,可见石榴树包滑坡目前处于蠕动变形阶段。
4. 滑坡变形机理分析
4.1 变形影响因素
石榴树包滑坡前缘直抵长江,为变形提供了良好的地形临空条件。滑坡下伏基岩为三叠系巴东组的紫红色、浅灰色泥岩、粉砂岩、泥灰岩的易滑岩组;滑坡体也为易滑岩组形成的土石混合体,因此本身物质易于受雨水的影响而发生软化泥化。滑坡体前缘坡脚为长江,江水对滑体前缘岸坡不断的冲刷、掏蚀,造成滑坡前缘坍塌,抗滑力减小。库水位下降过程中,由于中后部渗透性不良导致滑体内地下水位下降滞后于库水位,由此产生的较大动水压力使滑坡的整体稳定性减小。滑坡体结构较松散,渗透性相对较大,地表水易于汇集和下渗,每逢暴雨从滑坡后缘汇集来的地表水排泄于滑坡体上,使得堆积体饱水、抗剪强度降低,诱发浅表层变形。松散堆积物与下伏基岩接触面形成潜在滑动面,因坡体渗透性大,降雨也易下渗到滑动带,一方面滑动面长期处于地下水位之下,使滑动带(面)强度弱化;另一方面也使局部水力梯度急剧增大,诱发整体变形。
4.2 地下水的影响
由监测数据可知滑坡变形主要发生在库水位下降阶段及低水位运行期,结合滑坡地质形态,石榴树包滑坡属于动水压力型滑坡,可见地下水对滑坡变形有较大影响。
(1)地下水位监测结果
石榴树包滑坡布设的4个地下水位监测孔于2018年4月27日开始获取监测数据,截至2019年10月30日,经历两次库水位升降过程,地下水位随库水位、降雨变化曲线如下图9所示。
由图9可知,ZK1、ZK2、ZK4孔地下水位的的变化曲线与库水位变化趋势一致,变化幅度是随着离库水越远变化越小,而ZK5孔地下水位的变化曲线与库水位变化曲线无相似之处,说明ZK5孔地下水位变化与库水位无关,库水位的变化的影响范围在ZK4与ZK5孔之间。降雨对ZK2与ZK5孔的地下水位影响较大,对ZK1与ZK4孔的地下水位影响甚小。滑坡体地下水位对降雨的响应在库水位下降及低水位期间明显,在库水位上升及高水位运行期间响应不明显,响应雨量阈值约为40 mm。
①第一次升降过程(2018年4月27日—2018年10月14日)
ZK1孔水位升降最大29.84 m,ZK2水位升降最大27.73 m,ZK4孔水位升降最大8.91 m,ZK5孔里面水位升降最大14.08 m。
②第二次升降过程(2019年4月27日—2019年10月14日)
ZK1孔水位升降最大30.09 m,ZK2水位升降最大28.58 m,ZK4孔水位升降最大9.69 m,ZK5孔里面水位升降最大7.12 m。
(2)水力梯度变化特征
两个库水位升降过程的水力梯度随库水位及时间的变化曲线见图10,水力梯度变化特征见表1。
表 1 水力梯度变化特征Table 1. Variation characteristics of hydraulic gradient项目 水力梯度i2−1 水力梯度i4−2 水力梯度i5−4 高水位时 低水位时 降雨时 高水位 低水位 降雨时 高水位 低水位 降雨时 第一次升降 0.009 0.0068 0.67 0.11 0.465 0.068 0.0095 0.161 0.331 第二次升降 0.0097 0.0078 0.75 0.118 0.43 0.167 0.01 0.154 0.138 由图10可见,前三条水力梯度线存在突变,是受降雨影响所致。为便于观察,将受降雨影响小的ZK4与ZK1之间的水力梯度作于图中。可见四条曲线表现出相同的趋势,随着库水位的下降,水力梯度逐步增大,在低水位水力梯度逐渐减小;当库水位上升时,水力梯度快速减小,高水位时趋于稳定。
由表1可知,在剔除降雨影响下,水力梯度i2−1低水位与高水位基本无变化,水力梯度i4−2低水位时约是高水位的4倍,水力梯度i5−4低水位时约是高水位的15倍。当考虑降雨影响时,降雨时的水力梯度i2−1约是高水位的74倍;水力梯度i4−2却在减小,甚至小于高水位的水力梯度;水力梯度i5−4约是高水位的35倍。
综上,在不考虑降雨条件下,在两次循环的下降及低水位过程中,水力梯度i4−2与水力梯度i5−4都较大,水力梯度i2−1较小。在考虑降雨条件下,水力梯度i2−1增大较多,i4−2减小,i5−4增大。说明,滑坡中后部渗透压力较大,前缘在降雨后渗透压力会大幅增大。滑坡体中后部水位比较高,主要受后方山体地下水供给,可见滑坡滑动面大部分都长期处于地下水位以下。
5. 结论
(1)石榴树包滑坡滑坡体物质具有一定成层性,团块状分布,电阻率值低于50 Ω·m以下的区域主要以泥岩、粉砂岩等黏土岩形成的土石混合体为主,电阻率值高于200 Ω·m的区域主要以泥灰岩形成的土石混合体为主。
(2)降雨是石榴树包滑坡复活的主要原因,库水位升降与降雨联合作用使石榴树包滑坡持续变形。库水位下降及低水位运行过程中的变形大于库水位上升及高水位运行过程中的变形。前缘变形较小主要是由于前缘渗透性大,水力梯度较小的原因;中后部变形大主要是由于中后部渗透性小,水力梯度相对较大的原因。
(3)库水位变化主要影响滑坡前缘和中部地下水变化,前缘地下水基本与库水位同步;滑坡后部地下水与库水位基本无关,主要受降雨影响。在不考虑降雨影响下,低水位时水力梯度是高水位时的4~15倍,考虑降雨影响时水力梯度是高水位时的35~74倍,降雨影响较大。
(4)石榴树包滑坡一直处于蠕变阶段,受库水位周期性升降与降雨的影响,其变形将继续发展,还需进一步加强监测。
-
-
[1] 郑颖人, 陈祖煜, 王恭先. 边坡与滑坡工程治理[M]. 北京: 人民交通出版社, 2007. ZHENG Yingren, CHEN Zuyu, WANG Gongxian. Engineering treatment of slope & landslide[M]. Beijing: China Communications Press, 2007.(in Chinese)
[2] GUO W D. Pu-based solutions for slope stabilizing piles[J]. International Journal of Geomechanics,2013,13(3):292 − 310. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)GM.1943-5622.0000201
[3] ITO T, MATSUI T, HONG W P. Design method for stabilizing piles against landslide—one row of piles[J]. Soils and Foundations,1981,21(1):21 − 37. DOI: 10.3208/sandf1972.21.21
[4] XIAO S G. A simplified approach for stability analysis of slopes reinforced with one row of embedded stabilizing piles[J]. Bulletin of Engineering Geology and the Environment,2017,76(4):1371 − 1382. DOI: 10.1007/s10064-016-0934-y
[5] 铁道部第二勘测设计院. 抗滑桩设计与计算[M]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 1983. The Second Survey and Design Institute of Railway Ministry. Design and computation of anti-slide piles[M]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 1983.(in Chinese)
[6] 肖世国, 杨豪, 陈廷君. 嵌固于多种地层的抗滑桩设计计算方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(5):116 − 125. [XIAO Shiguo, YANG Hao, CHEN Tingjun. A calculation method for design of the stabilizing piles embedded in various strata[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(5):116 − 125. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 吴坤铭, 王建国, 谭晓慧. 基于可靠度分析确定刚性抗滑桩锚固深度[J]. 岩土工程学报,2012,34(2):237 − 242. [WU Kunming, WANG Jianguo, TAN Xiaohui. Determination of anchorage depth for rigid anti-slide piles based on reliability analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2012,34(2):237 − 242. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 胡晓军, 王建国. 基于强度折减的刚性抗滑桩锚固深度确定[J]. 土木工程学报,2007,40(1):65 − 68. [HU Xiaojun, WANG Jianguo. Determination of the anchorage depth of rigid anti-slide piles based on strength reduction method[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2007,40(1):65 − 68. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-131X.2007.01.011 [9] 于洋, 孙红月, 尚岳全. 锚固深度对双排抗滑桩力学性能影响[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2013,32(10):1999 − 2007. [YU Yang, SUN Hongyue, SHANG Yuequan. Influence of anchorage depth on mechanical behaviour of double-row anti-slide piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2013,32(10):1999 − 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 张文居, 赵其华, 刘晶晶. 抗滑桩锚固深度的可靠性设计[J]. 岩土工程学报,2006,28(12):2153 − 2155. [ZHANG Wenju, ZHAO Qihua, LIU Jingjing. Reliability design of anchoring depth for friction piles[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2006,28(12):2153 − 2155. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-4548.2006.12.020 [11] 肖尊群, 许彩云, 江勇, 等. 刚性抗滑桩结构锚固深度的模糊随机可靠性分析[J]. 岩土力学,2013,34(增刊1):386 − 392. [XIAO Zunqun, XU Caiyun, JIANG Yong, et al. Fuzzy random reliability analysis of rigid anti-sliding pile structure anchoring depth[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2013,34(Sup1):386 − 392. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 蒋建国, 邹银生, 周绪红. 刚性抗滑桩锚固深度的简化计算[J]. 工程力学,2001(增刊1):457 − 460. [JIANG Jianguo, ZOU Yinsheng, ZHOU Xuhong. Simplified calculation of anchorage depth of rigid anti-slide pile[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2001(Sup1):457 − 460. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 中华人民共和国铁道部. 铁路路基支挡结构设计规范: TB 10025—2006[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2006. Ministry of Railways of the People's Republic of China , Code for design on retaining structures of railway subgrade: TB 10025—2006[S]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2006. (in Chinese)
[14] 马显春, 罗刚, 邓建辉, 等. 陡倾滑面堆积层滑坡抗滑桩锚固深度研究[J]. 岩土力学,2018,39(增刊2):157 − 168. [MA Xianchun, LUO Gang, DENG Jianhui, et al. Study of anchorage depth of anti-sliding piles for steep-sliding accumulation landslides[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2018,39(Sup2):157 − 168. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] CHEN W F. Limit Analysis and Soil Plasticity[M]. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science, The Netherlands, 1975.
[16] 孙来宾, 肖世国. 抗滑桩受荷段前侧有限范围地层的地基抗力系数取值方法[J]. 岩土力学,2020,41(1):278 − 284. [SUN Laibin, XIAO Shiguo. Evaluation method for elastic foundation coefficient of finite downslope soil against loading segment of stabilizing piles[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(1):278 − 284. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 刘琛尧,晏启祥,孙润方,王绪,邓宝华,陈耀. 基于三维离散-连续耦合的岩溶隧道突水破坏模式研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(02): 163-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 盖孝乾. 隐伏溶洞对隧道围岩应力及地表沉降的影响研究. 工程机械与维修. 2023(01): 67-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郭书兰,阎长虹,俞良晨,闫超,李慧,徐源. 无锡浅埋岩溶发育特征及其与隧道安全距离研究. 南京大学学报(自然科学). 2023(05): 890-899 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙伟. 广东省英德市城南社区岩溶塌陷发育特征及成因分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(05): 74-80 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 朱丹晖,聂浩. 大溶腔小跨度公路隧道溶洞处理方案研究. 铁道勘察. 2023(06): 144-150+162 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨刚. 岩溶地段隧道施工安全管理关键措施研究. 价值工程. 2022(32): 28-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王亚强,王先龙,伍尚前,张建博. 隧道岩溶水引排及防治措施研究. 现代隧道技术. 2022(S1): 866-875 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS