Experimental analysis on dissolution characteristics of carbonate rocks in Liaoshan tunnel of Emei−Hanyuan expressway in Sichuan Province
-
摘要: 廖山隧道是峨汉高速的控制性工程之一,隧址区岩溶地质条件复杂,为了深入研究隧址区碳酸盐岩的溶蚀特征,文章以隧址区中生界三叠系中统雷口坡组典型白云质灰岩、灰岩及钙质泥岩试样为研究对象,开展静态溶蚀试验,定量分析了碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率特征及相关影响因素,最后定性探讨了扫描电镜下试样溶蚀过程的微观结构变化。结果表明:(1)试验条件下(20 ℃、1 atm、乙酸溶液、pH=5.30、静态溶蚀),隧址区雷口坡组灰岩溶蚀速率约3.48 mm/a,白云质灰岩溶蚀速率约1.57 mm/a,钙质泥岩溶蚀速率约0.90 mm/a;(2)碳酸盐岩的溶蚀受矿物组分及溶蚀环境控制,相同溶蚀环境下,溶蚀速率与方解石含量呈正相关,与白云石含量及溶蚀介质PH值呈负相关,总体上具有灰岩>白云质灰岩>钙质泥岩的特征;(3)有机酸与无机酸环境下灰岩溶蚀速率差异不大,总体趋势相同,而中性盐溶液与碱性环境则对灰岩溶蚀起到不同程度的抑制作用;(4)碳酸盐岩具有优先沿矿物成分、岩石微结构选择性溶蚀的特征,主要矿物含量的不同也使得碳酸盐岩的微观溶蚀过程存在一定差异。Abstract: The Liaoshan tunnel is one of the controlling projects of the E-han expressway, the karst geological conditions in the tunnel site area are complex. In order to deeply study the characteristics of carbonate dissolution in the field, this paper takes the typical dolomitic limestone, limestone and calcareous mudstone samples of the Mesozoic Triassic Middle Leikoupo Formation in the tunnel site area as the research object to carry out the static corrosion simulation experiment. The characteristics of dissolution rate of carbonate rock and related factors are analyzed quantitatively, and the changes of microstructure in the process of sample dissolution under SEM are discussed qualitatively. The results show that: (1) Under the experimental conditions (20 ℃, 1 atm, acetic acid solution, pH≈5.30, static dissolution), the dissolution rate of limestone in Leikoupo Formation is about 3.48 mm/a, that of dolomitic limestone is about 1.57 mm/a, and that of calcareous mudstone is about 0.90 mm/a. (2) The dissolution of carbonate rocks is controlled by the mineral composition and dissolution environment. Under the same dissolution environment, the dissolution rate of carbonate rocks is positively correlated with the content of calcite, and negatively correlated with the content of dolomite and the pH value of the dissolution medium, and generally characterized by limestone>dolomitic limestone>calcareous mudstone. (3) Under the environment of organic acid and inorganic acid, the dissolution rate of limestone has little difference and the general trend is the same, while the neutral salt solution and alkaline environment have different degrees of inhibition on the dissolution of limestone. (4) Carbonate rock has the characteristic of preferential selective dissolution along mineral composition and rock microstructure. The difference of the main mineral content also makes the micro dissolution process of the carbonate rock different.
-
0. 引言
西南地区是我国碳酸盐岩地层的广泛分布区,岩溶面积高达75.5×104 km2,约占川、渝、滇、黔四省市国土面积的66.5%。巨厚连片的碳酸盐岩地层广泛分布于各个地质历史时期,局部沉积厚度在一万米以上[1],为岩溶地貌及油气储层的发育创造了优越条件。近年来,伴随“一带一路”倡议与“西部大开发”等国家重大战略的推进,西南岩溶地区工程建设及油气资源开发进入高峰期,渝昆高铁等国家重点工程相继投建,四川盆地陆续发现以碳酸盐岩为储集层的大型油气田[2-3]。因此,深入分析碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征,探究碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程与发育模式,对于指导岩溶地区工程建设及揭示碳酸盐岩油气储层发育规律至关重要[4-5]。
针对碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用规律,国内外众多学者开展了模拟试验研究[6-13],探讨了岩石组构、溶蚀环境等内、外在因素的控溶机制。但限于室内试验条件,真实还原岩体的自然溶蚀环境是困难的。因此,试验条件及方法的差异也使得国内学者对碳酸盐岩溶蚀的难易程度存在两种不同的认识,一种是白云质灰岩>灰岩>灰质白云岩>白云岩[14],另一种是灰岩>白云质灰岩>灰质白云岩>白云岩[15]。因此,不同组构碳酸盐岩的溶蚀规律尚需作进一步探讨。此外,虽然以往学者从溶解动力学的角度探究了碳酸盐岩溶蚀机制,但对于碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀过程及结构变化的研究却尚为少见。
本文以在建廖山隧道隧址区三叠系中统雷口坡组碳酸盐岩为研究对象,开展静态溶蚀模拟试验,目的在于分析碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率特征及相关控制因素,探究碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀特征及微观溶蚀过程的结构变化,以期为岩溶地区工程建设及油气储层勘探开发提供参考。
1. 溶蚀机理
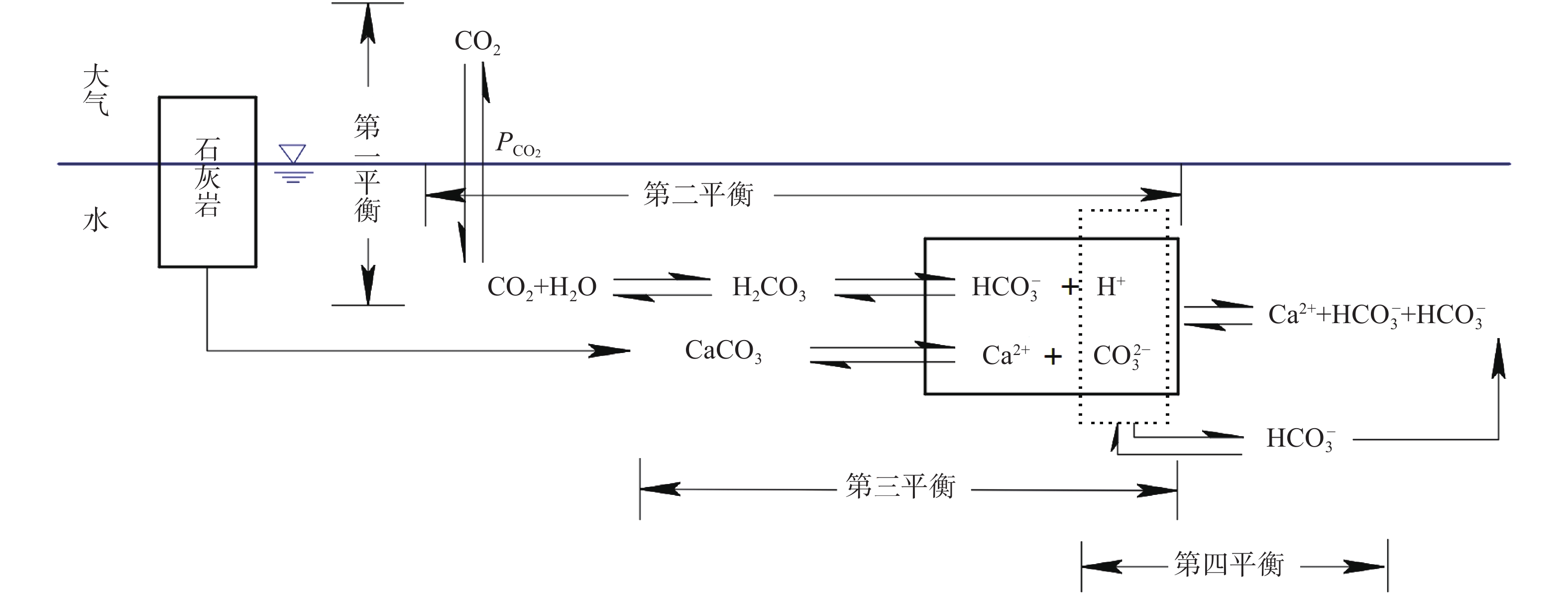
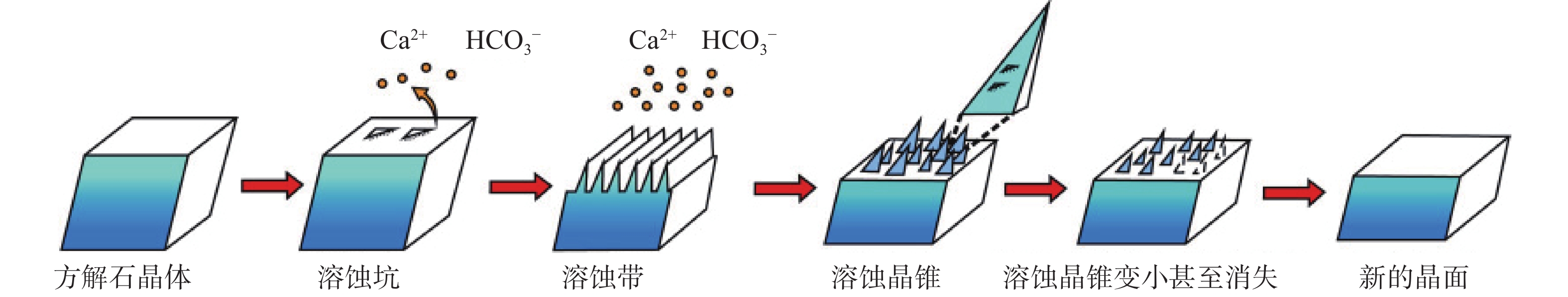
天然状态下,自然界碳酸盐岩的溶蚀是CO2-H2O-MeCO3(Me为Ca、Mg)系统间的溶解动力学平衡过程(图1),其溶蚀实质是岩石中碱金属矿物在岩溶水中H+作用下逐步溶解成游离的金属阳离子并向水中扩散的过程,即可溶岩去Ca、Mg等元素的过程。碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用的强弱主要取决于水-岩反应界面上H+浓度的大小,溶蚀过程可用如下三个化学反应方程式进行模拟[17]:
![]() 图 1 碳酸盐岩溶解反应综合模型[16]Figure 1. Comprehensive model of carbonate rock dissolution reaction
图 1 碳酸盐岩溶解反应综合模型[16]Figure 1. Comprehensive model of carbonate rock dissolution reaction(1)当pH≤5时,固体表面质子化作用:
$${\rm{MeC}}{{\rm{O}}_3}\left( s \right) + 2{{\rm{H}}^ + }\xrightarrow{{{k_1}}}{\rm{M}}{{\rm{e}}^{2 + }} + {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $$ (1) (2)当4≤pH≤6时,固体表面碳酸盐化作用:
$${\rm{MeC}}{{\rm{O}}_3}\left( s \right) + {{\rm{H}}_{\rm{2}}}{\rm{CO}}_{\rm{3}}^{\rm{*}}\xrightarrow{{{k_2}}}{\rm{M}}{{\rm{e}}^{2 + }} + {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $$ (2) (3)当pH>6时,固体表面水化作用:
$${\rm{MeC}}{{\rm{O}}_3}\left( s \right) \rightleftharpoons {\rm{M}}{{\rm{e}}^{2 + }} + {\rm{HCO}}_3^ - $$ (3) 式中:H2CO3*——岩溶水中H2CO3与CO2的总和; ki——第i(i=1,2,3)个反应的反应速率常数。 总溶蚀速率可表示为:
$$R = {k_1}a_{{{\rm{H}}^ + }}^n + {k_2}a_{{{\rm{H}}_2}{\rm{CO}}_3^*}^p{\rm{ + }}{k_3} + {k_{ - 3}}{a_{M{e^{2 + }}}}{a_{{\rm{CO}}_3^{2 - }}}$$ (4) 式中:
$a $ −活度;$n $ 、$p $ −反应级数。2. 静态溶蚀试验
2.1 试验对象
试样采自川西南三叠系中统雷口坡组碳酸盐岩地层,为在建四川峨眉-汉源高速(峨-汉高速)廖山隧道重点岩溶发育区域典型碳酸盐岩试样。岩性分别为灰岩、白云质灰岩及钙质泥岩,经X射线衍射全岩成分分析,岩样矿物组成如表1所示。
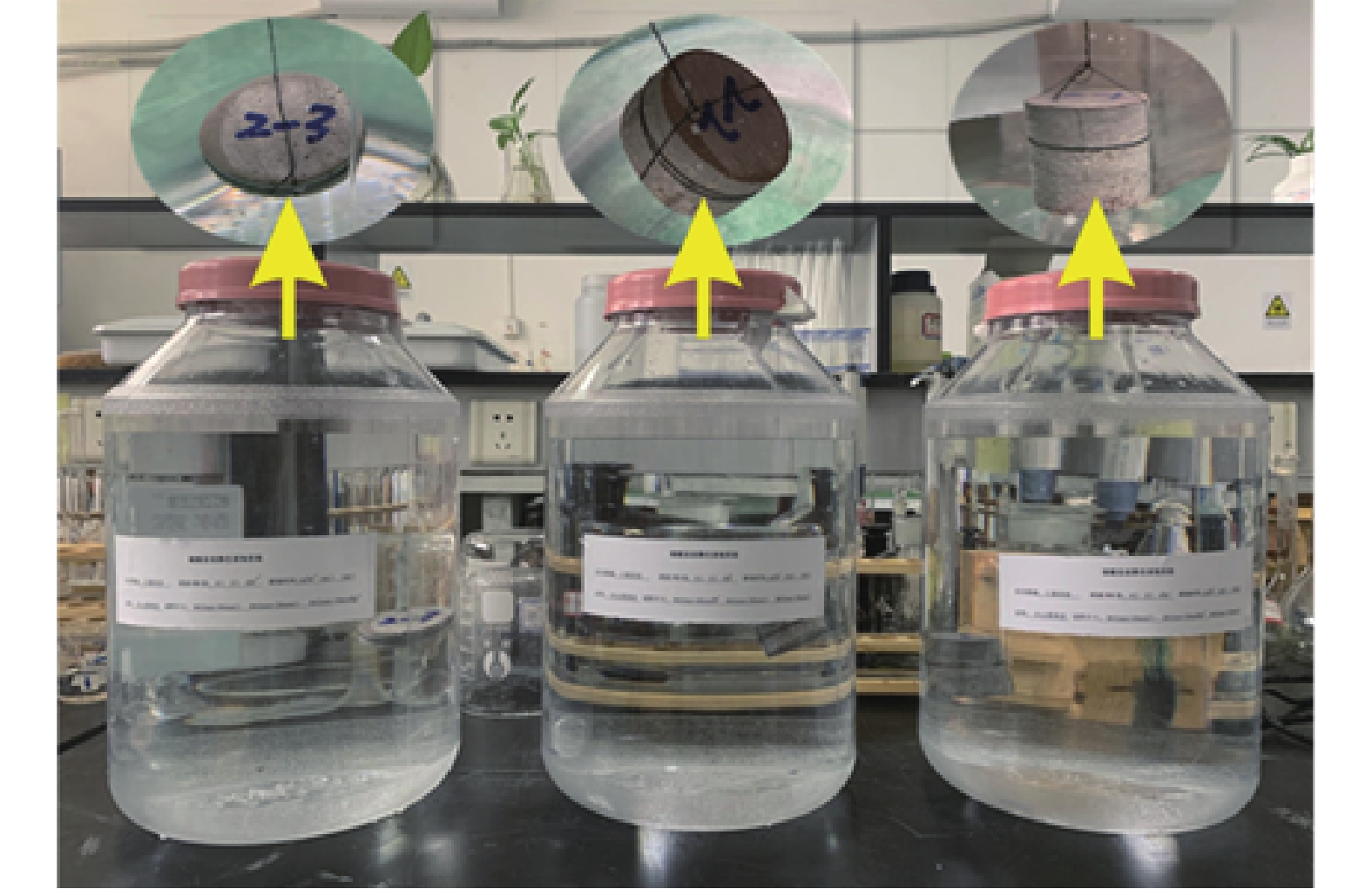
表 1 隧址区典型碳酸盐岩矿物组成X射线衍射分析Table 1. X-ray diffraction analysis of mineral composition of typical carbonate rocks in tunnel site试样编号 取样桩号 试样岩性 矿物成分/% 百分含量/% 钾长石 方解石 白云石 石英 X191250001 K31+917 灰岩 0.9 90.6 8.5 − 100.0 X191250002 K32+033 白云质灰岩 1.1 57.0 41.4 0.5 100.0 X191250003 K32+033 钙质泥岩 0.2 0.3 98.7 0.8 100.0 注:本次检测委托国土资源部西北矿产资源监督检测中心检测完成,“−”表示未检出或低于检出限。 根据隧道岩溶管道揭露次序,于隧道不同里程处采集岩石样品31块(图2),为保证岩样加工成品率及完整性,择优选取岩质较为完整的典型灰岩、白云质灰岩及钙质泥岩样品为原岩样品进行加工。利用ZS-100型岩芯钻取机及CB-300型岩石切割机制备直径为42 mm,高度分别为40,20 ,10 mm的圆柱体试样,并用MPD-1型试样磨抛机对表面进行抛光以备使用。
2.2 试验方法
根据水质分析成果,隧址区岩溶水属
${\rm{HCO}}_3^- $ -${\rm{SO}}_4^{2-} $ -Ca2+-Mg2+型水,水质呈弱酸性—弱碱性,内含少量乙酸等有机酸。考虑到碳酸溶液常温常压下极不稳定且室内条件下制备复杂、实施难度大,故试验拟采用乙酸溶液替代碳酸溶液作为溶蚀介质模拟溶蚀环境;此外,配置一定浓度的盐酸、乙酸钠及氢氧化钠溶液作为横向对比试验,进而探究碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率特征及其影响因素。溶蚀试验共分为六组(表2),共计18个试样;每组试验分别设置三个容积为10 L的溶蚀反应容器,每个容器内放入一个试样,使溶液体积与试样体积比大于180∶1,以保障溶液H+浓度在溶蚀周期内保持小范围波动,从而溶液pH值可以近似看作是相对稳定的。
表 2 溶蚀试验工况条件Table 2. dissolution experiment conditions试验分组及编号 试样岩性 试样尺寸/mm 溶蚀介质 溶液pH值 溶蚀时间 组别 编号 预设 实际 第一组 1-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 3.50 3.70 各试样分别累计溶蚀6, 14, 24 h 1-2 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 4.50 4.50 1-3 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第二组 2-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 2-2 Φ42×20 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 2-3 Φ42×10 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第三组 3-1 灰岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 3-2 Φ42×20 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 3-3 Φ42×10 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第四组 4-1 钙质泥岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 4-2 Φ42×20 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 4-3 Φ42×10 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第五组 5-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 氢氧化钠溶液 9.00 9.00 5-2 Φ42×10 乙酸钠溶液 7.00 7.00 5-3 Φ42×10 盐酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第六组 6-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 去离子水 7.00 7.00 6-2 白云质灰岩 Φ42×10 去离子水 7.00 7.00 6-3 钙质泥岩 Φ42×10 去离子水 7.00 7.00 注:溶液配制过程中存在乙酸电离平衡现象,溶液pH值难以精确控制,故实际pH值与预设pH值存在一定偏差。 2.3 试验流程
将制备好的岩样用去离子水清洗干净,烘干(105 ℃,12 h)并称重;选用乙酸、盐酸、乙酸钠、氢氧化钠与去离子水配置pH分别为3.7、4.5、5.3、7.0及9.0的溶液作为溶蚀介质;将溶液置于反应容器内,用细针线绑扎试样使其悬空且与溶液充分接触,将容器密封以防止有机酸挥发,令试样在常温常压(20 ℃,1 atm)条件下溶蚀;试验过程中,间隔6,8,10 h取出试样(累计溶蚀24 h),用软毛刷与去离子水将其表面清洗干净,烘干称重;取100 mL溶蚀介质于洁净、干燥的样品瓶中,检测溶蚀后试液pH值(图3)。
3. 溶蚀速率与微观溶蚀特征分析
3.1 溶蚀速率评价方法
根据试样溶蚀前后质量差异,可按式(5)计算不同工况条件下碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率大小,并以此为基础分析岩石溶蚀特征及相关影响因素。
$$v_1 = \frac{{{m_0} - {m_1}}}{{S \times \Delta t}}$$ (5) 式中:v1−溶蚀速率/(g·cm−2·d−1);
m0−溶蚀前试样质量/g;
m1−溶蚀后试样质量/g;
S−试样表面积/cm2;
Δt−溶蚀时间/d。
为直观量化溶蚀速率量级,根据单位换算关系cm·d−1=[g·cm−2·d−1]·ρ−1,可将其表示成如下形式:
$$v_2 = \frac{{{m_0} - {m_1}}}{{S \times \Delta t \times \rho }}$$ (6) 式中:v2−表征溶蚀速率(cm·d−1);
ρ−岩石密度(g·cm−3);其中,隧址区灰岩为2.70 g/cm3,白云质灰岩为2.55 g/cm3,钙质泥岩密度为2.45 g/cm3。
3.2 溶蚀速率特征及相关影响因素分析
根据溶蚀试验成果(表3),对比不同岩性碳酸盐岩溶蚀过程,隧址区碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率具有如下特征:
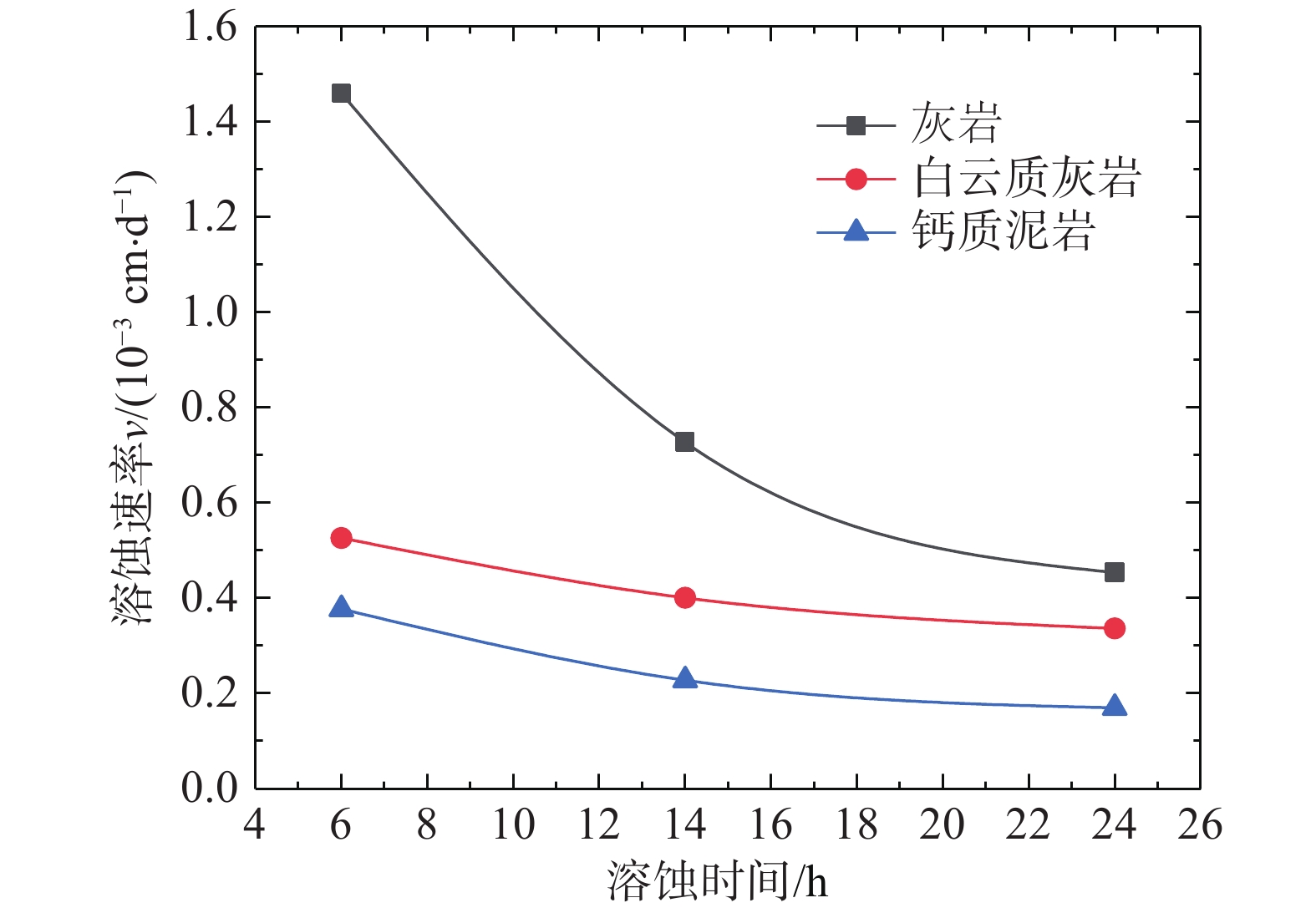
表 3 不同工况条件下溶蚀试验成果汇总Table 3. Summary of dissolution experiment results under different working conditions试样编号 试样岩性 试样规格/mm 试样质量m/g 溶液实际pH值 溶蚀速率v/(10−3cm·d−1) 初始 溶蚀6 h 溶蚀14 h 溶蚀24 h 初始 溶蚀6 h 溶蚀14 h 溶蚀24 h 溶蚀6 h 溶蚀14 h 溶蚀24 h 1-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 151.086 151.032 150.970 150.908 3.70 3.84 3.97 4.13 1.0524 0.9689 0.8673 1-2 Φ42×40 154.035 153.993 153.962 153.928 4.50 4.75 4.91 5.16 0.8185 0.6097 0.5213 1-3 Φ42×40 153.643 153.605 153.578 153.547 5.30 5.41 5.68 6.31 0.7406 0.5429 0.4677 2-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 150.054 150.027 150.006 149.985 5.30 5.59 5.71 5.96 0.5262 0.4009 0.3362 2-2 Φ42×20 76.4194 76.4035 76.3924 76.3836 5.30 5.82 5.86 5.92 0.4610 0.3355 0.2595 2-3 Φ42×10 46.6763 46.6569 46.6487 46.6416 5.30 5.48 5.61 5.75 0.7440 0.4536 0.3327 3-1 灰岩 Φ42×40 153.422 153.348 153.336 153.330 5.30 5.66 5.98 6.40 1.4594 0.7269 0.4536 3-2 Φ42×20 85.8408 85.8144 85.7900 85.7860 5.30 5.49 5.75 6.14 0.7746 0.6388 0.4020 3-3 Φ42×10 42.6727 42.6545 42.6442 42.6406 5.30 5.33 5.34 5.57 0.7063 0.7716 0.3114 4-1 钙质泥岩 Φ42×40 149.246 149.2274 149.2198 149.2125 5.30 5.42 5.89 6.33 0.3773 0.2278 0.1699 4-2 Φ42×20 70.8872 70.8728 70.8647 70.8603 5.30 5.31 5.60 5.82 0.4346 0.2910 0.2029 4-3 Φ42×10 41.9599 41.9523 41.9470 41.9428 5.30 5.28 5.52 5.79 0.3033 0.2207 0.1707 5-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 42.0705 42.0722 42.0672 42.0657 9.00 8.90 8.85 8.79 0.0660 0.0549 0.0466 5-2 Φ42×10 37.4267 37.4246 37.4228 37.4204 7.00 7.02 7.04 7.02 0.0815 0.0649 0.0611 5-3 Φ42×10 42.9626 42.9423 42.9239 42.9165 5.30 5.50 5.70 5.83 0.7882 0.6430 0.4475 6-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 42.0657 42.0631 42.0598 42.0555 7.00 7.00 7.00 7.00 0.1006 0.0976 0.0990 6-2 白云质灰岩 Φ42×10 45.5304 45.5287 45.5272 45.5259 7.00 7.00 7.00 7.00 0.0566 0.0580 0.0547 6-3 钙质泥岩 Φ42×10 36.6783 36.6771 36.6759 36.6739 7.00 7.00 7.00 7.00 0.0466 0.0407 0.0439 (1)碳酸盐岩溶蚀是一个极为缓慢的过程。试验条件下(20 ℃、1 atm、乙酸溶液、pH=5.30、静态溶蚀),溶蚀速率量级介于10−5~10−3cm/d。其中,灰岩溶蚀速率约3.48 mm/a,白云质灰岩约1.57 mm/a,钙质泥岩约0.90 mm/a(图4)。
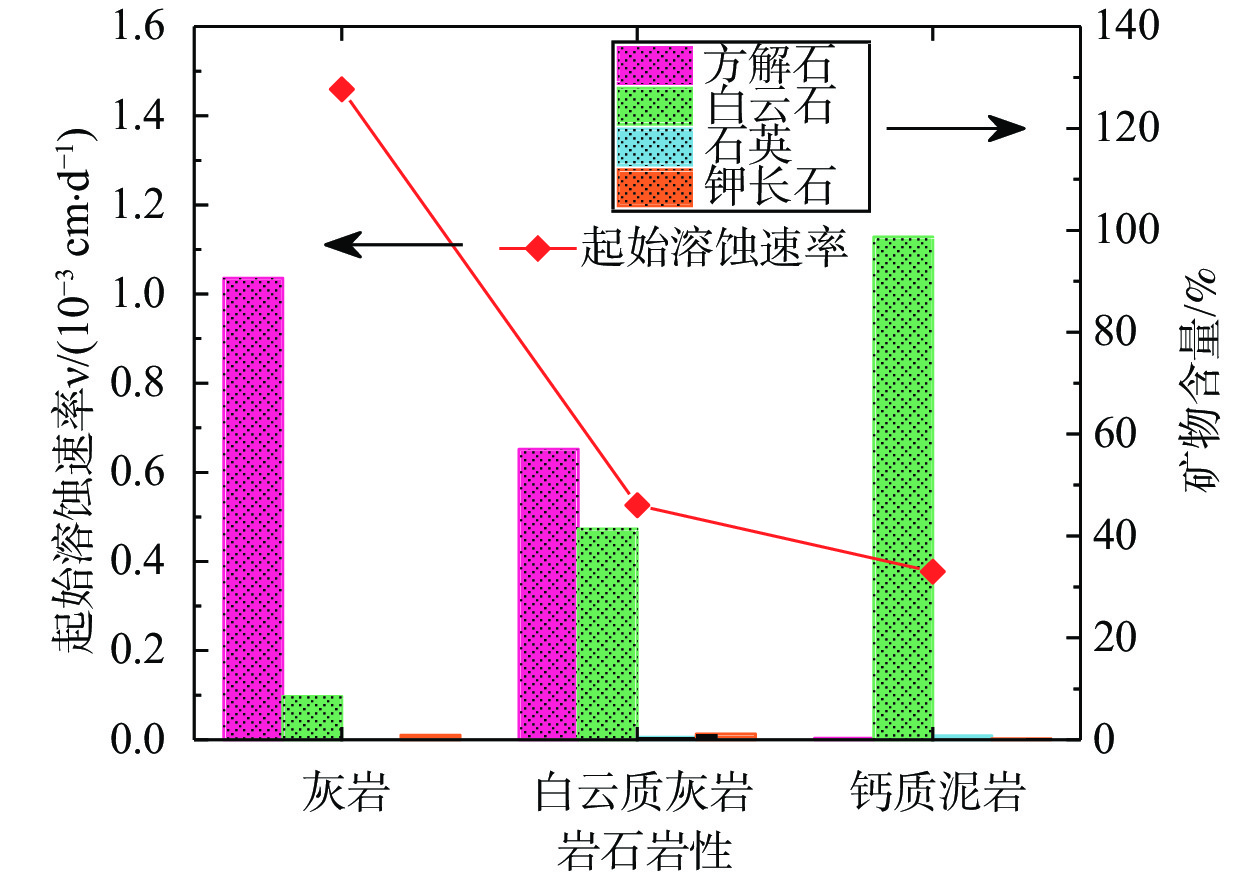
(2)岩石岩性是控制溶蚀速率的本质因素。在溶蚀反应的初期,白云质灰岩、灰岩及钙质泥岩均具有较大的起始溶蚀速率,随着溶蚀时间的推进溶液中氢离子浓度降低,各岩性试样溶蚀速率逐渐降低并趋于稳定,但总体上具有灰岩>白云质灰岩>钙质泥岩的特征,说明岩性是控制溶蚀速率最本质的因素。碳酸盐岩的溶蚀随岩性差异而表现出不同特征,本质上是由岩石内部矿物成分差异造成的;根据岩石起始溶蚀速率与其矿物组成关系曲线(图5),岩石的起始溶蚀速率与方解石含量呈正相关,与白云石含量呈负相关,亦说明相同溶蚀环境下方解石较白云石更易溶蚀。
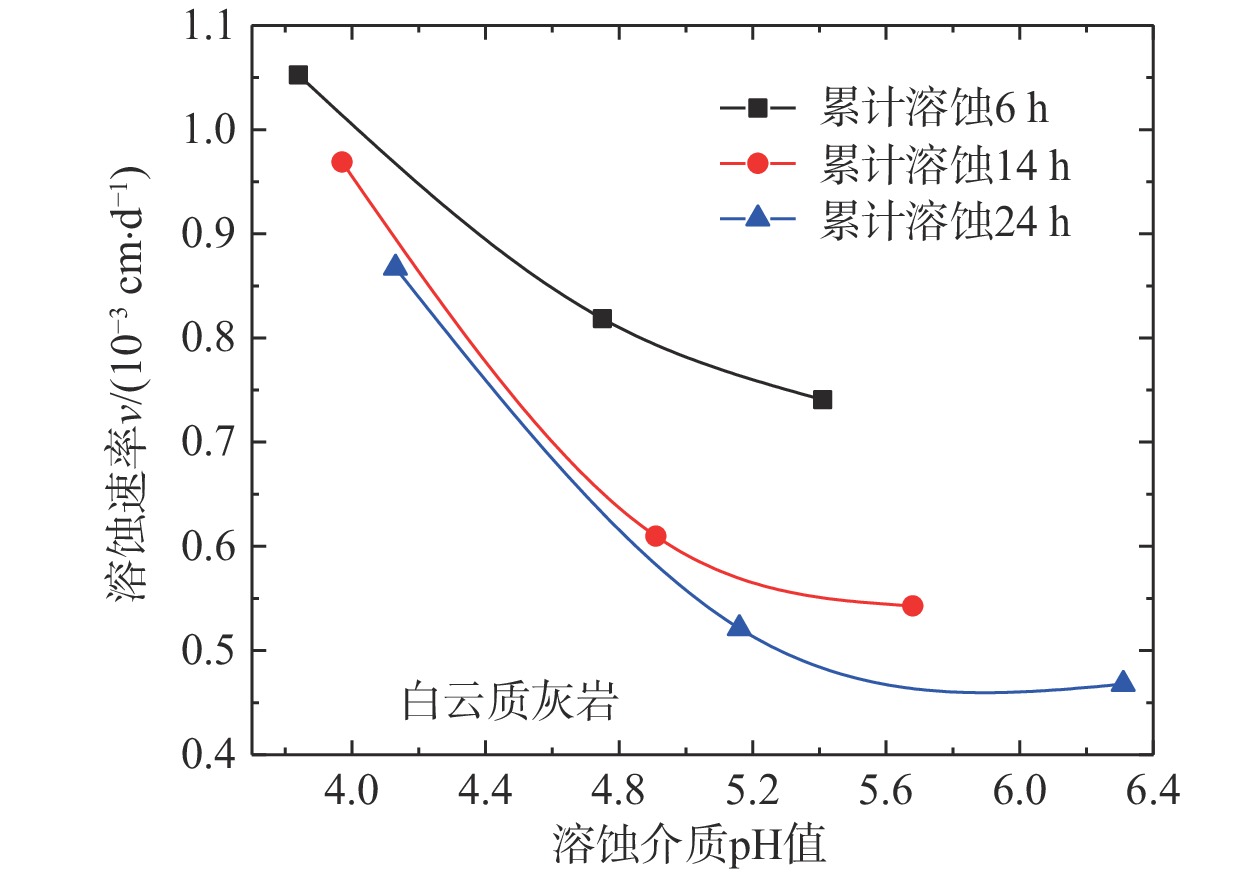
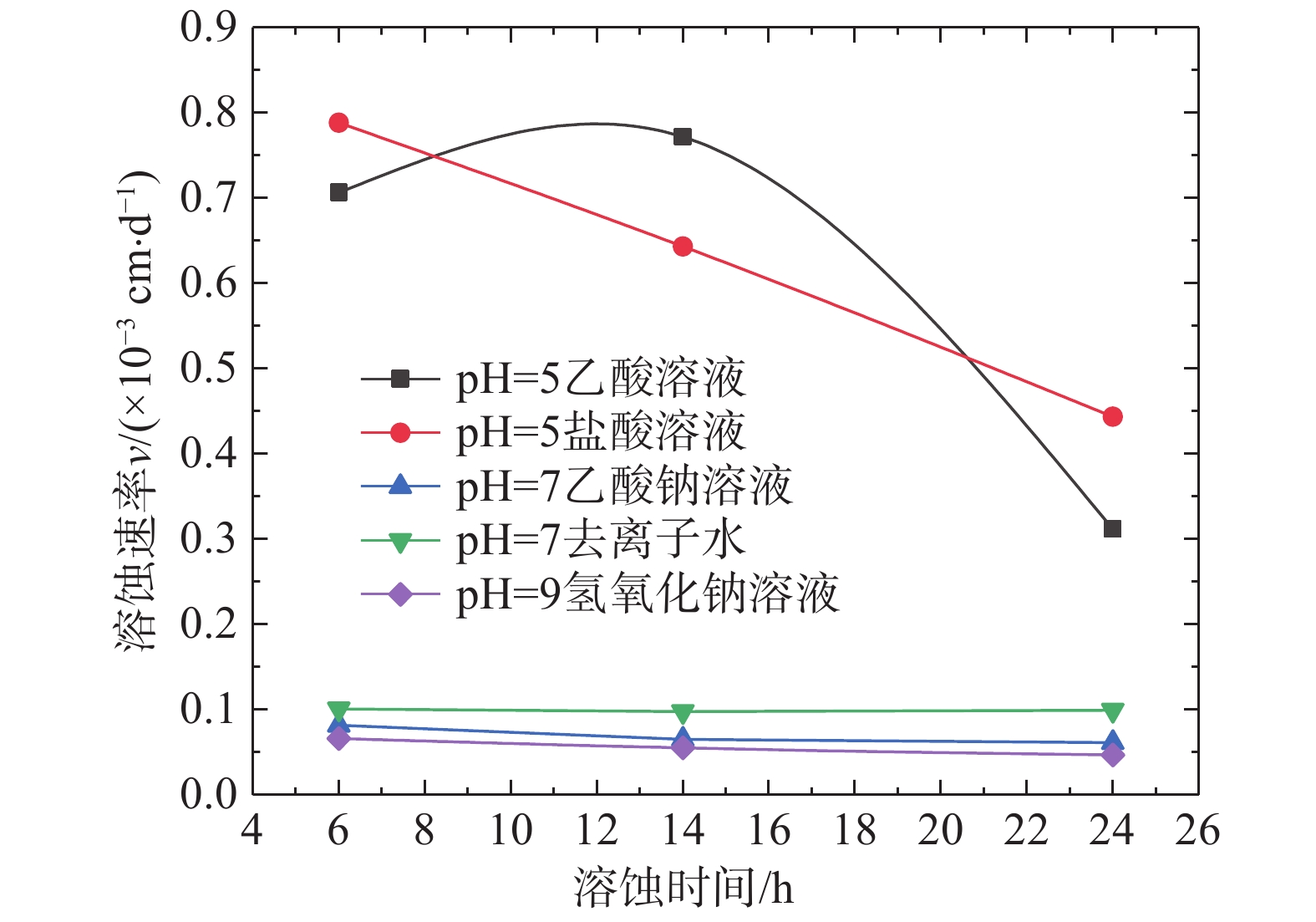
(3)溶蚀介质pH值是控制溶蚀速率的关键因素。碳酸盐岩溶蚀不仅与其矿物成分有着密切关系,还与外界溶蚀环境存在一定联系。由第一组组内对比试验显示(图6),相同尺寸的白云质灰岩试样在初始pH值为3.7、4.5、5.3的乙酸溶液中,溶蚀速率与溶液pH值呈负相关;此外,在给定初始pH值条件下,随着溶蚀时间的推进,溶液pH值逐渐增大,溶蚀速率也呈减小趋势。表明溶蚀介质pH值对可溶岩溶蚀速率影响较大,溶液中H+浓度越高,与可溶性岩石矿物结合的机会越高,岩石的溶蚀作用也就越强,这也是碳酸盐岩在溶蚀反应的初期具有较高起始溶蚀速率的根本原因。
(4)溶蚀环境对溶蚀速率具有一定影响。为探究无机酸环境与有机酸环境下碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征差异,选用pH值均为5.3的盐酸溶液和乙酸溶液分别模拟无机酸环境与有机酸环境,试验发现(图7),盐酸环境下灰岩具有较高的起始溶蚀速率,且随溶蚀时间的推进呈线性降低趋势;乙酸环境下灰岩溶蚀速率呈先升高而后逐渐降低的规律。造成这种差异的原因是乙酸为弱电解质,溶蚀反应打破了乙酸原有的电离平衡,促进溶液中乙酸分子的进一步电离,使得乙酸溶液中短时H+浓度高于盐酸溶液中H+浓度,表现出局部时间段溶蚀速率较高的现象;但随时间的推进,乙酸溶液中H+被消耗,未电离的乙酸分子逐渐减少,溶蚀速率也相应降低。总体来看,有机酸与无机酸环境下灰岩溶蚀速率差别不大,总体趋势近似一致。
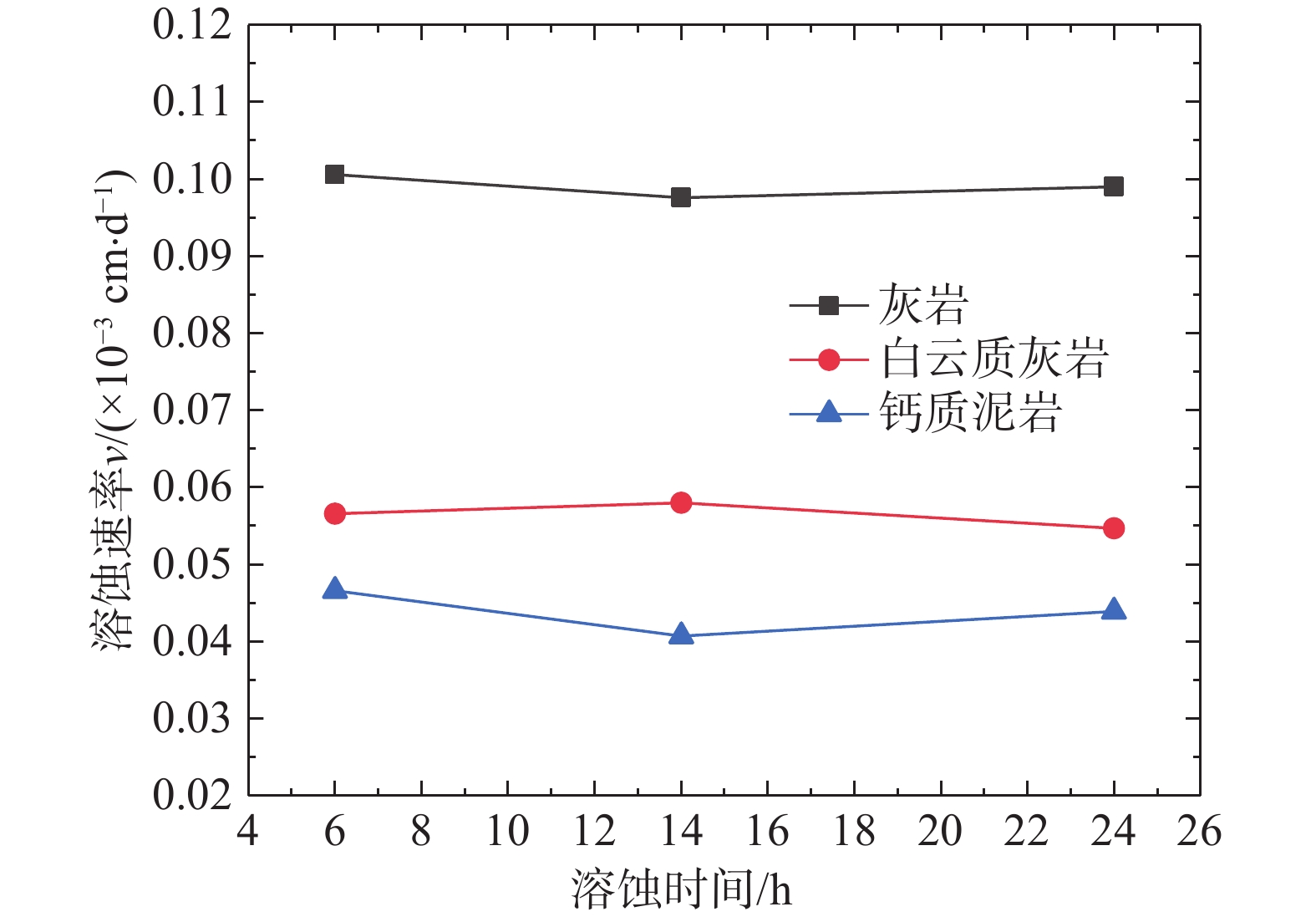
为进一步探究碱性环境与中性盐溶液环境下碳酸盐岩溶蚀特征,试验配制矿化度为65 mg/L的中性乙酸钠溶液以及pH值为9.0的氢氧化钠溶液模拟溶蚀环境,利用pH值为7.0的去离子水作为对比试验,发现溶蚀速率具有如下特征(图7):去离子水环境>中性乙酸钠溶液环境>氢氧化钠溶液环境;试验结果表明中性盐溶液与碱性溶液对灰岩溶蚀起到了不同程度的抑制作用,但较为有限。去离子水环境下碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率量级整体较小(图8),约为10−5cm/d,但仍具有灰岩>白云质灰岩>钙质泥岩的特征,灰岩溶解速率约为白云质灰岩与钙质泥岩溶解速率的两倍。
碳酸盐岩在不同溶蚀环境下的溶蚀特征一定程度上说明当岩溶水溶解较多可溶性岩石矿物时,水溶液Ca2+、Mg2+等离子含量升高,增大了水质的矿化度,促使溶蚀能力减弱;与此同时,碳酸盐岩矿物晶体的不断溶蚀消耗了大量侵蚀性H+,一定程度促进了Ca2+、Mg2+等碱金属离子的水解,从而促使岩溶水由酸性转化为弱碱性,削弱了岩溶水的溶蚀能力。
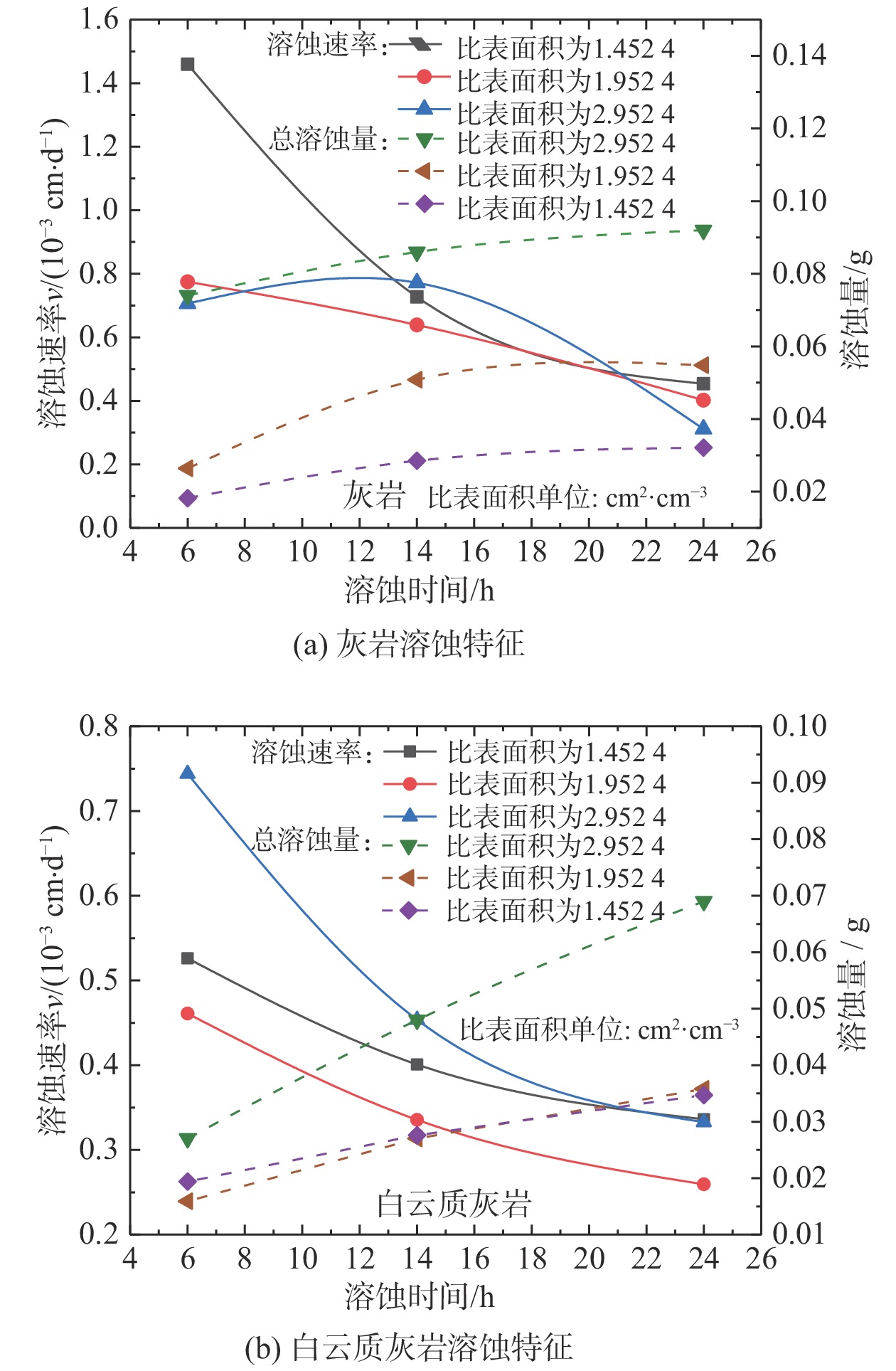
(5)天然状态下,岩体是由离散裂隙网络所分割的不连续介质,结构面的随机性也使得岩块具有不同的比表面积。通过开展组内对比试验发现(图9),碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率与试样比表面积之间不具备明显正相关关系,试验初期各岩样均具有较大起始溶蚀速率,但伴随溶蚀时间的推进溶蚀速率趋向平缓且大小趋于一致;说明溶蚀速率仅受岩性、pH值等因素控制,而比表面积仅通过作用于水-岩反应有效界面的大小进而影响总溶蚀量大小。
3.3 碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀特征分析
为深入探究碳酸盐岩微观尺度下溶蚀特征及溶蚀过程的微观结构变化,在上述研究的基础上进一步开展溶蚀周期为312 h的静态溶蚀试验,并以此为基础借助扫描电子显微镜(SEM)观察碳酸盐岩在不同溶蚀时刻下的微观形态特征,尝试探索碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀过程与发育模式(图10、图11)。
对比分析白云质灰岩与灰岩的动态溶蚀过程可以发现,试验环境下(20 ℃、1 atm、乙酸溶液、pH=5.30、静态溶蚀312 h)碳酸盐岩试样表面形态特征在宏观及微观两种尺度下均有明显改观,宏观层面上试样颜色明显变浅,且灰岩溶蚀率整体高于白云质灰岩溶蚀率,二者溶蚀程度强弱排序如表4所示;微观尺度下试样溶蚀前后形态特征差异则更为显著,溶蚀过程分析如下。
表 4 碳酸盐岩溶蚀程度对比Table 4. Comparison of dissolution degree of carbonate rocks岩性 溶蚀介质 试样编号 溶蚀周期/h 试样质量/g 溶蚀量/g 溶蚀率/‰ 溶蚀程度排序 白云质灰岩 PH=5.30 乙酸溶液 BH-1 312 1.0579 0.0104 9.8308 1 BH-2 24 1.2795 0.0015 1.1723 15 BH-3 72 1.4047 0.0032 2.2781 10 BH-4 14 1.4055 0.0024 1.7076 11 BH-5 14 1.5674 0.0014 0.8932 19 BH-6 120 1.1915 0.0067 5.6232 7 BH-7 24 1.3426 0.0013 0.9683 18 BH-8 6 1.1627 0.0016 1.3761 12 BH-9 312 1.4557 0.0123 8.4495 2 BH-10 6 1.0568 0.0012 1.1355 16 BH-11 192 1.0602 0.0073 6.8855 5 灰岩 PH=5.30 乙酸溶液 H-1 192 0.9194 0.0051 5.5471 8 H-2 120 1.5664 0.0057 3.6389 9 H-3 312 0.9910 0.0067 6.7608 6 H-4 6 1.3798 0.0008 0.5798 22 H-5 6 0.9798 0.0008 0.8165 20 H-6 14 1.2719 0.0008 0.6290 21 H-7 312 1.2467 0.0086 6.8982 4 H-8 312 0.9080 0.007 7.7092 3 H-9 72 1.1071 0.0013 1.1742 14 H-10 24 1.1787 0.0012 1.0181 17 H-11 24 0.8731 0.0012 1.3744 13 H-12 14 1.0593 0.0006 0.5664 23 3.3.1 白云质灰岩微观溶蚀过程
对于白云质灰岩,试样溶蚀前,矿物晶体呈规则长方体状,晶体间不规则堆积呈点、线、面状接触,可见晶间空隙,晶面光滑无痕,未见明显溶孔等溶蚀痕迹;溶蚀6 h后,晶体表面开始出现明显层状剥蚀现象,层状溶蚀纹理明显(图12a);随溶蚀时间的推进,矿物晶体棱角遭到不同程度的溶蚀而逐渐变得圆滑,晶体表面局部可见细小溶孔,同时晶间空隙逐步溶蚀扩大(图12b);当溶蚀进行到72 h时,方解石晶体沿解理面位置被溶蚀破坏明显,形似百叶窗状,局部似刀砍状,同时白云石晶体表面可见众多大小不等的溶蚀孔洞,晶体结构明显破坏,呈疏松孔隙状(图12c);随碳酸盐矿物晶体的进一步溶蚀,晶面由破碎状逐步变得平整光滑,局部可见被剥蚀掉晶体接触位置处所遗留的溶蚀晶坑且表面趋于圆滑(图12d);当溶蚀进行到192 h,溶缝沿方解石晶体解理面等微结构处扩展明显,可见若干组相互平行的溶蚀缝隙,且在多组解理相交部位处溶缝侧蚀扩展成半径较大的溶蚀孔洞,局部缝洞处可见方解石晶体溶蚀呈“溶蚀晶锥”状,白云石晶体表面溶蚀孔洞相互贯通并侧蚀扩大,局部晶体形态受溶蚀坍塌,此外晶间接触面处溶蚀作用显著,晶体颗粒间联系减弱(图12e);随着溶蚀作用的深入,内部原生裂隙溶蚀扩大,晶体表面凹凸不平,不同矿物的差异性溶蚀现象更加明显,具体表现在方解石晶体被明显蚀低且局部呈散体状结构,晶体颗粒边缘具有晶锥状残留痕迹,白云石发育有众多孔径、深度不等的溶孔,局部发育溶蚀坑(图12f)。
![]() 图 12 白云质灰岩溶蚀过程SEM形态图a~f均放大10000倍;a—试样编号BH-8,溶蚀时间6 h,出现层状剥蚀现象,纹层状溶蚀特征明显;b—试样编号BH-5,溶蚀时间14 h,晶间空隙溶蚀扩大,晶体棱角趋于圆滑;c—试样编号BH-3,溶蚀时间72 h,方解石晶体沿解理面溶蚀破坏明显,发育“百叶窗状”及“刀砍状”溶痕,白云石晶体溶蚀孔洞发育,呈千疮百孔状;d—试样编号BH-6,溶蚀时间120 h,晶体表面溶蚀碎屑脱落,晶面逐步变得光滑平整,局部发育溶蚀残坑;e—试样编号BH-11,溶蚀时间192 h,局部溶蚀缝发育方解石“溶蚀晶锥”,白云石晶体表面溶蚀孔洞溶蚀扩大贯穿;f—试样编号BH-1,溶蚀时间312 h,方解石晶体被明显蚀低且颗粒边缘具有晶锥状残留痕迹,白云石表面发育溶蚀孔洞且局部发育有溶蚀坑。Figure 12. SEM morpHhology of dolomitic limestone dissolution process
图 12 白云质灰岩溶蚀过程SEM形态图a~f均放大10000倍;a—试样编号BH-8,溶蚀时间6 h,出现层状剥蚀现象,纹层状溶蚀特征明显;b—试样编号BH-5,溶蚀时间14 h,晶间空隙溶蚀扩大,晶体棱角趋于圆滑;c—试样编号BH-3,溶蚀时间72 h,方解石晶体沿解理面溶蚀破坏明显,发育“百叶窗状”及“刀砍状”溶痕,白云石晶体溶蚀孔洞发育,呈千疮百孔状;d—试样编号BH-6,溶蚀时间120 h,晶体表面溶蚀碎屑脱落,晶面逐步变得光滑平整,局部发育溶蚀残坑;e—试样编号BH-11,溶蚀时间192 h,局部溶蚀缝发育方解石“溶蚀晶锥”,白云石晶体表面溶蚀孔洞溶蚀扩大贯穿;f—试样编号BH-1,溶蚀时间312 h,方解石晶体被明显蚀低且颗粒边缘具有晶锥状残留痕迹,白云石表面发育溶蚀孔洞且局部发育有溶蚀坑。Figure 12. SEM morpHhology of dolomitic limestone dissolution process3.3.2 灰岩微观溶蚀过程
对于灰岩,试样溶蚀前同样具有完整的矿物晶体形态,表面光滑平整且无明显溶蚀痕迹。在灰岩溶蚀的初期,矿物晶体棱边及晶格畸变处被溶蚀而变得圆滑,同时晶体表面出现众多细小溶痕(图13a);随溶蚀时间的推移,方解石沿晶体表面及解理处继续溶蚀,形成一组相互平行的溶蚀裂隙,同时白云石表面出现溶蚀孔洞(图13b);当溶蚀进行至72 h,方解石表面溶蚀破坏严重,呈沟槽状、阶梯状溶蚀,白云石晶体结构则相对较为完整,溶蚀作用相对较弱(图13c);当溶蚀作用持续至120 h,方解石沿解理裂隙面溶蚀发育强烈,矿物颗粒已不具完整晶体形态,白云石晶体则清晰,仅局部可见少量溶蚀孔洞(图13d);当溶蚀进行至192 h,晶体周围及晶间接触面位置处溶蚀作用强烈,具有显著层状、阶梯状溶蚀特征,部分岩石矿物被溶蚀剥落,可见明显蚀余凹槽分布其间(图13e);随着晶面溶蚀的深入发展,岩石矿物间的结合程度逐渐减弱,方解石晶体溶蚀呈晶锥状、针状及柱状结构,原始颗粒形态被完全破坏,白云石晶体表面则溶蚀出现大量蜂窝溶孔,呈麻面状分布,但晶形轮廓仍清晰可辨,表现出白云石与方解石显著的差异性溶蚀特征(图13f)。
![]() 图 13 灰岩溶蚀过程SEM形态图a~f均放大10000倍;其中,a—试样编号H-5,溶蚀时间6 h,矿物晶体棱边及晶格畸变处被溶蚀变得圆滑,晶体表面出现众多细小溶痕;b—试样编号H-11,溶蚀时间24 h,方解石晶体表面及解理处溶蚀形成相互平行的溶蚀裂隙,白云石表面出现溶蚀孔洞;c—试样编号H-9,溶蚀时间72 h,方解石表面呈沟槽状及阶梯状溶蚀,白云石晶体结构较为完整;d—试样编号H-2,溶蚀时间120 h,方解石颗粒不具完整晶体形态,白云石晶体则棱角清晰;e—试样编号H-1,溶蚀时间192 h,晶体周围及晶间接触面溶蚀作用强烈,可见明显溶蚀凹槽分布其间;f—试样编号H-7,溶蚀时间312 h,方解石晶体呈现出晶锥状、针状及柱状结构,白云石晶体表面溶蚀成蜂窝麻面,差异溶蚀现象明显。Figure 13. SEM morpHhology of limestone dissolution process
图 13 灰岩溶蚀过程SEM形态图a~f均放大10000倍;其中,a—试样编号H-5,溶蚀时间6 h,矿物晶体棱边及晶格畸变处被溶蚀变得圆滑,晶体表面出现众多细小溶痕;b—试样编号H-11,溶蚀时间24 h,方解石晶体表面及解理处溶蚀形成相互平行的溶蚀裂隙,白云石表面出现溶蚀孔洞;c—试样编号H-9,溶蚀时间72 h,方解石表面呈沟槽状及阶梯状溶蚀,白云石晶体结构较为完整;d—试样编号H-2,溶蚀时间120 h,方解石颗粒不具完整晶体形态,白云石晶体则棱角清晰;e—试样编号H-1,溶蚀时间192 h,晶体周围及晶间接触面溶蚀作用强烈,可见明显溶蚀凹槽分布其间;f—试样编号H-7,溶蚀时间312 h,方解石晶体呈现出晶锥状、针状及柱状结构,白云石晶体表面溶蚀成蜂窝麻面,差异溶蚀现象明显。Figure 13. SEM morpHhology of limestone dissolution process实质上碳酸盐岩的溶蚀过程是岩石内部主要可溶性矿物(方解石、白云石)微观溶蚀特征的宏观表现。方解石易沿晶体解理与晶面起伏处溶蚀,形成“溶蚀晶锥状”结构;而白云石则易沿晶体特有的菱形解理及其相交部位溶蚀,形成“蜂窝状”结构[12](图14、图15)。由于白云质灰岩与灰岩中方解石及白云石两种主要成矿矿物含量不同,也使得两种岩性岩石的微观溶蚀过程存在一定差异,因此,在宏观层面上碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率也表现出一定差异。
![]() 图 14 方解石溶蚀过程模式图[12]Figure 14. Schema graph of the processes for calcite dissolution
图 14 方解石溶蚀过程模式图[12]Figure 14. Schema graph of the processes for calcite dissolution![]() 图 15 白云石溶蚀过程模式图[12]Figure 15. Schema graph for dolomite dissolution processes
图 15 白云石溶蚀过程模式图[12]Figure 15. Schema graph for dolomite dissolution processes3.4 碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀特征分析
20世纪70年代以来,随着科技的进步与试验技术的完善,国内外学者对溶蚀机理开展了大量试验研究[10-18],其中以韩宝平为代表的国内学者提出了碳酸盐岩的选择性溶蚀,即可溶岩通常沿容易溶解的矿物成分及有利结构面优先选择性溶蚀的特征[19]。结合扫描电镜下碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀过程发现,碳酸盐岩在溶蚀过程中均表现出一定程度的差异溶蚀现象,说明岩溶蚀作用是以选择性溶蚀为主要方式进行的,而岩面溶蚀特征是碳酸盐岩选择性溶蚀的结果,具体溶蚀特征简如下:
3.4.1 沿矿物成分选择性溶蚀
当碳酸盐岩试样溶蚀312 h后,试样在微观尺度下发生明显的差异溶蚀现象。方解石晶体溶蚀后晶体结构塌落,已不具原有的晶体形态,呈“溶蚀晶锥”状结构、局部呈现“针状”或“柱状”结构;白云石晶体溶蚀后其晶体棱角特征鲜明,晶形仍清晰可辨,晶体表面溶蚀孔洞较为发育,呈“蜂窝麻面”状结构;由此看出,相同溶蚀环境下方解石的溶蚀程度远大于白云石,岩溶具有优先选择方解石矿物晶体进行溶蚀的特征(图16a)。
![]() 图 16 碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀特征a~d均放大5000倍;其中,a—试样编号H-7,溶蚀时间312 h,沿矿物成分选择性溶蚀,方解石晶体溶蚀后呈现出“溶蚀晶锥”状结构、局部呈现“针状”或“柱状”结构,白云石晶体表面溶蚀成“蜂窝麻面”状,方解石与白云石晶体差异溶蚀现象明显;b—试样编号BH-5,溶蚀时间14 h,沿矿物晶体表面选择性溶蚀,晶体表面呈现出台阶状,表面溶蚀碎屑剥离脱落,局部溶蚀孔洞发育扩张;c—试样编号H-5,溶蚀时间6 h,沿矿物晶体边缘选择性溶蚀,沿矿物晶体棱边出现溶蚀,逐渐变得模糊,局部晶体颗粒晶型似圆球状;d—试样编号BH-1,溶蚀时间312 h,沿矿物晶体解理、裂隙等微结构选择性溶蚀,方解石晶体沿解理处溶蚀形成一组相互平行的溶蚀沟槽,矿物晶体裂隙部位溶蚀扩大呈缝状;Cc-方解石晶体,Do-白云石晶体。Figure 16. Microcosmic dissolution characteristics of carbonate rocks
图 16 碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀特征a~d均放大5000倍;其中,a—试样编号H-7,溶蚀时间312 h,沿矿物成分选择性溶蚀,方解石晶体溶蚀后呈现出“溶蚀晶锥”状结构、局部呈现“针状”或“柱状”结构,白云石晶体表面溶蚀成“蜂窝麻面”状,方解石与白云石晶体差异溶蚀现象明显;b—试样编号BH-5,溶蚀时间14 h,沿矿物晶体表面选择性溶蚀,晶体表面呈现出台阶状,表面溶蚀碎屑剥离脱落,局部溶蚀孔洞发育扩张;c—试样编号H-5,溶蚀时间6 h,沿矿物晶体边缘选择性溶蚀,沿矿物晶体棱边出现溶蚀,逐渐变得模糊,局部晶体颗粒晶型似圆球状;d—试样编号BH-1,溶蚀时间312 h,沿矿物晶体解理、裂隙等微结构选择性溶蚀,方解石晶体沿解理处溶蚀形成一组相互平行的溶蚀沟槽,矿物晶体裂隙部位溶蚀扩大呈缝状;Cc-方解石晶体,Do-白云石晶体。Figure 16. Microcosmic dissolution characteristics of carbonate rocks3.4.2 沿岩石结构选择性溶蚀
(1)沿矿物晶体表面的溶蚀
由于岩溶发育具有选择岩石矿物优先溶蚀的特征,当溶蚀沿岩石表面发育时,方解石晶体表面首先被溶蚀而变得低洼,溶蚀性相对较差的白云石晶体则突出于岩石表面,从而形成白云石晶间溶孔,这种不同步溶蚀现象也使得岩石表面呈现凹凸不平状;此外,矿物晶体表面溶蚀所表现出的逐层阶梯状剥蚀特征与层状溶蚀纹理现象也反映了岩溶沿矿物晶体表面选择性溶蚀的特征(图16b)。
(2)沿矿物晶体边缘的溶蚀
随溶蚀时间的推进,矿物晶体边缘溶蚀特征愈加明显,晶体棱边与尖角处晶形变得愈加模糊,局部晶体颗粒形似圆球状,具有沿矿物晶体边缘溶蚀的特征。原因在于晶体在内、外应力的作用下,棱角处产生的应力集中加速了溶蚀的发育;另一方面,矿物晶体在生成的过程中由于受到外部发育环境的控制,使得矿物结晶物质与生长空间受到一定制约,常常造成晶体畸变、形成位错,自身的缺陷也加剧了晶体边缘溶蚀效应[20]。晶体边缘的溶蚀进一步削弱了晶间联系,促进了晶间孔洞的形成(图16c)。
(3)沿晶间接触位置的溶蚀
在成矿过程中,矿物晶体棱角、棱边、晶面通常以点、线、面的形式相互接触,在内力作用下形成有机统一的整体。对比矿物晶体溶蚀前后晶间结构形态,发现溶蚀前晶形完整,棱角鲜明,晶体间相互紧凑贴合;溶蚀后晶体棱角变得光滑圆润,晶间距离明显加大,晶间空隙发育强烈,形似“砌块状”(图13a),说明晶体选择沿接触部位及周边范围产生了显著的溶蚀现象。
(4)沿晶体解理、裂隙等微结构的溶蚀
矿物晶体溶蚀后结构较为松散多孔,晶体表面形成一组或几组相互平行或斜交的溶蚀凹槽,形似“百叶窗状”,局部似“刀砍状”;溶蚀沿晶体裂隙等微结构发育,使裂隙在深度与宽度方向上溶蚀扩大呈现缝状结构。溶蚀易沿矿物晶体解理、裂隙等微结构优先溶蚀的内在原因是由于方解石晶体与白云石晶体独特的结构特征造成的,两种矿物晶体在外界环境扰动下极容易分别沿{104}晶面与{1011}晶面产生三组完全的解理面,解理等微结构面在溶蚀作用下容易使内部Ca-O离子键与Mg-O离子键产生断裂,游离的离子迅速向水中扩散而产生局部溶蚀现象(图16d)。
4. 结论
本文以在建峨汉高速公路廖山隧道场区三叠系中统雷口坡组典型碳酸盐岩为研究对象,采用溶蚀模拟试验及扫描电镜试验相结合的方法,探究了碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率、溶蚀特征及溶蚀过程的微观结构变化,得到如下结论和认识:
(1)试验条件下(20 ℃、1 atm、乙酸溶液、pH=5.30、静态溶蚀),隧址区雷口坡组灰岩溶蚀速率约3.48 mm/a,白云质灰岩溶蚀速率约1.57 mm/a,钙质泥岩溶蚀速率约0.90 mm/a。在隧道运营全寿命周期内,存在裂隙溶蚀拓展形成岩溶管道,进而弱化岩体与衬砌结构、缩短隧道结构寿命等风险。
(2)碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用受岩性条件及溶蚀环境的控制。相同溶蚀环境下,碳酸盐岩矿物组分是控制溶蚀速率最本质的因素,溶蚀速率与方解石含量呈正相关,与白云石含量呈负相关。溶蚀环境是控制溶蚀速率的关键因素,溶蚀速率整体上与溶蚀介质PH呈负相关,有机酸与无机酸环境下灰岩溶蚀速率总体趋势相同,而中性盐溶液与碱性环境则对灰岩溶蚀起到了一定程度的抑制作用。
(3)碳酸盐岩溶蚀速率与岩体比表面积间不具备明显正相关关系,说明天然裂隙岩体比表面积仅通过影响水-岩反应有效界面的大小进而控制总溶蚀量大小,起到加速隧道裂隙岩体溶蚀进程的作用,而与溶蚀速率本身大小无关,说明隧道围岩越破碎则发育溶洞的可能性越大。
(4)碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀过程表明,溶蚀作用具有优先沿矿物成分、岩石微结构选择性溶蚀的特征。相同溶蚀环境下,方解石的可溶性远大于白云石,岩溶具有优先选择方解石矿物进行溶蚀的特征;此外,矿物晶体表面、晶粒边缘、晶间接触位置及晶体解理、裂隙等结构薄弱处也是优先溶蚀的部位。碳酸盐岩的溶蚀过程是岩石内部主要可溶性矿物(即方解石、白云石)微观溶蚀特征的宏观表现,碳酸盐岩矿物含量的不同也使得其微观溶蚀过程存在一定差异。
-
图 1 碳酸盐岩溶解反应综合模型[16]
Figure 1. Comprehensive model of carbonate rock dissolution reaction
图 12 白云质灰岩溶蚀过程SEM形态图
a~f均放大10000倍;a—试样编号BH-8,溶蚀时间6 h,出现层状剥蚀现象,纹层状溶蚀特征明显;b—试样编号BH-5,溶蚀时间14 h,晶间空隙溶蚀扩大,晶体棱角趋于圆滑;c—试样编号BH-3,溶蚀时间72 h,方解石晶体沿解理面溶蚀破坏明显,发育“百叶窗状”及“刀砍状”溶痕,白云石晶体溶蚀孔洞发育,呈千疮百孔状;d—试样编号BH-6,溶蚀时间120 h,晶体表面溶蚀碎屑脱落,晶面逐步变得光滑平整,局部发育溶蚀残坑;e—试样编号BH-11,溶蚀时间192 h,局部溶蚀缝发育方解石“溶蚀晶锥”,白云石晶体表面溶蚀孔洞溶蚀扩大贯穿;f—试样编号BH-1,溶蚀时间312 h,方解石晶体被明显蚀低且颗粒边缘具有晶锥状残留痕迹,白云石表面发育溶蚀孔洞且局部发育有溶蚀坑。
Figure 12. SEM morpHhology of dolomitic limestone dissolution process
图 13 灰岩溶蚀过程SEM形态图
a~f均放大10000倍;其中,a—试样编号H-5,溶蚀时间6 h,矿物晶体棱边及晶格畸变处被溶蚀变得圆滑,晶体表面出现众多细小溶痕;b—试样编号H-11,溶蚀时间24 h,方解石晶体表面及解理处溶蚀形成相互平行的溶蚀裂隙,白云石表面出现溶蚀孔洞;c—试样编号H-9,溶蚀时间72 h,方解石表面呈沟槽状及阶梯状溶蚀,白云石晶体结构较为完整;d—试样编号H-2,溶蚀时间120 h,方解石颗粒不具完整晶体形态,白云石晶体则棱角清晰;e—试样编号H-1,溶蚀时间192 h,晶体周围及晶间接触面溶蚀作用强烈,可见明显溶蚀凹槽分布其间;f—试样编号H-7,溶蚀时间312 h,方解石晶体呈现出晶锥状、针状及柱状结构,白云石晶体表面溶蚀成蜂窝麻面,差异溶蚀现象明显。
Figure 13. SEM morpHhology of limestone dissolution process
图 14 方解石溶蚀过程模式图[12]
Figure 14. Schema graph of the processes for calcite dissolution
图 15 白云石溶蚀过程模式图[12]
Figure 15. Schema graph for dolomite dissolution processes
图 16 碳酸盐岩微观溶蚀特征
a~d均放大5000倍;其中,a—试样编号H-7,溶蚀时间312 h,沿矿物成分选择性溶蚀,方解石晶体溶蚀后呈现出“溶蚀晶锥”状结构、局部呈现“针状”或“柱状”结构,白云石晶体表面溶蚀成“蜂窝麻面”状,方解石与白云石晶体差异溶蚀现象明显;b—试样编号BH-5,溶蚀时间14 h,沿矿物晶体表面选择性溶蚀,晶体表面呈现出台阶状,表面溶蚀碎屑剥离脱落,局部溶蚀孔洞发育扩张;c—试样编号H-5,溶蚀时间6 h,沿矿物晶体边缘选择性溶蚀,沿矿物晶体棱边出现溶蚀,逐渐变得模糊,局部晶体颗粒晶型似圆球状;d—试样编号BH-1,溶蚀时间312 h,沿矿物晶体解理、裂隙等微结构选择性溶蚀,方解石晶体沿解理处溶蚀形成一组相互平行的溶蚀沟槽,矿物晶体裂隙部位溶蚀扩大呈缝状;Cc-方解石晶体,Do-白云石晶体。
Figure 16. Microcosmic dissolution characteristics of carbonate rocks
表 1 隧址区典型碳酸盐岩矿物组成X射线衍射分析
Table 1 X-ray diffraction analysis of mineral composition of typical carbonate rocks in tunnel site
试样编号 取样桩号 试样岩性 矿物成分/% 百分含量/% 钾长石 方解石 白云石 石英 X191250001 K31+917 灰岩 0.9 90.6 8.5 − 100.0 X191250002 K32+033 白云质灰岩 1.1 57.0 41.4 0.5 100.0 X191250003 K32+033 钙质泥岩 0.2 0.3 98.7 0.8 100.0 注:本次检测委托国土资源部西北矿产资源监督检测中心检测完成,“−”表示未检出或低于检出限。 表 2 溶蚀试验工况条件
Table 2 dissolution experiment conditions
试验分组及编号 试样岩性 试样尺寸/mm 溶蚀介质 溶液pH值 溶蚀时间 组别 编号 预设 实际 第一组 1-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 3.50 3.70 各试样分别累计溶蚀6, 14, 24 h 1-2 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 4.50 4.50 1-3 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第二组 2-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 2-2 Φ42×20 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 2-3 Φ42×10 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第三组 3-1 灰岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 3-2 Φ42×20 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 3-3 Φ42×10 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第四组 4-1 钙质泥岩 Φ42×40 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 4-2 Φ42×20 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 4-3 Φ42×10 乙酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第五组 5-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 氢氧化钠溶液 9.00 9.00 5-2 Φ42×10 乙酸钠溶液 7.00 7.00 5-3 Φ42×10 盐酸溶液 5.50 5.30 第六组 6-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 去离子水 7.00 7.00 6-2 白云质灰岩 Φ42×10 去离子水 7.00 7.00 6-3 钙质泥岩 Φ42×10 去离子水 7.00 7.00 注:溶液配制过程中存在乙酸电离平衡现象,溶液pH值难以精确控制,故实际pH值与预设pH值存在一定偏差。 表 3 不同工况条件下溶蚀试验成果汇总
Table 3 Summary of dissolution experiment results under different working conditions
试样编号 试样岩性 试样规格/mm 试样质量m/g 溶液实际pH值 溶蚀速率v/(10−3cm·d−1) 初始 溶蚀6 h 溶蚀14 h 溶蚀24 h 初始 溶蚀6 h 溶蚀14 h 溶蚀24 h 溶蚀6 h 溶蚀14 h 溶蚀24 h 1-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 151.086 151.032 150.970 150.908 3.70 3.84 3.97 4.13 1.0524 0.9689 0.8673 1-2 Φ42×40 154.035 153.993 153.962 153.928 4.50 4.75 4.91 5.16 0.8185 0.6097 0.5213 1-3 Φ42×40 153.643 153.605 153.578 153.547 5.30 5.41 5.68 6.31 0.7406 0.5429 0.4677 2-1 白云质灰岩 Φ42×40 150.054 150.027 150.006 149.985 5.30 5.59 5.71 5.96 0.5262 0.4009 0.3362 2-2 Φ42×20 76.4194 76.4035 76.3924 76.3836 5.30 5.82 5.86 5.92 0.4610 0.3355 0.2595 2-3 Φ42×10 46.6763 46.6569 46.6487 46.6416 5.30 5.48 5.61 5.75 0.7440 0.4536 0.3327 3-1 灰岩 Φ42×40 153.422 153.348 153.336 153.330 5.30 5.66 5.98 6.40 1.4594 0.7269 0.4536 3-2 Φ42×20 85.8408 85.8144 85.7900 85.7860 5.30 5.49 5.75 6.14 0.7746 0.6388 0.4020 3-3 Φ42×10 42.6727 42.6545 42.6442 42.6406 5.30 5.33 5.34 5.57 0.7063 0.7716 0.3114 4-1 钙质泥岩 Φ42×40 149.246 149.2274 149.2198 149.2125 5.30 5.42 5.89 6.33 0.3773 0.2278 0.1699 4-2 Φ42×20 70.8872 70.8728 70.8647 70.8603 5.30 5.31 5.60 5.82 0.4346 0.2910 0.2029 4-3 Φ42×10 41.9599 41.9523 41.9470 41.9428 5.30 5.28 5.52 5.79 0.3033 0.2207 0.1707 5-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 42.0705 42.0722 42.0672 42.0657 9.00 8.90 8.85 8.79 0.0660 0.0549 0.0466 5-2 Φ42×10 37.4267 37.4246 37.4228 37.4204 7.00 7.02 7.04 7.02 0.0815 0.0649 0.0611 5-3 Φ42×10 42.9626 42.9423 42.9239 42.9165 5.30 5.50 5.70 5.83 0.7882 0.6430 0.4475 6-1 灰岩 Φ42×10 42.0657 42.0631 42.0598 42.0555 7.00 7.00 7.00 7.00 0.1006 0.0976 0.0990 6-2 白云质灰岩 Φ42×10 45.5304 45.5287 45.5272 45.5259 7.00 7.00 7.00 7.00 0.0566 0.0580 0.0547 6-3 钙质泥岩 Φ42×10 36.6783 36.6771 36.6759 36.6739 7.00 7.00 7.00 7.00 0.0466 0.0407 0.0439 表 4 碳酸盐岩溶蚀程度对比
Table 4 Comparison of dissolution degree of carbonate rocks
岩性 溶蚀介质 试样编号 溶蚀周期/h 试样质量/g 溶蚀量/g 溶蚀率/‰ 溶蚀程度排序 白云质灰岩 PH=5.30 乙酸溶液 BH-1 312 1.0579 0.0104 9.8308 1 BH-2 24 1.2795 0.0015 1.1723 15 BH-3 72 1.4047 0.0032 2.2781 10 BH-4 14 1.4055 0.0024 1.7076 11 BH-5 14 1.5674 0.0014 0.8932 19 BH-6 120 1.1915 0.0067 5.6232 7 BH-7 24 1.3426 0.0013 0.9683 18 BH-8 6 1.1627 0.0016 1.3761 12 BH-9 312 1.4557 0.0123 8.4495 2 BH-10 6 1.0568 0.0012 1.1355 16 BH-11 192 1.0602 0.0073 6.8855 5 灰岩 PH=5.30 乙酸溶液 H-1 192 0.9194 0.0051 5.5471 8 H-2 120 1.5664 0.0057 3.6389 9 H-3 312 0.9910 0.0067 6.7608 6 H-4 6 1.3798 0.0008 0.5798 22 H-5 6 0.9798 0.0008 0.8165 20 H-6 14 1.2719 0.0008 0.6290 21 H-7 312 1.2467 0.0086 6.8982 4 H-8 312 0.9080 0.007 7.7092 3 H-9 72 1.1071 0.0013 1.1742 14 H-10 24 1.1787 0.0012 1.0181 17 H-11 24 0.8731 0.0012 1.3744 13 H-12 14 1.0593 0.0006 0.5664 23 -
[1] 金新锋. 宜万铁路沿线岩溶发育规律及其对隧道工程的影响[D]. 中国地质科学院, 2007. JIN Xinfeng. Regularity of karst development along the Yichang-Wanzhou railway and its influence on tunnel construction[D]. Chinese Academy of Geological Sciences, 2007. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 罗平, 张静, 刘伟, 等. 中国海相碳酸盐岩油气储层基本特征[J]. 地学前缘,2008,15(1):36 − 50. [LUO Ping, ZHANG Jing, LIU Wei, et al. Characteristics of marine carbonate hydrocarbon reservoirs in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers,2008,15(1):36 − 50. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.2008.01.004 [3] 佘敏, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 从表生到深埋藏环境下有机酸对碳酸盐岩溶蚀的试验模拟[J]. 地球化学,2014,43(3):276 − 286. [SHE Min, SHOU Jianfeng, SHEN Anjiang et al. Experimental simulation of dissolution for carbonate rocks in organic acid under the conditions from epigensis to deep burial environments[J]. Geochimica,2014,43(3):276 − 286. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 张正红, 乔占峰, 潘文庆, 等. 碳酸盐岩礁滩储层的形成和发育规律—溶蚀模拟试验[J]. 海相油气地质,2017,22(3):57 − 66. [ZHANG Zhenghong, QIAO Zhanfeng, PAN Wenqing et al. Formation and development of reef-shoal reservoir: Extending knowledge from the dissolution experiment[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2017,22(3):57 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2017.03.007 [5] 李苍松, 吴丰收, 赵岩杰, 等. 基于溶蚀试验的微观岩溶形态分形特征和水化学动力学特征研究[J]. 现代隧道技术,2018,55(2):110 − 120. [LI Cangsong, WU Fengshou, ZHAO Yanjie, et al. Fractal and hydro-chemical characteristics of microscopic karst morphology based on dissolution experiments[J]. Modern Tunnelling Technology,2018,55(2):110 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 聂跃平. 黔南地区碳酸盐岩的溶蚀试验初探[J]. 中国岩溶,1984(1):41 − 47. [NIE Yueping. A preliminary study and test on the dissolution of carbonate rocks in south Guizhou Province[J]. Carsologica Sinica,1984(1):41 − 47. (in Chinese with English abstract) [7] 韩宝平. 雾迷山喀斯特微观机理的研究[J]. 中国矿业学院学报,1986(4):80 − 84. [HAN Baoping. Study on micro-corrosion mechanism of sinian system Wuminshan formation[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,1986(4):80 − 84. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 刘琦, 卢耀如, 张凤娥, 等. 动水压力作用下碳酸盐岩溶蚀作用模拟试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2010,31(增刊1):96 − 101. [LIU Qi, LU Yaoru, ZHANG Fenge, et al. Study of simulation experiment for carbonate rocks dissolution under hydrodynamic pressure[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2010,31(Sup1):96 − 101. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 张良喜, 赵其华, 胡相波, 等. 某地区白云岩室内溶蚀试验及微观溶蚀机理研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2012,20(4):576 − 584. [ZHANG Liangxi, ZHAO Qihua, HU Xiangbo, et al. Laboratory dissolution test on dolomite and its micro-dissolution mechanism[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2012,20(4):576 − 584. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2012.04.014 [10] 佘敏, 寿建峰, 贺训云, 等. 碳酸盐岩溶蚀机制的试验探讨: 表面溶蚀与内部溶蚀对比[J]. 海相油气地质,2013,18(3):55 − 61. [SHE Min, SHOU Jianfeng, HE Xunyun, et al. Experiment of dissolution mechanism of carbonate rocks: surface dissolution and internal dissolution[J]. Marine Origin Petroleum Geology,2013,18(3):55 − 61. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9854.2013.03.007 [11] 佘敏, 寿建峰, 沈安江, 等. 埋藏有机酸性流体对白云岩储层溶蚀作用的模拟试验[J]. 中国石油大学学报(自然科学版),2014,38(3):10 − 17. [SHE Min, SHOU Jianfeng, SHEN Anjiang, et al. Experimental simulation of dissolution and alteration of buried organic acid fluid on dolomite reservoir[J]. Journal of China University of Petroleum(Edition of Natural Science),2014,38(3):10 − 17. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 朱文慧, 曲希玉, 邱隆伟, 等. 盐酸及乙酸介质中的碳酸盐岩溶蚀表面特征及机理—以南堡凹陷为例[J]. 矿物岩石地球化学通报,2015,34(3):619 − 625. [ZHU Wenhui, QU Xiyu, QIU Longwei, et al. Characteristics and erosion mechanism of carbonate in acetic acid and hydrochloride solutions: An example from the Nanpu depression[J]. Bulletin of Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry,2015,34(3):619 − 625. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2802.2015.03.018 [13] 田雯. 桩海地区下古生界碳酸盐岩表生条件下溶蚀过程模拟试验[J]. 矿物学报,2019,39(1):108 − 116. [TIAN Wen. Experimental simulation of dissolution process of the Lower Paleozoic carbonate rocks in Zhuanghai Area under supergene conditions[J]. Acta Mineralogica Sinica,2019,39(1):108 − 116. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 翁金桃. 方解石和白云石的差异溶蚀作用[J]. 中国岩溶,1984,3(1):29 − 38. [WENG Jintao. The different corrosion of calcites and dolomites[J]. Carsologica Sinica,1984,3(1):29 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 杨俊杰, 黄思静, 张文正, 等. 表生和埋藏成岩作用的温压条件下不同组成碳酸盐岩溶蚀成岩过程的试验模拟[J]. 沉积学报,1995,13(4):49 − 54. [YANG Junjie, HUANG Sijing, ZHANG Wernzheng, et al. Experimental simulation of dissolution for carbonate with different composition under the conditions from epigenesist to burial diagenesis environment[J]. Acta Sedimentologica Sinica,1995,13(4):49 − 54. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 王炜, 黄康俊, 鲍征宇, 等. 不同类型鲕粒灰岩储集层溶解动力学特征[J]. 石油勘探与开发,2011,38(4):495 − 502. [WANG Wei, HUANG Kangjun, BAO Zhengyu, et al. Dissolution kinetics of different types of oolitic limestones in northeastern Sichuan Basin[J]. Petroleum Exploration and Development,2011,38(4):495 − 502. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 邹成杰. 水利水电岩溶工程地质[M]. 北京: 水利电力出版社, 1994. ZOU Chengjie. Karst engineering geology of water conservancy and hydropower[M]. Beijing: Water Resources and Electric Power Press, 1994. (in Chinese)
[18] BAI Y E, LIU Q, GU Z F, et al. The dissolution mechanism and karst development of carbonate rocks in karst rocky desertification area of Zhenfeng Guanling Huajiang County, Guizhou, China[J]. Carbonates and Evaporites,2019,34(1):45 − 51. DOI: 10.1007/s13146-017-0386-x
[19] 韩宝平. 喀斯特微观溶蚀机理研究[J]. 中国岩溶,1993(2):4 − 9. [HAN Baoping. Extraction and analysis of generalized karst geological information in global changes[J]. Carsologica Sinica,1993(2):4 − 9. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 何婷, 张覃. 磷矿石中白云石晶体化学特性研究[J]. 矿冶工程,2012,32(5):41 − 43. [ZHANG Ting, ZHANG Tan. Study on crystal chemistry characteristics of dolomite in phosphate ores[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering,2012,32(5):41 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 林诗哲,胡新丽,张海燕,李宁杰,刘欣宇. 白鹤滩水电站库区红层砂岩干湿循环下结构劣化及渗透性演化规律. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 67-77 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李乔楚,陈军华. 集成决策解释模型和交叉影响矩阵的岩溶塌陷隐患区燃气管道安全风险分析及应用. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(06): 158-166 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)




 下载:
下载:
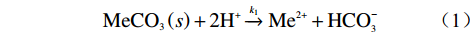
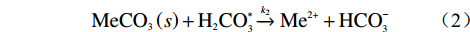
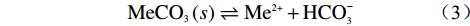
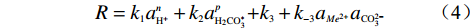

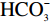
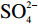
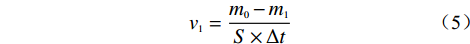
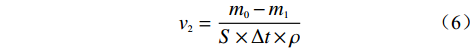






 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS