Characteristics and spatial-temporal distribution law of karst collapse in Sanzhou basin in Gaoming District of Foshan City, Guangdong Province
-
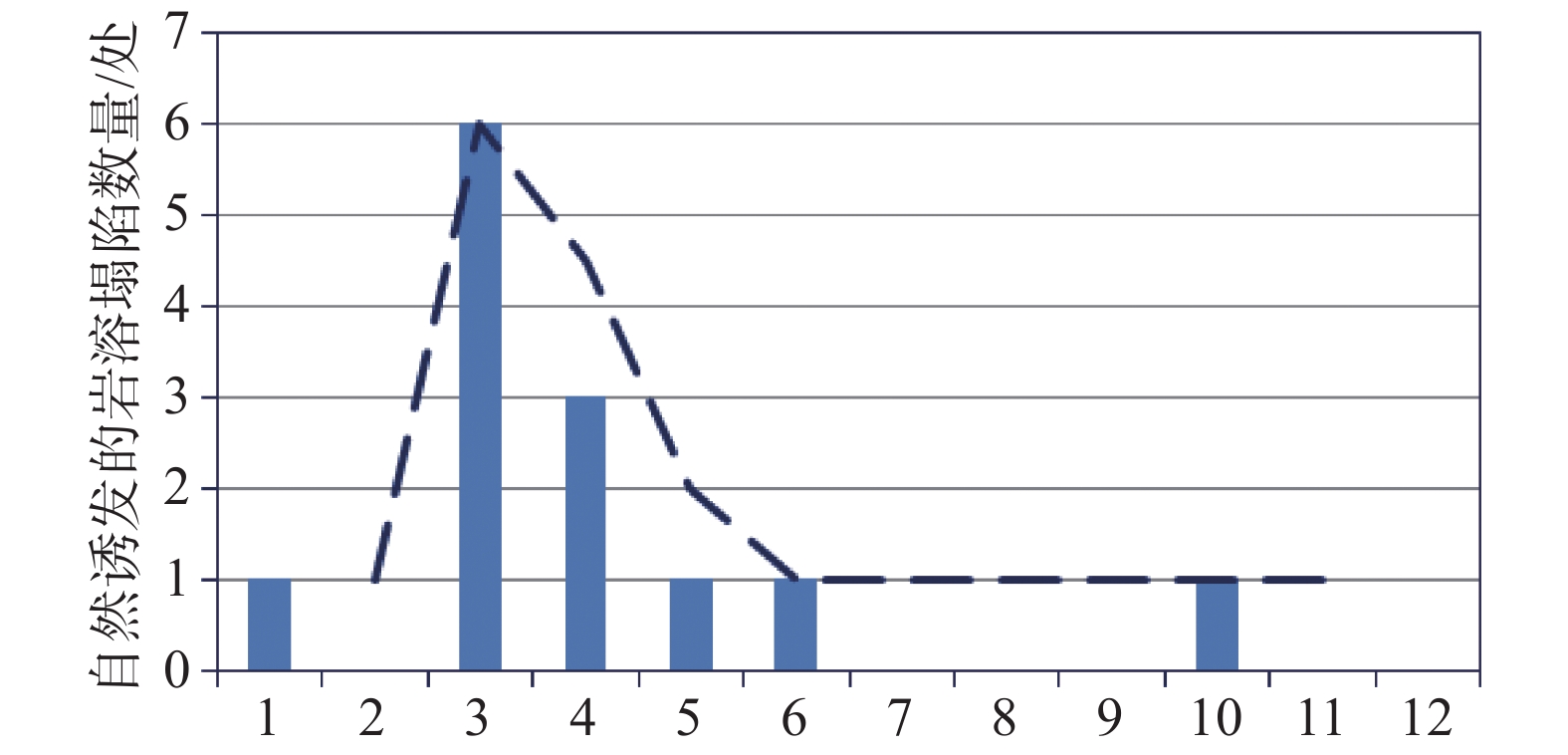
摘要: 以佛山市高明区三洲盆地作为研究区,在系统收集区内区域地质、构造、工程、水文、环境、历史灾害等基础上,通过野外走访调查,查明了研究区岩溶塌陷发育特征,并对其时空分布规律进行了分析。结果表明:(1)区内岩溶塌陷规模以小型为主,其平面形态以圆形、似圆形为主,其剖面形态以漏斗状居多,并且剖面形态随覆盖层厚度增大总体呈现由圆柱状—坛状—漏斗状—碟状的变化规律;(2)空间上岩溶塌陷的分布受地层岩性、地质构造、覆盖层厚度及结构、地下水迳流和人类工程活动等影响;(3)时间上人为塌陷的发生主要与采矿活动和钻探施工时间关系密切,而自然塌陷主要发生在每年旱涝交替期间(即3—4月份)。Abstract: Sanzhou basin in Gaoming District of Foshan City is selected as the research area. data of regional geology, geological structure, engineering geology, hydrogeology, environmental geology and historical geological disasters in the study area are collected systematically, the characteristics of karst collapse are found out through field investigation. And the spatial-temporal distribution law is analyzed. The results show that: (1)The scale of karst collapse is mainly small, its plane shape features are mainly circular and quasi circular, and its profile shape features are mainly funnel-shaped. With the increase of the overburden thickness, the profile shape features of karst collapse generally change from circular-shape to jar-shape to funnel-shape and then to disc-shape. (2)The spatial distribution of karst collapse is affected by stratum lithology, geological structure, overburden thickness and its structure, groundwater runoff and human engineering activities. (3)The temporal distribution of man-made karst collapse is closely related to mining activity and drilling construction. The temporal distribution of karst collapse induced by nature is mainly during the alternate period of drought and flood (especially from March to April).
-
0. 引言
目前,基于GIS技术的滑坡易发性评价已成为滑坡研究领域的热点,研究者们基于地形地貌、水文地质和人类工程活动等方面选取滑坡影响因子,采用评价模型对区域滑坡灾害的易发性进行评价分析。主流的评价模型主要有基于统计分析和机器学习的方法,如逻辑回归[1-2]、信息量[3-6]、支持向量机[7]和人工神经网络[7-10]模型等。诸多研究表明,与单一的评价模型相比,多模型耦合的方法可以提高评价精度和预测能力,更具有科学性和合理性[11-12]。如SAHA等[8]采用逻辑回归(LR)、人工神经网络(ANN)、支持向量机(SVM)和随机森林(RF)模型及其耦合模型对印度Rudraprayag地区进行滑坡易发性评价,结果表明ANN-RF-LR耦合模型的稳健性最好,评价精度和预测能力最高;陈飞等[9]采用信息量与神经网络组合模型对江西省上犹县进行了滑坡易发性评价,结果表明组合模型的评价精度优于单一信息量模型;连志鹏等[3]通过优势耦合模型对湖北省五峰县的滑坡进行了易发性评价研究,结果也表明耦合模型预测精度明显高于单一模型。
近年来,信息量模型(I)由于其模型的语义明确、易于实现等优点已被广泛应用于山区复杂地形区域的滑坡易发性评价中,并取得了较好的效果[3-6,9]。但信息量模型只能获得指标因子对应的信息量值,无法准确地表达各指标因子的权重大小和相关性,所以在一定程度上,很难准确客观地进行易发性评价。RBF神经网络(RBFNN)模型是以径向基函数作为激活函数的一种性能良好的前馈神经网络,具有最佳逼近和克服局部极小值问题的优点[13]。可以利用RBF神经网络数据拟合功能,建立模型并映射出历史滑坡分布和影响因子之间的非线性关系,是区域滑坡灾害易发性评价的新技术。因此,本文通过RBF神经网络和信息量模型的耦合,优化区域滑坡灾害易发性评价结果。
甘肃省岷县位于青藏高原边缘,地形复杂,地质条件脆弱,土体结构稳定性差,滑坡灾害频发,严重制约了当地的土地开发利用、工矿建设和生态环境保护。文章以岷县为研究区,综合考虑滑坡发生的内在、外在诱发因素,筛选了高程、坡度、坡向、平面曲率、距断层距离、地层、降雨量、距水系的距离、NDVI、距道路的距离10个指标因子,采用RBF神经网络-信息量耦合模型(RBFNN-I)对研究区滑坡灾害进行易发性评价研究。最后,采用合理性和受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)对耦合模型和单一模型的评价结果对比分析,以期建立一种有效的滑坡灾害易发性评价模型,为岷县滑坡灾害预防治理和防灾减灾工作提供参考,有效地减少滑坡灾害给人民生命财产和生产生活带来的损失。
1. 研究方法
1.1 信息量模型
信息量(I)模型的原理是通过信息熵综合分析各指标因子对区域滑坡易发性的贡献值,确定滑坡分布与环境因子之间的空间关系。根据已经发生的滑坡区域所提供的信息把区域内各指标因子的实测值转化为能反映区域稳定性的信息熵,通过统计各个影响因素对滑坡灾害贡献的信息熵来确定导致灾害发生的“最优因素组合”,将多个影响因素的信息熵叠加实现区域滑坡易发性评价[5-6]。其表达式为:
$$ I({x_i},H) = \ln \left( {\frac{{{{{N_i}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{N_i}} N}} \right. } N}}}{{{{{S_i}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{S_i}} S}} \right. } S}}}} \right) $$ (1) 式中:
$ I({x_i},H) $ ——指标因子对滑坡灾害发生提供的信息 量值;$ {x_i} $ ——评价单元内指标因子的等级;Ni——研究区指标因子
$ {x_i} $ 的滑坡灾害面积;N——研究区内滑坡灾害总面积;
Si——
研究区内指标因子 $ {x_i} $ 的面积;S——研究区的总面积。
可以根据单一指标因子的信息量值计算整个研究区内评价单元的信息量,计算表达式为:
$$ I = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {({x_i},H)} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^n {\ln \left( {\frac{{{{{N_i}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{N_i}} N}} \right. } N}}}{{{{{S_i}} \mathord{\left/ {\vphantom {{{S_i}} S}} \right. } S}}}} \right)} $$ (2) 式中:n——研究区选取的指标因子总数;
I——总信息量值,是评价滑坡灾害易发性的综合指标,其总信息量值I越大,说明滑坡易发性越高,反之则说明滑坡易发性较低。
1.2 RBF神经网络模型
RBF神经网络(RBFNN)模型是由输入层、隐含层和输出层构成(图1)。从输入层到隐含层是非线性变换,不需要权值连接,从隐含层到输出层变换是线性的,也就是整个网络的输出是隐含层输出结果的线性加权和。第一层为输入层,主要是将输入的样本传递给隐含层,起到传输信号的作用。第二层为隐含层,隐含层含有若干隐节点,每个隐节点的激活函数采用径向基函数;第三层为输出层,是将隐含层空间映射到输出层[13-14],对应的映射关系为:
$$ {y_j} = \sum\limits_{i = 1}^h {{\omega _{ij}}{R_i}({x_p} - {c_i})} $$ (3) 式中:i=1,2,3,···,h——隐含层有h个节点;
j=1,2,3,···,n——输出层有n个节点;
$ {\omega _{ij}} $ ——隐含层到输出层的连接权值;$x_p $ ——n维的输入向量,$ {x_p} = {(x_1^p,x_2^p, \cdots ,x_n^p)^T} $ ;$ {c_i} $ ——第i个高斯核函数的中心值,与输入向量的维数相同;$ {R_i}({x_p} - {c_i}) $ ——基函数。选用高斯函数作为基函数,定义第i个隐含单元的激活函数为:
$$ {R_i}({x_p} - {c_i}) = \exp \left( { - \frac{1}{{2\sigma _i^2}}{{\left\| {{x_p} - {c_i}} \right\|}^2}} \right) $$ (4) 式中:
$ \left\| {{x_p} - {c_i}} \right\| $ ——输入向量到$ {c_i} $ 的欧氏距离;$ {\sigma _i} $ ——第i个高斯核函数的中心点宽度。1.3 RBFNN-I模型及精度验证方法
RBFNN-I模型是将影响滑坡灾害的各指标因子不同等级的信息量值作为模型的输入参数,是否发生滑坡作为目标类型,经过反复训练创建标准的RBFNN-I模型,其建模流程见图2。
滑坡灾害易发性评价结果是否准确对区域滑坡风险早期识别和监测预警工作有直接的影响作用,因此对评价结果进行精度检验十分必要,文中主要从评价结果合理性检验和模型精度检验两个方面对评价结果进行检验。合理性检验是对评价模型检验的方法之一,主要通过分析各等级易发区的面积和空间分布状况,及其实际发生的滑坡点在各等级易发区内的分布数量来检验模型的合理性[15]。受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)分析是滑坡易发性评价中常用的模型精度评价方法[4-7]。首先将未发生滑坡的单元被正确预测的比例(特异性)定义为X轴,然后将已发生滑坡的单元被正确预测的比例(敏感性)定义为Y轴,绘制得到ROC曲线。通常计算ROC曲线线下面积(AUC)来评价模型的准确度,AUC值越大表明模型的性能越好。
2. 研究区概况
2.1 研究区概况
岷县位于甘肃省定西市西南部,洮河中游,是甘南高原东缘与陇中黄土高原和西秦岭陇南山地交汇处(图3)。境内地形起伏大,呈南高北低趋势,海拔约2040~3754 m,以山地为主,约占县域面积的88%;气候属于温带半湿润气候,高寒阴湿,年均气温5.5℃,年均降水量598.3 mm,南部和东部区域植被覆盖率较高;水系多呈树状,支流较多,分属长江和黄河两大流域;地质环境脆弱,岩性以上古生代的海陆交互相层的灰岩、砂岩、泥炭、砾岩为主,地层从晚古生代泥盆纪中期到第四纪均有出露,走滑型的断裂带较多,地震滑坡主要分布在临潭—宕昌断裂带矩形区[16-17]。同时,岷县受到“5·12”汶川地震和“7·22”岷县地震的影响,地表岩层破碎,在强降雨和地震的作用下,山洪、泥石流和滑坡等自然灾害频发。
2.2 滑坡灾害数据编录
滑坡灾害数据编录是进行滑坡易发性评价分析的基础。首先根据研究区范围内的高分辨率遥感影像数据(Landsat8:2018年;GF-6:2019年;Google Earth:2020年),将研究区划分为5行10列,共50个格网,以《滑坡灾害防治手册-认识滑坡:防治滑坡》为指南[18],依据遥感影像滑坡解译标志,通过目视解译的方法识别滑坡灾害点,然后结合现场核查,得到岷县滑坡灾害点共549处,单体滑坡面积最大为31164 m2,面积最小为203 m2,面积大于10000 m2的滑坡30处,滑坡灾害的总面积1.98 km2,约占整个研究区的0.055%(图3)。岷县的滑坡灾害类型主要以浅层、小型滑坡为主。为解决建模过程中的滑坡点和非滑坡点的比例平衡问题,在非滑坡区域随机生成间距大于1 km的随机点549个,共得到1098个样本点。
3. 建立评价指标体系
3.1 指标因子的选取与分级
根据指标因子选取的原则和滑坡的形成机理,参考近年来国内外学者在滑坡易发性评价研究中最常使用的指标因子以及岷县的实际情况,并考虑指标因子数据的可量化、可获取性,本研究从地形地貌、地质构造、气象水文、地表覆盖和人类活动五个方面选取了10个指标因子,分别是高程、坡度、坡向、平面曲率、距断层距离、地层、降雨量、距水系距离、归一化植被指数(NDVI)和距道路距离。选取的指标因子的数据类型主要分为连续型和离散型数据集,依据不同的数据类型和已有的相关研究经验确定每个指标因子的分级标准[1-9]。将各指标因子制作成空间范围一致且分辨率相同的栅格专题图层(图4)。
3.1.1 地形地貌类指标因子
基于GIS软件从岷县DEM数据提取地形地貌类的指标因子,主要有高程、坡度、坡向和平面曲率见图4(a)−图4(d)。高程与岩土体的含水率、人类活动强度和植被覆盖度等都具有很高的相关性,是滑坡灾害发育的主要影响因素之一,岷县高程的分布范围在2039~3817 m,按100 m的间隔重分类为10个等级。坡度与坡体的应力分布、地表径流、堆积物厚度等方面有密切的关系,不同坡度范围内,滑坡的发育类型和规模存在明显差异[19],岷县坡度的分布范围在0~67°,以坡度值为5°间隔进行划分,并对坡度值分布较少的等级区间进行合并得到10个等级。坡向对滑坡灾害的影响主要源于不同坡向的太阳辐射强度和降雨量不同,从而对地表温度、水分蒸发量、植被覆盖情况和坡面的风化程度等方面产生影响,造成滑坡灾害发育的空间分布差异性,文中将其分为平地、北向、东北、东向、东南、南向、西南、西向、西北9个等级。平面曲率描述了地表沿水平方向的弯曲和变化情况,是对地形表面扭曲变化程度的定量化度量因子,且凹凸变化与地形曲率一致,文中将其分为10个等级,见图4(d)。
3.1.2 地质构造类指标因子
基于GIS软件从岷县1∶20万地质图中提取地质构造类指标因子见图4(e)−图4(f)。断层能够改变岩体的构造形式和力学强度,且断层活动产生的挤压和拉裂作用使得地层结构面的裂隙更为发育,是影响滑坡形成和发育的重要因素[20]。岷县位于祁连加里东造山带和西秦岭复合造山带的结合部位,境内有多条活跃断层,因此以1 km的缓冲距离创建了11个距断层距离的分级。地层是滑坡发育的物质基础,不同地层的岩土体类型和结构特征在抗风化能力、抗剪强度和抗侵蚀性等方面有显著的差异,能够直接影响斜坡的形变和稳定性[21],岷县的地层发育较为齐全,文中按年代从新到老进行地层等级的划分,依次是第四系、侏罗系、三叠系、二叠系、石炭系和泥盆系。
3.1.3 气象水文类指标因子
选取的气象水文类指标因子主要是降雨量和距水系距离,见图4(g)−图4(h)。降雨是造成滑坡灾害的主要诱发因素,主要原因是雨水渗入岩土体内部,会增加坡体的容重,降低岩土体的抗剪强度和摩擦力,极易使坡体失稳而诱发滑坡灾害[22],对2000—2017年岷县逐月降雨数据进行整理分析,按照自然间断法划分为9个等级。水系与滑坡灾害之间的关系密切,主要表现在当坡体距离水系越近时,所受到的冲刷、侵蚀作用就越强,特别在河道拐弯处的侧蚀作用极强,文中以200 m的缓冲距离创建了11个距水系距离的分级。
3.1.4 地表覆盖类指标因子
选取的地表覆盖类指标因子是植被,植被能够减缓地表径流对坡体的侵蚀程度,增加土壤的渗透性和降低孔隙水压力,并且植被的根系对坡体具有一定的稳固作用,对滑坡灾害发育有至关重要的作用[23]。归一化植被指数(NDVI)是衡量植被生长发育状态和植被覆盖度的重要指标,因此本文基于ENVI软件通过Landsat8影像数据提取NDVI值,并将其分为9个等级,如图4(i)所示。
3.1.5 人类活动类指标因子
交通建设是人类活动的一种重要表现形式,距道路距离通常作为滑坡易发性分析的指标因子之一。在道路建设之前,坡体是平衡的。施工的扰动会改变地形,影响道路沿线的自然环境,直接或间接的对滑坡灾害的发生起到一定的促进作用。因此本文以200 m的缓冲距离建立了11个距道路距离的分级,如图4(j)所示。
3.2 指标因子的检验与筛选
在进行模型的建立和训练之前,为了保证输入模型的指标因子之间具有独立性和客观性,本文采用Pearson相关系数法[24]对选取的10个指标因子进行检验与筛选,统计其相关性系数R,结果如表1所示。由表可知,高程与降雨量、距道路距离相关性系数R分别为0.75和0.52,均大于0.5,其余各指标因子之间的相关性都较低,因此,经综合考虑后剔除高程指标因子,将剩余的9个指标因子用于建立岷县滑坡灾害易发性评价指标体系。在此基础上,将研究区按照基本网格单元30 m×30 m进行划分,计算得到每个指标因子不同等级的面积以及各等级内滑坡分布的面积。通过信息量模型公式(1)得到各指标因子分类等级的信息量值,结果如表2所示。
表 1 指标因子相关性检验表Table 1. Correlation of controlling index factors高程 坡度 坡向 平面曲率 距断层距离 地层 降雨量 距水系距离 NDVI 距道路距离 高程 1 坡度 −0.06 1 坡向 −0.01 0.03 1 平面曲率 0.05 0.05 0.04 1 距断层距离 0.37 −0.20 0.00 0.10 1 地层 −0.32 −0.14 −0.06 0.04 −0.01 1 降雨量 0.75 −0.11 −0.01 0.09 0.19 −0.33 1 距水系距离 0.48 −0.09 0.01 −0.02 0.20 −0.13 0.25 1 NDVI 0.32 −0.08 0.00 0.04 0.35 −0.13 0.38 0.14 1 距道路距离 0.52 −0.14 −0.03 −0.01 0.17 −0.24 0.47 0.26 0.25 1 表 2 指标因子分类等级信息量值计算表Table 2. The classification information for index factors of landslide指标因子 分类等级 滑坡面积/km2 滑坡面积比例A/% 分级面积/km2 分级面积比例B/% 频率比(A/B) 信息量值I
坡度/(°)0~5 0.05 2.55 299.99 8.40 0.30 −1.20 5~10 0.10 4.96 546.03 15.28 0.32 −1.14 10~15 0.22 11.06 687.10 19.23 0.58 −0.54 15~20 0.36 18.21 713.50 19.97 0.91 −0.09 20~25 0.48 24.03 617.77 17.29 1.39 0.33 25~30 0.40 20.25 410.29 11.48 1.76 0.57 30~35 0.23 11.83 202.24 5.66 2.09 0.74 35~40 0.08 4.01 72.21 2.02 1.98 0.68 40~45 0.05 2.33 18.55 0.53 4.47 1.50 >45 0.02 0.77 5.13 0.14 5.39 1.68 坡向 平地 0.00 0.00 1.37 0.04 0.00 0.00 北向 0.05 2.69 452.59 12.67 0.21 −1.56 东北 0.09 4.51 510.81 14.30 0.32 −1.14 东向 0.28 13.97 503.66 14.10 0.99 −0.01 东南 0.46 23.03 416.25 11.65 1.98 0.68 南向 0.46 23.17 354.90 9.93 2.33 0.85 西南 0.39 19.89 400.81 11.22 1.77 0.57 西向 0.19 9.46 471.18 13.18 0.72 −0.33 西北 0.06 3.28 461.22 12.91 0.25 −1.39 平面曲率 <−0.8 0.01 0.64 20.21 0.57 1.13 0.12 −0.8~−0.6 0.05 2.28 43.79 1.23 1.86 0.62 −0.6~−0.4 0.13 6.60 142.80 4.00 1.65 0.50 −0.4~−0.2 0.31 15.84 458.93 12.85 1.23 0.21 −0.2~0 0.58 29.18 1144.97 32.05 0.91 −0.09 0~0.2 0.55 27.58 1010.38 28.28 0.98 −0.02 0.2~0.4 0.24 11.93 501.62 14.04 0.85 −0.16 0.4~0.6 0.08 4.05 171.91 4.81 0.84 −0.17 0.6~0.8 0.03 1.32 53.27 1.49 0.89 −0.12 >0.8 0.01 0.59 24.92 0.70 0.85 −0.16 距断层距离/km <1 0.42 21.35 282.66 7.91 2.70 0.99 1~2 0.36 18.02 282.74 7.91 2.28 0.82 2~3 0.23 11.83 253.39 7.09 1.67 0.51 3~4 0.13 6.74 198.62 5.56 1.21 0.19 4~5 0.16 8.33 186.26 5.21 1.60 0.47 5~6 0.19 9.60 176.83 4.95 1.94 0.66 6~7 0.14 6.83 166.75 4.67 1.46 0.38 7~8 0.03 1.55 124.82 3.49 0.44 −0.82 8~9 0.02 1.23 136.00 3.81 0.32 −1.14 9~10 0.02 1.23 95.39 2.67 0.46 −0.78 >10 0.27 13.29 1701.76 46.73 0.29 −1.24 地层 第四系 0.47 23.67 694.20 19.43 1.22 0.20 侏罗系 0.00 0.00 5.79 0.16 0.00 0.00 三叠系 0.53 26.85 1195.33 33.46 0.80 −0.22 二叠系 0.68 34.41 973.57 27.25 1.26 0.23 石炭系 0.01 0.32 31.15 0.87 0.37 −0.99 泥盆系 0.29 14.75 672.76 18.83 0.78 −0.25 降雨量/mm 554~571 0.32 16.02 156.72 4.39 3.65 1.29 571~582 0.66 33.36 445.17 12.46 2.68 0.99 582~590 0.51 25.58 595.83 16.68 1.53 0.43 590~598 0.27 13.65 746.20 20.89 0.65 −0.43 598~606 0.16 8.24 607.02 16.99 0.48 −0.73 606~615 0.04 1.96 438.82 12.28 0.16 −1.83 615~626 0.01 1.19 333.59 9.33 0.13 −2.04 626~639 0.00 0.00 169.48 4.74 0.00 0.00 639~659 0.00 0.00 79.96 2.24 0.00 0.00 距水系距离/km <0.2 0.52 26.08 412.24 11.54 2.26 0.82 0.2~0.4 0.25 12.74 395.79 11.08 1.15 0.14 0.4~0.6 0.19 9.47 378.06 10.58 0.89 −0.12 0.6~0.8 0.18 9.33 355.84 9.96 0.94 −0.06 0.8~1.0 0.19 9.65 328.86 9.20 1.05 0.05 1.0~1.2 0.18 8.88 295.52 8.27 1.07 0.07 1.2~1.4 0.16 8.19 260.91 7.30 1.12 0.11 1.4~1.6 0.12 6.05 225.50 6.31 0.96 −0.04 1.6~1.8 0.03 1.41 188.56 5.28 0.27 −1.31 1.8~2.0 0.07 3.38 153.32 4.30 0.78 −0.25 >2.0 0.10 4.82 578.20 16.18 0.30 −1.20 NDVI −0.75~−0.15 0.00 0.00 5.20 0.15 0.00 0.00 −0.15~0.08 0.00 0.09 3.70 0.10 0.88 −0.13 0.08~0.27 0.26 13.2 99.87 2.80 4.72 1.55 0.27~0.40 0.49 24.85 158.74 4.44 5.59 1.72 0.40~0.50 0.47 23.85 299.27 8.38 2.85 1.05 0.50~0.60 0.39 19.66 419.73 11.75 1.67 0.51 0.60~0.70 0.25 12.74 595.47 16.67 0.76 −0.27 0.70~0.80 0.11 5.43 1030.79 28.84 0.19 −1.66 0.80~1.00 0.00 0.18 960.04 26.87 0.01 −4.61 距道路距离/km <0.2 0.46 23.40 285.40 7.99 2.93 1.08 0.2~0.4 0.20 10.29 268.18 7.51 1.37 0.31 0.4~0.6 0.13 6.6 252.80 7.08 0.93 −0.07 0.6~0.8 0.16 8.28 235.52 6.59 1.26 0.23 0.8~1.0 0.18 9.19 216.71 6.07 1.52 0.42 1.0~1.2 0.12 6.28 202.54 5.67 1.11 0.10 1.2~1.4 0.12 6.19 190.95 5.34 1.16 0.15 1.4~1.6 0.12 6.14 176.72 4.95 1.24 0.22 1.6~1.8 0.09 4.60 161.19 4.51 1.02 0.02 1.8~2.0 0.11 5.51 146.41 4.09 1.34 0.29 >2.0 0.27 13.52 1436.39 40.20 0.34 −1.08 4. 岷县滑坡易发性评价
4.1 基于RBFNN-I耦合模型
为了满足对RBFNN-I耦合模型进行建模与训练,从1098个(滑坡点549个,非滑坡点549个)总样本点中随机选取80%的数据(滑坡点439个,非滑坡点439个)作为训练样本点,剩余20%的数据作为检验样本点,进行标准耦合模型的训练。在模型确定以后,将研究区的全部栅格数据作为数据源,调用已训练完成的RBFNN-I耦合模型预测每个栅格数据的滑坡易发性指数,最后在GIS中绘制并输出预测结果。依据中国地质调查局《地质灾害调查技术要求(1∶50000)》(DD2019-08)[25]中关于滑坡灾害易发性评价的技术标准,对研究区滑坡易发性进行分级。采用自然间断分级法将RBFNN-I耦合模型的评价结果划分为极高易发区、高易发区、中易发区、低易发区4个等级分区,生成岷县滑坡灾害易发性分区图(图5)。
4.2 评价结果检验分析
4.2.1 评价结果合理性检验
为了检验已建模型的客观性和稳定性,统计RBFNN-I模型计算得到的极高、高、中和低4个等级的易发区面积,以及各等级易发区内滑坡点的分布数量,统计结果如表3所示。
表 3 岷县滑坡灾害易发性分区合理性检验表Table 3. Rationality test table of landslide susceptibility zone in Min Xian模型类型 易发区等级 P/个 Cp /% S/km2 Sp/% R RBFNN-I 极高易发区 308 56.10 373.70 10.41 5.39 高易发区 175 31.88 717.96 20.00 1.59 中易发区 51 9.29 975.40 27.17 0.34 低易发区 15 2.73 1522.80 42.42 0.06 注:P代表各等级易发区内滑坡点的数量;Cp代表各等级易发区内的滑坡点数量的比例;S代表各等级易发区的面积;
Sp代表各等级易发区面积占整个研究区总面积的比例;R代表Cp和Sp的比值。从表3中可知,通过RBFNN-I模型得到低易发区的面积比例在划分的各等级分区中最大;极高易发区内滑坡点所占比例为56.10%;耦合模型的比率R值均由低易发区向极高易发区逐渐增大。综上所述,文中构建的RBFNN-I模型计算得到的岷县滑坡易发性区划结果符合模型合理性检验标准。
4.2.2 评价模型精度检验
滑坡灾害易发性评价结果是否准确直接关系到评价模型的可靠性,通过检验评价模型的结果,可以准确地比较出不同评价模型的预测性能,以便选择出最优的滑坡易发性评价模型。因此,文中为了检验耦合模型的性能,分别将单一I、RBFNN模型和RBFNN-I模型的评价结果进行ROC曲线检验分析,得到三种评价模型的ROC曲线,并且统计每种评价模型的ROC曲线下面积AUC值作为一个定量的评价指标来衡量模型预测的准确度,更加直观的表示各种模型的评价结果(图6)。
从图6中可知,RBFNN-I模型的AUC为0.853,表明耦合模型的预测效果较高;并且耦合模型的AUC值优于单一RBFNN和I模型的0.790和0.756,表明RBFNN-I模型比单一RBFNN和I模型具有更好的预测能力,更能较为客观准确地岷县滑坡灾害易发性进行评价。
4.3 岷县滑坡易发性与指标因子分析
指标因子的重要性反映了不同指标因子对于区域滑坡易发性的影响程度,有的指标因子对滑坡的发育作用比较重要,而有的指标因子则对滑坡的影响比较小。因此,计算分析各指标因子的重要性,可以为滑坡灾害管理工作提供指导依据。将通过筛选后的9个指标因子的信息量值作为模型的输入数据,通过RBFNN-I模型分析计算得到每个指标因子的重要性(图7)。
从图7中可知,距断层距离、降雨量、距道路距离和NDVI这4个指标因子的重要性最高,是影响岷县滑坡灾害分布的主控因子。结合表2分析,距断层距离在0~7 km内的频率比值均大于1,且在1 km范围内最大,说明距离断层越近的坡体越容易发生滑坡;降雨量在554~590 mm范围内频率比值均大于1,说明易于发生滑坡。随着降雨量的增加,频率比值并没有显著的增加,主要是由于岷县的地质条件受断层活动等影响极其脆弱,坡体在短时间的降雨作用下就会出现失稳现象,发生滑坡;距道路在0.2 km范围内时,频率比值远大于1,说明距离道路越近滑坡灾害越容易发生,主要是因为岷县的地貌以山地为主,近年来全县的交通建设快速发展,在施工过程中普遍存在削坡扩基等现象,容易造成道路沿线的植被破坏和岩土体失稳,也加剧了地表风化和水土流失,若遭遇强降雨等极端天气极易发生滑坡;NDVI值小于0.08和大于0.60时,频率比值均小于1,且随着NDVI值增大,该值有减小的趋势,DAI等[26]研究认为裸地类型滑坡发生相对较少,当植被覆盖度越高时,植物的根固作用越强,能够降低坡体的侵蚀程度,增加稳定性。
5. 结论
文章以甘肃省岷县为研究区,结合环境条件和历史滑坡灾害的分布特征,运用RBFNN-I模型展开了滑坡灾害易发性评价,得到以下结论:
(1)文章采用的RBFNN-I模型评价的结果与研究区历史滑坡的实际分布情况相吻合。评价精度相比单一的RBFNN模型提高了6.3%,相比单一的I模型精度提高了9.7%,表明RBFNN-I模型具有更高的准确度,能在一定程度上解决单一模型主观性较强、可靠性低等问题,是一种有效的区域滑坡灾害易发性评价方法。
(2)岷县滑坡灾害的极高易发区和高易发区超过总面积的25%,在岷县西部的中寨镇—梅川镇—茶埠镇地区分布比较密集,主要分布在临潭—宕昌断裂带,以及洮河及其支流、闾井河和蒲麻河两侧河谷地带;中易发区主要分布在麻子川镇北部和蒲麻镇东北部地区、寺沟镇和禾驮镇的南部地区、闾井镇的中部、马坞镇和锁龙乡的北部地区分布;低易发区分布在南部和东部地区的高山地带以及中部地形平缓的地区,主要分布在秦许乡,麻子川镇、闾井镇、锁龙乡和马坞镇的南部。距断层距离、降雨量、距道路距离和NDVI是影响岷县滑坡灾害分布的主控因子。
-
图 1 研究区地质图(据1∶50万广东省地质图修编)
1—第四系海陆交互相沉积层;2—古近系华涌组;3—古近系宝月组;4—白垩系三水组;5—侏罗系金鸡组;6—三叠系小坪组;7—石炭系测水组;8—石炭系石磴子组;9-—石炭系大赛坝组;10—泥盆系天子岭组;11—石炭-泥盆系帽子峰组;12—泥盆系春湾组;13—泥盆系老虎头组;14—泥盆系杨溪组;15—寒武系水石组;16—寒武系高滩组;17—寒武系牛角河组;18—南华系活道组;19—南华系大绀山组;20—侏罗系二长花岗岩;21—三叠系二长花岗岩;22—三叠系花岗闪长岩;23—二叠系二长花岗岩;24—志留系二长花岗岩;25—三洲盆地范围;26—地质界线;27—断层;28—向斜轴部;29—岩溶塌陷点及编号;30—地下水径流方向
Figure 1. Geological map of the study area(According to 1∶50000 geological map revision of Guangdong Province)
表 1 研究区岩溶塌陷基本特征表
Table 1 Basic characteristics of karst collapse in the study area
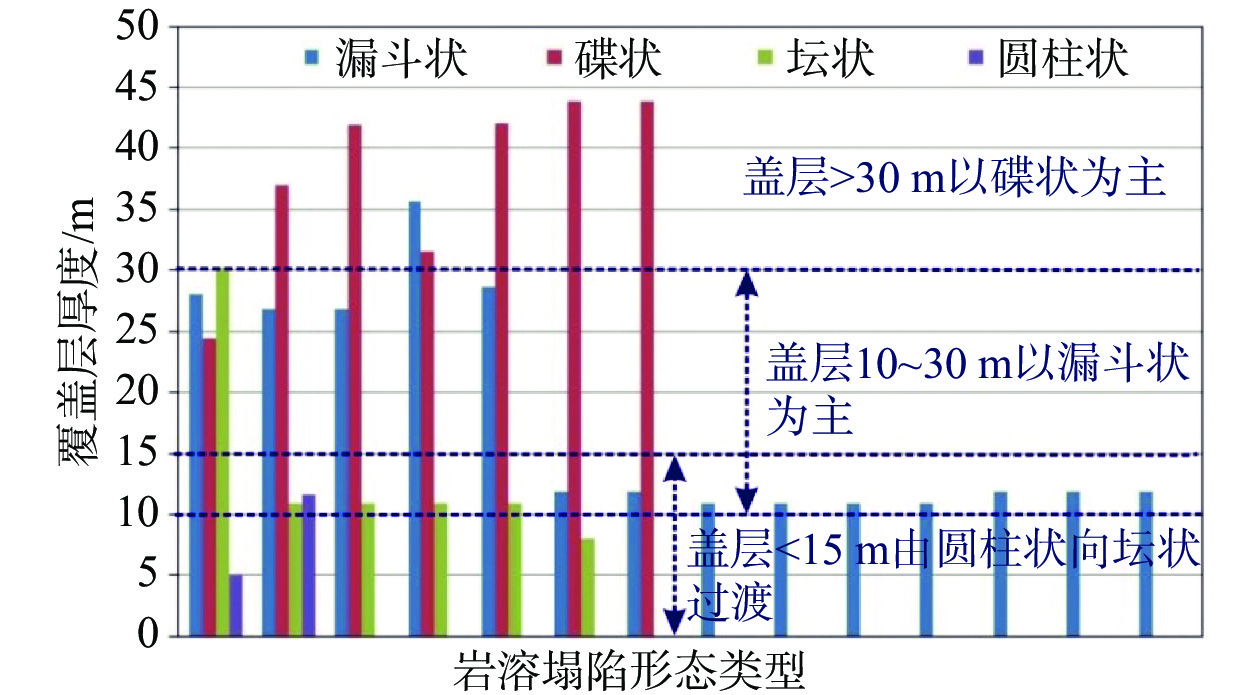
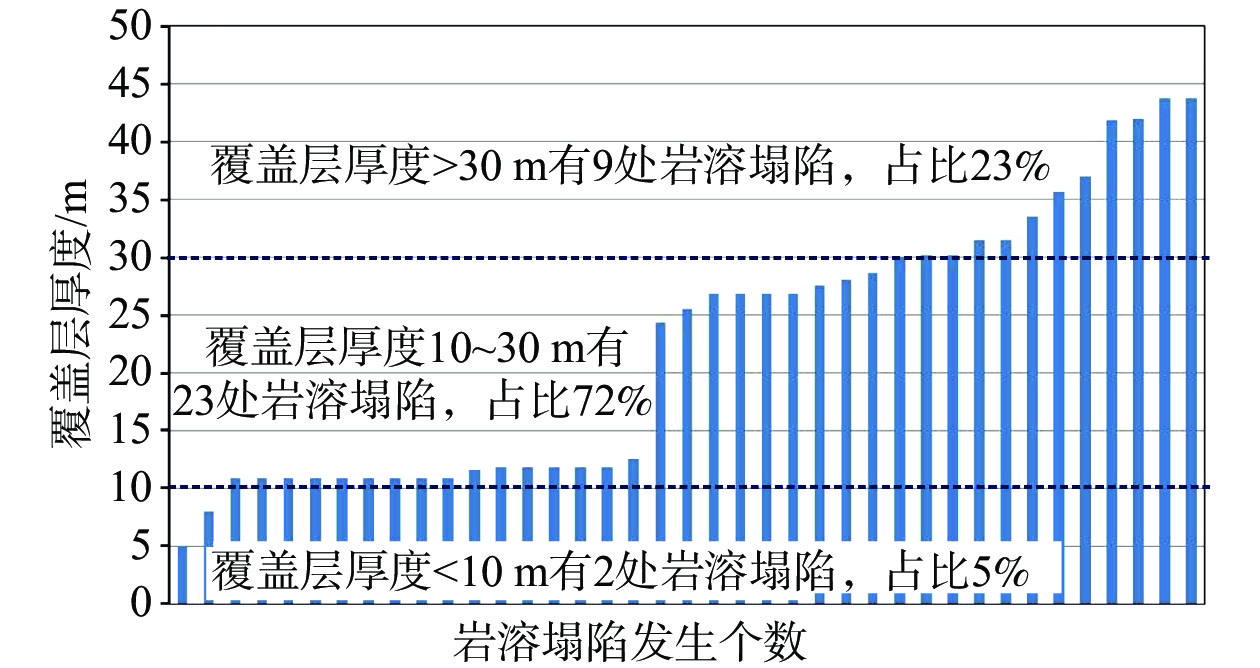
序号 编号 位置 发灾日期 规模/(m×m×m) 形态 覆盖层/m 诱因 长 宽 深 (平面/剖面) 厚度 结构 1 TX1 富湾李家村开田北侧 2005-04-25 22.5 22 7 似圆形/漏斗状 28.00 双层 自然 2 TX2 富湾西安河内 直径:5 4 圆形/未知* 26.80 双层 自然 3 TX3 富湾李家村开田东侧 直径:4.6 7 圆形/漏斗状 26.80 双层 自然 4 TX4 富湾李家村开田北东侧 2005-05-08 18 15 7 似圆形/漏斗状 26.80 双层 自然 5 TX5 富湾李家村开田东南鱼塘底 直径:3.7 0.8 圆形/碟状 24.40 多层 自然 6 TX6 富湾西安河内 2006-03-10
干鱼塘时发现10 6 3.5 似圆形/未知* 26.80 双层 自然 7 TX7 直径:5 3.2 圆形/未知* 29.90 双层 自然 8 TX8 直径:4 3.0 圆形/未知* 27.60 多层 自然 9 TX9 0.8 1 1.0 长条形/未知* 33.50 双层 自然 10 TX10 0.8 1 1.0 长条形/未知* 31.50 多层 自然 11 TX11 富湾关家村南侧 2005-11-14 直径:14 — 似圆形/碟状 37.00 多层 钻探 12 TX12 富湾安华路中部 2011-01-13 直径:30 4~5 似圆形/碟状 41.90 多层 钻探 13 TX13 富湾安华路北侧(6)号楼旁 2011-01-13 直径:15 1~2 圆形/碟状 31.50 多层 钻探 14 TX14 富湾安华路北侧 2011年1月 直径:2 0.5 似圆形/碟状 42.00 多层 钻探 15 TX15 富湾官棠村东侧甘蔗地内 1991-08-17 4.6 4 5 长条形/未知* 25.50 多层 钻探 16 TX16 荷城街道纪念中学升旗广场 2012-09-30 直径:20 0.2 圆形/碟状 43.80 多层 钻探 17 TX17 荷城街道纪念中学足球场 2012-09-10 直径:25 1.5 圆形/碟状 43.80 多层 钻探 18 TX18 荷城街道沧江路跨线桥处 2008-03-06 直径:3.2 3 似圆形/漏斗状 35.70 多层 钻探 19 TX19 富湾佛山监狱门口 2011-01-09 直径:4 1.5 似圆形/坛状 30.20 多层 钻探 20 TX20 富湾佛山监狱门口以东西江河床 2011-01-09发现 直径:3.2 3 圆形/未知* 30.20 多层 自然 21 TX21 明城西部滃江村西侧田间 2012-04-28 3.7 3.3 3 似圆形/漏斗状 11.90 多层 采矿抽水 22 TX22 明城西部洞心村村口田间 2003-03-19 直径:4 1.65 圆形/漏斗状 11.90 单层 采矿抽水 23 TX23 明城西部洞心村村口民房旁 2002年10月 直径:2 1.5 圆形/漏斗状 11.90 单层 采矿抽水 24 TX24 明城西部三桠村东侧田间 2010-05-21 4 2 圆形/漏斗状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 25 TX25 明城西部三桠村东侧水泥路 2010-06-13 10.5 7.3 2.8 长条形/坛状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 26 TX26 明城西部三桠村东南侧田间 2010-06-20 直径:3 — 圆形/漏斗状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 27 TX27 明城西部黎山村东侧水泥路 2010年7月 直径:4 2 圆形/坛状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 28 TX28 明城西部三桠村东侧 2010-08-19 直径:4 1.2 圆形/坛状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 29 TX29 明城西部三桠村南东侧 2011年5月 3 2 1.5 椭圆形/坛状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 30 TX30 明城西部黎山村南侧田间 2011-09-16 直径:2 1.2 圆形/坛状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 31 TX31 明城西部黎山村东侧 2012-03-05 直径:1.5 0.8 圆形/漏斗状 10.90 多层 采矿抽水 32 TX32 明城西部朗心村北侧鱼塘边 2011-06-23 5.5 4 2.5 椭圆形/漏斗状 10.90 单层 采矿抽水 33 TX33 明城西部下高朗东侧田间 2012-01-07 直径:2 6 圆形/圆柱状 5.00 双层 采矿抽水 34 TX34 明城西部巷口村西侧田间 2009-09-16 直径:2 1.2 圆形/未知* 12.50 单层 采矿抽水 35 TX35 明城西部朗心村南侧田间 2002-10-18 直径:2 1 圆形/漏斗状 11.90 单层 采矿抽水 36 TX36 明城西部鲤江村南侧田间 2012-06-25 直径:2 1.1 圆形/漏斗状 11.90 双层 采矿抽水 37 TX37 明城东部八达园大酒店东侧 2008-06-29 4.6 3.8 2 似圆形/漏斗状 28.60 单层 自然 38 TX38 明城北部新岗陈村南侧 2008-10-16 3 2.6 1.1 似圆形/圆柱状 11.60 单层 自然 39 TX39 明城谭朗村委海涌村西北侧 2016-10-11 7.5 4.3 1.8 椭圆形/坛状 8.00 单层 养殖抽水 注:未知*指的是因缺资料查证导致未知。 表 2 研究区金鸡组地层中岩溶塌陷点岩土体特征表
Table 2 soil Characteristics of karst collapse in Jinji group in the study area
塌陷编号 塌陷点岩土体特征 TX1 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(3.90 m)、粉土(5.30 m)、细砂(17.30 m)、残坡积土(1.50 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX2 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(3.80 m)、含淤质粉土(2.70 m)、细砂(17.00 m)、砾砂(0.90 m)、残坡积土(2.40 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX3 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(3.90 m)、粉砂(11.10 m)、粉质黏土(2.20 m)、残坡积土(9.60 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX4 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(3.90 m)、粉砂(11.10 m)、粉质黏土(2.20 m)、残坡积土(9.60 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX5 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(3.90 m)、淤泥质土(6.40 m)、粉砂(4.20 m)、细砂(0.90 m)、粉土(1.80 m)、残坡积土(7.20 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX6 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(3.80 m)、含淤质粉土(2.70 m)、细砂(17.00 m)、砾砂(0.90 m)、残坡积土(2.40 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX7 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(2.60 m)、淤质粉土(3.40 m)、细砂(8.60 m)、粉砂(3.90 m)、残坡积土(11.40 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX8 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉土(1.60 m)、粉砂(2.00 m)、淤泥质土(9.90 m)细砂(5.00 m)、粉质黏土(4.90 m)、残坡积土(4.20 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX9 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(5.20 m)、淤泥(1.80 m)、粉细砂(8.80 m)、淤泥质土(13.00 m)、粉细砂(4.70 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX10 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉土(2.20 m)、细砂(3.50 m)、粉砂(1.70 m)、细砂(1.90 m)、淤泥质土(12.20 m)、淤质粉土(1.50 m)、细砂(7.00 m)、残坡积土(1.50 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX11 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:粉质黏土(6.70 m)、粉土(2.40 m)、细砂(9.40 m)、淤泥质土(0.90 m)、细砂(2.20 m)、粉质黏土(1.60 m)、粉土(3.80 m)、残坡积土(10.00 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX12 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:人工填土(1.80 m)、粉质黏土(1.50 m)、淤泥(7.20 m)、粗砂(13.10 m)、中砂(18.30 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX13 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:人工填土(4.00 m)、粉质黏土(0.80 m)、淤泥(7.00 m)、中砂(5.40 m)、淤泥(9.00 m)、中砂(5.30 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX14 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:人工填土(3.70 m)、淤泥(4.50 m)、粉砂(1.80 m)、淤泥(3.80 m)、粉砂(4.80 m)、中砂(13.70 m)、粉砂(9.70 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX18 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:人工填土(7.50 m)、粉质黏土(5.50 m)、淤泥质土(5.00 m)、粉砂(2.80 m)、粗砂(3.20 m)、粉土(1.00 m)、粗砂(0.50 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩 TX19 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:人工填土(9.50 m)、粉质黏土(1.40 m)、含砂粉土(2.50 m)、中砂(0.40 m)、粉土(0.70 m)、含砂粉土
(3.00 m)、粉质黏土(5.30 m)、粉土(3.20 m)、粗砂(4.20 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩TX20 ①覆盖层土体自上而下分别为:人工填土(9.50 m)、粉质黏土(1.40 m)、含砂粉土(2.50 m)、中砂(0.40 m)、粉土(0.70 m)、含砂粉土
(3.00 m)、粉质黏土(5.30 m)、粉土(3.20 m)、粗砂(4.20 m);②下伏基岩为金鸡组角砾状灰岩表 3 研究区不同时段岩溶塌陷发生频数表
Table 3 Frequency of karst collapse in different periods in the study area
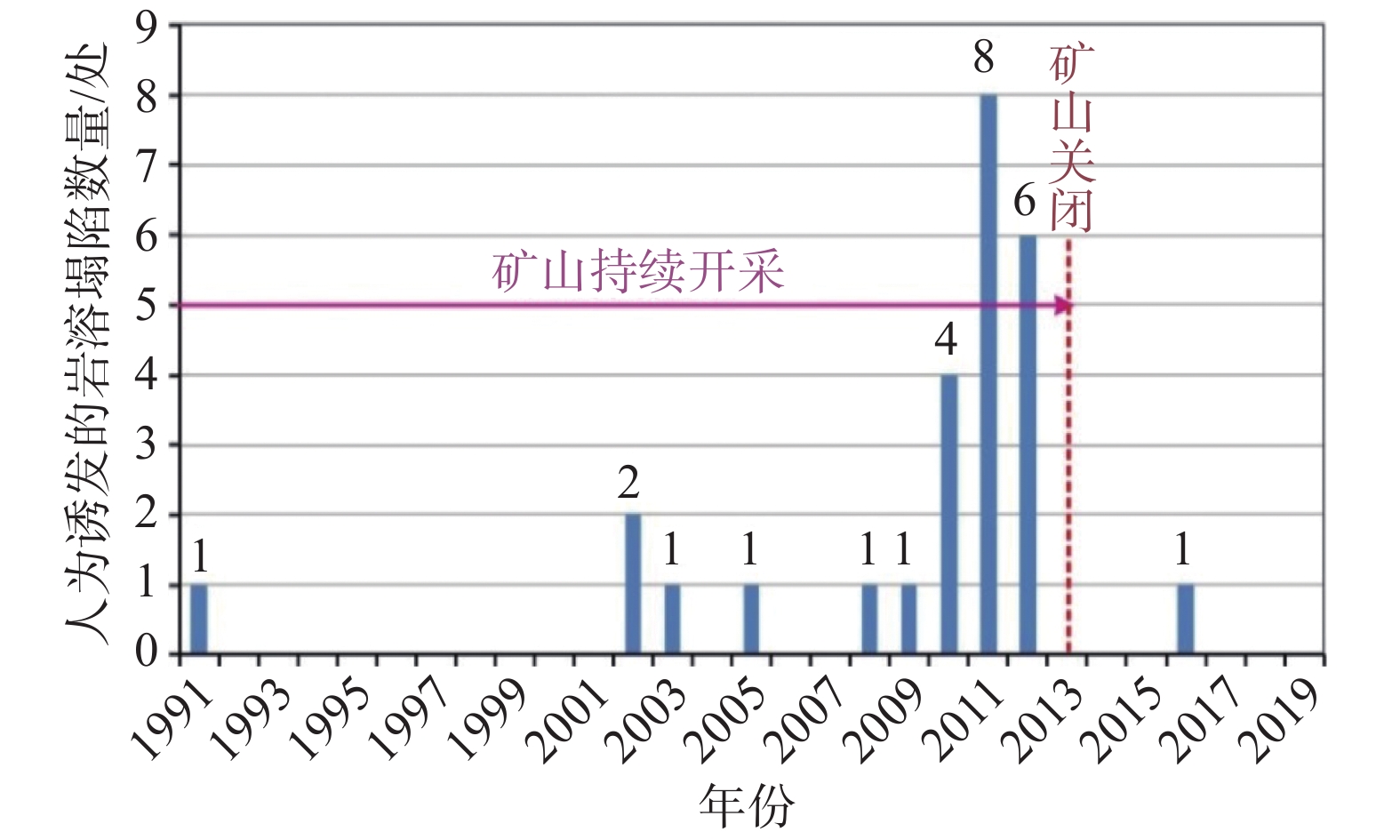
时段 岩溶塌陷发生次数/处 总数 自然塌陷 人为塌陷 1995年以前 1 1 — 1995—2000年 0 — — 2000—2005年 9 5 4 2005—2010年 14 6 8 2010—2013年 14 1 13 2013年以后 1 — 1 -
[1] 国务院办公厅. 国务院办公厅关于佛山市城市总体规划的通知(国办函﹝2016﹞107号)[EB].2016. General Office of the State Council. Notice on the overall planning of Foshan City[EB]. 2016.(in Chinese)
[2] 佛山市统计局, 国家统计局佛山调查队. 2019年佛山市国民经济和社会发展统计公报[R]. 2020. Foshan Municipal Bureau of Statistics, Foshan investigation team of National Bureau of Statistics. National economic and social development statistics bulletin of Foshan in 2019[R].2020.(in Chinese)
[3] 广东省佛山地质局. 佛山市城市地质调查报告(2010年度)[R]. 2011. Foshan Geological Bureau of Guangdong Province. Urban geological survey report of Foshan City(2010year)[R]. 2011.(in Chinese)
[4] 广东省佛山地质局. 广东省佛山市南海区大沥镇黄岐海北片区地质灾害勘查报告[R]. 2009. Foshan Geological Bureau of Guangdong Province. Geological hazard investigation report of Huangqi Haibei area, Daili Town, Nanhai District, Foshan City, Guangdong Province[R]. 2009.(in Chinese)
[5] 广东佛山地质工程勘察院. 广东省佛山市高明区荷城街道富湾安华路地面塌陷地质灾害勘查报告[R]. 2011. Guangdong Foshan Geological Engineering Survey Institute. Geological disaster investigation report of ground collapse of Fuwan Anhua Road, Hecheng Street, Gaoming District, FoshanCity, Guangdong Province[R]. 2011.(in Chinese)
[6] 董好刚, 黄长生, 陈雯, 等. 珠江三角洲环境地质控制性因素及问题分析[J]. 中国地质,2012,39(2):539 − 549. [DONG Haogang, HUANG Changsheng, CHEN Wen, et al. The controlling factors of environment geology in the Pearl River Delta Economic Zone and an analysis of existing problems[J]. Geology in China,2012,39(2):539 − 549. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3657.2012.02.025 [7] 郑晓明, 金小刚, 陈标典, 等. 湖北武汉岩溶塌陷成因机理与致塌模式[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(5):75 − 82. [ZHENG Xiaoming, JIN Xiaogang, CHEN Biaodian, et al. Mechanism and modes of Karst collapse in Wuhan City, Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(5):75 − 82. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 蒙彦, 郑小战, 雷明堂, 等. 珠三角地区岩溶分布特征及发育规律[J]. 中国岩溶,2019,38(5):746 − 751. [MENG Yan, ZHENG Xiaozhan, LEI Mingtang, et al. Karst distribution and development in the Pearl River Delta[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2019,38(5):746 − 751. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 张永定, 张澄博, 李洪艺, 等. 广州市西北区岩溶分布规律浅析[J]. 热带地理,2011,31(3):257 − 261. [ZHANG Yongding, ZHANG Chengbo, LI Hongyi, et al. Distribution characteristics of karst in northwestern Guangzhou[J]. Tropical Geography,2011,31(3):257 − 261. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5221.2011.03.005 [10] 刘江龙, 刘会平, 吴湘滨. 广州市地面塌陷的形成原因与时空分布[J]. 灾害学,2007,22(4):62 − 65. [LIU Jianglong, LIU Huiping, WU Xiangbin. Mechanism and temporal-spatial distribution of ground collapse in Guangzhou[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2007,22(4):62 − 65. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2007.04.014 [11] 周长松, 邹胜章, 朱丹尼, 等. 广昆铁路复线秀宁隧道大皮坡—中村段岩溶塌陷成因[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(3):146 − 152. [ZHOU Changsong, ZOU Shengzhang, ZHU Danni, et al. An analysis of the cause of Karst collapses near the Dapipo-Zhongcun section of the Xiuning tunnel of the Guangzhou-Kunming railway[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(3):146 − 152. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 余政兴, 金福喜, 段选亮. 河床透-阻型岩溶塌陷形成机理[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):57 − 66. [YU Zhengxing, JIN Fuxi, DUAN Xuanliang. Formation mechanism of Karst collapse with unconfined aquifer-aquitaed system in riverbed[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):57 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 蒙彦, 黄健民, 贾龙. 基于地下水动力特征监测的岩溶塌陷预警阈值探索—以广州金沙洲岩溶塌陷为例[J]. 中国岩溶,2018,37(3):408 − 414. [MENG Yan, HUANG Jianmin, JIA Long. Early warning threshold of sinkhole collapse based on dynamic characteristics from groundwater monitoring: a case study of Jinshazhou of Guangzhou, China[J]. Carsologica Sinica,2018,37(3):408 − 414. (in Chinese with English abstract) [14] 郑小战. 广花盆地岩溶地面塌陷灾害形成机理及风险评估研究[D].长沙: 中南大学, 2009. ZHENG Xiaozhan. Research on Genetic Mechanism and Risk Evaluation of the Karst Collapse in Guanghua Basin[D].Changsha: Central South University, 2009.(in Chinese with English abstract)
[15] 包全坡. 珠三角岩溶地区桥梁桩基成孔技术[J]. 江苏建筑,2012(6):75 − 77. [BAO Quanpo. Bridge pile foundation drilling technology in Karst area of Pearl River Delta[J]. Jiangsu Construction,2012(6):75 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6270.2012.06.026 [16] 杜均恩, 马超槐, 张国恒. 广东长坑金, 银矿成矿特征[J]. 广东地质,1993(3):1 − 8. [DU Jun’en, MA Chaohuai, ZHANG Guoheng. Metallogenic characteristics of gold and silver deposits in Changkeng, Guangdong Province[J]. Guangdong Geology,1993(3):1 − 8. (in Chinese with English abstract) [17] 罗锡宜, 韩庆定, 邹杰, 等. 佛山市高明区西江新城及周边岩溶发育规律探讨[J]. 华南地震,2017,37(2):34 − 38. [LUO Xiyi, HAN Qingding, ZOU Jie, et al. Study on Karst development law of xijiang new town and surrounding area in Gaoming district of Foshan[J]. South China Journal of Seismology,2017,37(2):34 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 杨华铨,柳金峰,孙昊,赵万玉,张文涛. 四川木里县项脚沟“7·5”特大型泥石流特征及发展趋势分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 100-107 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 王元欢,沈昊文,谢万银,鲁科,胡桂胜. 火后泥石流启动降雨阈值分析——以四川乡城县仁额拥沟泥石流为例. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(01): 108-115 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 徐伟,郑玄,欧文,铁永波,付小麟,宋钰朋,殷万清. 四川凉山州地质灾害灾情特征与主要致灾类型. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(05): 78-89 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 周瑞宸,胡卸文,金涛,曹希超,周永豪,张瑜. 重庆市2022年8月森林火灾火烧区特点及火后泥石流易发性评价. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(05): 150-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄光林,胡卸文,席传杰,周瑞宸,何坤. 四川天全县白果树沟“7·15”泥石流成灾机理. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2024(06): 90-97 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 陈宫燕,李婷,陈军,普布桑姆,阿旺卓玛,旺杰. 基于栅格径流汇流模拟的西藏林芝市泥石流灾害预警模型初探. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(01): 110-120 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 张友谊,王云骏,袁亚东. 基于分形理论和模型试验的沟道物源动储量评价模型. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(05): 40-49 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)











 下载:
下载:



















 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS