Development and distribution rules of geohazards in Diexi- Songpinggou scenic area in a meizoseismal area
-
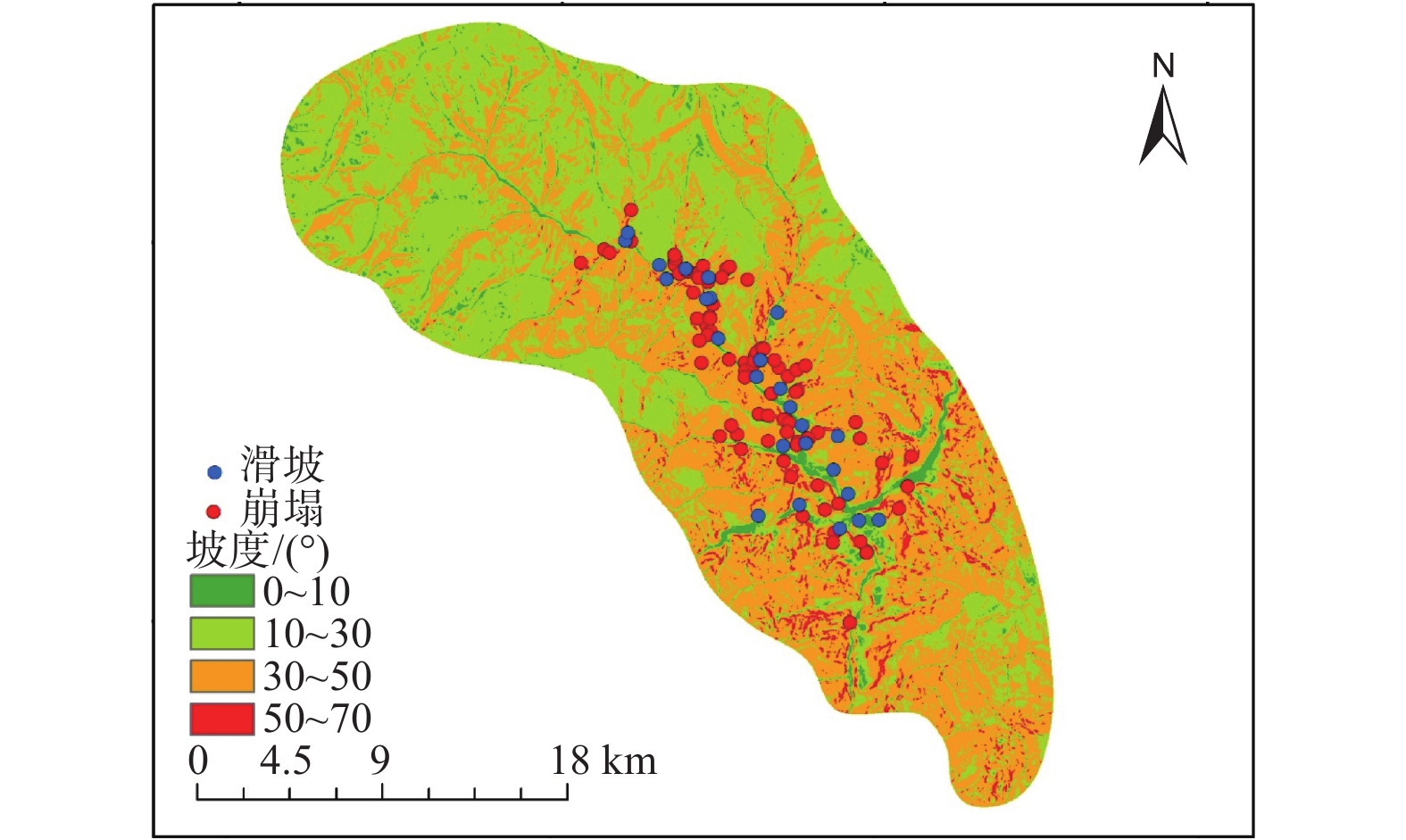
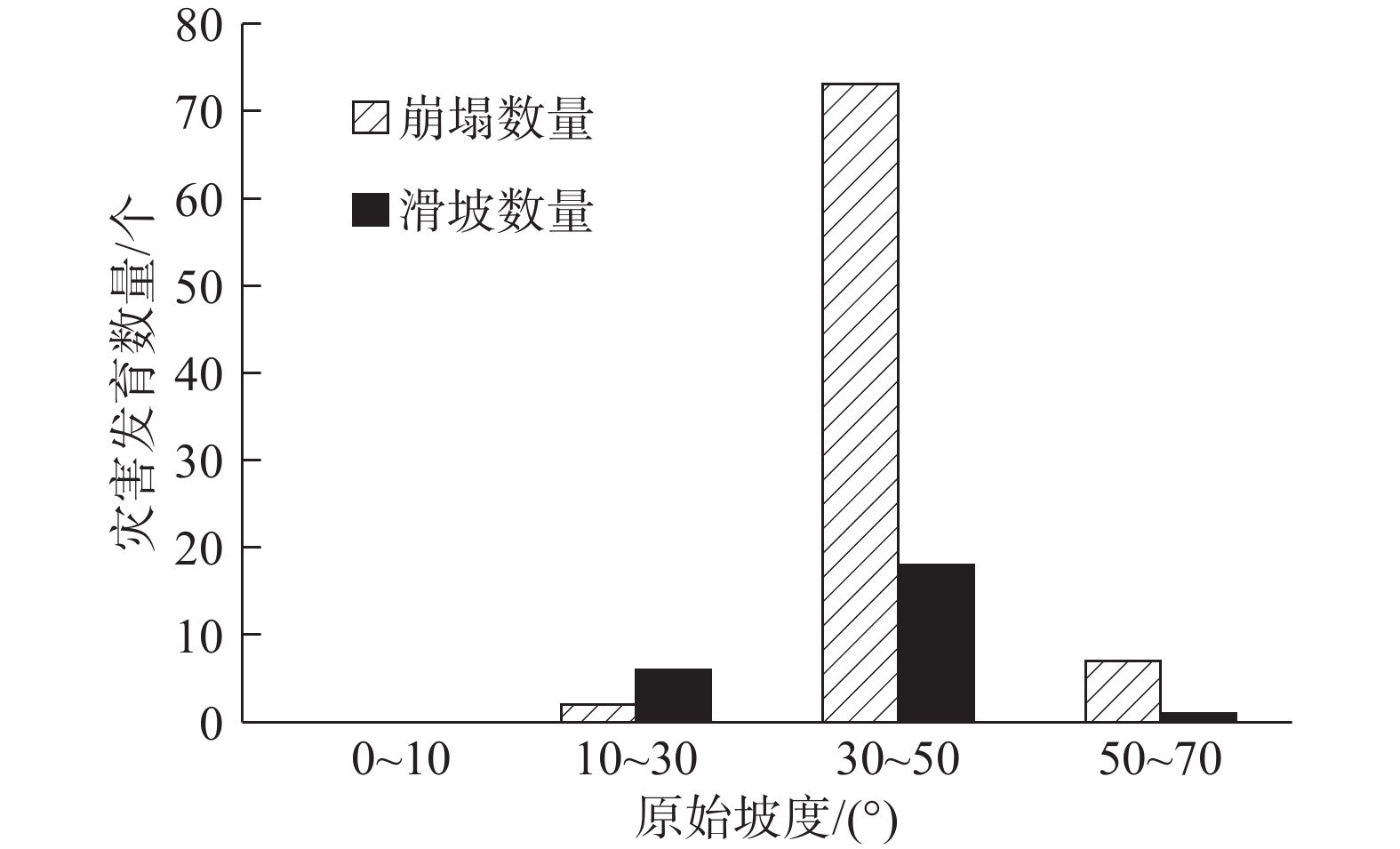
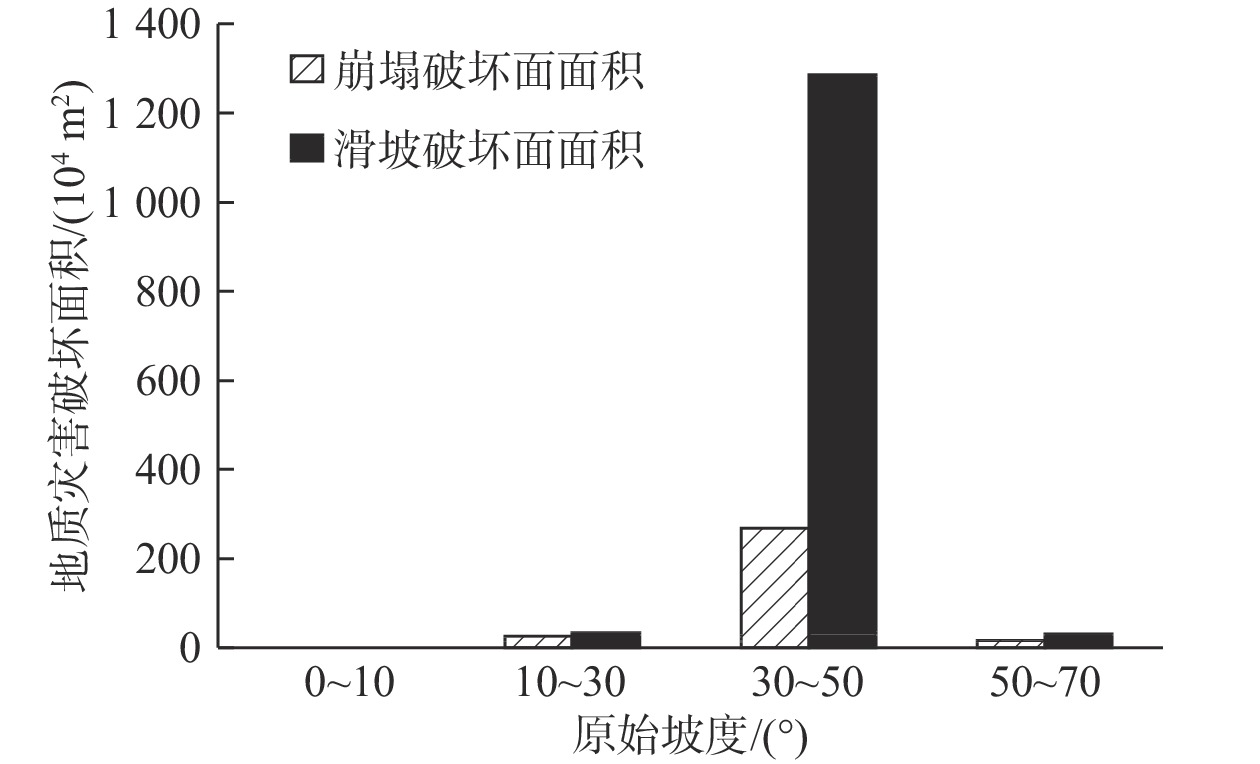
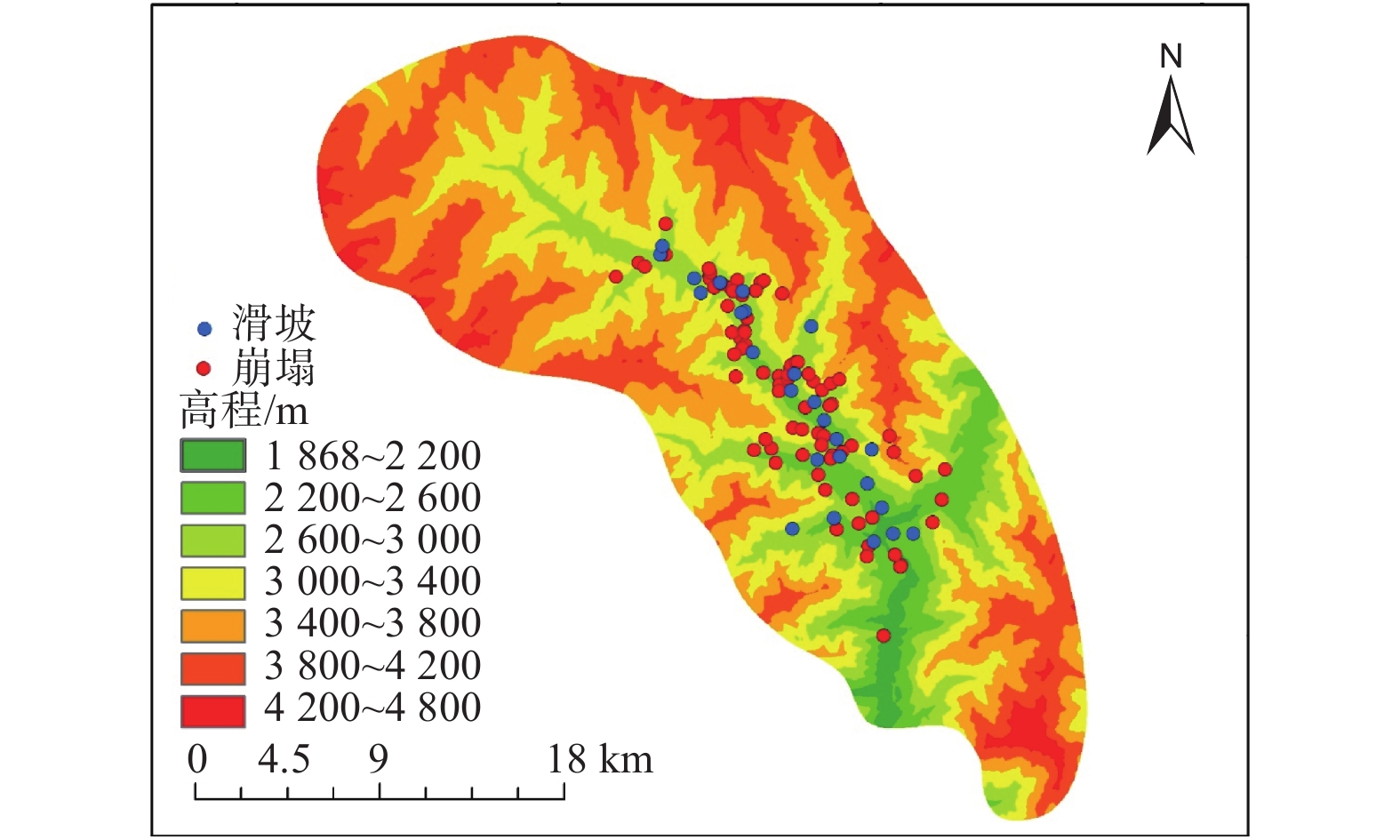
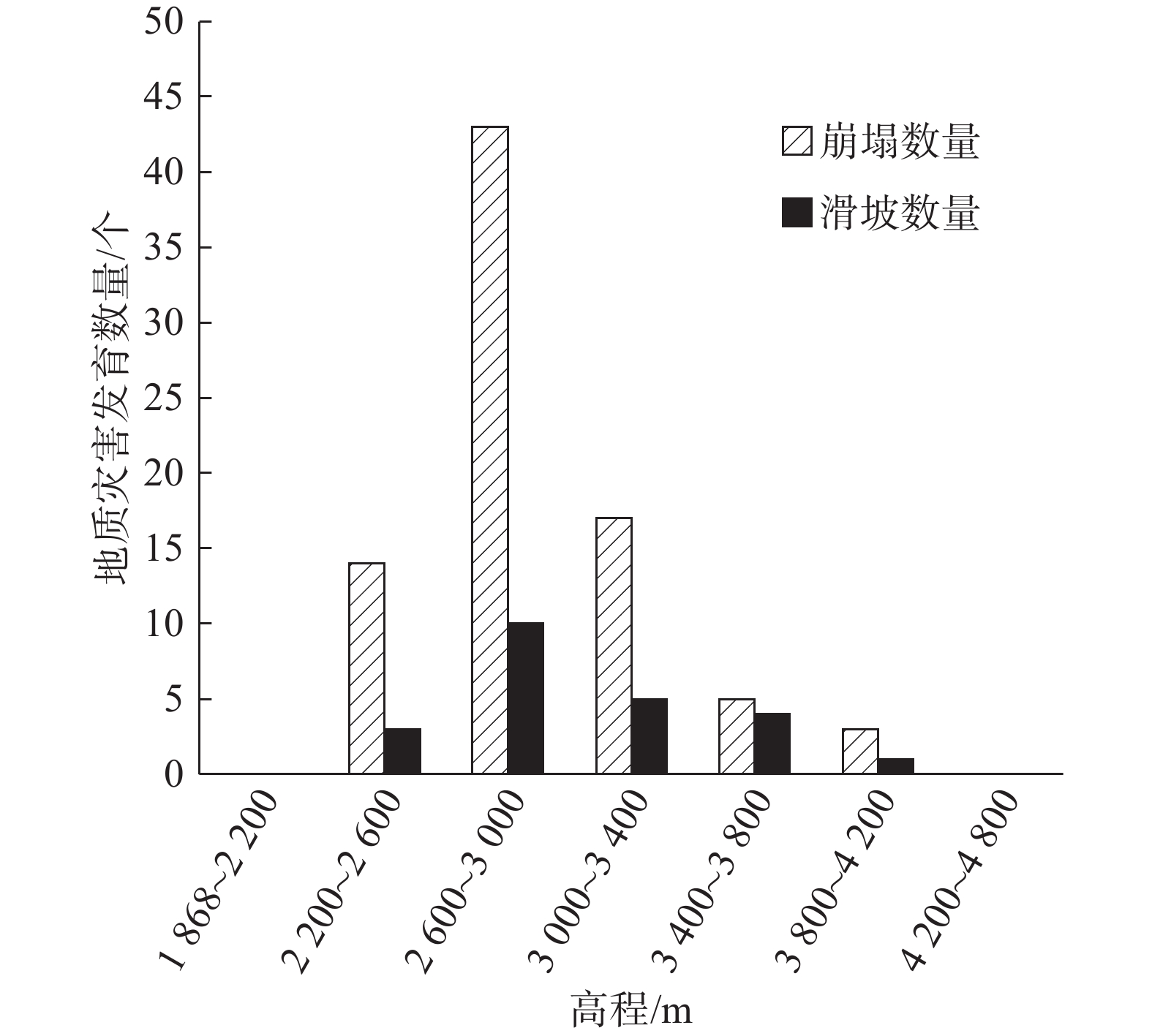
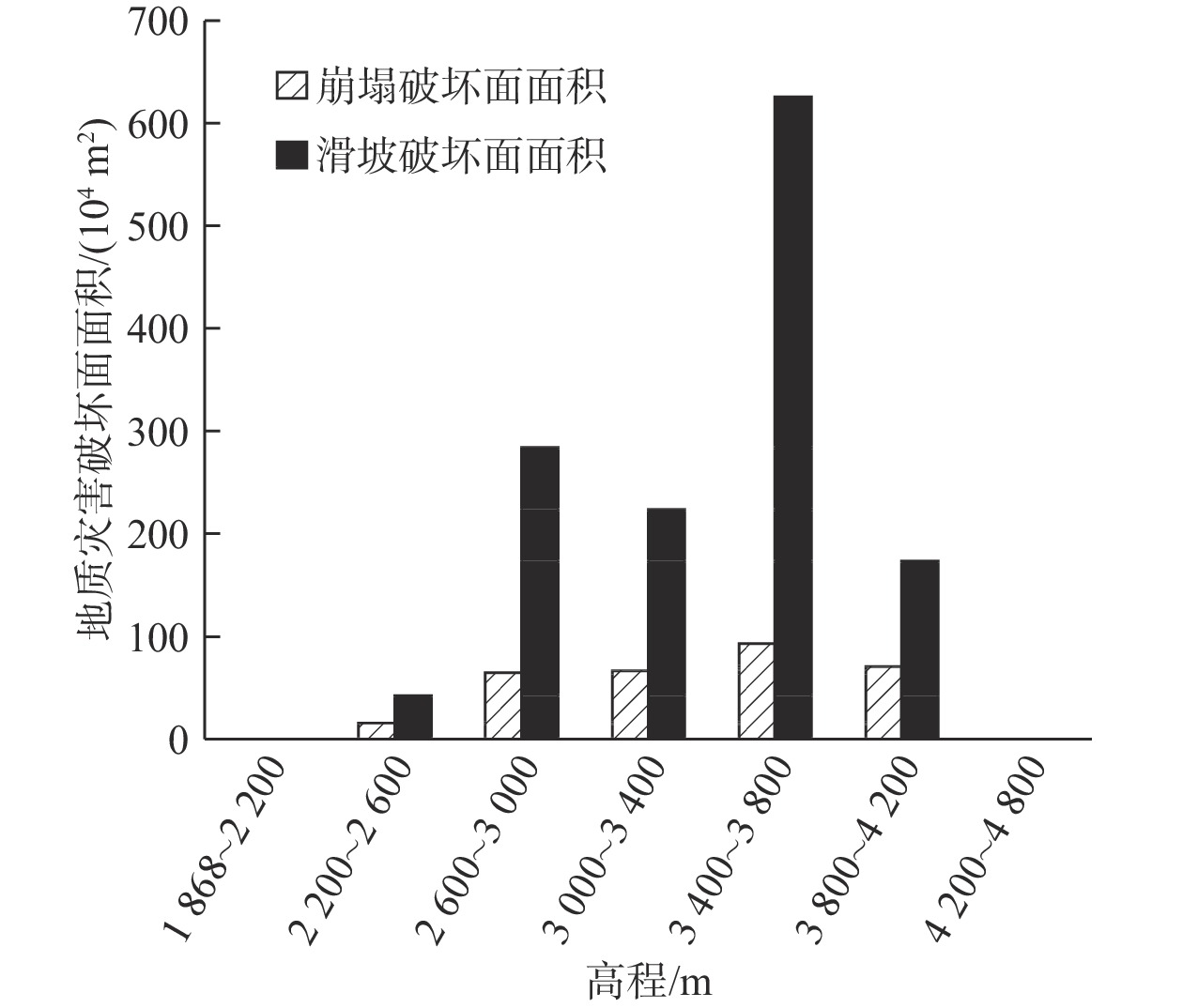
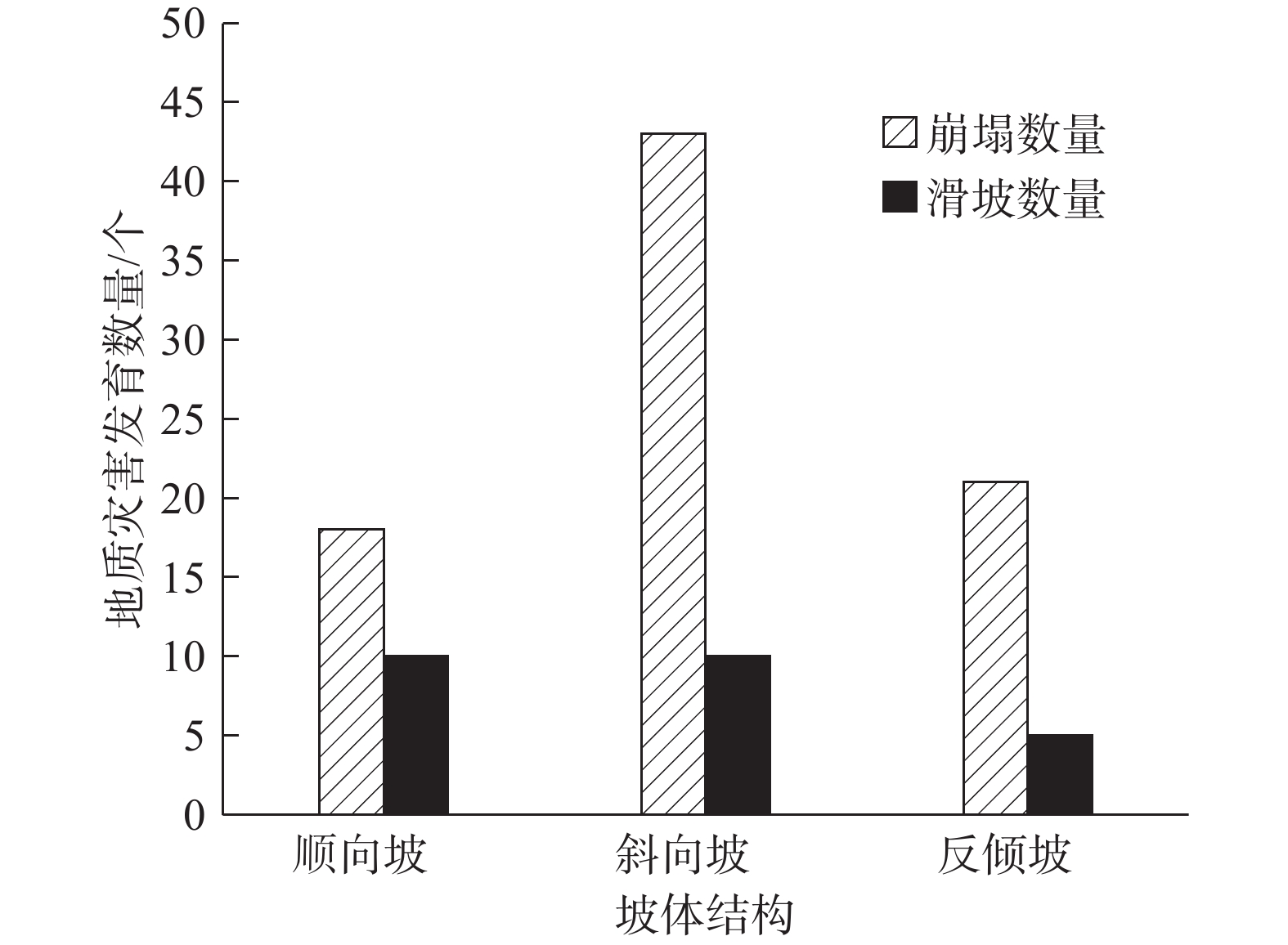
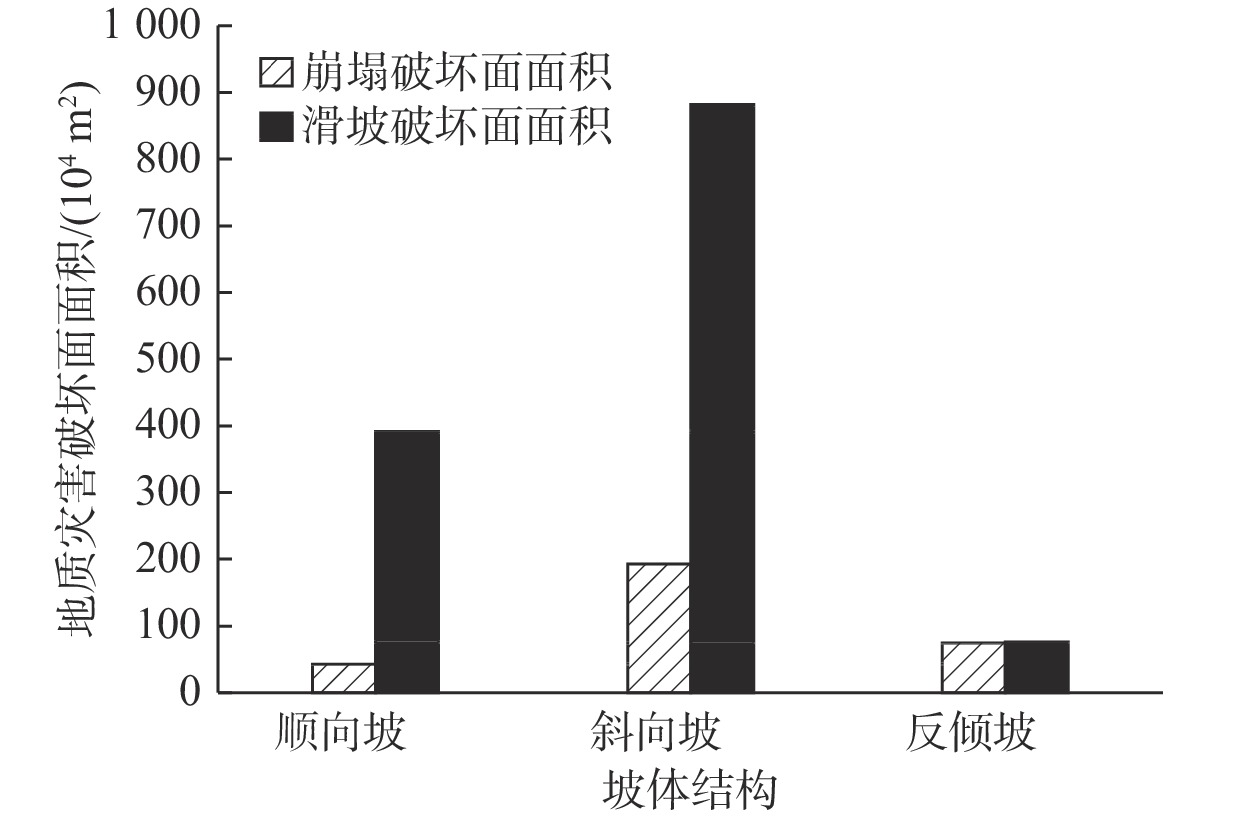
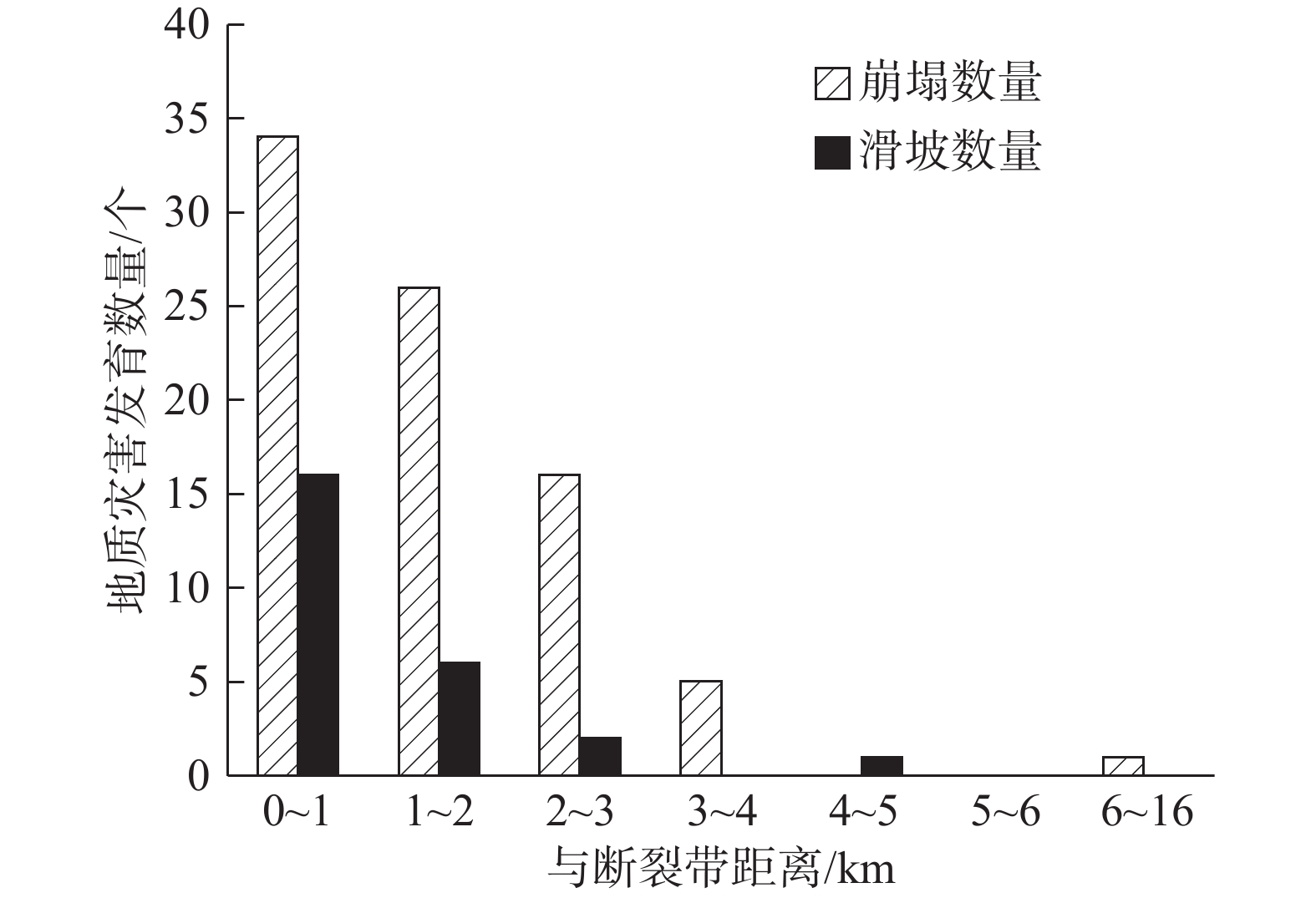
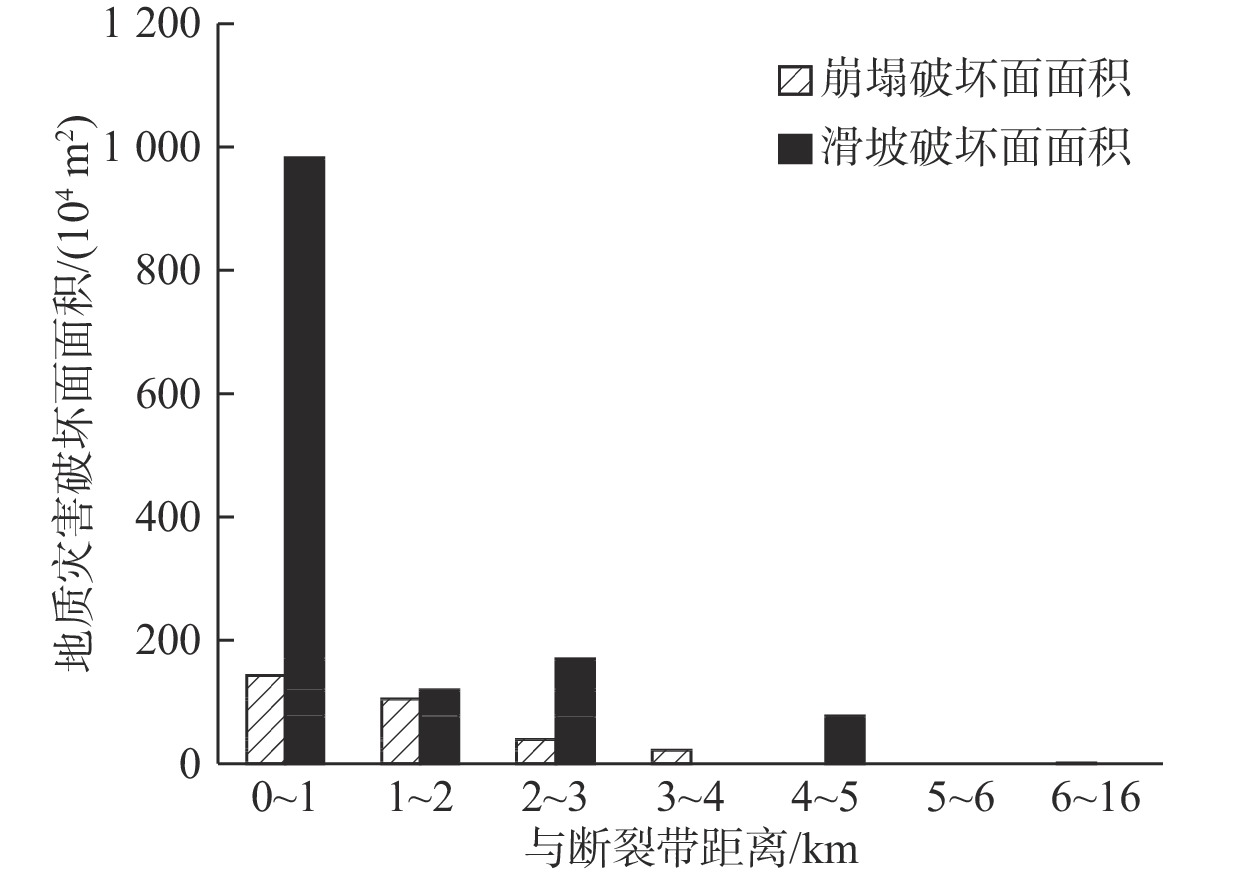
摘要: 以强震区叠溪松坪沟景区为研究范围区,通过多元信息手段调查,共发现地质灾害107处,其中崩塌82处,滑坡25处。地质灾害的发育分布的影响因素包括:原始坡度、高程、坡体结构、水系距离及断裂带距离等。灾害发育分布在坡度30°~50°数量多且规模大;高程2200~3400 m灾害发育数量多,尤其是高程2600~3000 m占总量的42.5%,规模则在高程为3400~3600 m较大;斜向坡体发育地质灾害数量及规模均较大,其次为顺向坡和反倾坡;水系对灾害一般最大影响距离为4.0 km,其中0~1.0 km范围内灾害发育,且规模较大;地质灾害沿地震断裂带呈次“串珠状”分布,0~2.0 km范围内最为显著发育,且符合一定的拟合规律。通过统计归纳分析,厘定了强震区叠溪松坪沟景区范围内地质灾害的发育的主要影响因素,系统的总结了其分布规律,为研究区内的基础建设以及防灾减灾提供了科学依据和参考。Abstract: The Songpinggou scenic area in Diexi was taken as the study area and there are 107 geological disasters were found, including 82 collapses and 25 landslides in this meizoseismal area. The influencing factors of the development and distribution of geological disasters include: original slope, development elevation, slope structure, water system distance and fault zone distance. The number and scale of disasters are distributed in the slope of 30 ° to 50 ° and the number and scale of disasters are large; the number of disasters with elevation of 2200~3400 m accounts for 42.5% of the total, especially the elevation of 2600~3000 m accounts for 42.5% of the total; the number and scale of geological disasters developed in oblique slope are relatively large, followed by consequent slope and reverse slope; the maximum influence distance of water system on disaster is 4.0 km, in which the range of 0~1 km is within. The results show that the geological disasters are developed and large-scale; the distribution of geological disasters along the seismic fault zone is sub "string beads", and the most significant development is in the range of 0~4.0 km, which conforms to a certain fitting law. Based on the statistical analysis, the main influencing factors of the development of geological disasters in the Songpinggou scenic area of Diexi are determined, and the distribution rules are systematically summarized, which provides scientific basis and reference for the infrastructure construction and disaster prevention and mitigation in the study area.
-
0. 前言
老滑坡是斜坡长期变形稳定后的产物,通常处于稳定状态,但不排除在其他外部因素诱发下复活[1-2]。老滑坡的复活多是受降雨、地震、河流侵蚀、冰雪冻融、人类工程活动引起,目前尤为常见。陇海铁路沿线、川藏公路沿线、关中天水盆地以及舟曲县均存在多处老滑坡,这些老滑坡的活动迹象一直是工程建设关注的主要问题[2-8]。
舟曲县位于甘肃省南部,处于中国西藏高原隆起的东北缘,属西秦岭南部构造带。舟曲县因其特殊的地形、岩性和地质构造,是长江中上游著名的滑坡易发区域。由于气候多变、地震频繁、山体脆弱等因素,滑坡和泥石流多发。它也是甘肃省乃至全国地质灾害最严重的地区之一。据1993年调查统计,舟曲县发生山体滑坡100多起,其中灾害性山体滑坡超过30处[9]。区内曾经发生多起老滑坡复活事件,例如,舟曲县峰迭乡水泉沟西南滑坡受2010年泥石流影响,局部发生变形,滑坡前缘受到降雨冲刷,具有一定危险性[10]。舟曲南桥滑坡,属碎屑流滑坡,近二十年来有活动迹象,受降雨和地震影响,有蠕动变形特征[11]。舟曲锁儿头滑坡一直在发生变形,受降雨影响活动性明显,目前的已对该滑坡进行了长期监测,监测显示滑坡位移与降雨量呈增长趋势[12]。舟曲泄流坡滑在2008年汶川地震后开始活跃,该滑坡属顺层页岩滑坡,缓慢蠕动变形,近年来受到降雨的影响,有复活趋势[13]。舟曲南峪江顶崖滑坡在长期的降雨影响下,以及河流侵蚀坡脚,经过持续的活动变形,在2018年7月12日发生复活[1]。以上滑坡均受到了2008汶川地震影响,导致该地区脆弱的地质环境急剧恶化,加剧了地层结构的破坏,增加了松散的岩屑和沉积物。县城老滑坡所在坡体有变形产生,随后一些滑坡发生复活,尤其是降雨季节滑坡的稳定性问题显得尤为重要。
北京时间2019年7月19日晚18时,垭豁口滑坡复活,约3.92 × 106 m3滑体顺坡而下,堵塞河道,造成河水位上升,交通中断。这次滑坡只是局部以流滑形式产出,整体还处于变形阶段。该滑坡的关键问题在于:(1)它的复活原因;(2)特殊的动力学机制;(3)特殊的地貌和地层特征。鉴于此,本文主要报道2019年7月垭豁口滑坡事件的发生原因,并探讨滑坡的形成机制,以期为工程应急处置和具体工程防治提供借鉴。
1. 地质环境特征
垭豁口滑坡区位于甘肃省舟曲县境内,舟曲县属于构造侵蚀地貌,山高谷深,沟壑纵横,该区的地质特征和岩性单元主要受构造活动和地震活动影响较大。舟曲县历史上常发生强烈地震,历史记录中曾发生过16次Ms≥7.0级的地震。垭豁口滑坡位于在两条走滑断层之间,研究区内的两条走滑断层分别呈近东西向和北东向(图1)。舟曲县年平均降雨量为435.8 mm,汛期6—9月降雨量通常高于平均值。汛期时最大日降水量63.3 mm,最大小时降水量47.0 mm。
研究区可见地层为下石炭统板岩、中—上石炭统灰岩、泥盆系千枚岩板岩和第四系冲洪积物。垭豁口滑坡周边基岩主要为下石炭纪的泥质板岩。这类岩体风化严重,易于形成黏土质风化层,并且遇水时膨胀,抗剪性能极差。滑坡前缘为岷江,由南向北流动。滑坡周边、坡脚处以及滑坡对岸有部分建筑物(图1)。研究区内坡体破碎,结构松散,斜坡较陡。总体而言舟曲县地质环境脆弱,水土流失较为严重。地层一直遭受断层活动、历史强震、降雨以及人类工程活动的影响。因此,舟曲县是甘肃乃至全国地质灾害发育的地区。
垭豁口滑坡1989年首次发生时,形成了堰塞湖,造成过严重灾害。本次通过遥感解译,并结合野外详细勘察,查明了原始滑坡以及新复活滑坡的边界。图2为摄于2019年6月30日的垭豁口老滑坡全景图。
2. 2019年复活的垭豁口滑坡
根据滑坡工程地质图(图1),处于休眠期的垭豁口滑坡前后缘海拔分别为1300 m和1960 m,滑坡东西长约1.3 km,滑坡覆盖面积约0.197 km2。而2019年复活后的垭豁口滑坡覆盖面积约0.33 km2。图3(a)和图3(b)分别为垭豁口滑坡2019年复活前后的遥感影像图,表1为垭豁口滑坡历史变形破坏事件统计。
表 1 垭豁口滑坡变形破坏事件统计Table 1. Approximate timeline of slope deformation and failure at the Yahuokou landslide时间轴 垭豁口滑坡活动特征 1989年 滑坡首次滑动,堵塞河道形成堰塞湖 2019-07-16 斜坡中部可见20 cm裂缝,并且该部位30 m的下部土方松动。 2019-07-17 在斜坡下部的路面上可见22 cm的裂缝 2019-07-18 道路塌陷,滑体向前移动约20 m,堆积宽度约30 m。 2019-07-19 滑坡再次发生。在中间部分,滑体向前推动45 m,宽度为50 m。一条300 m长的公路在滑坡的前缘被毁。滑坡体积约
3.92×106 m3,主体距岷江100 m。2019-07-20 滑体又向下推动了10 m,道路周围的农田都发生变形。 2019-07-21 安装了滑坡监测仪器(图3) 2019-08-09—12 滑坡仍在变形。滑坡体处于连续滑动状态,前缘变形区向岷江扩展。 2019-08-14—16 滑坡前缘和中部裂隙增大、变宽,隆起高度增大,偶有碎块落入河中。山体滑坡的松散堆积物坠入河中堵塞宽度约4~8.5 m,部分河道窄至4.8 m。河道上下游水位差约0.4 m,河床略有抬升。 历经多日连续降雨后,2019年7月19日垭豁口滑坡发生复活,约3.92×106 m3滑体一滑而下,堆积坡脚堵塞河道,向坡前推移约45 m,300 m长的公路被滑坡摧毁。滑坡可见高陡后壁,滑动方向约为120°,坡体平均坡度30°,坡度较缓,滑体平均厚度约为20 m(图3)。坡脚堆积的滑体坠入岷江,滑坡前缘剪出口清晰可见,剪出口岩体为揉皱的灰质板岩,层理清晰,局部覆盖碎石土。滑坡下部开口宽度约400 m,中部较窄200 m。中部滑坡流滑区域狭长,前缘堆积体从平面图上看呈现出近似扇形堆积体。滑坡上部区域分为南北两块,见图3(b),此次滑坡发生主要来源于南部区域。
在2019年7月19日之前,滑坡就存在变形迹象。2019年7月16日至19日期间,滑坡上部可见明显裂隙,而在滑坡下部,路基也有鼓胀现象。在7月19日滑坡下滑后,第二天,上部滑体仍然有变形,滑体又向前推移了10 m,毁坏道路及农田。并且滑坡下部排水渠道也被破坏,部分滑体涌入河道,见图4(a)—图4(c)。
垭豁口滑坡自复活后,变形持续发生,滑坡整体还有可能滑动,因此,对该滑坡进行详细的应急调查,清理了河道淤积滑体,并且通过钻探查明了滑坡地层,并在钻孔中布设了滑坡滑速监测仪,见图3(b)。
自7月至8月滑坡一直有活动迹象,监测数据显示(图5),自7月21至8月3日,滑坡上部块体滑速逐渐降低,并趋于稳定。但是,自7月21日至7月30日,滑坡中部和下部块体的滑速达到了0.9 m/h。
8月9日至8月12日,滑坡又发生变形,坡体中下部小路已被冲毁。滑坡体处于蠕动状态,前缘变形区向岷江扩展(图6)。到8月14日至8月16日,滑体前缘南侧裂缝增大、逐渐拓宽,隆起高度增加,偶有碎屑流坠入河中。滑体松散堆积物逐渐坠入河中,堵塞部分河道,原先8~10 m宽的河道变窄至4.8 m。8月15日15时至8月16日7时,滑坡后缘产生1.6 cm裂隙。滑坡中部产生了1 m滑动,平均速度为0.1 m/h。而滑坡下部滑塌了1.83 m,平均速度为0.2 m/h,滑坡前缘向河流推进0.8 m。随后监测到滑体滑动速度有所下降,至8月16日午时后,滑体的滑速度下降到0.1 m/h以下。图5也说明了7月30日至8月14日之间,降雨确实对滑坡活动产生了一定的影响。
滑坡前缘河床轻微隆起,河道上下游水位差约0.4 m。此时开展了第二轮应急抢救,使用挖掘机清理河道及道路滑坡堆积体。8月16日后,滑体中部滑速小范围内波动,滑坡仍处于蠕变阶段。值得庆幸的是,复活的滑坡只造成了部分经济损失,未造成人员伤亡。
3. 滑坡机理探讨
垭豁口滑坡属碎屑流,滑距较长,见图3(c)。滑坡基岩为反倾的碳质板岩,滑坡体主要为板岩碎屑以及部分黏土。钻孔揭示滑坡体岩性由上至下依次为:上层为碎石土和卵砾石,中部为灰黑色砾石及黏土,砾石多为板岩岩屑;下部为含水较高的风化灰色板岩。钻孔岩心可见,滑动面具有明显的擦痕,与水平向夹角8°~19°(图7),且滑动带平均厚度0.6 m,滑体上部较薄,下部逐渐增厚,上部滑动面深度在1.5~8.8 m,中部滑动带深度在15.8~16 m,而下部滑动带深度可达22.6~24 m。
滑坡探槽(图8)揭示该滑坡属缓慢流滑形式,滑带上的擦痕清晰顺直,相对较为光滑。上部滑体为松散的碎屑,下部滑体为软黏土(图8、图9),且滑带厚约0.6~1.0 m。
垭豁口滑坡诱发因素有降雨、地震、人类工程活动、河流侵蚀和断层活动等。该区域内新构造运动非常活跃,区域断层水平滑动速率约1.3 ± 0.1 mm/a,垂向滑动速率约0.39 ± 0.04 mm/a[14]。由于该滑坡位于两条断层之间(图1),近30年来,在该区域附件震级大于Ms5.0的地震多有发生[7, 14-20],地震及滑坡的活动性均受控于区域内的走向断层。
因此,该滑坡的活动性与活动断裂关系密切。根据此次滑坡的应急调查,以及滑速监测,初步判定滑坡复活的主要因素是降雨。强降雨冲刷坡面,连续降雨通过裂隙渗透至滑坡内部,导致滑带软化,抗剪强度急剧降低。降雨及滑速监测数据表明(图5),在集中降雨日,滑坡上中下块体滑动速度呈波动状态,滑坡持续蠕变,且变形逐渐增加。河流对滑坡的侵蚀主要表现为前缘坡脚的侧向侵蚀和冲刷,削弱了滑坡前缘支撑。在滑坡体上修路建房,开挖或加载均对滑坡稳定性造成一定影响。
表1统计了垭豁口滑坡的变形发展历史,此次滑坡复活后,通过详细勘察,初步将滑坡的发生机制总结为(图10):
(1)滑坡发生的主要原因是滑体内部含水量过高,来不及排出,导致滑体发生塑性挤出和缓慢滑动。在滑坡上部(图3和图10),北部块体首先发生滑动。随后,上部南侧块体受到牵引作用,逐渐滑动。上部块体先发生缓慢的塑性流动,在陡坡段滑速加剧。最终,滑坡上部整体滑塌,失稳。上部滑体堆积在中部平台地段,形成“滑移-加载效应”。因而在滑坡中部(图10),受上部堆积体的加载和推挤作用。逐渐产生塑性流动,在中部滑体后缘形成拉槽。该滑坡的变形模式可概括为:蠕变-拉裂-流滑。最终,在滑坡体下部(图10),也以此方式复活。总之,滑坡的上、中、下三部分均以此方式传递应力,逐步被激活,缓慢滑入江中。同时,在蠕变和产生张拉裂缝的作用下,形成了三个相对独立的滑体。
(2)目前滑坡仍处于活跃期,威胁滑坡对岸居民安全(图11)。应急处置只是疏通河道,周边居民部分搬迁撤离。已经实施了滑坡的滑速监测,急需进一步开展具体的防治工程。
4. 结论
2019年7月19日,垭豁口滑坡复活,约3.92 × 106 m3滑体顺坡而下,堵塞河道,造成河道水位上升,交通中断。为查明滑坡的发生机制,判断滑坡后期的活动性,本文基于现场详细勘察、物探工程,以及滑坡监测等手段,探讨了滑坡的动力学过程,主要得到以下结论:
(1)滑带证据显示该滑坡属于流滑运动机制。滑坡的主要诱因是降雨,降水入渗至滑体内部,造成滑带含水率剧增,导致的塑性挤出和缓慢蠕动,最终发生流滑。滑坡发生过程可概括为:首先是上部滑体发生缓慢的塑性流动和滑移,滑坡上部总体滑塌,失稳。其次,上部滑体堆积在滑坡中部,然后对中部原始块体进行预加载和推压。中部块体开始变形,至中部块体后缘形成拉槽,发生塑性流动,失稳。最后,中部块体堆载至滑坡下部,又连带下部滑体复活,三部分滑体一起流入江中,上部块体和中部块体依次对其下部滑体造成堆载,即“滑移—加载效应”。总的变形过程为蠕变—拉裂—流滑。特殊之处在于,滑坡的上、中、下三部分均以这种方式传递应力,逐步被激活,同时形成了三块相对独立的滑体,缓慢地滑入江中。
(2)经过持续降雨后,2019年7月20日至8月16日,垭豁口滑坡历经初期的复活,只是局部以流滑形式产出,而整体仍然处于蠕变阶段,威胁着河对岸的居民。初步的应急处置措施已经实施,包括立警示牌,疏通河道,开展滑坡的监测,后期需要具体的工程防治措施以确保滑坡的稳定。
-
-
[1] 黄润秋, 李为乐. “5·12”汶川大地震触发地质灾害的发育分布规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2008,27(12):2585 − 2592. [HUANG Runqiu, LI Weile. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards induced by Wenchuan earthquake on 12th May, 200[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2008,27(12):2585 − 2592. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2008.12.028 [2] 许强, 李为乐. 汶川地震诱发大型滑坡分布规律研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2010,18(6):818 − 826. [XU Qiang, LI Weile. Distribution of large-scale landslides induced by the Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2010,18(6):818 − 826. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2010.06.002 [3] 戴岚欣, 许强, 范宣梅, 等. 2017年8月8日四川九寨沟地震诱发地质灾害空间分布规律及易发性评价初步研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(4):1151 − 1164. [DAI Lanxin, XU Qiang, FAN Xuanmei, et al. A preliminary study on spatial distribution patterns of landslides triggered by Jiuzhaigou earthquake in Sichuan on August 8th, 2017 and their susceptibility assessment[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(4):1151 − 1164. (in Chinese with English abstract) [4] 王佳运, 张成航, 高波, 等. 玉树震区地质灾害分布规律与发育特征[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(4):508 − 515. [WANG Jiayun, ZHANG Chenghang, GAO Bo, et al. Distribution regularity and development characteristics of geohazards in Yushu earthquake area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(4):508 − 515. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.04.005 [5] 殷志强, 赵无忌, 褚宏亮, 等. “4·20”芦山地震诱发地质灾害基本特征及与“5·12”汶川地震对比分析[J]. 地质学报,2014,88(6):1145 − 1156. [YIN Zhiqiang, ZHAO Wuji, CHU Hongliang, et al. Basic characteristics of geohazards induced by Lushan earthquake and compare to them of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2014,88(6):1145 − 1156. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 殷志强, 徐永强, 陈红旗, 等. 2014年云南鲁甸地震触发地质灾害发育分布规律及与景谷、盈江地震对比研究[J]. 地质学报,2016,90(6):1086 − 1097. [YIN Zhiqiang, XU Yongqiang, CHEN Hongqi, et al. The development and distribution characteristics of geohazards induced by August 3, 2014 Ludian earthquake and comparison with Jinggu and Yingjiang earthquakes[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica,2016,90(6):1086 − 1097. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.06.003 [7] 陈成, 胡凯衡. 汶川、芦山和鲁甸地震滑坡分布规律对比研究[J]. 工程地质学报,2017,25(3):806 − 814. [CHEN Cheng, HU Kaiheng. Comparison of distribution of landslides triggered by Wenchuan, Lushan, and Ludian earthquakes[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2017,25(3):806 − 814. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] FAN X M, GIANVITO SCARINGI, XU Q, et al. Coseismic landslides triggered by the 8th August 2017 Ms 7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake (Sichuan, China): factors controlling their spatial distribution and implications for the seismogenic blind fault identification[J]. Landslides,2018,15:967 − 983. DOI: 10.1007/s10346-018-0960-x
[9] 程强. 汶川强震区公路沿线地震崩滑灾害发育规律研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2011,30(9):1747 − 1760. [CHENG Qiang. Research on development rules of seismic landslide and collapse along highways in highly seismic region of Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2011,30(9):1747 − 1760. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 程强, 胡朝旭, 杨绪波. 九寨沟地震区公路沿线地质灾害发育规律及防治对策[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2018,29(4):114 − 120. [CHENG Qiang, HU Chaoxu, YANG Xubo. Developmental regularity and preventive countermeasures of geological hazards along the highway in Jiuzhaigou earthquake area[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2018,29(4):114 − 120. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 梁靖, 裴向军, 温勇, 等. 2017年九寨沟地震地质灾害发育分布规律研究[J]. 自然灾害学报,2019,28(5):181 − 188. [LIANG Jing, PEI Xiangjun, WEN Yong, et al. Research on development and distribution rules of geohazards in Jiuzhaigou earthquake in 2017[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2019,28(5):181 − 188. (in Chinese with English abstract) [12] 王绚, 范宣梅, 陈怡, 等. 九寨沟震后地质灾害分布特征与活动性预测[J]. 人民长江,2020,51(9):114 − 121. [WANG Xuan, FAN Xuanmei, CHEN Yi, et al. Distribution characteristics and activity prediction of geological disasters in Jiuzhaigou Valley after“2017.08.08”earthquake[J]. Yangtze River,2020,51(9):114 − 121. (in Chinese with English abstract) [13] 高会会, 裴向军, 崔圣华, 等. 汶川震区震后地质灾害发育分布及演化特征统计分析[J]. 长江科学院院报,2019,36(8):73 − 80. [GAO Huihui, PEI Xiangjun, CUI Shenghua, et al. Geological hazards after earthquake in Wenchuan earthquake area: distribution and evolvement features[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute,2019,36(8):73 − 80. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20180109 [14] 李明威, 唐川, 陈明, 等. 汶川震区北川县泥石流流域崩滑体时空演变特征[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(3):182 − 190. [LI Mingwei, TANG Chuan, CHEN Ming, et al. Spatio-temporal evolution characteristics of landslides in debris flow catchment in Beichuan County in the Wenchuan earthquake zone[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(3):182 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 陈冠, 孟兴民, 乔良, 等. “7•22”岷县漳县地震地质灾害分布、特征及与影响因子间关系分析[J]. 工程地质学报,2013,21(5):750 − 760. [CHEN Guan, MENG Xingmin, QIAO Liang, et al. Distribution, characteristics, and associated influencial factors of the geohazards induced by Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake on 22 July, 2013, Gansu, China[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2013,21(5):750 − 760. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2013.05.011 [16] 习朝辉. 强震区地质灾害多源信息识别及发育分布特征研究-以叠溪松坪沟为例[D]. 成都: 成都理工大学, 2019. XI Zhaohui. Recognition and development of geological disasters based on multi-source information in meizoseismal areas—Take DieXi Songpinggou as an example[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University Tecchnology, 2019. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[17] 张世殊, 裴向军, 张雄, 等. 强震区泥石流坡面物源发育规律与侵蚀坡度效应研究[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2016,35(增刊2):4139 − 4147. [ZHANG Shishu, PEI Xiangjun, ZHANG Xiong, et al. Source development and slope gradient effect of debris flow source in earthquake zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2016,35(Sup2):4139 − 4147. (in Chinese with English abstract) [18] 郭沉稳, 姚令侃, 段书苏, 等. 汶川、芦山、尼泊尔地震触发崩塌滑坡分布规律[J]. 西南交通大学学报,2016,51(1):71 − 77. [GUO Chenwen, YAO Lingkan, DUAN Shusu, et al. Distribution regularities of landslides induced by Wenchuan earthquake, Lushan earthquake and Nepal earthquake[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2016,51(1):71 − 77. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-2724.2016.01.011 [19] 许冲, 田颖颖, 马思远, 等. 1920年海原8.5级地震高烈度区滑坡编录与分布规律[J]. 工程地质学报,2018,26(5):1188 − 1195. [XU Chong, TIAN Yingying, MA Siyuan, et al. Inventory and spatial distribution of landslides inⅸ-xihigh intensity areas of 1920 Haiyuan (China) 8.5 earthquake[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2018,26(5):1188 − 1195. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 刘琛尧,晏启祥,孙润方,王绪,邓宝华,陈耀. 基于三维离散-连续耦合的岩溶隧道突水破坏模式研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2024(02): 163-171 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 盖孝乾. 隐伏溶洞对隧道围岩应力及地表沉降的影响研究. 工程机械与维修. 2023(01): 67-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 郭书兰,阎长虹,俞良晨,闫超,李慧,徐源. 无锡浅埋岩溶发育特征及其与隧道安全距离研究. 南京大学学报(自然科学). 2023(05): 890-899 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 孙伟. 广东省英德市城南社区岩溶塌陷发育特征及成因分析. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2023(05): 74-80 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 朱丹晖,聂浩. 大溶腔小跨度公路隧道溶洞处理方案研究. 铁道勘察. 2023(06): 144-150+162 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨刚. 岩溶地段隧道施工安全管理关键措施研究. 价值工程. 2022(32): 28-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 王亚强,王先龙,伍尚前,张建博. 隧道岩溶水引排及防治措施研究. 现代隧道技术. 2022(S1): 866-875 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:











 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS