Application of geographic detector in identifying influencing factors of landslide stability: A case study of the Jiangda County, Tibet
-
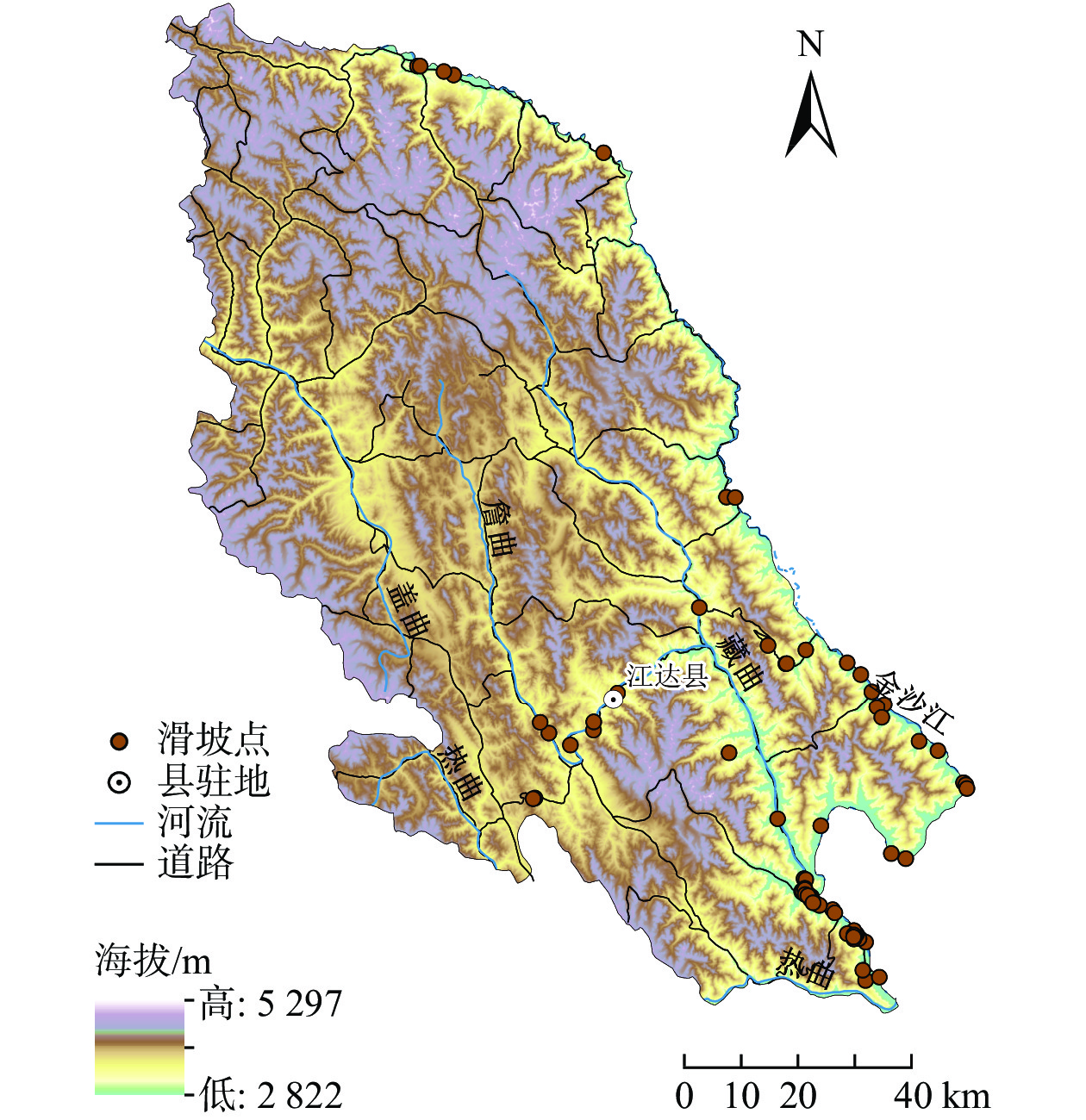
摘要: 高山峡谷区是滑坡灾害频发地区,随着气候变化和人类活动加剧,滑坡呈多发、频发态势。本文选择坐落于横断山高山峡谷区的西藏江达县作为研究区,利用野外调查获取的85个滑坡数据,选取坡度、河流密度、地貌类型、降水量、距断层距离、道路密度、地震动峰值加速度、岩性等8个稳定性影响因素,运用地理探测器对滑坡稳定性的影响因素进行了探测。结果表明:(1)按滑坡体体积划分等级,江达县滑坡主要以中、小型滑坡为主;按其稳定性划分,50%以上的滑坡处于稳定状态;按危险等级划分,以Ⅲ级、Ⅳ级为主;江达县滑坡主要沿河流与道路分布,全县地面调查发现85处滑坡全部分布于河流附近,其中71.76%的滑坡分布于道路两侧。(2)江达县滑坡稳定性的主要影响因子为地貌类型、河流密度、道路密度和距断层距离,其贡献率分别为0.501,0.477,0.465,0.332;当影响因子两两相互作用时,因子解释力总是大于单个因子对滑坡稳定性的解释力,即当两种影响因子相互作用时,对于滑坡的失稳具有促进作用。Abstract: The high mountain and gorge area is an typically area, where geological disasters happen frequently. Especially landslide is one of the most serious geological disasters. Recently relative researches on geological disasters showed that landslides had an increasing trends due to the impacts of both climate change and human activities. In this study, Jiangda County in Tibet Autonomous region was selected as our study area, which located in the high mountain and gorge area of the Hengduan Mountain Region. In addition, using the landslide data for 85 sites based on field survey, choosing Slope, River density, Geomorphic type, Precipitation, the distance from the fault, Road density, the ground motion peak acceleration and Lithology as 8 influencing factors on landslide, and then employing the Geodetector model to analyze the impact of various variables on landslide stability. The results showed that 1) according to the volume of landslide, medium and small landslides are main types in Jiangda County; According to its stability, more than 50% of the landslide is in a stable state; according to the danger level, they are mainly divided into Ⅲ, Ⅳ. In space, it is mainly along rivers and roads in Jiangda County, which caused by the limitations of the field survey besides physical factors. Because all 85 landslide survey sites located near rivers, and more than 71% sites are distributed on both sides of the road. 2) The geomorphic type, River density, Road density and the distance from the fault are major factors to affect the stability of the landslide in Jiangda County, its contribution rate are 0.501, 0.477, 0.465 and 0.332, respectively. When the influence factors interact in pairs, the explanatory power of factors is always greater than that of a single factor to the stability of landslides. In other words, when the two influencing factors interact, they always promote the instability of landslides.
-
Keywords:
- landslide stability /
- geographic detector /
- alpine canyon /
- influence factors
-
0. 引言
近年来,矿区地质灾害愈发严重,其中尾矿坝由于堆放工业废渣及废弃物,具有高势能,存在人造泥石流溃坝危险[1]。矿山环境污染是采矿活动引发的主要环境问题之一,基于尾矿坝严重的安全隐患,世界上很多国家把对尾矿坝的安全监测列为国家劳动部门安全监察的重要内容[2-4]。当险情发生时,由于灾区环境风险,常规的监测手段无法及时获取灾情。无人机同现有的常规手段相比,可以解决灾情勘察人员由于安全隐患无法接近灾区的问题,能够速获取空间要素,具有高精度、高时效、低成本的优势,是一种快速部署、零伤亡的灾情获取技术手段[5-9]。利用无人机遥感监测地面空间要素一直是学者们关注的热点。文献[10]进行了单相机无人机航摄试验,并开发了相应的地面监测软件;文献[11]对辽宁省某市铁矿开采区域进行了无人机动态遥感监测;文献[12]利用无人机摄影测量监测程潮铁矿西部塌陷区的地表塌陷变形。文献[13]利用无人机影像对云南省滇东北地区滑坡的活动性、发生发展过程进行监测,分析山体滑坡体特征。文献[14]以锦屏二级水电站出线场边坡落石灾害所在区域为例,将无人机摄影测量技术应用于高陡边坡危岩体调查中。随着无人机技术应用范围越来越广泛,这为尾库坝监测防灾及精细测量提供一种新思路。
采用无人机技术进行沉陷监测具有非接触性,大面积采集监测数据的优点。获取高精度的成图是无人机监测的保证。本文基于无人机低空摄影测量获取的航摄照片,经POS(Position and Orientation System)数据误差纠正,选取合理的像控点布设方案,利用获取的尾矿坝高分辨率两期DEM(Digital Elevation Model)数据进行尾矿坝沉降变形分析,对0~120 m,Y=0~700 m地表高程主要分析区域的变化情况做剖面分析,精度符合实际要求,为实际工况下无人机低空摄影测量提供参考,具有一定工程应用价值。
1. 无人机低空摄影成图方法
无人机低空摄影测量是对地面监测的一种新型手段。无人机采集地表信息的一般流程有航线规划、布设像控点和提取信息,它通过获取高清晰度航摄影片,获取POS数据,联系地面控制点,利用畸变改正等方法,经过空三解算,获取高精度DEM数据以及高分辨率正射影像[15-16]。无人机低空摄影测量获取的航片需要确定投影坐标以及DEM数据网格间距,精度越高则分辨率越高[17]。基于无人机低空摄影测量的尾矿坝地表沉降主要技术流程如图1所示。
2. 无人机航测影像POS数据系统误差分析
无人机低空摄影测量有一定的系统误差,对数字摄影测量精度造成影响的原因有很多种,但是最重要的是相机的分辨率;相机拍摄时存在的安置误差;原始POS数据系统误差[18]。通过设计合理的航飞方案可以提高影像质量,提高航片的重叠度减少误差,建立误差改正模型纠正原始POS数据系统误差。无人机飞行时的6个外方位元素
$ {X}_{\mathrm{s}} $ ,$ {Y}_{\mathrm{s}} $ ,$ {Z}_{\mathrm{s}} $ ,$ \varPhi $ ,$ \varOmega $ ,$ { K} $ 是由共线方程反算得到,这是摄影测量的一个基本问题[19-20]。共线方程的建立如式(1):$$\begin{aligned} &{ x-{x}_{0}+\Delta x= } {-f\frac{{a}_{1}\left(X-{X}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{b}_{1}\left(Y-{Y}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{c}_{1}\left(Z-{Z}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)}{{a}_{2}\left(X-{X}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{b}_{2}\left(Y-{Y}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{c}_{2}\left(Z-{Z}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)} }\\ &{y-{y}_{0}+\Delta y= } {-f\frac{{a}_{3}\left(X-{X}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{b}_{3}\left(Y-{Y}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{c}_{3}\left(Z-{Z}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)}{{a}_{2}\left(X-{X}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{b}_{2}\left(Y-{Y}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)+{c}_{2}\left(Z-{Z}_{\mathrm{s}}\right)}} \end{aligned} $$ (1) 式中:
$ {x}_{0} $ ,$ {y}_{0} $ ——像主点;$ x $ ,$ y $ ——以像主点为原点的像平面坐标;$ \Delta x $ ,$ \Delta y $ ——相机畸变改正数;$ f $ ——像片主距;$X_{\rm{s}}$ ,$Y_{\rm{s}}$ ,$Z_{\rm{s}}$ ——外方位线元素;$ X $ ,$ Y $ ,$ Z $ ——物点的地面坐标;$ {a}_{1} $ ,$ {a}_{2} $ ,$ {a}_{3} $ ,$ {b}_{1} $ ,$ {b}_{2} $ ,$ {b}_{3} $ ,$ {c}_{1} $ ,$ {c}_{2} $ ,$ {c}_{3} $ ——旋转矩阵的9个元素。通过地面控制点反算获取影像精确的外方位元素,得到POS数据误差的改正参数,建立两种针对单张相片和多张相片的误差改正模型。其中单张相片误差改正公式如式(2):
$$ \left\{\begin{aligned}&\Delta{X}_{\mathrm{P}i}={X}_{i}-{X}_{\mathrm{P}i},\Delta{Y}_{\mathrm{P}i}={Y}_{i}-{Y}_{\mathrm{P}i}\\ &\Delta{Z}_{\mathrm{P}i}={Z}_{i}-{Z}_{\mathrm{P}i},\Delta{\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}i}={\varPhi }_{i}-{\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}i}\\ &\Delta{\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}i}={\varOmega }_{i}-{\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}i},{\Delta { K}}_{\mathrm{P}i}={{ K}}_{i}-{{ K}}_{\mathrm{P}i}\end{aligned}\right. $$ (2) 式中:
$ {X}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ {Y}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ {Z}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ {\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ {\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$K_{{\rm{P}}i}$ —原始POS数据的外方 位元素;$ {X}_{i} $ ,$ {Y}_{i} $ ,$ {Z}_{i} $ ,$ {\varPhi }_{i} $ ,$ {\varOmega }_{i} $ ,$K_i $ —地面控制点反算获取的外 方位元素;i—表示计算的影像张数,
$i=\mathrm{1,2,}\cdots ,n$ ;$ \Delta {X}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ \Delta {Y}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ \Delta {Z}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ \Delta {\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ \Delta {\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}i} $ ,$ {\Delta { K}}_{\mathrm{P}i} $ —表示第i张影 像外方位元素 的改正值。如果选取多张相片进行误差改正,则误差取平均值计算多张相片误差改正公式如式(3):
$$ \left\{\begin{aligned} &\Delta {X}_{\mathrm{P}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\Delta X}_{\mathrm{P}i}/n,\Delta {Y}_{\mathrm{P}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\Delta {Y}_{\mathrm{P}i}/n\\ &\Delta {Z}_{\mathrm{P}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\Delta {Z}_{\mathrm{P}i}/n,\Delta {\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\Delta {\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}i}/n\\ &\Delta {\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}\Delta {\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}i}/n,\Delta {{ K}}_{\mathrm{P}}=\sum _{i=1}^{n}{\Delta { K}}_{\mathrm{P}i}/n\end{aligned}\right. $$ (3) 通过改正模型纠正原始POS数据误差如表1所示。
表 1 外方位元素的改正值和误差来源Table 1. Correction values and error sources of elements with external orientation外方位元素 改正值 改正误差 $ {X}_{i} $ 奇数行带$ \Delta {X}_{\mathrm{P}} $ 相反性误差
偏移误差偶数行带$ -\Delta {X}_{\mathrm{P}} $ $ {Y}_{i} $ 奇数行带$ \Delta {Y}_{\mathrm{P}} $ 相反性误差
偏移误差偶数行带$ -\Delta {Y}_{\mathrm{P}} $ $ {Z}_{i} $ $ \Delta {Z}_{\mathrm{P}} $ 偏移误差 $ {\varPhi }_{i} $ $ \Delta {\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P}} $ 视准轴误差 $ {\varOmega }_{i} $ $ \Delta {\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}} $ $ {{ K}}_{i} $ $ \Delta {{ K}}_{\mathrm{P}} $ 3. 实验区概况与控制点布置方案
3.1 实验区概况
本次实验区深处亚欧大陆腹地,地形地貌复杂,气候干旱少雨,绿洲生态维持主要依赖高山雨雪形成的河流。尾矿坝较多,属典型的山谷型尾矿库。其中研究区尾矿坝具有高势能的人造泥石流危险源,一旦溃坝容易造成特大事故和河流污染,对矿区的安全及其它方面也会产生一定影响。尾矿坝位于图2所示的研究范围内,尾矿坝用于存放工业废渣,而且在进行数据采集之前就已经出现过部分边坡的滑落。因此需要对尾矿坝进行无人机摄影测量监测,通过数据分析判断边坡是否再次出现滑坡灾害,以确保矿区地质安全[21-22]。
3.2 控制点布置方案
为获取实验区无人机影像,设计合理的飞行方案,分别在2018年8月2日及2019年8月5日采用固定翼和多旋翼无人机对实验区进行航拍,获取两期原始航片数据。为了保证生成具有高精度的DEM,飞行前在地面做好控制点并记录其大地坐标,将控制点清晰记录在影像上。无人机飞行参数设置相对航高为95 m,航向重叠度为85%,旁向重叠度为80%。在完成航摄后,应对照片进行质量检查,主要包括:照片的清晰度和重叠度,有没有航摄漏洞,航摄区域与需要观测区域的覆盖情况。如果在检查时发现有些照片不符合要求,进行补飞,以免影响后续处理的精度[23]。
控制点的选取和布设可以保证低空摄影测量的精度。做空中三角测量需要布设的地面控制点和检查点进行区域网平差[24]。采用高精度水准仪按照一等测量规范在实验区域架设仪器获取两期尾矿坝区域控制点高程数据,高精度全站仪获取控制点点位数据。实验区主要为尾矿坝区域,矿区两侧有山路环绕,便于行走及架设仪器。因此以尾矿坝为主要区域,然后沿矿区两侧山路在路边进行布设控制点。
针对控制点数量对成图的精度影响问题,在第一次航拍前实验选取最佳控制点数量提高成图精度。参考“均匀布设原则”,按照控制点依次增加2个,最后累加到14个的7种控制点布设方案。建模时,把用全站仪及水准仪测量的对应控制点坐标及高程输入到软件中,并且把纠正过的POS数据输入到Pix4Dmapper软件中,建立对应的三维立体模型。对生成的模型进行分析,读取不同控制点布设方案下各控制点的坐标,比较平面及高程精度。经过处理的7种控制点布设方案的数据误差如图3所示。
由图3可以看出,随着控制点数量的增加,数据精度也在逐渐增加,数量到达8个之后,精度逐渐降低并趋于稳定,所以此次尾矿坝控制点数量选取为8个,数据精度达到最高。
将原始外方位元素代入控制点坐标进行反算,利用Matlab软件设计系统误差改正模型计算出POS数据改正参数,然后对原始POS数据进行改正。选取第一期部分影像原始POS数据与纠正后POS数据对比如表2所示。
表 2 原始POS数据与纠正后POS数据对比Table 2. Comparison of original POS data and corrected POS dataID $ |\Delta X| $
/m$|\Delta Y|$
/m$ |\Delta Z| $/m $|\Delta {\varPhi }_{\mathrm{P} }|$
/(°)$ |\Delta {\varOmega }_{\mathrm{P}}| $/(°) $ |\Delta {{ K}}_{\mathrm{P}}| $/(°) D35 0.013 0.046 0.093 0.18 0.13 0.87 D36 0.056 0.099 0.034 0.20 0.43 0.50 D42 0.074 0.060 0.089 0.47 0.59 0.61 D43 0.025 0.054 0.051 0.78 0.78 0.84 D92 0.076 0.012 0.060 0.14 0.11 0.26 D93 0.047 0.083 0.081 0.28 0.25 0.55 由表2可以看出改正的外方位元素精度得到提高,生成的正射影像及DEM数据相对提高。此次获得的原始POS数据精度较高,经区域网平差后,线元素误差在0.1 m以内,角元素误差在1 °以内,但还是满足不了沉降观测高精度的要求,所以需要纠正POS数据提高精度。用Pix4Dmapper软件进行后续处理生成正射影像与DEM数据,投影坐标系为WGS84-UTM44N坐标系,第一期POS数据纠正前正射影像与纠正后正射影像对比如图4所示。两期控制点与DEM坐标点位误差如图5所示。
通过图4可知用纠正后POS数据生成第一期正射影像的定位精度高于原始POS数据。由于目前的无人机没有搭载后差分POS数据处理系统,因此要纠正POS数据进行影像定位,提高定位精度。由图5可知两期地面控制点和生成DEM数据的对应监测点坐标的差值在毫米级别,控制点的误差基本控制在3 mm之内,说明其生成的坐标精度可靠,可以用于接下来的尾矿坝地表沉陷分析。
4. 尾矿坝地表沉陷特征
对本次研究区域进行位移沉降分析,首先需要得到DEM数据的坐标信息,生成的2018年8月2日及2019年8月5日DEM数据整体差值如图6所示。根据Pix4Dmapper软件生成的三维尾矿坝图如图7所示。
将尾矿坝两期DEM数据整体差值覆于数字模型表面上,经过ArcGIS平台的技术处理[25],得到尾矿坝整体沉降图如图8所示。
对于尾矿坝整体的主要分析区域为0~120 m,Y=0~700 m地表高程的变化情况。为了分析研究区域地表塌陷区的沉降情况,对两期实验所得到的模型区域内,分别在Y=350 m、Y=100 m和X=60 m剖面线上,提取相应点的高程差值,分析其高程在三次监测情况下的变化,如图9、10、11所示。
由图8可知,尾矿坝整体出现了沉降,尾矿坝两侧山坡西坡受尾矿坝沉降及西南暖湿气流的影响,在南北或偏南北走向山脉的西坡和西南坡形成大量降水,出现沉降现象。由X=60 m剖面可知尾矿坝南坡沉降范围最大。由于尾矿坝内部存在矿区工业废水,经过一年的废水流失,以及该实验区降水量大,受日照及降雨影响,尾矿坝的地质发生了解构现象,导致了整体沉降。南部尾矿坝下坡是尾矿坝的坡顶区域,坡度大,降雨量受面广,受沉降位移的影响较为明显,加快了地表塌陷区的沉降。尾矿坝北部因为坡度小,受降雨及日照影响小,所以沉降范围小于南部。对于剖面Y=500 m,根据剖面线上各点高程的变化情况可知,此剖面线上沉降位移为0.08 m左右。分析其原因,主要是因为此剖面所处区域比较平坦,属于尾矿坝中部地区,沉降比较稳定。对于剖面Y=100 m,尾矿坝下坡沉降范围在0.16 m之内。
综上所述,当前利用无人机低空摄影测量技术为监测地表沉降提供了新的方法,比传统监测方式更加便捷。与传统监测相比,低空摄影测量技术能够从多角度进行影像采集,能够充分地获取监测区域的地形地物信息。
5. 结论
文章基于无人机低空航摄技术获取实验区数据,并进行数据处理,利用高精度成图方法,得到实验区尾矿坝地表沉陷图。实验结果表明:
(1)通过改正原始POS数据误差,是可以提高无人机摄影测量成图精度的,这为无人机在精细测量方向上有更多的研究潜力。无人机成图精度并不是随着像控点数量的增加而增加,要根据实际情况做出决策。
(2)经过实际工程的应用,利用无人机监测尾矿坝地表沉陷的高精度成图方法获得的精度是可靠的,可以达到毫米级,这对现有监测手段是一种有效的补充。
(3)尾库坝安全监测一直是矿区安全生产的重要保证。由于光照、温度、雨量、风速和土壤质地等因子的综合作用,尾矿坝发生沉降,尾矿坝北部因为坡度小,受降雨及日照影响小,所以沉降范围小于南部。通过无人机低空摄影测量监测,对矿区安全生产起到一定的预警作用。需要指出的是,本次试验研究的是植被覆盖较少的尾矿坝区域,沉降变形主要靠人工识别和分析,下一步的研究工作将针对植被覆盖广的区域以及对矿区地质灾害信息进行自动识别和统计分析。
-
表 1 地层岩性硬度划分表
Table 1 Stratum lithology hardness division table
类别 代表岩石 稳定性赋值 极硬岩 花岗岩、二长花岗岩、闪长岩、
辉长岩、石英闪长岩、玄武玢岩、
硅质岩、超镁铁质岩类4 次硬岩 碳酸盐岩、碎屑岩、大理岩、白云岩、
石灰岩、中酸性基性火山岩、
赤铁矿、夹灰岩、地层并层等3 次软岩 千枚岩、板岩、灰岩、石膏等 2 极软岩 页岩、黏土岩、泥岩、
砂岩、砾岩及各种土体等1 表 2 按滑坡体体积划分的滑坡等级
Table 2 Landslide grade divided by volume
规模 标准/(104 m3) 数量/个 占比/% 小型 V<10 45 52.94 中型 10≤V<100 26 30.59 大型 100≤V<1000 11 12.94 特大型 1000≤V 3 3.53 总计 85 100.00 表 3 按稳定性划分的滑坡等级
Table 3 Landslide grade divided by stability
稳定性评价 数量/个 占比/% 稳定 14 16.47 较稳定 29 34.12 稳定性较差 4 4.71 不稳定 33 38.82 易发 5 5.88 总计 85 100.00 表 4 按危险性划分的滑坡等级
Table 4 Landslide grade divided by danger
险情等级 数量/个 占比/% Ⅰ级 0 0.00 Ⅱ级 2 2.35 Ⅲ级 17 20.00 Ⅳ级 66 77.65 总计 85 100.00 表 5 因子探测结果
Table 5 Factor detection results
坡度 X1 距断层距离 X2 岩性 X3 河流密度 X4 地貌类型 X5 道路密度 X6 降水量 X7 地震动峰值加速度 X8 q值 0.168 0.332 0.101 0.477 0.501 0.465 0.122 0.129 表 6 交互作用探测结果
Table 6 Interaction detection results
交互因素 交互值 交互值比较 交互结果 坡度∩距断层距离 0.728 >q(坡度)+q(距断层距离) 非线性增强 坡度∩岩性 0.418 >q(坡度),q(岩性) 非线性增强 坡度∩河流密度 0.677 >q(坡度)+q(河流密度) 非线性增强 坡度∩地貌 0.827 >q(坡度),q(地貌) 非线性增强 坡度∩道路密度 0.748 >q(坡度),q(道路密度) 非线性增强 坡度∩降水量 0.424 >q(坡度)+q(降水量) 非线性增强 坡度∩地震动峰值加速度 0.404 >q(坡度)+q(地震动峰值加速度) 非线性增强 距断层距离∩岩性 0.433 >q(距断层距离)+q(岩性) 非线性增强 距断层距离∩河流密度 0.739 >Max(q(距断层距离),q(河流密度)) 双因子增强 距断层距离∩地貌 0.938 >q(距断层距离),q(地貌) 非线性增强 距断层距离∩道路密度 0.783 >Max(q(距断层距离),q(道路密度)) 双因子增强 距断层距离∩降水量 0.413 >Max(q(距断层距离),q(降水量)) 双因子增强 距断层距离∩地震动峰值加速度 0.445 >Max(q(距断层距离),q(地震动峰值加速度)) 双因子增强 岩性∩河流密度 0.557 >q(岩性)+q(河流密度) 非线性增强 岩性∩地貌 0.781 >q(岩性)+q(地貌) 非线性增强 岩性∩道路密度 0.547 >Max(q(岩性),q(道路密度)) 双因子增强 岩性∩降水量 0.221 >Max(q(岩性),q(降水量)) 双因子增强 岩性∩地震动峰值加速度 0.339 >q(岩性)+q(地震动峰值加速度) 非线性增强 河流密度∩地貌 0.831 >Max(q(河流密度),q(地貌)) 双因子增强 河流密度∩道路密度 0.700 >Max(q(河流密度),q(道路密度)) 双因子增强 河流密度∩降水量 0.540 >Max(q(河流密度),q(降水量)) 双因子增强 河流密度∩地震动峰值加速度 0.559 >q(河流密度)+q(地震动峰值加速度) 非线性增强 地貌∩道路密度 0.815 >Max(q(地貌),q(道路密度)) 双因子增强 地貌∩降水量 0.735 >q(地貌)+q(降水量) 非线性增强 地貌∩地震动峰值加速度 0.544 >Max(q(地貌),q(地震动峰值加速度)) 双因子增强 道路密度∩降水量 0.617 >q(道路密度)+q(降水量) 非线性增强 道路密度∩地震动峰值加速度 0.521 >Max(q(道路密度),q(地震动峰值加速度)) 双因子增强 降水量∩地震动峰值加速度 0.267 >Max(q(降水量),q(地震动峰值加速度)) 双因子增强 表 7 生态探测结果
Table 7 Ecological detection results
坡度X1 距断层距离X2 岩性X3 河流密度X4 地貌X5 道路密度X6 降水量X7 地震动峰加速度X8 坡度 距断层距离 N 岩性 N Y 河流密度 Y N Y 地貌 Y N Y N 道路密度 Y N Y N N 降水量 N Y N Y Y Y 地震动峰加速度 N N N Y Y Y N -
[1] 陈冠, 孟兴民, 郭鹏, 等. 白龙江流域基于GIS与信息量模型的滑坡危险性等级区划[J]. 兰州大学学报(自然科学版),2011,47(6):1 − 6. [CHEN Guan, MENG Xingmin, GUO Peng, et al. Landslide susceptibility mapping based on GIS and information value model in Bailong river basin[J]. Journal of Lanzhou University (Natural Sciences),2011,47(6):1 − 6. (in Chinese with English abstract) [2] 张永双, 郭长宝, 杨志华, 等. 青藏高原东缘地形急变带滑坡灾害特征与危险性研究[M]. 武汉: 中国地质大学出版社, 2018. ZHANG Yongshuang, GUO Changbao, YANG Zhihua, et al. Study on the characteristics and risks of landslide disasters in the sudden Change Zone of the Eastern Tibetan Plateau[M]. Wuhan: China University of Geosciences Press, 2018.(in Chinese)
[3] 柳丙善, 李世海, 赵卿. 清江隔河岩水库茅坪滑坡的主要影响因素分析[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2008,19(2):36 − 43. [LIU Bingshan, LI Shihai, ZHAO Qin. Research on the main factors causing Maoping Landslide based upon the insitu investigation[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2008,19(2):36 − 43. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8035.2008.02.008 [4] 陈剑, 李晓, 杨志法. 三峡库区滑坡的时空分布特征与成因探讨[J]. 工程地质学报,2005,13(3):305 − 309. [CHEN Jian, LI Xiao, YANG Zhifa. On the distribution and mechanism of landslides in the Three Gorges reservoir area[J]. Journal of Engineering Geology,2005,13(3):305 − 309. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9665.2005.03.004 [5] 尹小涛, 王水林. 基于可靠度理论的滑坡稳定性及其影响因素分析[J]. 岩土力学,2008,29(6):1551 − 1556. [YIN Xiaotao, WANG Shuilin. Stability and its influential factors analysis of landslides based on reliability theory[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2008,29(6):1551 − 1556. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7598.2008.06.022 [6] TURKAN B A, ERGIN G. Landslide-Triggering Factors in Korucak Subbasin, North Anatolian, Turkey[J]. Procedia Earth and Planetary Science,2015,15:566 − 572. DOI: 10.1016/j.proeps.2015.08.104
[7] 杨华阳, 许向宁, 杨鸿发. 基于证据权法的九寨沟地震滑坡危险性评价[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(3):20 − 29. [YANG Huayang, XU Xiangning, YANG Hongfa. The Jiuzhaigou co-seismic landslide hazard assessment based on weight of evidence method[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(3):20 − 29. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 张向营, 张春山, 孟华君, 等. 基于Random Forest和AHP的贵德县北部山区滑坡危险性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2018,45(4):142 − 149. [ZHANG Xiangying, ZHANG Chunshan, MENG Huajun, et al. Landslide hazard evaluation in the northern mountainous area of Guide County based on Random Forest and AHP[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2018,45(4):142 − 149. (in Chinese with English abstract) [9] 杨可明, 郭海会, 钱小丽, 等. 结合信息熵改进的证据权法与滑坡危险度区划[J]. 地理与地理信息科学,2013,29(3):104 − 108. [YANG Keming, GUO Haihui, QIAN Xiaoli, et al. Improving weights of evidence method based on entropy and zoning the landslide hazard[J]. Geography and Geo-Information Science,2013,29(3):104 − 108. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 张倬元. 滑坡防治工程的现状与发展展望[J]. 地质灾害与环境保护,2000,11(2):89 − 97. [ZHANG Zhouyuan. The present status, technical advance and development trends of landslide reme dial measures[J]. Journal of Geological Hazrds and Environment Preservation,2000,11(2):89 − 97. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-4362.2000.02.001 [11] 王恭先. 滑坡防治中的关键技术及其处理方法[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报,2005,24(21):3818 − 3827. [WANG Gongxian. Key technique in landslide control and its handling measures[J]. Chinese Journal of Rock Mechanics and Engineering,2005,24(21):3818 − 3827. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6915.2005.21.003 [12] 罗丽娟, 赵法锁. 滑坡防治工程措施研究现状与应用综述[J]. 自然灾害学报,2009,18(4):158 − 164. [LUO Lijuan, ZHAO Fasuo. Status of research and application of engineering measures for preventing and controlling landslide[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2009,18(4):158 − 164. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-4574.2009.04.027 [13] NIE Z B, ZHANG Z H, ZHENG H, et al. Stability analysis of landslides using BEM and variational inequality based contact model[J]. Computers and Geotechnics,2020,123:1 − 7.
[14] 闫玉平, 肖世国. 考虑滑带强度参数分区取值的堆积层滑坡稳定性分析方法[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2020,31(2):44 − 49. [YAN Yuping, XIAO Shiguo. Stability analysis method for bedrock-talus landslides considering strength parameter partition of slip shear band[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2020,31(2):44 − 49. (in Chinese with English abstract) [15] 刘磊, 徐勇, 李远耀, 等. 湘西陈溪峪滑坡变形机理及稳定性评价[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2019,46(2):21 − 28. [LIU Lei, XU Yong, LI Yuanyao, et al. A study of deformation mechanism and stability evaluation of the Chenxiyu landslide in western Hunan[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2019,46(2):21 − 28. (in Chinese with English abstract) [16] 王劲峰, 徐成东. 地理探测器: 原理与展望[J]. 地理学报,2017,72(1):116 − 134. [WANG Jinfeng, XU Chengdong. Geodetector: Principle and prospective[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica,2017,72(1):116 − 134. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11821/dlxb201701010 [17] 李涛, 廖和平, 褚远恒, 等. 重庆市农地非农化空间非均衡及形成机理[J]. 自然资源学报,2016,31(11):1844 − 1857. [LI Tao, LIAO Heping, CHU Yuanheng, et al. Spatial disequilibrium and its formation mechanism of farmland conversion in Chongqing[J]. Journal of Natural Resources,2016,31(11):1844 − 1857. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.11849/zrzyxb.20151371 [18] 闫举生, 谭建民. 基于不同因子分级法的滑坡易发性评价: 以湖北远安县为例[J]. 中国地质灾害与防治学报,2019,30(1):52 − 60. [YAN Jusheng, TAN Jianmin. Landslide susceptibility assessment based on different factor classification methods—A case study in Yuan'an County of Hubei Province[J]. The Chinese Journal of Geological Hazard and Control,2019,30(1):52 − 60. (in Chinese with English abstract) [19] 张铎, 吴中海, 李家存, 等. 滇西北永胜-宾川地区滑坡发育的影响因子分析及其动力成因与意义探讨[J]. 自然灾害学报,2016,25(1):176 − 190. [ZHANG Duo, WU Zhonghai, LI Jiacun, et al. Analysis of the influential factor of landslide in Yongsheng-Binchuan region of northwest Yunnan and the exploration of its dynamic cause and significance[J]. Journal of Natural Disasters,2016,25(1):176 − 190. (in Chinese with English abstract) [20] 谢帅, 刘士彬, 段建波, 等. OSDS注册用户空间分布特征及影响因素分析[J]. 地球信息科学学报,2016,18(10):1332 − 1340. [XIE Shuai, LIU Shibin, DUAN Jianbo, et al. Spatial distribution characteristics of OSDS registered users and its influencing factors[J]. Journal of Geo-Information Science,2016,18(10):1332 − 1340. (in Chinese with English abstract) [21] 田丰, 张军, 冉有华, 等. 甘肃陇南市泥石流灾害危险性及影响因子评价[J]. 灾害学,2017,32(3):197 − 203. [TIAN Feng, ZHANG Jun, RAN Youhua, et al. Assessment of debris flow disaster hazard and influence factors in Longnan district[J]. Journal of Catastrophology,2017,32(3):197 − 203. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-811X.2017.03.033 [22] 方然可, 刘艳辉, 苏永超, 等. 基于逻辑回归的四川青川县区域滑坡灾害预警模型[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2021,48(1):181 − 187. [FANG Ranke, LIU Yanhui, SU Yongchao, et al. A early warning model of regional landslide in Qingchuan County,Sichuan Province based on logistic regression[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2021,48(1):181 − 187. (in Chinese with English abstract) [23] 郭伟, 王晨辉, 李鹏, 等. 基于LoRa的地质灾害分布式实时监测系统设计[J]. 水文地质工程地质,2020,47(4):107 − 113. [GUO Wei, WANG Chenhui, LI Peng, et al. Design of the distributed real -time monitoring system for geological hazards based on LoRa[J]. Hydrogeology & Engineering Geology,2020,47(4):107 − 113. (in Chinese with English abstract) [24] 张茂省.发挥新型举国体制优势提高地质灾害防治能力[J]. 西北地质, 2019, 52(2): Ⅰ-Ⅱ. ZHANG Maosheng. Maximising the advantages of the new national system for improving the ability to prevent and mitigate geological disasters[J]. Northwestern Geology, 2019, 52(2): Ⅰ-Ⅱ. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[25] 张茂省, 薛强, 贾俊, 等. 山区城镇地质灾害调查与风险评价方法及实践[J]. 西北地质,2019,52(2):125 − 135. [ZHANG Maosheng, XUE Qiang, JIA Jun, et al. Methods and practices for the investigation and risk assessment of geo-hazards in mountainous towns[J]. Northwestern Geology,2019,52(2):125 − 135. (in Chinese with English abstract) [26] 李滨, 张青, 王文沛, 等. 金沙江乌东德水电站坝区高陡边坡地质灾害监测预警研究[J]. 地质力学学报,2020,26(4):556 − 564. [LI Bin, ZHANG Qing, WANG Wenpei, et al. Geohazard monitoring and risk management of high-steep slope in the Wudongde dam area[J]. Journal of Geomechanics,2020,26(4):556 − 564. (in Chinese with English abstract) -
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 许春萌,段勇. 多旋翼无人机航测在山区水库测量中的应用. 水利科技与经济. 2024(05): 101-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孟庆胤,王浩宇,聂明哲,余小军,陈荣健,傅金阳. 尾矿库坝面安全隐患智能巡检机器人研发及应用. 矿业研究与开发. 2024(07): 230-238 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 胡东升,程小凯,张雅飞,李涛,廉旭刚. 空天地一体化监测联合反演开采沉陷概率积分预计参数研究. 煤炭工程. 2023(01): 81-86 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘鹏 ,王亮 ,贾旭斌 . 基于无人机影像的高精度滑坡体边界识别研究. 工程勘察. 2023(06): 61-65+72 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 龚弦,马源,何学志,张丽娇,王卫. 无人机遥感技术在矿山地质调查中的研究进展. 中国非金属矿工业导刊. 2023(03): 64-67+71 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 曾文浩,宁迪,刘国伟. 基于遥感技术的矿山地质环境监测实践. 中国资源综合利用. 2023(07): 132-139 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 周小龙,贾强,石鹏卿,何斌,郭富赟,胡文博,李攀龙. 免像控无人机航测技术在舟曲县立节北山滑坡-泥石流灾害应急处置中的应用. 中国地质灾害与防治学报. 2022(01): 107-116 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)





 下载:
下载:




























































 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS