Experimental analysis of horizontal frost heaving force of loess in Lanzhou City of Gansu Province Area
-
摘要: 为研究不同含水率黄土在一维冻结融化过程中温度场和水平冻胀力的变化特征规律,选取兰州地区黄土进行了封闭系统下的一维冻结融化试验。研究结果表明:土体的降温过程分为四个阶段,降温冻结初期各深度土体的温度下降速率较快;土体温度下降到0.4 ℃时降温曲线出现转折点,土层各深度降温速曲线出现近乎平行于横坐标的平稳段;冻结后期各深度土体的温度下降速率较慢。最大水平冻胀力沿着土体深度先是稳定变化较为小,然后增大到最大值最后减小。水平冻胀力最大值随含水率有很明显的变化,含水率越高水平冻胀力越大,而其他值的大小受含水率的影响较小,水平冻胀力最大值出现在相对深度0.6~0.8处。Abstract: In order to study the variation of temperature field and horizontal frost heaving force during the one-dimensional freezing and melting process of loess with different water content, the one-dimensional freezing and melting test under closed system was carried out on the loess from Lanzhou Area. The results show that the cooling process of the soil can be divided into four stages. The temperature drop rate of the soil at each depth is faster when the temperature is frozen. When the temperature drops to 0.4 ℃, the cooling curve shows a turning point, and the depth of the soil decreases. A plateau that is nearly parallel to the abscissa; the temperature of the soil at each depth is slower at the late stage of freezing. The maximum horizontal frost heaving force changes little along the soil depth, then increases to the maximum and finally decreases. The maximum value of horizontal frost heaving force changes obviously with the water content. The higher the water content is, the greater the horizontal frost heaving force is, while the other values are less affected by the water content. The maximum value of horizontal frost heaving force appears at the relative depth of 0.6 to 0.8.
-
Keywords:
- horizontal frost heave force /
- model test /
- frozen soil /
- temperature field /
- frost heave
-
0. 引言
冻土是指温度低于0 ℃,且含冰的岩土,其由水、冰、气体和固体矿物颗粒组成[1]。它是一种多相体系,其性质受未冻水含量和含冰量的控制,而含冰量的多少会随温度的变化而变化。因此冻土是一种不同于普通土的特殊土体。我国冻土分布面积广大,永久性和季节性冻土面积约占全国陆地总面积的2/3,冻土主要分布在我国西北和纬度较高的东北部地区[2]。随着“一带一路”国家战略的进一步推进,西部地区将建设许多重大工程项目。这些工程在低温作用下不可避免的会产生冻害问题,比如水平冻胀力造成支挡结构和输水渠道的破坏,冻胀造成公路路面开裂、造成铁路轨面不平顺,这些问题都是冻土地区工程建设所要面对的挑战,因此对冻土、土体水平冻胀力的发展及其危害等问题进行深入研究显得尤为重要。
EIGENBROD[3]研究发现土体的体积会随着冻融循环次数的增加而增大,但后期会慢慢趋于稳定。李岩等[4]利用大型三维模拟冻结试验系统,对竖向直排冻结条件下不同深度土体的水平冻胀力分布特性进行了试验研究。刘鸿绪等[5-6]在冻胀力学方面做了大量的研究,指出法向冻胀力的大小与地表的总冻胀量无关,地表的总冻胀量是整个冻结深度范围内土体冻胀率线性叠加的宏观表现,还提出土体在冻结过程中,首先产生水平冻胀压应力,然后该压应力逐渐减小并变为冻缩温度拉应力。孙彦福等[7]认为在季节冻结层和季节融化层之间存在水平冻胀力,根据水平冻胀力与冻结锋面的关系将其分为平行水平冻胀力和垂直水平冻胀力,并提出水平冻胀力有其发生、发展及消退的独特规律。姜龙等[8]通过室内冻结试验研究了温度、含水量、干密度和冻胀率等因素与法向冻胀力的关系并且分析了土体上覆荷载对土体冻胀的影响。胡坤等[9]通过大量一维冻胀试验研究了不同约束条件下土体水分场、冻胀量、冻胀率和冻胀力的变化规律以及土体冻胀量与冻胀力之间的关系。王建州等[10]通过室内模型试验研究了季冻区越冬深基坑在冻结-融化过程中水平冻胀力的变化规律。吕长霖[11]通过自行研制的一维冻胀试验系统,研究了不同水平约束刚度和竖向荷载条件下冻胀敏感性土的冻胀规律以及水平冻胀力。VINSON等[12]和LING等[13]研究了含水率对冻结土体动态特性的影响。
国内外学者对土体冻胀机理、冻胀特性、法向冻胀力的发展规律、冻害治理措施和冻害预测模型做了大量的研究,发现了大量规律并提出了许多理论。但对一维冻结条件下水平冻胀力的发展研究较少,通过室内模型试验研究水平冻胀力变化的报道也比较少。在我国黄土地区,既有普速铁路在建设时修筑了大量素黄土路基,由于黄土特殊的物理力学性质造成部分路基的冻害比较严重,由于维修天窗时间的限制冻害线路处理和维修的难度较大。本文以季节性冻土区黄土路基为研究对象,采用室内模型试验方法,研究了路基在一维冻结过程中土体温度和水平冻胀力的变化规律,给出了土体温度的变化曲线,水平冻胀力与时间之间的关系。以期通过不同含水率条件下黄土一维冻胀试验来探索黄土路基冻胀灾害防治的有效措施和方法。
1. 模型试验
1.1 材料性质
试验土料取自甘肃省兰州市九州台地区,基本物理指标依据《铁路工程土工试验规程》[14]中的相关规定进行,试验测得其基本物理指标如表1所示。
表 1 黄土基本物理指标Table 1. Basic physical properties of loess比重
Gs液限
wL/%塑限
wp/%塑性指数
Ip最优含水率
wopc/%最大干密度
ρdmax/(g·cm−3)2.71 28.38 15.21 13.17 13.6 1.89 1.2 试验装置
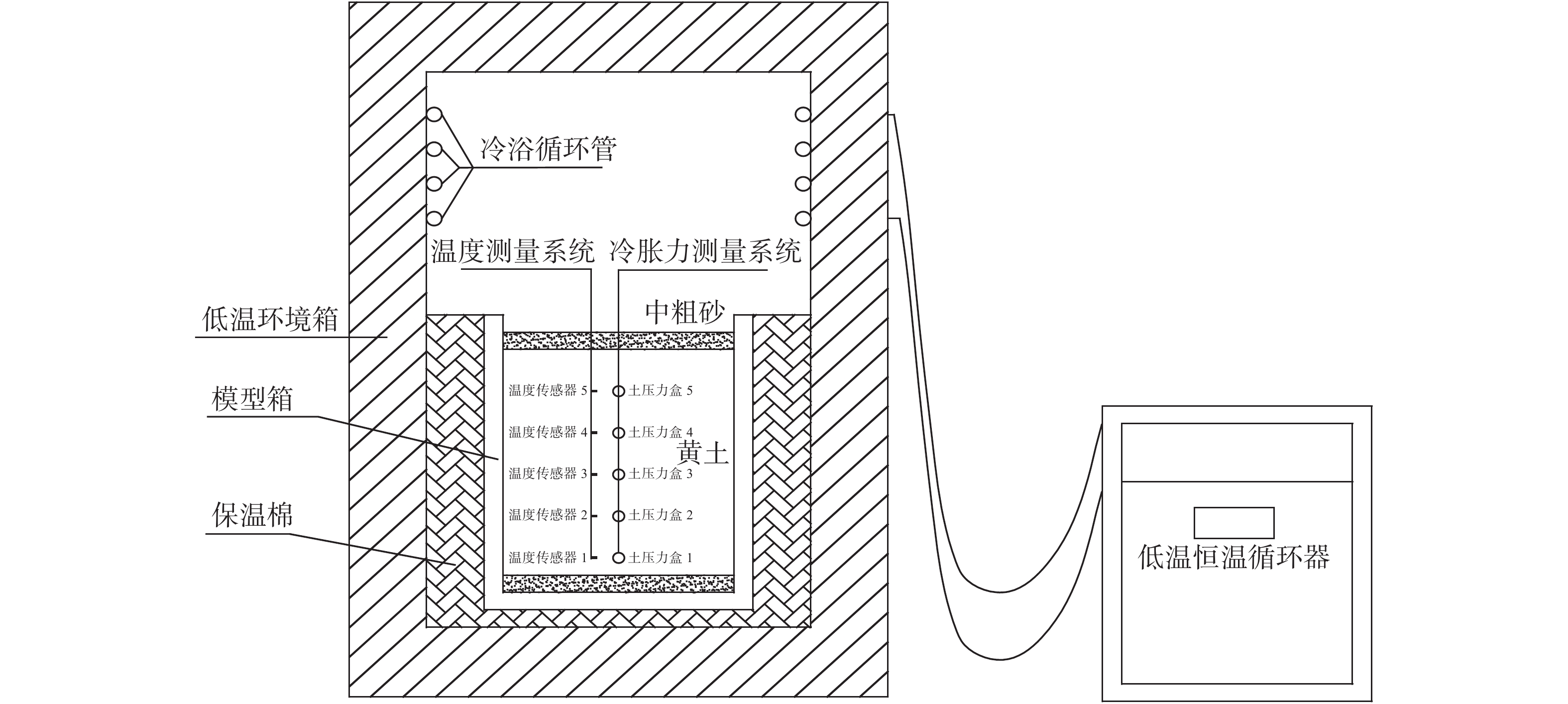
试验采用单向封闭冻结试验系统,试验系统可以按照试验要求控制温度,该系统由温度控制系统、环境箱和模型箱、测量系统3部分组成(图1)。
温度控制系统使用杭州雪中炭恒温技术有限公司生产的低温恒温循环器,其输出温度范围为−30 ℃~+50 ℃,精度0.2 ℃,循环液使用无水乙醇。
使用试验室环境箱其尺寸为2 m×2 m×1.8 m。模型箱由角钢和有机玻璃制成,尺寸为0.8 m×0.6 m×0.8 m,侧壁和底部均粘贴保温棉。
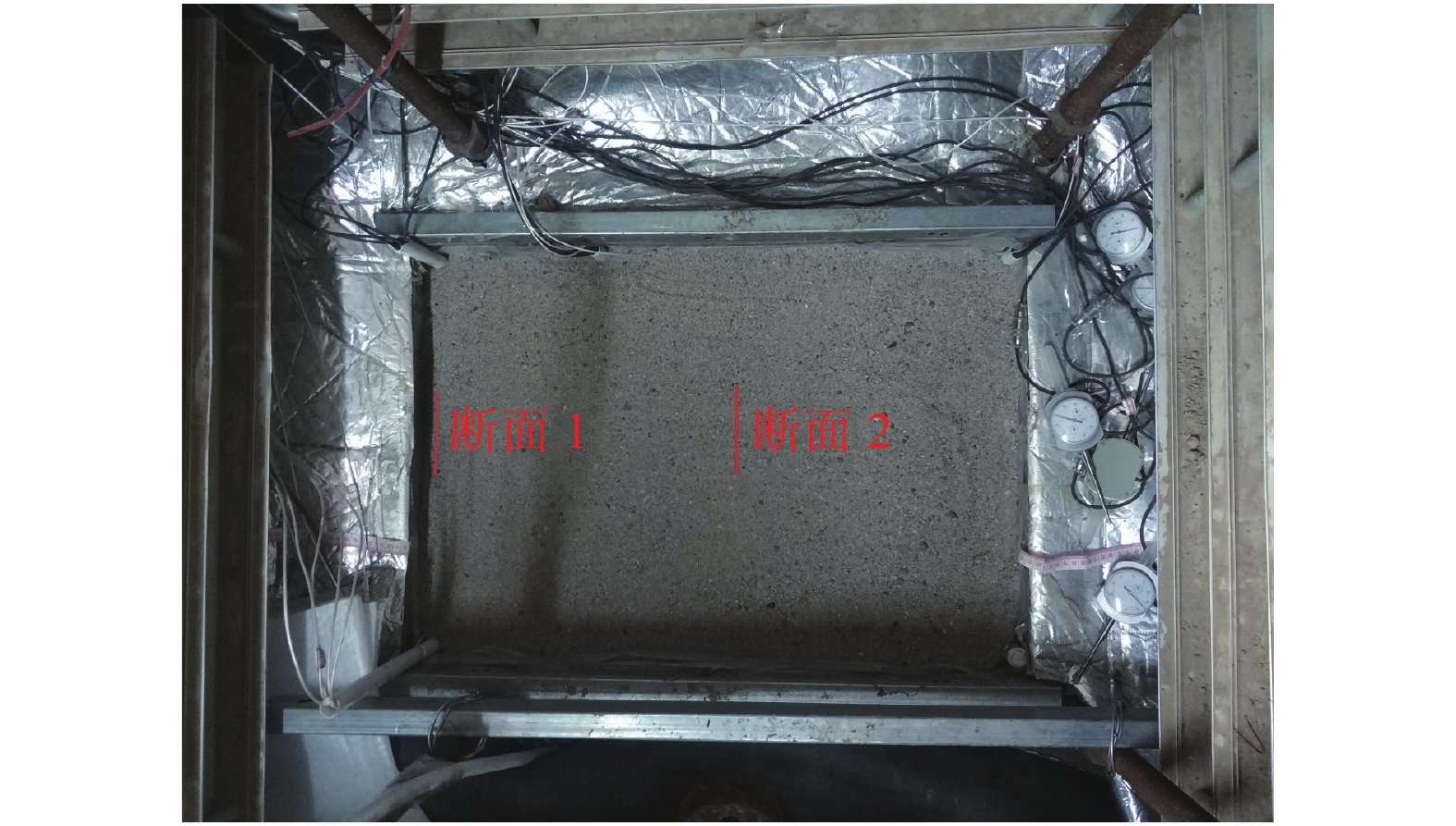
测量系统包括:(1)水平冻胀力的测量:使用定制的微型土压力盒,其外形尺寸为Φ30 mm×9 mm,量程为200 kPa,精度为±0.5%,为了使水平冻胀力测量准确,埋设土压力盒时保证其正面与模型箱壁严格平行,土压力盒均居中布置;(2)温度的测量:温度测量采用铂热电阻pt100,其工作范围:−50~+200 ℃,精度为0.1 ℃。温度测量传感器的埋设位置和微型土压力盒在相同深度并且错开一定的水平距离,土体从上表面开始沿深度每隔12 cm设置一个;(3)数据采集:使用32通道静态应变采集仪,LCXAF温度巡检仪和安装相关采集软件的计算机。为保证试验数据的准确与可靠性,温度和冻胀力测量传感器均布设了两个断面(图2)。
1.3 试验技术路线
本研究采用闭式一维冻胀模型试验系统,来模拟冷源单向冻结条件。试验过程中记录温度场和水平冻胀力的变化数据。试验中土体的含水率分别为14%、16%和20%,压实度为0.9,研究采用封闭系统,环境箱温度为−20 ℃。在模型箱和环境箱之间的空隙中填充保温棉,由于其导热系数很小,可以认为试验设备的温度边界条件能满足试验设计的一维冻结条件。为了模拟自然条件下的排水边界条件,模型箱底部铺5 cm中粗砂。按照试验方案将拌和均匀的土分层填入模型箱,填土过程中将温度传感器和土压力盒按照试验要求安装在相应位置,填筑完成后对箱内土体进行补水,然后将箱内土体静置72 h,使土体中水分分布均匀。开启低温环境试验箱的温度控制系统,设置控制温度为−20 ℃,对模型进行降温冻结并定期检查所采集的数据。当土体温度下降到试验方案的设计值时,停止冻结。设置控制温度为20 ℃来模拟融化过程。填筑完成后的模型如图2所示。
2. 试验结果分析
2.1 温度场
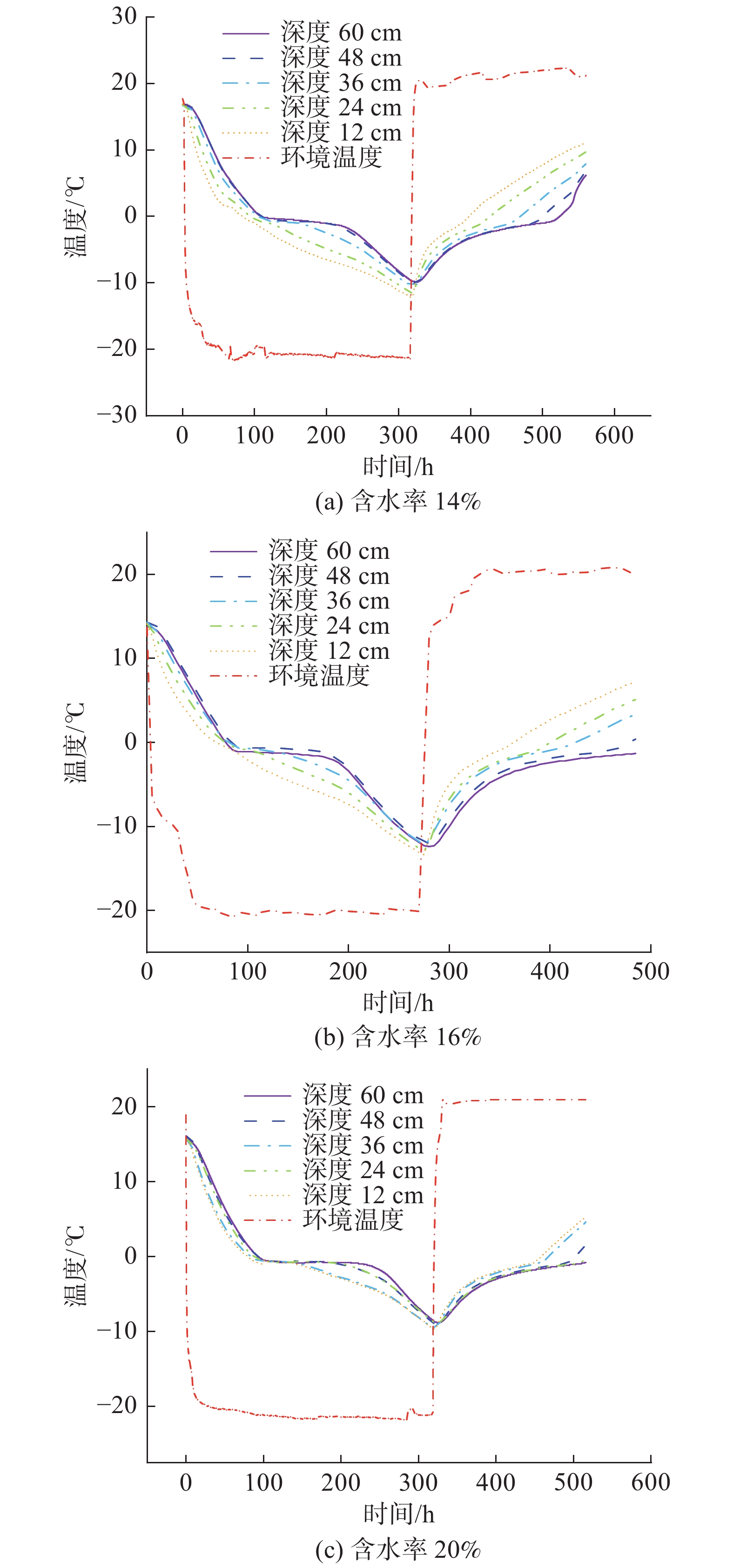
图3为一个冻融循环周期试验过程中土体不同深度处温度的变化曲线。以土体含水率14%、16%和20%的结果为例进行说明,环境箱内的环境温度在试验开始25 h后达到试验所设定的温度并且基本稳定。试验进行320 h后由冻结阶段转变为融化阶段,环境温度快速上升到试验设定的温度。由温度变化曲线可以看出,距离土体表面越远温度曲线就越对称,降温速率相近。靠近表面的点,土体冻结和融化过程曲线差异较大,升温的速率大于降温的速率并且在0.4 ℃出现转折,降温阶段的温度变化速率0.051 ℃/h,升温阶段的温度变化速率0.1558 ℃/h。
温度变化到0.4 ℃处时较深处的土体降温速率出现一个平稳阶段,降温曲线基本平行于横坐标,并且在降温和升温两个阶段表现出很强的对称性。造成这一现象的主要原因是土体中的水分释放相变潜热,并且含水率越高这种现象越明显。冻结后期(土体温度从0.4 ℃下降到试验降温结束)各深度处土体的温度下降速率较慢,这主要是土体冻结后土体导热系数和比热容发生了变化。含水率不同的土体温度变化规律相似,土体不同深度处的升温过程与降温阶段对称。
2.2 水平冻胀力
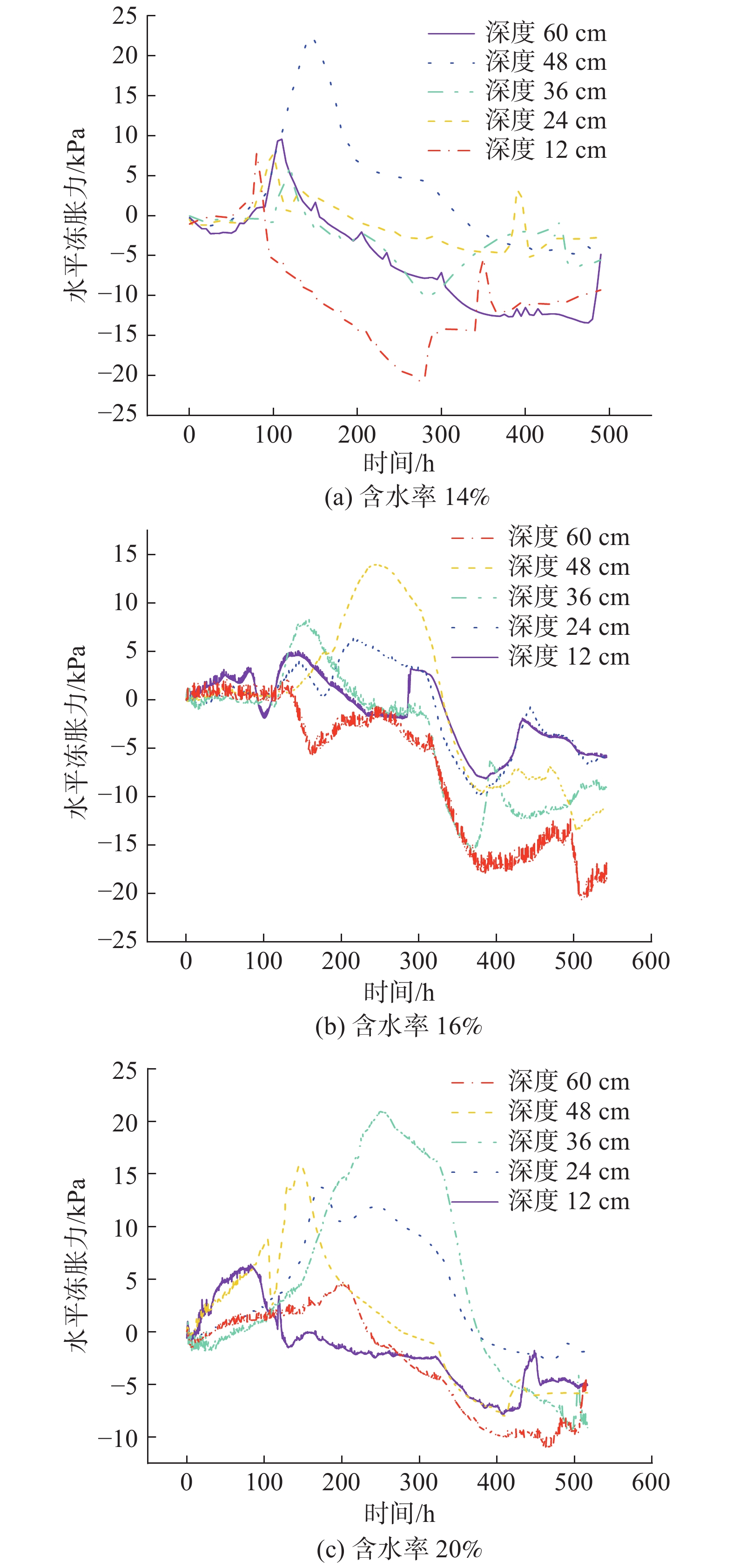
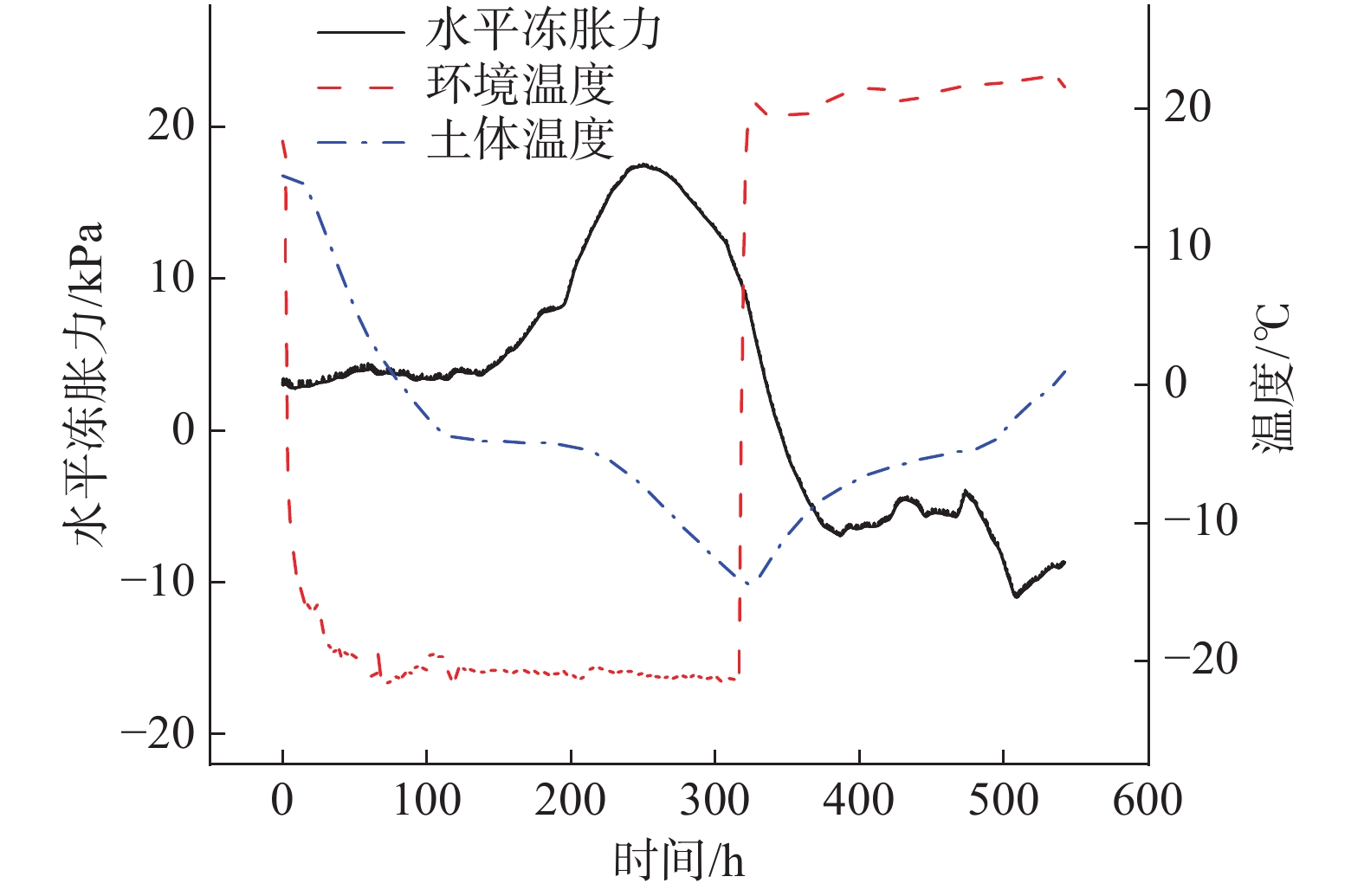
土体冻结过程中,随着土体温度的逐渐降低土中的液态水变为冰(固态水),未冻水含量减少,土体含冰量增加,同时伴随着土体体积逐渐增大,并且土体产生冻胀位移和冻胀力。一个冻融循环周期土体水平冻胀力与冻结时间的关系如图4所示。由图可知,当温度降低到起始冻结温度时土体开始产生水平冻胀力,起始冻胀力为0.6 ℃;随着环境箱内的温度进一步的降低,水平冻胀力快速增长并达到最大值,土体某一点最大水平冻胀力对应的温度称为最大冻胀力温度:然后温度继续下降时水平冻胀力逐渐减小:随着温度的进一步降低,水平冻胀力出现负值。当温度开始回升时水平冻胀力有波动增大的趋势。距离表面为12 cm处的土地冻结150 h后土地开始出现水平冻胀力,水平冻胀力先逐渐增加并出现最大值,冻结260 h之后水平冻胀力然后逐渐减小。
根据曲线变化趋势,可将一个冻融循环过程中水平冻胀力的变化分为4个区段:①土体温度在−0.6 ℃以上基本不产生水平冻胀力;②当土体温度下降到−0.6 ℃时水平冻胀力开始增长,当土体温度下降到某一温度(最大冻胀力温度)时水平冻胀力出现最大值,不同含水率的土体出现冻胀力最大值的温度不同;③土体温度低于最大冻胀力温度后,土体中水平冻胀力逐渐降低;④融化阶段当土体温度开始升高时水平冻胀力产生波动,又进一步有所增大。
在封闭一维冻结条件,随着环境箱温度下降,土体温度也逐渐降低,当土体温度降至起始冻结温度后,含水量超过起始冻胀含水量的土体将会产生冻胀并且在水平方向出现水平冻胀的内应力。此时,在垂直方向由于土体表面是无约束的,因而会产生冻胀量。当土体温度继续降低土体中的未冻水大部分会逐渐冻结转化为固态的冰,在此期间冻胀过程基本完成,水平冻胀力达到最大值。当土体温度继续降低时,由于土体中未冻水含量较少因而产生的冻胀很小,土颗粒的降温收缩的效果将会大于未冻水冻结而产生的体积增大,土体收缩会使水平冻胀力逐渐减小;土体降温至某一温度值水平冻胀力则会减小到零,此时土中水由于冻结而增大的体积和土颗粒由于冷缩减小的体积相等;土体温度继续降低水平冻胀力出现负值,由于土压力盒不能测量拉应力,理论上负值的水平冻胀力的量值最大等于土体冻结前的土压力。
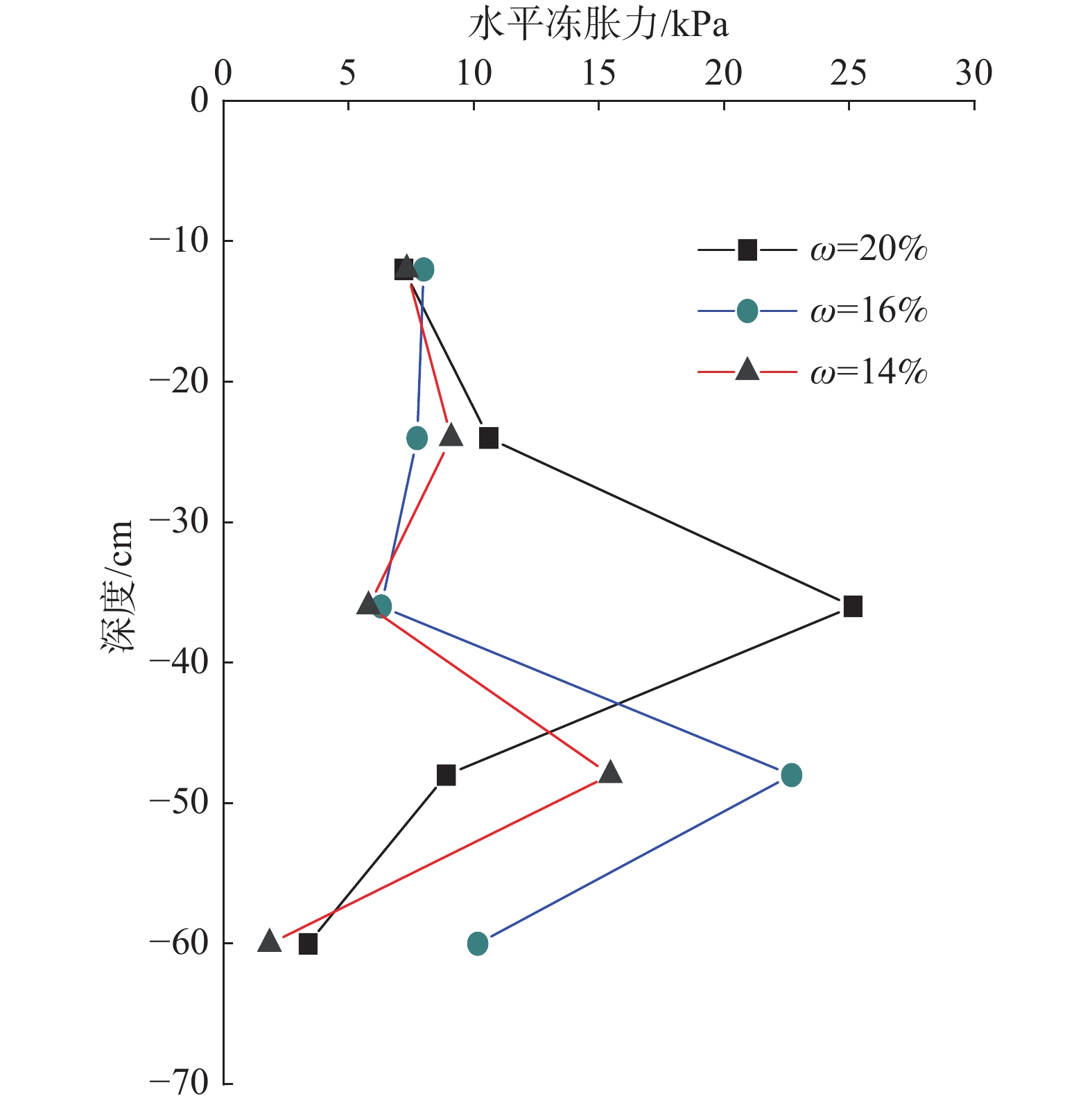
最大水平冻胀力沿深度的分布如图5所示,由图可知,最大水平冻胀力的量值在0~24 cm处相对稳定,变化较小,在36~48 cm处出现最大值。总体趋势沿着土体深度先是较为稳定,数值变化较小;然后增大出现最大值最后减小。水平冻胀力最大值随含水率有很明显的变化,而其它值的大小受含水率的影响较小。水平冻胀力最大值出现在相对深度0.6~0.8处,含水率为14%的土体最大水平冻胀力为15.46 kPa,含水率16%的土体为22.69 kPa,含水率20%的土体为25.12 kPa。
2.3 水平冻胀力、土体温度和环境温度之间的关系
为了更方便的分析水平冻胀力、土体温度和环境温度之间的关系,以土体含水率为14%试验中深度36 cm的数据为例绘制图6,环境温度可以很快达到设定温度,水平冻胀力在土体温度低于0.6 ℃时开始产生,随着土体温度降低水平冻胀力逐渐增大并出现最大值,然后土体温度继续降低时水平冻胀力减小;融化阶段,当土体温度高于0.6 ℃时水平冻胀力有一定的波动变化。
2.4 含水率对温度和水平力的影响
影响土体冻胀特性的因素有:土质、含水率、温度和压实度等。而在相同的土质条件下,含水率则是冻胀的主要影响因素。本研究分别进行了不同含水率的试验,结果如图5和图6所示。试验结果表明,不同含水率土体的温度和水平冻胀力的变化规律相似,含水率越高的土体降温速率就越快,不同含水率土体的最大水平冻胀力不同,含水率越高土体水平冻胀力越大。
3. 结论
通过室内闭式一维冻胀模型试验研究了兰州地区黄土的温度场及冻胀力的变化规律,主要结论如下:
(1)土体不同深度处的降温过程可分为三个阶段,降温冻结初期各深度土体的温度下降速率较快;土体温度下降到0.4 ℃时降温曲线出现转折点,土层各深度降温速曲线出现近乎平行于横坐标的平稳段,并且含水率越高这种现象越明显;冻结后期各深度土体的温度下降速率较慢。土体不同深度处的升温过程与降温过程曲线对称。
(2)冻胀力变化曲线按照变化趋势分为三个阶段:稳定不发展阶段,增长阶段,减小阶段,不同含水率土体经历各阶段的时间有所不同。
(3)在相同土质和温度条件下冻胀力发展的起始温度相同,含水率不同的土体最大冻胀力温度不同。
(4)最大水平冻胀力沿着土体深度先较为稳定,然后增大最后减小,最大值出现在相对深度0.6−0.8处。
(5)水平冻胀力在土体温度低于0.6 ℃时开始产生,随着土体温度降低水平冻胀力逐渐增大并出现最大值,然后土体温度继续降低时水平冻胀力减小。
-
表 1 黄土基本物理指标
Table 1 Basic physical properties of loess
比重
Gs液限
wL/%塑限
wp/%塑性指数
Ip最优含水率
wopc/%最大干密度
ρdmax/(g·cm−3)2.71 28.38 15.21 13.17 13.6 1.89 -
[1] 徐斅祖, 王家澄, 张立新. 冻土物理学[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2001. XU Xuezu, WANG Jiacheng, ZHANG Lixin. Physics of frozen soils[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2001. (in Chinese with English abstract)
[2] 童长江, 管枫年. 土的冻胀与建筑物冻害防治[M]. 北京: 水利水电出版社, 1985: 96−103. TONG Changjiang, GUAN Fengnian. Prevention of frost heave of soil and freezing damage of buildings [M]. Beijing: Water Re-sources and Electric Power Press, 1985: 96−103. (in Chinese)
[3] EIGENBROD K D. Effects of cyclic freezing and thawing on volume changes and permeabilities of soft fine-gained soils[J]. Canadian Geotechnical Journal,1996,33(4):529 − 537. DOI: 10.1139/t96-079-301
[4] 李岩, 刘波, 张建新. 竖向直排冻结条件水平冻胀力试验研究[J]. 岩土力学,2014,35(11):3199 − 3206. [LI Yan, LIU Bo, ZHANG Jianxin. Experimental research on horizontal frost heaving force of vertical straight freezing[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(11):3199 − 3206. (in Chinese with English abstract) [5] 刘鸿绪. 对土冻结过程中若干冻胀力学问题的商榷(续)[J]. 冰川冻土,1990,12(4):351 − 357. [LIU Hongxu. Discussion on some problems of frost-heaving mechanics in freezing process of soil[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,1990,12(4):351 − 357. (in Chinese with English abstract) [6] 刘鸿绪, 朱卫中, 朱广祥, 等. 再论冻胀量与冻胀力之关系[J]. 冰川冻土,2001,23(1):63 − 66. [LIU Hongxu, ZHU Weizhong, ZHU Guangxiang, et al. Research on the relationship of frost-heaving forces and amount of frost-heaving again[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology,2001,23(1):63 − 66. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0240.2001.01.011 [7] 孙彦福, 刘秀英. 关于平行水平冻胀力问题的探讨[J]. 低温建筑技术,1999,21(4):37 − 38. [SUN Yanfu, LIU Xiuying. About parallel horizontal frost heaving force problem discussed in this paper[J]. Low Temperature Architecture Technology,1999,21(4):37 − 38. (in Chinese with English abstract) [8] 姜龙, 王连俊, 张喜发, 等. 季冻区公路路基低液限黏土法向冻胀力试验[J]. 中国公路学报,2008,21(2):23 − 27. [JIANG Long, WANG Lianjun, ZHANG Xifa, et al. Experiment on normal frozen-heave force of low liquid-limit clay of highway roadbed in seasonal frost region[J]. China Journal of Highway and Transport,2008,21(2):23 − 27. (in Chinese with English abstract) DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7372.2008.02.005 [9] 胡坤, 周国庆, 李晓俊, 等. 不同约束条件下土体冻胀规律[J]. 煤炭学报,2011,36(10):1653 − 1658. [HU Kun, ZHOU Guoqing, LI Xiaojun, et al. Experiments on frost heave of artificial frozen soils with different constraints[J]. Journal of China Coal Society,2011,36(10):1653 − 1658. (in Chinese with English abstract) [10] 王建州, 刘书幸, 周国庆, 等. 深季节冻土地区基坑工程水平冻胀力试验研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报,2018,47(4):815 − 821. [WANG Jianzhou, LIU Shuxing, ZHOU Guoqing, et al. Model experiment on frost-heave force of foundation pit at deepseasonal frozen regions[J]. Journal of China University of Mining & Technology,2018,47(4):815 − 821. (in Chinese with English abstract) [11] 吕长霖. 一维冻结条件下土体冻胀与基础水平冻胀力试验研究[D]. 徐州: 中国矿业大学, 2018. LYU Changlin. Experimental study on soil frost heave and horizontal frost heave force of foundation under one-dimensional freezing condition [D]. Xuzhou: China University of Mining and Technology, 2018. (in Chinese)
[12] VINSON T S, CHAICHANAVONG T, CZAJKOWSKI R L. Behavior offrozen clays under cyclic axial loading[J]. Journal of the Geotechnical Engineering Division,1978,104(GT7):779 − 800.
[13] LING X Z, ZHANG F, LI Q L, et al. Dynamic shear modulus and damping ratio of frozen compacted sand subjected to freeze–thaw cycle under multi-stage cyclic loading[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2015,76:111 − 121. DOI: 10.1016/j.soildyn.2015.02.007
[14] 中华人民共和国铁道部. 铁路工程土工试验规程: TB 10102—2010[S]. 北京: 中国铁道出版社, 2010. Ministry of Railways of the People's Republic of China. Code for Soil Test of Railway Engineering: TB 10102—2010[S]. Beijing: China Railway Publishing House, 2010. (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 雷华阳,张文振,冯双喜,霍海峰. 水汽补给下砂土水分迁移规律及冻胀特性研究. 岩土力学. 2022(01): 1-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 孙巍锋,常洲,兰恒星,晏长根,杨万里,徐伟. 高寒阴湿区边坡浅层土体温湿响应规律研究. 水文地质工程地质. 2022(05): 204-213 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)




 下载:
下载:
 邮件订阅
邮件订阅 RSS
RSS